- [English]
- Bandgap Tuning and Quenching Effects of In(Zn)P@ZnSe@ZnS Quantum Dots
-
Sang Yeon Lee, Su Hyun Park, Gyungsu Byun, Chang-Yeoul Kim
-
J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):226-235. Published online June 27, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00003
-
-
2,379
View
-
42
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
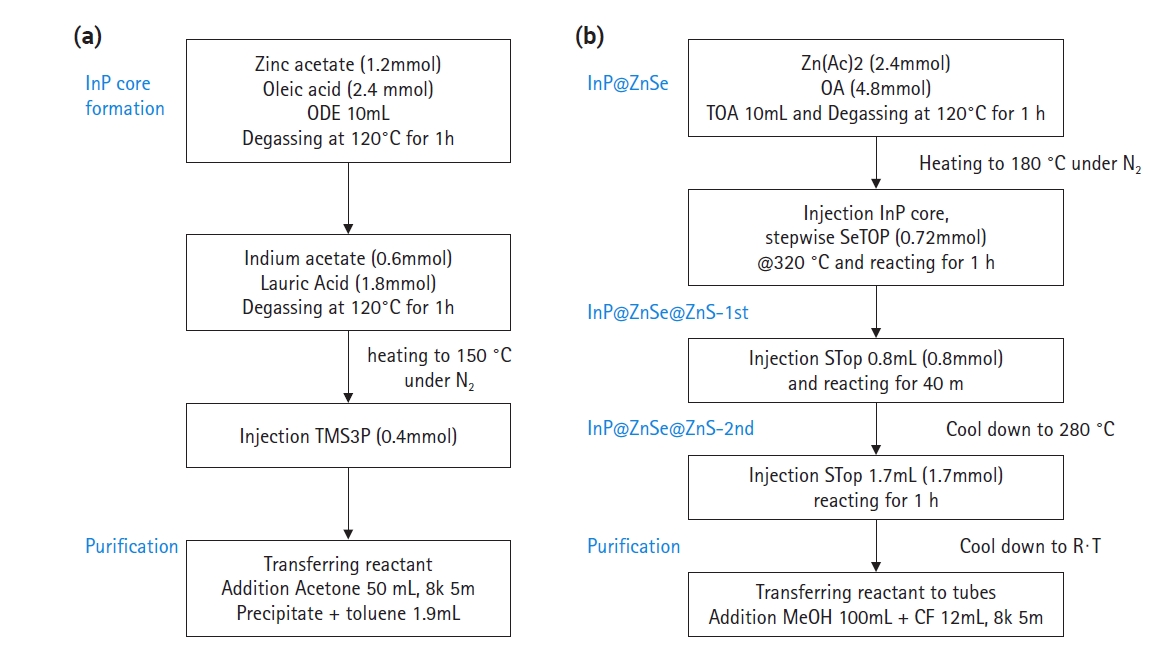
- InP quantum dot (QDs) have attracted researchers’ interest due to their applicability in quantum dot light-emitting displays (QLED) or biomarkers for detecting cancers or viruses. The surface or interface control of InP QD core/shell has substantially increased quantum efficiency, with a quantum yield of 100% reached by introducing HF to inhibit oxide generation. In this study, we focused on the control of bandgap energy of quantum dots by changing the Zn/(In+Zn) ratio in the In(Zn)P core. Zinc incorporation can change the photoluminescent light colors of green, yellow, orange, and red. Diluting a solution of as-synthesized QDs by more than 100 times did not show any quenching effects by the Förster resonance energy transfer phenomenon between neighboring QDs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Enhancing luminescence of QD thin films, polymer composite films, and LED devices by nanostructures
Hongcheng Yang, Junjie Hao, Mingyu Sun, Yujie Song, Kai Wang, Yujie Song, Xiao Wei Sun, Wenda Zhang
The Innovation.2025; : 101121. CrossRef
|