Most viewed
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Most viewed
Most-read articles are from the articles published in 2024 during the last three month.
- [English]
- A Review of Inorganic Solid Electrolytes for All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries: Challenges and Progress
- Seul Ki Choi, Jaehun Han, Gi Jeong Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Jaewon Choi, MinHo Yang
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):293-301. Published online August 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00206
- 11,812 View
- 288 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
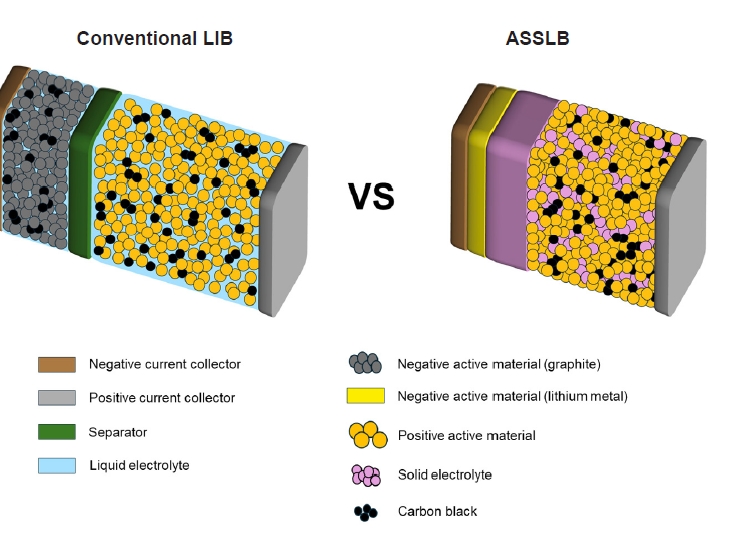
PDF - All-solid-state lithium batteries (ASSLBs) are receiving attention as a prospective next-generation secondary battery technology that can reduce the risk of commercial lithium-ion batteries by replacing flammable organic liquid electrolytes with non-flammable solid electrolytes. The practical application of ASSLBs requires developing robust solid electrolytes that possess ionic conductivity at room temperature on a par with that of organic liquids. These solid electrolytes must also be thermally and chemically stable, as well as compatible with electrode materials. Inorganic solid electrolytes, including oxide and sulfide-based compounds, are being studied as promising future candidates for ASSLBs due to their higher ionic conductivity and thermal stability than polymer electrolytes. Here, we present the challenges currently facing the development of oxide and sulfide-based solid electrolytes, as well as the research efforts underway aiming to resolve these challenges.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A facile synthesis of bulk LiPON in solution for solid-state electrolytes
Osma J. Gomez, Adam Antar, Alex T. Hall, Leopoldo Tapia-Aracayo, Joshua Seo, Nam Kim, Zihan Sun, Ryan Lim, Fu Chen, Yue Li, John Cumings, Gary Rubloff, Sang Bok Lee, David Stewart, Yang Wang
Journal of Materials Chemistry A.2025; 13(34): 28368. CrossRef - Uniform lithium deposition using Cu teepee structures for anode-free lithium metal batteries
Seo Yun Jung, Jaehun Han, Seul Ki Choi, Se Youn Cho, Jong Ho Won, Jaewon Choi, Minho Yang
Chemical Engineering Journal.2025; 522: 167302. CrossRef - Garnet-type LLZO electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries: Interfaces, conductivity, in-situ processing, and industrial prospects
Kaleab Habtamu Ayalew, Nithyadharseni Palaniyandy, Mkhulu K. Mathe, Phumlani F. Msomi
Chemical Engineering Journal.2025; 524: 168098. CrossRef
- A facile synthesis of bulk LiPON in solution for solid-state electrolytes
- [English]
- Research Trends in Electromagnetic Shielding using MXene-based Composite Materials
- Siyeon Kim, Jongmin Byun
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):57-76. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.57
- 8,339 View
- 163 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
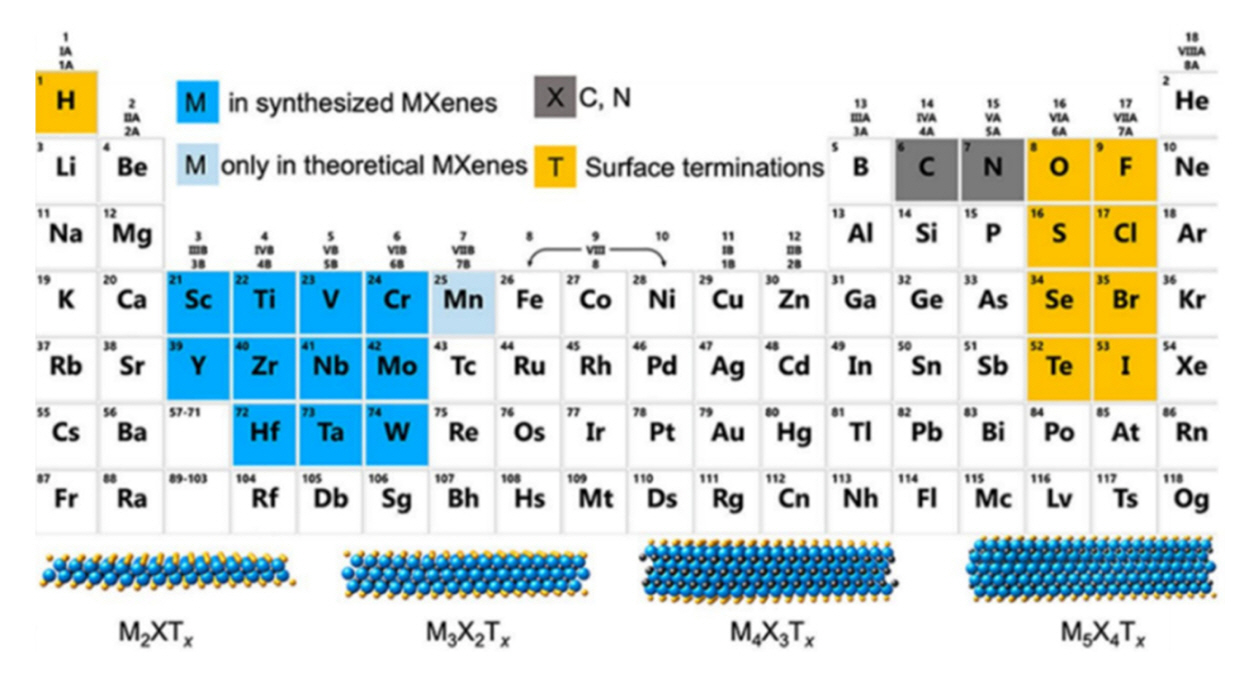
PDF Recent advancements in electronic devices and wireless communication technologies, particularly the rise of 5G, have raised concerns about the escalating electromagnetic pollution and its potential adverse impacts on human health and electronics. As a result, the demand for effective electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials has grown significantly. Traditional materials face limitations in providing optimal solutions owing to inadequacy and low performance due to small thickness. MXene-based composite materials have emerged as promising candidates in this context owing to their exceptional electrical properties, high conductivity, and superior EMI shielding efficiency across a broad frequency range. This review examines the recent developments and advantages of MXene-based composite materials in EMI shielding applications, emphasizing their potential to address the challenges posed by electromagnetic pollution and to foster advancements in modern electronics systems and vital technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Designing dual phase hexaferrite (SrFe12O19) – Perovskite (La0.5Nd0.5FeO3) composites for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption and band gap modulation
Pramod D. Mhase, Varsha C. Pujari, Santosh S. Jadhav, Abdullah G. Al-Sehemi, Sarah Alsobaie, Sunil M. Patange
Composites Communications.2025; 54: 102284. CrossRef - Microstructure tailoring of Nb-based MAX phase by low temperature synthesis with layer-structured Nb2C powder and molten salt method
Chaehyun Lim, Wonjune Choi, Jongmin Byun
Materials Characterization.2025; 225: 115106. CrossRef - Fabrication of MOF@MXene composites via surface modification of MXene under acidic conditions
Ji-Haeng Jeong, Woong-Ryeol Yu
Functional Composites and Structures.2025; 7(2): 025006. CrossRef - V2CTx MXene@ZIF-8 composite as an efficient adsorbent for Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution
Sarina Khojasteh Fard, Golshan Mazloom, Manoochehr Sobhani, Mohsen Tamtaji
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering.2025; 13(6): 120099. CrossRef
- Designing dual phase hexaferrite (SrFe12O19) – Perovskite (La0.5Nd0.5FeO3) composites for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption and band gap modulation
- [English]
- Recent Advances in Thermoelectric Materials and Devices: Improving Power Generation Performance
- Momanyi Amos Okirigiti, Cheol Min Kim, Hyejeong Choi, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Kwi-Il Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):1-15. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00395
- 9,823 View
- 217 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
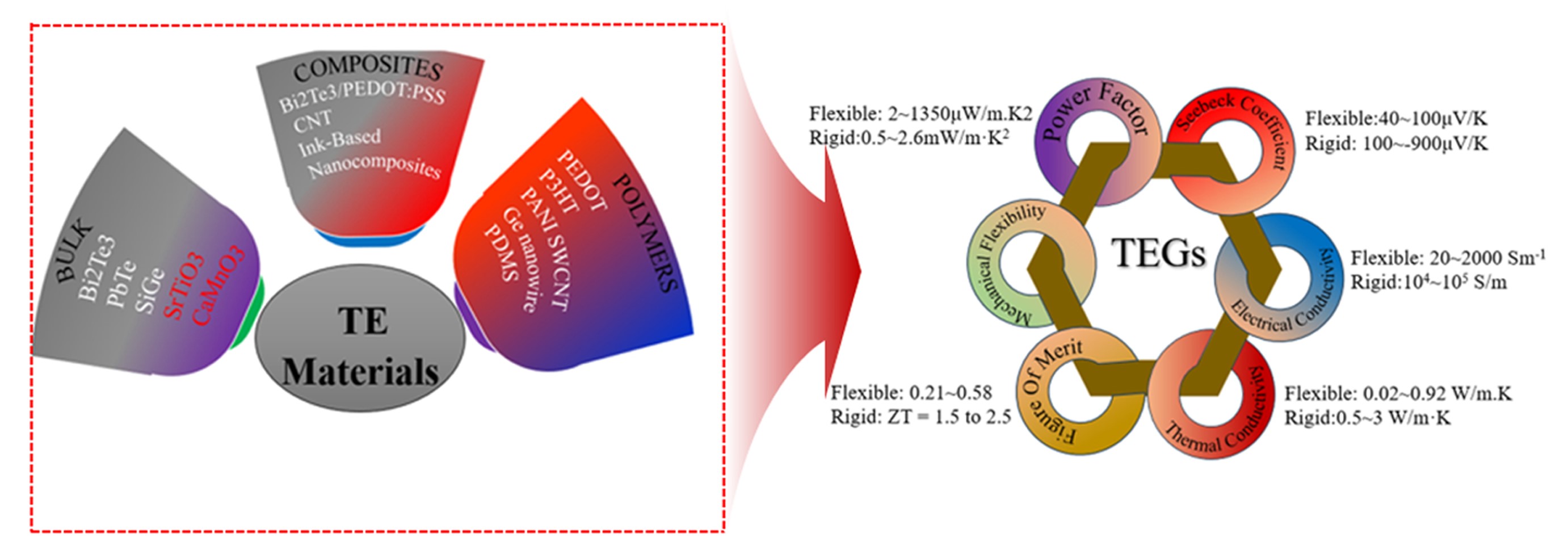
PDF - Thermoelectric materials have been the focus of extensive research interest in recent years due to their potential in clean power generation from waste heat. Their conversion efficiency is primarily reflected by the dimensionless figure of merit, with higher values indicating better performance. There is a pressing need to discover materials that increase output power and improve performance, from the material level to device fabrication. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of recent advancements, such as Bi2Te3-based nanostructures that reduce thermal conductivity while maintaining electrical conductivity, GeTe-based high entropy alloys that utilize multiple elements for improved thermoelectric properties, porous metal-organic frameworks offering tunable structures, and organic/hybrid films that present low-cost, flexible solutions. Innovations in thermoelectric generator designs, such as asymmetrical geometries, segmented modules, and flexible devices, have further contributed to increased efficiency and output power. Together, these developments are paving the way for more effective thermoelectric technologies in sustainable energy generation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- State-of-the-art research in conducting polymer thermoelectric composites: Design strategies, doping innovations, and emerging technologies
Vilakshana Acharya, Shivani Verma, Seema Gupta, Gaurav Pandey, Aanchal Sethi, Pooja Rawat
Journal of Applied Physics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Mathematical and simulation modeling of photovoltaic systems utilizing thermoelectric modules for effective thermal management
Muhammad Sohaib Tahir, Xue Dong, Muhammad Mansoor Khan
Results in Engineering.2025; 27: 106344. CrossRef - Summary of Publications in the Special Issue: Advances in Corrosion Resistant Coatings
Yong X. Gan
Coatings.2025; 15(11): 1350. CrossRef - Standard Reference Thermoelectric Modules Based on Metallic Combinations and Geometric Design
EunA Koo, Hanhwi Jang, SuDong Park, Sang Hyun Park, Sae-byul Kang
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(18): 10273. CrossRef - Research Trends in Magneto-Mechano-Electric (MME) Energy Harvesting Devices
So Ie Jeong, Geon-Tae Hwang
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 529. CrossRef - Transient In-Situ Identification of Thermal Parameters in Commercial Thermoelectric Modules using Transfer-Function Models
Gurum Ahmad Pauzi, Irfan Alfiansyah, Agus Riyanto, Donni Kis Apriyanto, Yanti Yulianti, Warsito Warsito
Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan Fisika Al-Biruni.2025; 14(2): 187. CrossRef
- State-of-the-art research in conducting polymer thermoelectric composites: Design strategies, doping innovations, and emerging technologies
- [English]
- Advances in Powder Metallurgy for High-Entropy Alloys
- Sheetal Kumar Dewangan, Cheenepalli Nagarjuna, Hansung Lee, K. Raja Rao, Man Mohan, Reliance Jain, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):480-492. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00297
- 5,065 View
- 169 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
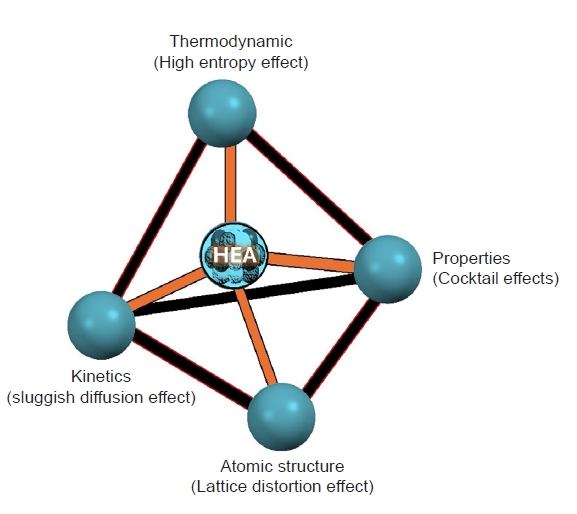
PDF - High-entropy alloys (HEAs) represent a revolutionary class of materials characterized by their multi-principal element compositions and exceptional mechanical properties. Powder metallurgy, a versatile and cost-effective manufacturing process, offers significant advantages for the development of HEAs, including precise control over their composition, microstructure, and mechanical properties. This review explores innovative approaches integrating powder metallurgy techniques in the synthesis and optimization of HEAs. Key advances in powder production, sintering methods, and additive manufacturing are examined, highlighting their roles in improving the performance, advancement, and applicability of HEAs. The review also discusses the mechanical properties, potential industrial applications, and future trends in the field, providing a comprehensive overview of the current state and future prospects of HEA development using powder metallurgy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Pressure and Temperature on the Microstructure and Vickers Microhardness of the CoCrFeMnNiAl1.5 Alloy During Conventional Sintering and High-Frequency Induction Sintering
Leonardo Baylón García, José Manuel Mendoza Duarte, Ivanovich Estrada Guel, Audel Santos Beltrán, Hansel Manuel Medrano Prieto, Gustavo Rodríguez Cabriales, Enrique Rocha Rangel, José Luis Hernández Rivera, Roberto Martínez Sánchez, Alfredo Martínez Garcí
Coatings.2026; 16(3): 275. CrossRef - Sustainable powder metallurgy route to Densify oxide-derived CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy
Taehyeob Im, Minjong Kim, Gertrude Mugwe Mongella, Nelson Bayi, Caroline Sunyong Lee
Materials Today Sustainability.2026; 34: 101330. CrossRef - Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
Eunhyo Song, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 254. CrossRef - Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang, Oanh, Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 191. CrossRef - Latest Advancements and Mechanistic Insights into High-Entropy Alloys: Design, Properties and Applications
Anthoula Poulia, Alexander E. Karantzalis
Materials.2025; 18(24): 5616. CrossRef
- Effect of Pressure and Temperature on the Microstructure and Vickers Microhardness of the CoCrFeMnNiAl1.5 Alloy During Conventional Sintering and High-Frequency Induction Sintering
- [English]
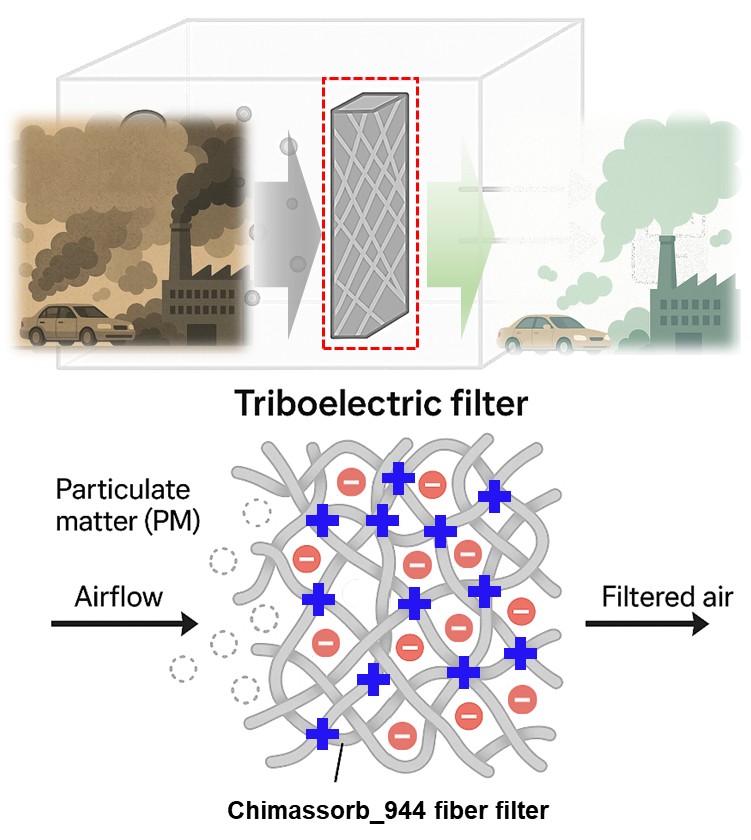
- A Self-Powered Cationic Microfiber-Based Triboelectric Air Filter for High-Speed Particulate Matter Removal and Smart Monitoring
- Tae-hyung Kim, Jin-Kyeom Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):481-491. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00465
- 869 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Particulate matter (PM) pollution demands air filters that combine high efficiency with low pressure drop. Here, we report a self-powered electrostatic filter based on an electrospun cationic microfiber web of Chimassorb 944 (C-fiber). The C-fiber functions as a triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG), generating a surface charge density of 85.8 85.8 μC/m2 when paired with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which creates a strong electrostatic field for capturing sub-micron particles, including the most penetrating particle size (MPPS). As a result, the triboelectrically charged C-fiber filter maintains >80% filtration efficiency at a high wind speed of 60 cm/s, far exceeding uncharged mechanical filters (<20%) while retaining low air resistance. Kelvin probe force microscopy (KPFM) visualizes the surface-potential change after particle capture, and the gradual decay of TENG output provides a built-in indicator of dust loading. This strategy offers a promising platform for next-generation smart air purification systems.
- [English]
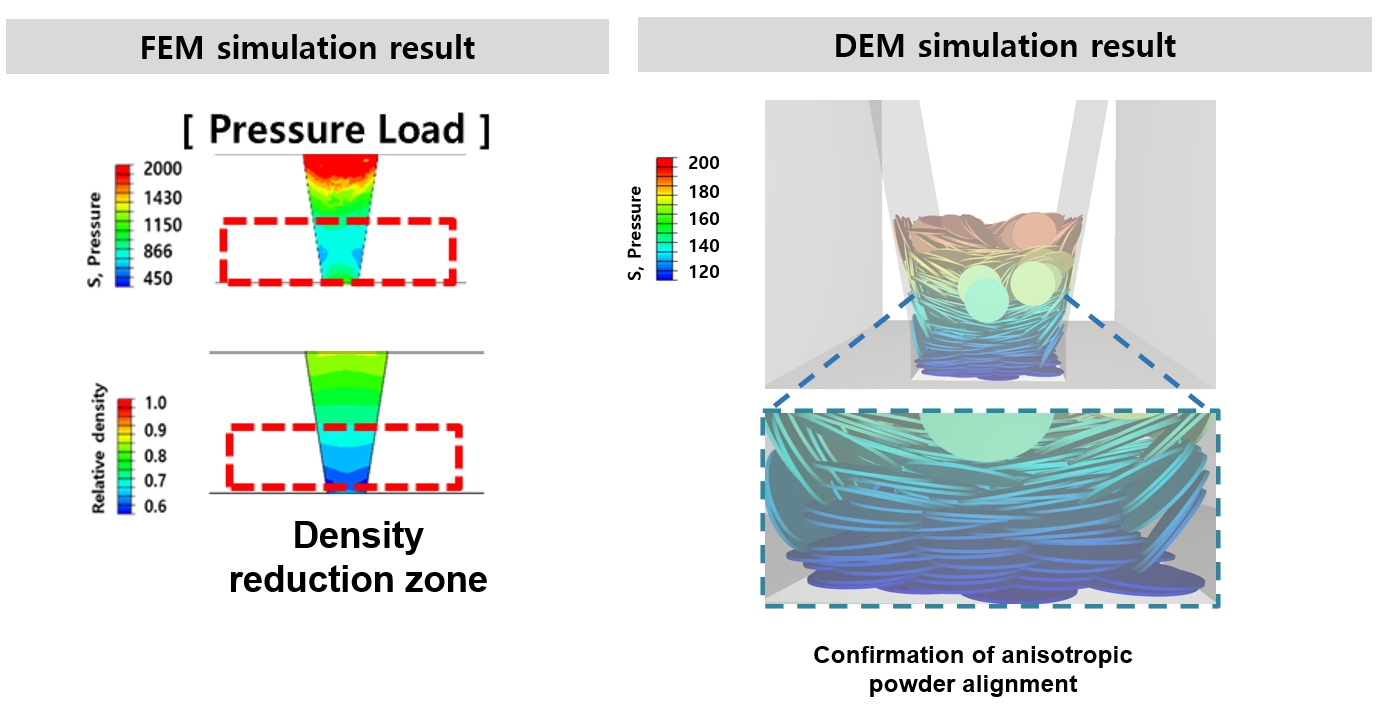
- Finite Element and Discrete Element Analyses of Anisotropic Powder Compaction for Axial Flux Motor Cores
- Jeong Ah Lee, Do Won Lee, , Hyojeong Ha, Ki Hyuk Kwon, Eon Byeong Park, Taeyoung Kim, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):451-458. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00409
- 867 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigates the compaction behavior of anisotropic, plate-like powders used in axial flux motor cores through a combined FEM–DEM approach. A porous continuum FEM model captures stress and density evolution during die pressing, revealing strong gradients along the compaction direction, with higher stress and densification near the upper punch and reduced compaction in the lower region. Guided by these results, DEM simulations examine particle packing, orientation, and contact pressure in representative zones. The DEM analysis shows that higher local pressure promotes denser packing and in-plane particle alignment near the upper punch, while the lower region exhibits more random orientations and lower contact forces. As a result, the multi-scale FEM–DEM framework clarifies how anisotropic particle behavior governs local densification and offers practical guidance for die design and process optimization to achieve more uniform density and controlled magnetic-property-relevant particle alignment in axial flux motor cores.
- [English]
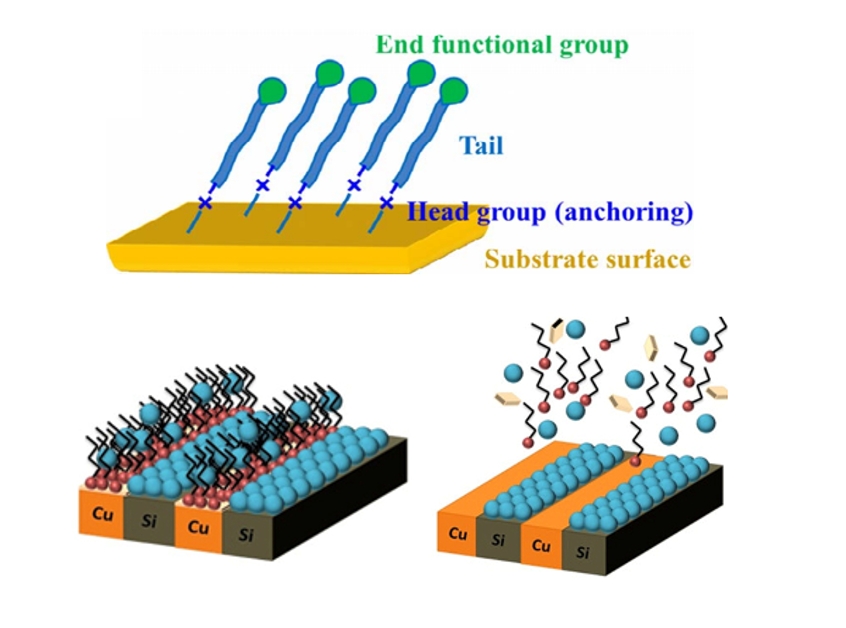
- Self-Assembled Monolayers in Area-Selective Atomic Layer Deposition and Their Challenges
- Si Eun Jung, Ji Woong Shin, Ye Jin Han, Byung Joon Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):179-190. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00094
- 4,828 View
- 181 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Area-selective atomic layer deposition (AS-ALD) is a bottom-up process that selectively deposits thin films onto specific areas of a wafer surface. The surface reactions of AS-ALD are controlled by blocking the adsorption of precursors using inhibitors such as self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) or small molecule inhibitors. To increase selectivity during the AS-ALD process, the design of both the inhibitor and the precursor is crucial. Both inhibitors and precursors vary in reactivity and size, and surface reactions are blocked through interactions between precursor molecules and surface functional groups. However, challenges in the conventional SAM-based AS-ALD method include thermal instability and potential damage to substrates during the removal of residual SAMs after the process. To address these issues, recent studies have proposed alternative inhibitors and process design strategies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Temperature-Dependent Surface Structural Change in Self-Assembled Monolayers Studied with Vibrational Sum-Frequency Generation and QM/MD Simulation
Hojeong Yoon, Saima Sadiq, Junhyeok Park, Kyungwon Kwak, Minhaeng Cho
The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters.2026; 17(4): 1119. CrossRef
- Temperature-Dependent Surface Structural Change in Self-Assembled Monolayers Studied with Vibrational Sum-Frequency Generation and QM/MD Simulation
- [English]
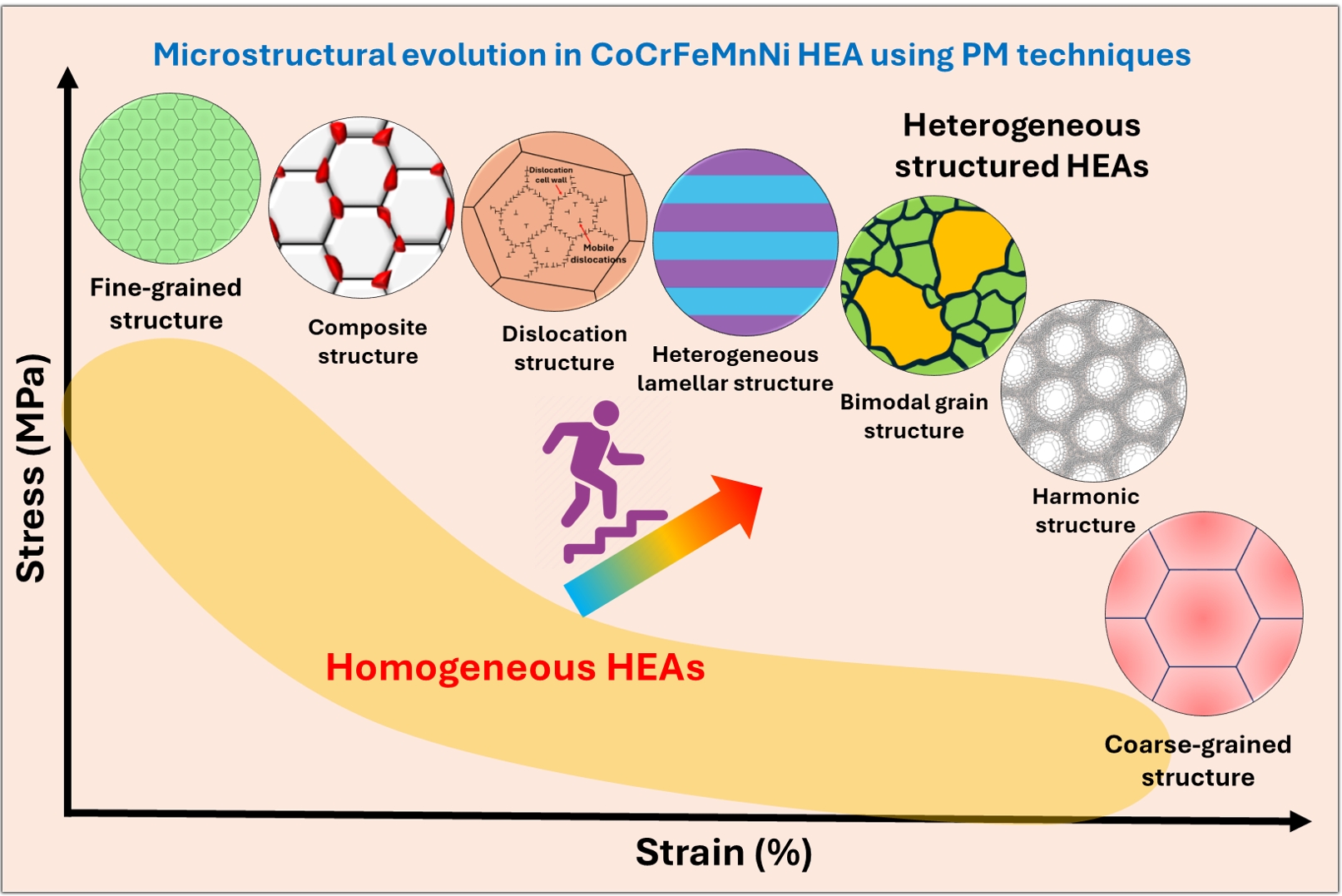
- A Review of Recent Developments in CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloys Processed by Powder Metallurgy
- Cheenepalli Nagarjuna, Sheetal Kumar Dewangan, Hansung Lee, Eunhyo Song, K. Raja Rao, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):145-164. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00430
- 4,555 View
- 119 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In recent years, high-entropy alloys (HEAs) have attracted considerable attention in materials engineering due to their unique phase stability and mechanical properties compared to conventional alloys. Since the inception of HEAs, CoCrFeMnNi alloys have been widely investigated due to their outstanding strength and fracture toughness at cryogenic temperatures. However, their lower yield strength at room temperature limits their structural applications. The mechanical properties of HEAs are greatly influenced by their processing methods and microstructural features. Unlike traditional melting techniques, powder metallurgy (PM) provides a unique opportunity to produce HEAs with nanocrystalline structures and uniform compositions. The current review explores recent advances in optimizing the microstructural characteristics in CoCrFeMnNi HEAs by using PM techniques to improve mechanical performance. The most promising strategies include grain refinement, dispersion strengthening, and the development of heterogeneous microstructures (e.g., harmonic, bimodal, and multi-metal lamellar structures). Thermomechanical treatments along with additive manufacturing techniques are also summarized. Additionally, the review addresses current challenges and suggests future research directions for designing advanced HEAs through PM techniques.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
Wooyoung Lee, Munsu Choi, Sungwook Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Myungsuk Song, Taek-Soo Kim, Jungwan Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim, Hyunjoo Choi, Soo-Hyun Joo
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 954: 149811. CrossRef - Structural and mechanical characteristics of high-entropy CoCrFeMnNi alloys manufactured by vacuum induction melting
V. K. Drobyshev, I. A. Panchenko, S. V. Konovalov, E. M. Zapolskaya
Russian Physics Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Sustainable powder metallurgy route to Densify oxide-derived CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy
Taehyeob Im, Minjong Kim, Gertrude Mugwe Mongella, Nelson Bayi, Caroline Sunyong Lee
Materials Today Sustainability.2026; 34: 101330. CrossRef - Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang, Oanh, Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 191. CrossRef
- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
- [Korean]
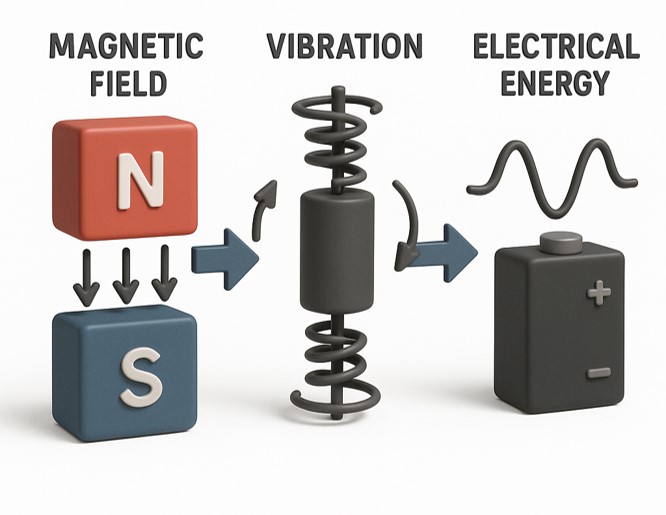
- Research Trends in Magneto-Mechano-Electric (MME) Energy Harvesting Devices
- So Ie Jeong, Geon-Tae Hwang
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):529-541. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00493
- 794 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Magneto-mechano-electric (MME) energy harvesters have emerged as a promising solution for maintenance-free power generation in rapidly expanding Internet of Things (IoT) environments, where replacing or wiring batteries is impractical. MME devices convert weak alternating magnetic fields, ubiquitous around power infrastructures, into useful electrical energy through sequential magnetic, mechanical, and electrical transduction processes. This review summarizes recent advances across triboelectric-, piezoelectric-, and hybrid MME architectures. Triboelectric MME generators employing nano-engineered polymer surfaces, flash-induced surface modification, and nanoscale pattern replication demonstrate low-cost fabrication routes while achieving significantly enhanced voltage and current outputs. Piezoelectric MME systems based on Mn-doped PMN-PZT single crystals highlight strategies for improving mechanical quality factors and resonance-driven power generation. Further, hybrid MME designs that integrate piezoelectric and electromagnetic induction mechanisms enable high-power outputs exceeding tens of milliwatts, sufficient to operate multifunctional IoT platforms and charge practical energy-storage devices. Collectively, these studies illustrate a transition of MME harvesting technologies from laboratory concepts to application-ready self-powered systems. Future opportunities lie in broadband resonance design, modular harvester integration, advanced power management, and multi-source hybridization for robust long-term operation in real environments.
- [Korean]
- Comparison of the Properties of Rare-Earth Zirconate Thermal Barrier Coatings for Hydrogen-Fueled Gas Turbines
- Gun-Woong Lee, Min-Soo Nam, Min-Ji Kim, HyunSuk Jung, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):472-480. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00423
- 781 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) for hydrogen-fueled gas turbines withstand higher combustion temperatures and increased steam concentrations compared to conventional natural-gas systems. These harsh operating conditions significantly accelerate the thermal degradation of widely used YSZ coatings, emphasizing the need for alternative top-coat materials with improved phase stability and reduced thermal conductivity. In this study, rare-earth zirconate ceramics, Gd2Zr2O7 (GdZO), Tm2Zr2O7 (TmZO), and a mixed composition (Gd0.5Tm0.5)2Zr2O7 (Gd/TmZO), are synthesized and investigated as potential next-generation TBC candidates. Each material was comparatively examined with a focus on crystal structure, thermophysical properties, and thermal conductivity. Furthermore, high-temperature steam exposure experiments were performed to simulate hydrogen combustion environments. Microstructural analyses, high-temperature degradation behavior, and phase stability evaluations were carried out to obtain fundamental experimental data. This study provides essential baseline information for the design and development of high-performance TBC materials suitable for the hydrogen-fueled gas turbine systems.
- [Korean]
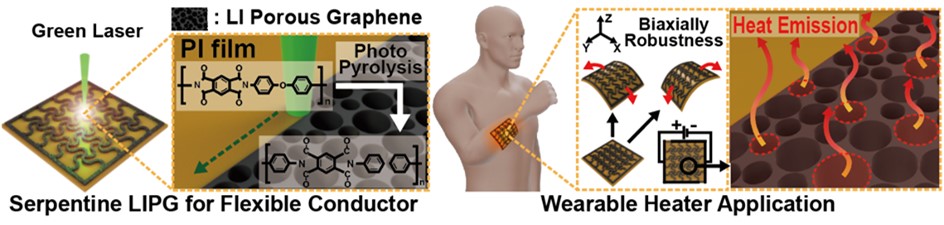
- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
- Min Gi An, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):492-500. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00332
- 750 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A flexible heater with high thermal efficiency and mechanical durability was developed by fabricating laser-induced porous graphene (LIPG) electrodes on polyimide films using a 532 nm green laser. Laser power, scan speed, and line distance were precisely optimized based on photothermal simulations to generate uniform porous graphene structures with large surface area and excellent heat dissipation characteristics. Raman, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analyses confirmed that the optimized LIPG exhibited highly graphitized features with low oxygen defects. Scanning electron microscope analysis revealed that porous morphologies formed only within a specific laser scan speed range, whereas excessive or insufficient irradiation resulted in collapsed or absent porosity. The serpentine-patterned LIPG heater maintained stable electrical resistance under repeated multidirectional bending, demonstrating excellent flexibility and mechanical stability. The heater also achieved rapid and uniform heating up to 80 °C within seconds, maintaining consistent temperature distribution even on curved surfaces.
- [Korean]
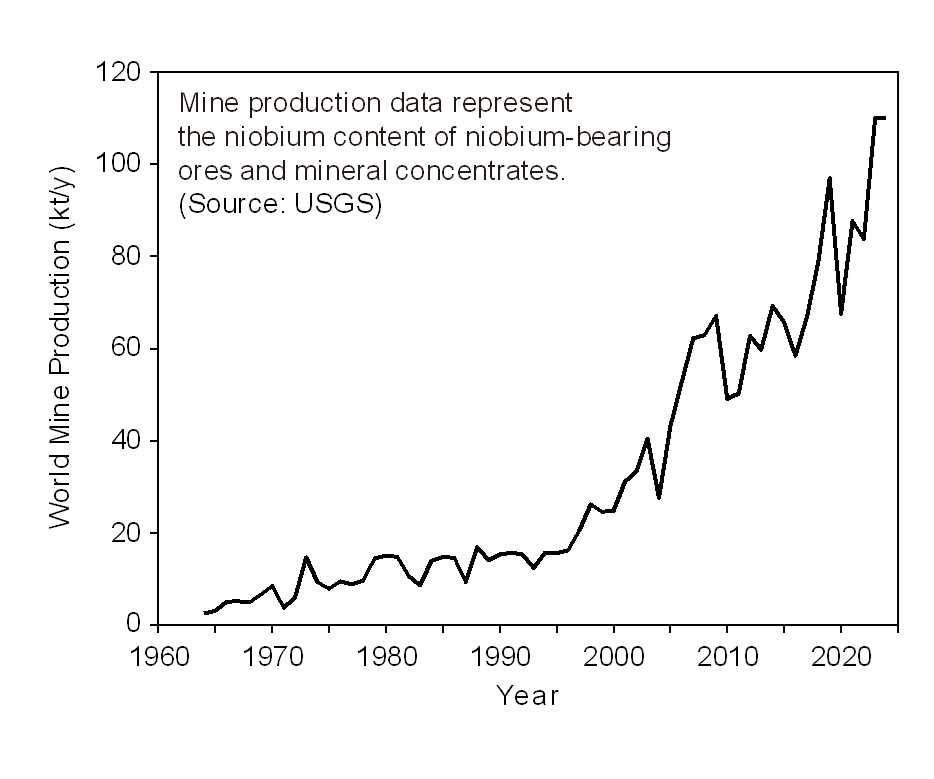
- Smelting and Recycling of Niobium
- Ho-Sang Sohn
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):517-528. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00367
- 727 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Global annual production of niobium is only around 100,000 tonnes; however, it is a critical metal for modern industry and is mined in only a limited number of regions. This study reviews the current status of niobium smelting and recycling technologies. Approximately 90% of niobium is produced as ferroniobium (FeNb) for use in steel alloys, although niobium is also utilized in superalloys, superconductors, capacitors, semiconductors, and other applications. Niobium coexists with tantalum in columbite and tantalite ores. These ores are decomposed by hydrofluoric acid digestion or alkali fusion, followed by solvent extraction to separate Nb2O5 and Ta2O5. Niobium metal and FeNb are produced from Nb2O5 primarily via aluminothermic reduction, although metallic niobium can also be manufactured by thermal reduction using Mg, Ca, or C, as well as by molten salt electrolysis. Crude niobium is subsequently refined into high-purity niobium through molten salt electrolytic refining, high-temperature vacuum treatment, and electron beam melting. Because most niobium is used as an alloying element in stainless steel and high-strength low-alloy steel, recycling practices for niobium remain poorly documented.
- [Korean]
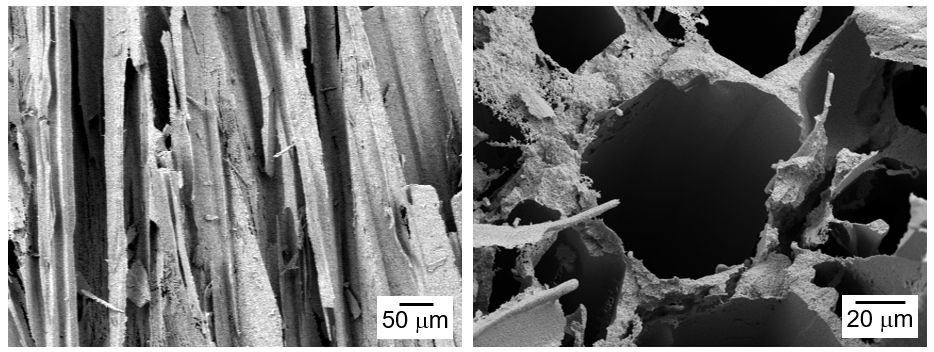
- Preparation of Porous W-Cu by Freeze Casting of Tert-butyl Alcohol Slurry Mixed with WO3-CuO Powder
- Youngmin Kim, Ji Young Kim, Minju Son, Wonyong Kwon, Eui Seon Lee, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):466-471. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00437
- 723 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The influence of process conditions on the microstructure of porous W-Cu, fabricated by freeze casting using tert-butyl alcohol as the freezing agent, was investigated. The slurries containing 10 vol% of WO3-CuO powder were prepared by milling with a small amount of citric acid and polyethylene glycol as dispersants. The slurries with dispersion stability were frozen in a mold with the lower part cooled to -25°C, followed by sublimation in a vacuum to remove the freezing agent. The sintered W-1 vol% Cu in a hydrogen atmosphere exhibited aligned pores with the size of 50 μm, which were generated by sublimation of directionally solidified tert-butyl alcohol crystals. In the cross-section of the specimen, hexagonal pores corresponding to the crystal structure of tert-butyl alcohol was observed. Microstructure analysis of the struts revealed that Cu was distributed non-uniformly due to the mutual insolubility and low wettability of the W-Cu system.
- [Korean]
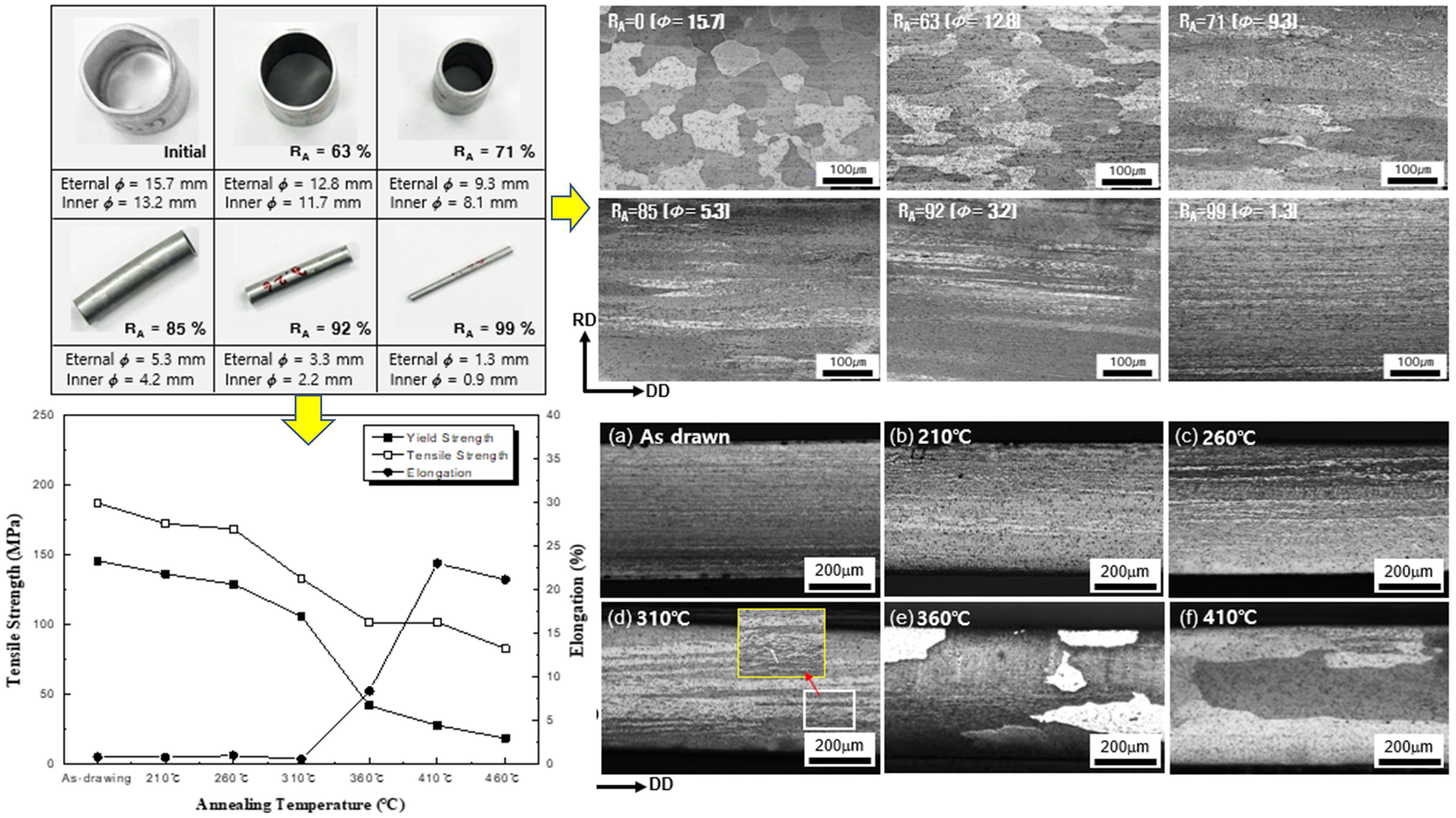
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AA3003 Tube for Heat Exchanger Processed by Floating Plug Drawing
- Hyeon-Jun Heo, Sung Jun Oh, Seong-Hee Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):459-465. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00346
- 722 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An AA3003 tube was severely deformed by cold floating plug drawing, and then annealed at temperatures from 210 to 460℃. The as drawn Al tube exhibited a typical deformation structure in which the grains were greatly elongated along the drawing direction. The hardness increased with increasing the reduction of cross-sectional area (RA), became 68Hv after RA= 99%. Up to 310℃, the Al tube still mainly exhibited a deformed structure. While complete recrystallization occurred at temperatures above 360℃. The hardness decreased with increasing the annealing temperature, and it became 33Hv after annealing at 410℃. Both the tensile and yield strengths also decreased with increasing the annealing temperature, but the decrease was larger in yield strength than in tensile strength. The elongation increased with increasing the annealing temperature. The changes in the strength and the elongation with the annealing temperature were the largest at 360℃, in which the complete recrystallization occurred.
- [Korean]
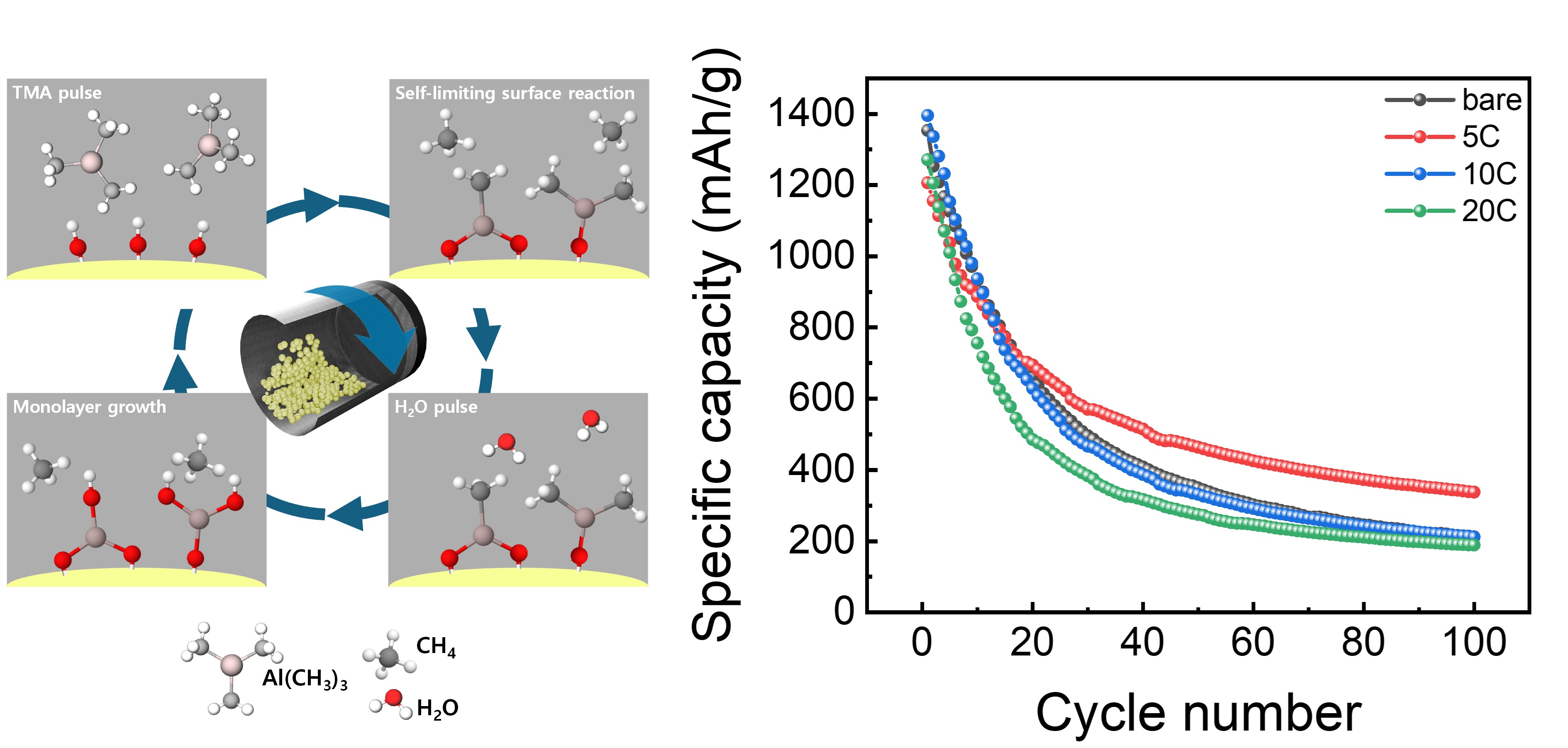
- Enhancement of the Electrochemical Performance of SiOx Anodes by Al2O3 Coating via Powder Atomic Layer Deposition
- Donggeon Shin, Yoonsoo Han
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):501-508. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00416
- 711 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Silicon based anode materials offer high theoretical capacity but suffer from severe volume expansion and unstable interfacial properties during repeated lithiation and delithiation, resulting in rapid performance degradation. In this study, a thin aluminum oxide coating layer was deposited on Si/SiOx Carbon anode materials using a powder atomic layer deposition (PALD) process to address these limitations. EDS mapping and XRD analyses confirmed the uniform formation of an amorphous aluminum oxide coating with increasing thickness as the deposition cycles increased. Electrochemical evaluation showed that the electrode coated with 5 PALD cycles exhibited approximately 78% higher capacity retention after 100 cycles at 1 A g-1 and a higher initial Coulombic efficiency compared to the bare electrode. The coated electrode also delivered approximately 22% higher capacity at a high current density of 5 A g-1, indicating enhanced rate capability. Cyclic voltammetry analysis revealed increased surface controlled reaction contributions and improved reaction kinetics. These results demonstrate that PALD derived aluminum oxide coatings effectively stabilize the electrode electrolyte interface and enhance the electrochemical performance of silicon based anodes, highlighting their potential for next generation high capacity lithium ion batteries. generation high capacity lithium ion battery anode materials.
- [English]
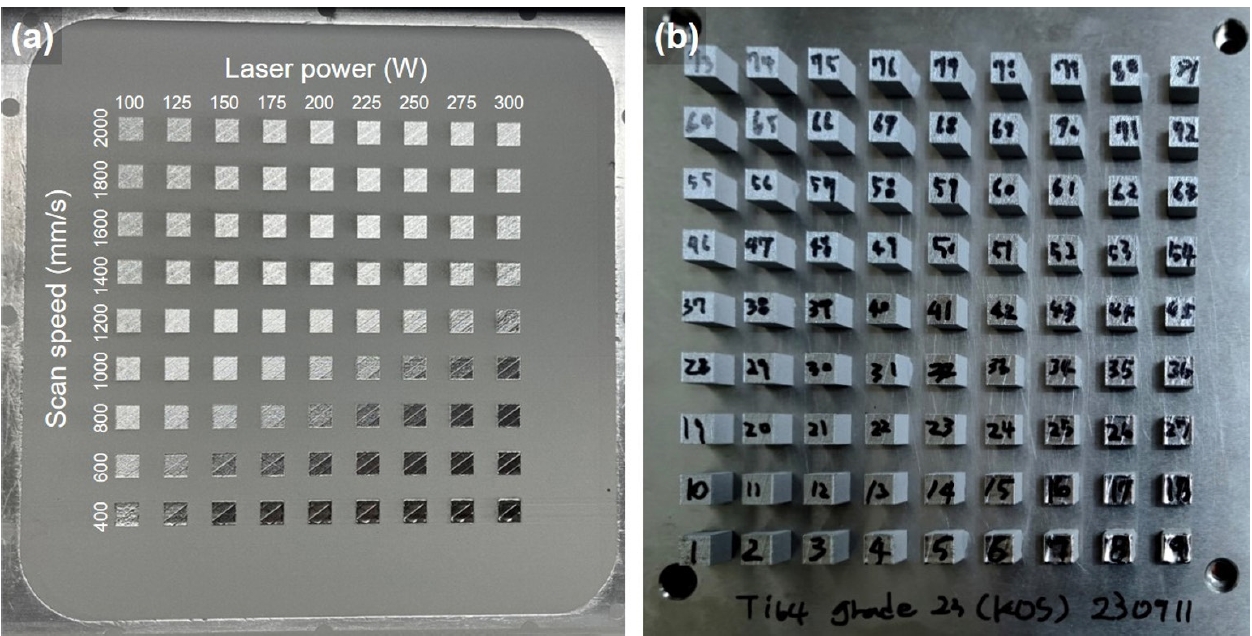
- Data-driven Approach to Explore the Contribution of Process Parameters for Laser Powder Bed Fusion of a Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
- Jeong Min Park, Jaimyun Jung, Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Yeon Woo Kim, Ji-Hun Yu
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):137-145. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00038
- 4,753 View
- 120 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In order to predict the process window of laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) for printing metallic components, the calculation of volumetric energy density (VED) has been widely calculated for controlling process parameters. However, because it is assumed that the process parameters contribute equally to heat input, the VED still has limitation for predicting the process window of LPBF-processed materials. In this study, an explainable machine learning (xML) approach was adopted to predict and understand the contribution of each process parameter to defect evolution in Ti alloys in the LPBF process. Various ML models were trained, and the Shapley additive explanation method was adopted to quantify the importance of each process parameter. This study can offer effective guidelines for fine-tuning process parameters to fabricate high-quality products using LPBF.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Data-Driven analysis relates mechanical properties to pore morphology in laser powder bed fusion
Jaemin Wang, Seungyeon Lee, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park, Dierk Raabe
Acta Materialia.2026; 304: 121751. CrossRef - From physics to intelligence: a review of AI-driven modeling strategies in laser direct energy deposition additive manufacturing
Seyedeh Fatemeh Nabavi, Saeid Nahavandi, Hamid Garmestani
Optics & Laser Technology.2026; 199: 114946. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef - Automated segmentation and analysis of microscopy images of laser powder bed fusion melt tracks
Aagam Shah, Reimar Weissbach, David A. Griggs, A. John Hart, Elif Ertekin, Sameh Tawfick
Journal of Manufacturing Processes.2025; 154: 61. CrossRef - Coefficient of Thermal Expansion of AlSi10Mg, 316L Stainless Steel and Ti6Al4V Alloys Made with Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Selami Emanet, Edem Honu, Kekeli Agbewornu, Evelyn Quansah, Congyuan Zeng, Patrick Mensah
Materials.2025; 18(19): 4468. CrossRef - Adaptive slicing for increased productivity of metal laser powder bed fusion
Lars Vanmunster, Louca R. Goossens, Laurent Sergeant, Brecht Van Hooreweder, Bey Vrancken
Additive Manufacturing.2025; 112: 105000. CrossRef
- Data-Driven analysis relates mechanical properties to pore morphology in laser powder bed fusion
- [English]
- Epsilon Iron Oxide (ε-Fe2O3) as an Electromagnetic Functional Material: Properties, Synthesis, and Applications
- Ji Hyeong Jeong, Hwan Hee Kim, Jung-Goo Lee, Youn-Kyoung Baek
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):465-479. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00290

- 3,539 View
- 92 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Iron oxide (ε-Fe₂O₃) is emerging as a promising electromagnetic material due to its unique magnetic and electronic properties. This review focuses on the intrinsic properties of ε-Fe₂O₃, particularly its high coercivity, comparable to that of rare-earth magnets, which is attributed to its significant magnetic anisotropy. These properties render it highly suitable for applications in millimeter wave absorption and high-density magnetic storage media. Furthermore, its semiconducting behavior offers potential applications in photocatalytic hydrogen production. The review also explores various synthesis methods for fabricating ε-Fe₂O₃ as nanoparticles or thin films, emphasizing the optimization of purity and stability. By exploring and harnessing the properties of ε-Fe₂O₃, this study aims to contribute to the advancement of next-generation electromagnetic materials with potential applications in 6G wireless telecommunications, spintronics, high-density data storage, and energy technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Review of GPR Data Analysis for Bridge Deck Evaluation: From Conventional Methods to Emerging Artificial Intelligence Approaches
Babak Enami Alamdari, Yu Tang, Danilo Erricolo, Lesley H. Sneed
Journal of Nondestructive Evaluation.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemical Pressure Induced Strain Control of Magnetic Anisotropy in the Simple Perovskite ϵ-Fe2O3
Subir Roy, Gurleen K. Uppal, Alberto Acosta, Rachel Nickel, Charles A. Roberts, Johan van Lierop
Nano Letters.2026; 26(1): 34. CrossRef - Superparamagnetism of Baked Clays Containing Polymorphs of Iron Oxides: Experimental Study and Theoretical Modeling
Petr Kharitonskii, Andrei Krasilin, Nadezhda Belskaya, Svetlana Yanson, Nikita Bobrov, Andrey Ralin, Kamil Gareev, Nikita Zolotov, Dmitry Zaytsev, Elena Sergienko
Magnetochemistry.2025; 11(12): 103. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Review of GPR Data Analysis for Bridge Deck Evaluation: From Conventional Methods to Emerging Artificial Intelligence Approaches
- [Korean]
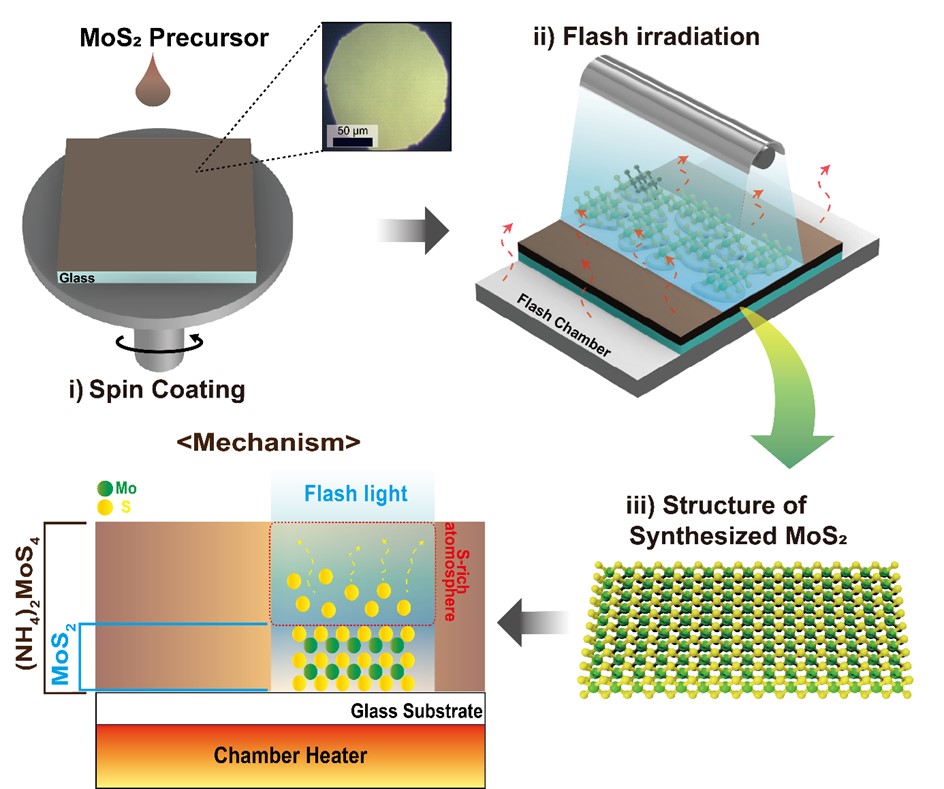
- Ultrafast Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide via Flashlamp Annealing
- Chan Hyeon Yang, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):509-516. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00339
- 690 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study presents the synthesis of molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) using flashlamp annealing and provides a comprehensive investigation of its structural and physical properties. The proposed flash-induced approach enables rapid production of high-quality MoS₂, offering superior process efficiency compared to conventional synthesis techniques. The structural, electronic, and thermal characteristics of the synthesized MoS₂ were systematically examined using multiple analytical methods, with particular attention to how synthesis conditions influence layer structure, crystallinity, and defect density. The results indicate that MoS₂ produced through this method exhibits material properties suitable for high-performance electronic devices and energy storage applications. Moreover, this work demonstrates the potential of flash-induced synthesis for scalable and practical fabrication of MoS₂-based nanomaterials, thereby contributing to the broader advancement of transition metal dichalcogenide technologies across diverse nanotechnology applications.
- [English]
- Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
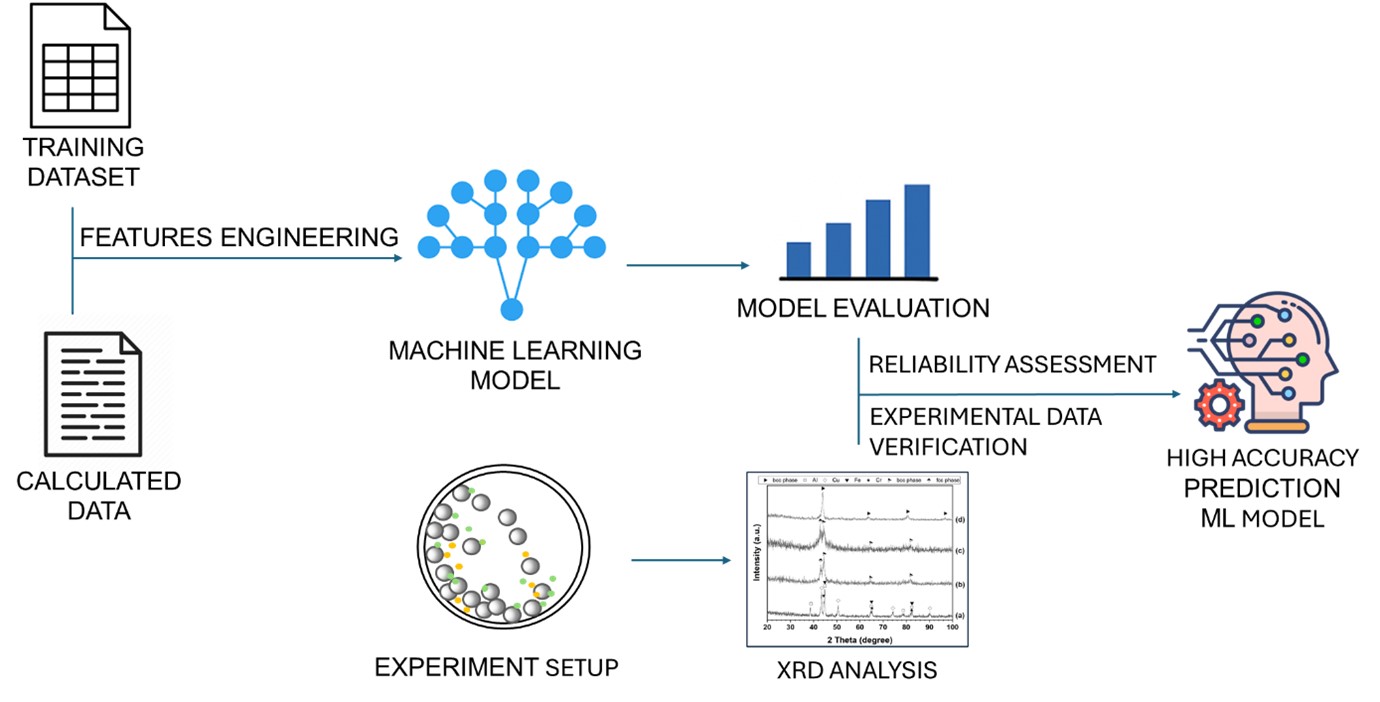
- Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang Oanh, , Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):191-201. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00143
- 2,462 View
- 81 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - High-entropy alloys (HEAs) exhibit complex phase formation behavior, challenging conventional predictive methods. This study presents a machine learning (ML) framework for phase prediction in HEAs, using a curated dataset of 648 experimentally characterized compositions and features derived from thermodynamic and electronic descriptors. Three classifiers—random forest, gradient boosting, and CatBoost—were trained and validated through cross-validation and testing. Gradient boosting achieved the highest accuracy, and valence electron concentration (VEC), atomic size mismatch (δ), and enthalpy of mixing (ΔHmix) were identified as the most influential features. The model predictions were experimentally verified using a non-equiatomic Al₃₀Cu₁₇.₅Fe₁₇.₅Cr₁₇.₅Mn₁₇.₅ alloy and the equiatomic Cantor alloy (CoCrFeMnNi), both of which showed strong agreement with predicted phase structures. The results demonstrate that combining physically informed feature engineering with ML enables accurate and generalizable phase prediction, supporting accelerated HEA design.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
Wooyoung Lee, Munsu Choi, Sungwook Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Myungsuk Song, Taek-Soo Kim, Jungwan Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim, Hyunjoo Choi, Soo-Hyun Joo
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 954: 149811. CrossRef - Preparation and Arc Erosion Behavior of Cu-Based Contact Materials Reinforced with High Entropy Particles CuCrNiCoFe
Jiacheng Tong, Jun Wang, Huimin Zhang, Haoran Liu, Youchang Sun, Zhiguo Li, Wenyi Zhang, Zhe Wang, Yanli Chang, Zhao Yuan, Henry Hu
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B.2025; 56(5): 5948. CrossRef - Recent progresses on high entropy alloy development using machine learning: A review
Abhishek Kumar, Nilay Krishna Mukhopadhyay, Thakur Prasad Yadav
Computational Materials Today.2025; 8: 100038. CrossRef
- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
- [English]
- Cryogenic Tensile Behavior of Ferrous Medium-entropy Alloy Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Seungyeon Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jae Wung Bae, Jeong Min Park
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):8-15. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.8
- 4,538 View
- 139 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The emergence of ferrous-medium entropy alloys (FeMEAs) with excellent tensile properties represents a potential direction for designing alloys based on metastable engineering. In this study, an FeMEA is successfully fabricated using laser powder bed fusion (LPBF), a metal additive manufacturing technology. Tensile tests are conducted on the LPBF-processed FeMEA at room temperature and cryogenic temperatures (77 K). At 77 K, the LPBF-processed FeMEA exhibits high yield strength and excellent ultimate tensile strength through active deformation-induced martensitic transformation. Furthermore, due to the low stability of the face-centered cubic (FCC) phase of the LPBF-processed FeMEA based on nano-scale solute heterogeneity, stress-induced martensitic transformation occurs, accompanied by the appearance of a yield point phenomenon during cryogenic tensile deformation. This study elucidates the origin of the yield point phenomenon and deformation behavior of the FeMEA at 77 K.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Stronger weld than base metal in face-centered cubic alloy through multi-scale heterogeneity
Yoona Lee, Sangwon Park, Dongwon Shin, Marcia Myung Hye Ahn, Wei Xiong, Nokeun Park, Hyoung Seop Kim, Je In Lee, Wookjin Lee, Yoon Suk Choi, Jeong Min Park, Namhyun Kang
Materials Research Letters.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Effect of Building Orientation on Tensile Properties of Hastelloy X alloy Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seong-June Youn, GooWon Noh, Seok Su Sohn, Young-Sang Na, Young-Kyun Kim
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(2): 130. CrossRef - Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang, Oanh, Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 191. CrossRef - Cryogenic tensile behavior of carbon-doped CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloys additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Haeum Park, Hyeonseok Kwon, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Jungho Choe, Hyokyung Sung, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jung Gi Kim, Jeong Min Park
Additive Manufacturing.2024; 86: 104223. CrossRef - Recent progress in high-entropy alloys for laser powder bed fusion: Design, processing, microstructure, and performance
Asker Jarlöv, Zhiguang Zhu, Weiming Ji, Shubo Gao, Zhiheng Hu, Priyanka Vivegananthan, Yujia Tian, Devesh Raju Kripalani, Haiyang Fan, Hang Li Seet, Changjun Han, Liming Tan, Feng Liu, Mui Ling Sharon Nai, Kun Zhou
Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports.2024; 161: 100834. CrossRef
- Stronger weld than base metal in face-centered cubic alloy through multi-scale heterogeneity
- [English]
- Comparative Review of the Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Fabricated via Wrought and Powder Metallurgy Processes
- Raj Narayan Hajra, Gargi Roy, An Seong Min, Hyunseok Lee, Jeoung Han Kim
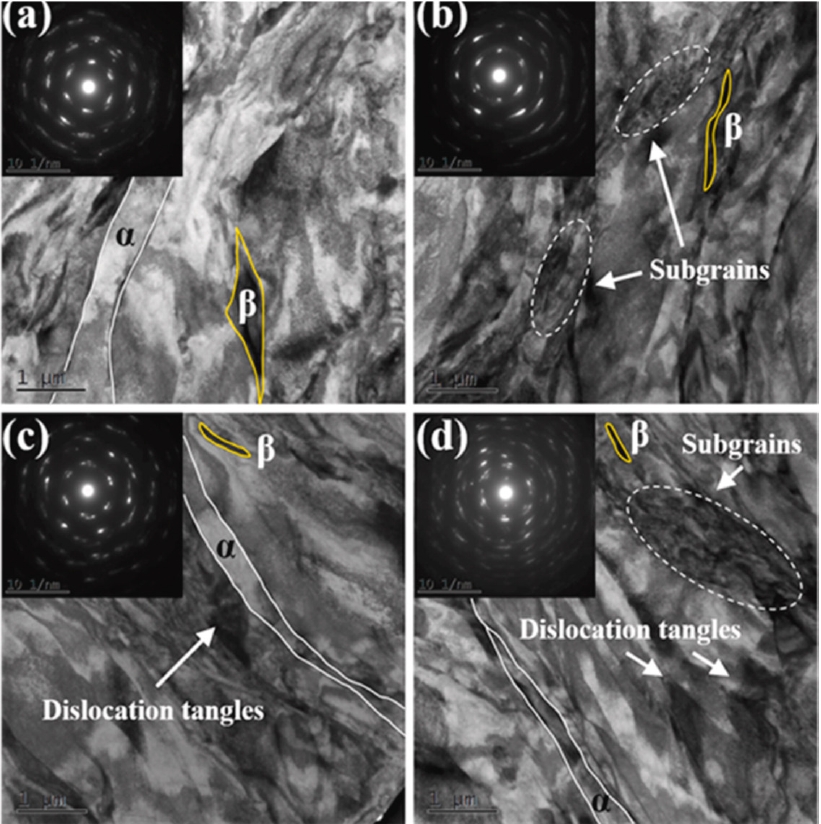
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):365-373. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00213
- 2,855 View
- 67 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This review examines the microstructural and mechanical properties of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy produced by wrought processing and powder metallurgy (PM), specifically laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) and hot isostatic pressing. Wrought methods, such as forging and rolling, create equiaxed alpha (α) and beta (β) grain structures with balanced properties, which are ideal for fatigue resistance. In contrast, PM methods, particularly LPBF, often yield a martensitic α′ structure with high microhardness, enabling complex geometries but requiring post-processing to improve its properties and reduce stress. The study evaluated the effects of processing parameters on grain size, phase distribution, and material characteristics, guiding the choice of fabrication techniques for optimizing Ti-6Al-4V performance in aerospace, biomedical, and automotive applications. The analysis emphasizes tailored processing to meet advanced engineering demands.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Removal of Organic and Inorganic Contaminants from Titanium Turning Scrap via Alkali and Acid Two-Step Cleaning
Seong Min An, Raj Narayan Hajra, Chan Hee Park, Jin-Ho Yoon, Jinsung Rho, Chang-Min Yoon, Jeoung Han Kim
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(7): 855. CrossRef - Effect of oxygen content in feedstock powders on microstructure and mechanical properties of ELI Ti-6Al-4V fabricated via laser powder bed fusion
Woo Hyeok Kim, Sang Woo Kim, Raj Narayan Hajra, Gargi Roy, Jeoung Han Kim
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 307. CrossRef
- Removal of Organic and Inorganic Contaminants from Titanium Turning Scrap via Alkali and Acid Two-Step Cleaning
- [English]
- Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy through Selective Laser Melting: Comprehensive Study on the Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
- Gargi Roy, Raj Narayan Hajra, Woo Hyeok Kim, Jongwon Lee, Sangwoo Kim, Jeoung Han Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):1-7. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.1

- 6,090 View
- 134 Download
- 9 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study explores the profound impact of varying oxygen content on microstructural and mechanical properties in specimens HO and LO. The higher oxygen concentration in specimen HO is found to significantly influence alpha lath sizes, resulting in a size of 0.5-1 μm, contrasting with the 1-1.5 μm size observed in specimen LO. Pore fraction, governed by oxygen concentration, is high in specimen HO, registering a value of 0.11%, whereas specimen LO exhibits a lower pore fraction (0.02%). Varied pore types in each specimen further underscore the role of oxygen concentration in shaping microstructural morphology. Despite these microstructural variations, the average hardness remains consistent at ~370 HV. This study emphasizes the pivotal role of oxygen content in influencing microstructural features, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of the intricate interplay between elemental composition and material properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Additive manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V based oxide dispersion strengthened alloy using in-situ oxide-dispersed powders and bound metal deposition
Woo Hyeok Kim, Raj Narayan Hajra, Hyung-Ki Park, Jung-Yeul Yun, Jeoung Han Kim
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2026; 1050: 185574. CrossRef - Mechanical response and microstructural evolution of a composite joint fabricated by green laser dissimilar welding of VCoNi medium entropy alloy and 17-4PH stainless steel
Hadiseh Esmaeilpoor, Mahdi Aghaahmadi, Hyun Jong Yoo, Chan Woong Park, Tae Jin Jang, Seok Su Sohn, Jeoung Han Kim
Journal of Materials Science & Technology.2025; 213: 223. CrossRef - High-integrity diffusion bonding of laser powder bed fused, forged, and rolled Ti–6Al–4V alloys
Seoyeon Jeon, Hyunjong Ha, Dong Jun Lee, Hyeonil Park, Yong Nam Kwon, Hyunjoo Choi, Hyokyung Sung
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2025; 35: 2108. CrossRef - Removal of Organic and Inorganic Contaminants from Titanium Turning Scrap via Alkali and Acid Two-Step Cleaning
Seong Min An, Raj Narayan Hajra, Chan Hee Park, Jin-Ho Yoon, Jinsung Rho, Chang-Min Yoon, Jeoung Han Kim
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(7): 855. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef - Obtaining functionally-graded metal-matrix materials Ti‒6Al‒4V + WC in the process of 3D printing by the method of additive plasma-arc deposition
V. Korzhyk, A. Grynyuk, O. Babych, O. Berdnikova, Ye. Illiashenko, O. Bushma
The Paton Welding Journal.2025; 2025(8): 29. CrossRef - Obtaining functionally-graded metal-matrix materials ti‒6al‒4v + wc by the method of additive plasma-arc deposition
V.M. Korzhyk, A.A. Grynyuk, O.A. Babych, O.M. Berdnikova, Ye.V. Illiashenko, O.I. Bushma
Avtomatičeskaâ svarka (Kiev).2025; 2025(5): 48. CrossRef - Comparative Review of the Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Fabricated via Wrought and Powder Metallurgy Processes
Raj Narayan Hajra, Gargi Roy, An Seong Min, Hyunseok Lee, Jeoung Han Kim
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 365. CrossRef - A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 390. CrossRef
- Additive manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V based oxide dispersion strengthened alloy using in-situ oxide-dispersed powders and bound metal deposition
- [English]
- Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
- Linh Ba Vu, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son, Seungki Jo
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):119-125. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00045

- 3,200 View
- 81 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The n-type Bi2-xSbxTe3 compounds have been of great interest due to its potential to achieve a high thermoelectric performance, comparable to that of p-type Bi2-xSbxTe3. However, a comprehensive understanding on the thermoelectric properties remains lacking. Here, we investigate the thermoelectric transport properties and band characteristics of n-type Bi2-xSbxTe3 (x = 0.1 – 1.1) based on experimental and theoretical considerations. We find that the higher power factor at lower Sb content results from the optimized balance between the density of state effective mass and nondegenerate mobility. Additionally, a higher carrier concentration at lower x suppresses bipolar conduction, thereby reducing thermal conductivity at elevated temperatures. Consequently, the highest zT of ~ 0.5 is observed at 450 K for x = 0.1 and, according to the single parabolic band model, it could be further improved by ~70 % through carrier concentration tuning.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
Yeon-Joo Lee, Pil-Ryung Cha, Hyoung-Seop Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(1): 144. CrossRef - Enhanced energy harvesting performance of bendable thermoelectric generator enabled by trapezoidal-shaped legs
Momanyi Amos Okirigiti, Cheol Min Kim, Hyejeong Choi, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Journal of Power Sources.2025; 631: 236254. CrossRef - Flexible hybrid thermoelectric films made of bismuth telluride-PEDOT:PSS composites enabled by freezing-thawing process and simple chemical treatment
Cheol Min Kim, Seoha Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Bitna Bae, Momanyi Amos Okirigiti, Gwang Hyun Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Haksu Jang, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Materials Today Chemistry.2025; 44: 102532. CrossRef - Enhanced Electrical Properties of 3D Printed Bi2Te3-Based Thermoelectric Materials via Hot Isostatic Pressing
Seungki Jo
Ceramist.2025; 28(1): 126. CrossRef - Hot isostatic pressing-driven fine-tuning of electrical properties in p- and n-type (Bi,Sb)2Te3 thermoelectric materials
Seungki Jo, Jeong Min Park, Linh Ba Vu, Haeum Park, Soo Ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Jungho Choe, Kyung Tae Kim
Ceramics International.2025; 51(26): 51107. CrossRef - Compensation of increased carrier concentration and thermal conductivity in enhancing thermoelectric efficiency in Sn-doped Sb-In-Te alloys
Yunjae Kim, Seungwoo Ha, Gyujin Chang, Gwan Hyeong Lee, Jaewoo Park, Chanwoo Ju, Se Yun Kim, TaeWan Kim, Sang-il Kim
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
- [English]
- Trends in Materials Modeling and Computation for Metal Additive Manufacturing
- Seoyeon Jeon, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):213-219. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00150
- 2,699 View
- 74 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Additive Manufacturing (AM) is a process that fabricates products by manufacturing materials according to a three-dimensional model. It has recently gained attention due to its environmental advantages, including reduced energy consumption and high material utilization rates. However, controlling defects such as melting issues and residual stress, which can occur during metal additive manufacturing, poses a challenge. The trial-and-error verification of these defects is both time-consuming and costly. Consequently, efforts have been made to develop phenomenological models that understand the influence of process variables on defects, and mechanical/electrical/thermal properties of geometrically complex products. This paper introduces modeling techniques that can simulate the powder additive manufacturing process. The focus is on representative metal additive manufacturing processes such as Powder Bed Fusion (PBF), Direct Energy Deposition (DED), and Binder Jetting (BJ) method. To calculate thermal-stress history and the resulting deformations, modeling techniques based on Finite Element Method (FEM) are generally utilized. For simulating the movements and packing behavior of powders during powder classification, modeling techniques based on Discrete Element Method (DEM) are employed. Additionally, to simulate sintering and microstructural changes, techniques such as Monte Carlo (MC), Molecular Dynamics (MD), and Phase Field Modeling (PFM) are predominantly used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
Yeon-Joo Lee, Pil-Ryung Cha, Hyoung-Seop Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(1): 144. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef
- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
- [English]
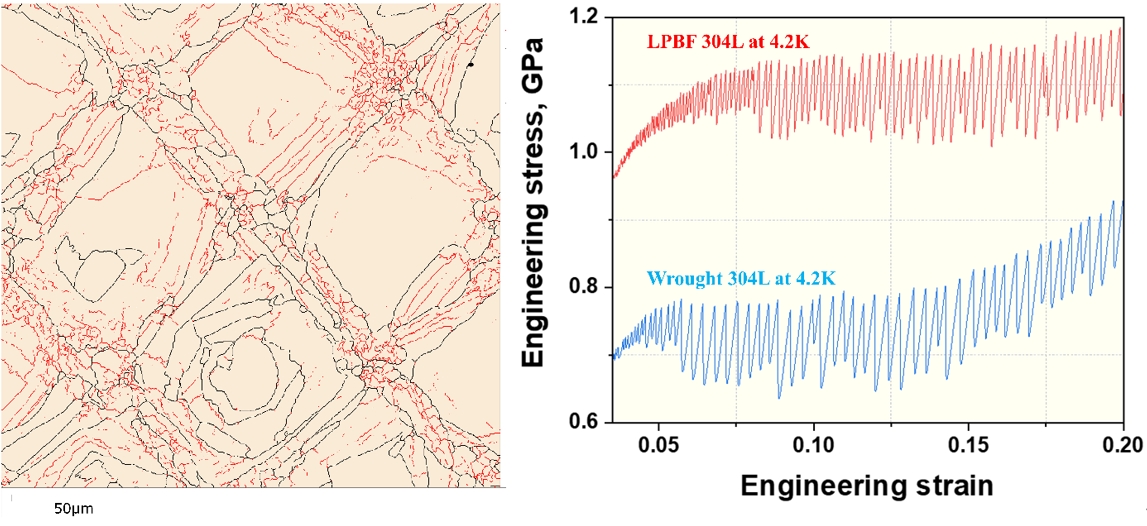
- Ultra-Low-Temperature (4.2 K) Tensile Properties and Deformation Mechanism of Stainless Steel 304L Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Seung-Min Jeon, Young-Sang Na, Young-Kyun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):95-103. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00066
- 1,939 View
- 57 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the ultra-low-temperature (4.2 K) tensile properties and deformation mechanisms of stainless steel 304L manufactured via laser powder bed fusion (LPBF). The tensile properties of LPBF 304L were compared to those of conventional 304L to assess its suitability for cryogenic applications. The results revealed that LPBF 304L exhibited a significantly higher yield strength but lower ultimate tensile strength and elongation than conventional 304L at 4.2 K. The temperature dependence of the yield strength also favored LPBF 304L. Microstructural analysis demonstrated that LPBF 304L features a high density of dislocation cells and nano-inclusions, contributing to its greater strength. Furthermore, strain-induced martensitic transformation was observed as a key deformation mechanism at cryogenic temperatures, where austenite transformed into both hexagonal-closed packed (HCP) and body-centered cubic (BCC) martensite. Notably, BCC martensite nucleation occurred within a single HCP band. These findings provide critical insights into the mechanical behavior of LPBF 304L at cryogenic temperatures and its potential for applications in extreme environments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extremely low-temperature tensile behavior of 316L stainless steel additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Haeum Park, Heechan Jung, Min Young Sung, Young-Kyun Kim, Jaimyun Jung, Yoona Lee, Namhyun Kang, Kyung Tae Kim, Young-Sang Na, Seok Su Sohn, Jeong Min Park
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 950: 149460. CrossRef - Twinning- and transformation-induced high cryogenic strength and ductility of the CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy: Experiment and MD simulation
Yuze Wu, Zhide Li, Charlie Kong, M.W. Fu, Hailiang Yu
International Journal of Plasticity.2026; 196: 104553. CrossRef - Understanding the unique appearance behavior of shear bands during tensile deformation of α-brass at 4.2 K
Seon-Keun Oh, Sang-Hun Shim, Young-Kyun Kim, Young-Sang Na
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2025; 945: 148989. CrossRef
- Extremely low-temperature tensile behavior of 316L stainless steel additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
- [English]
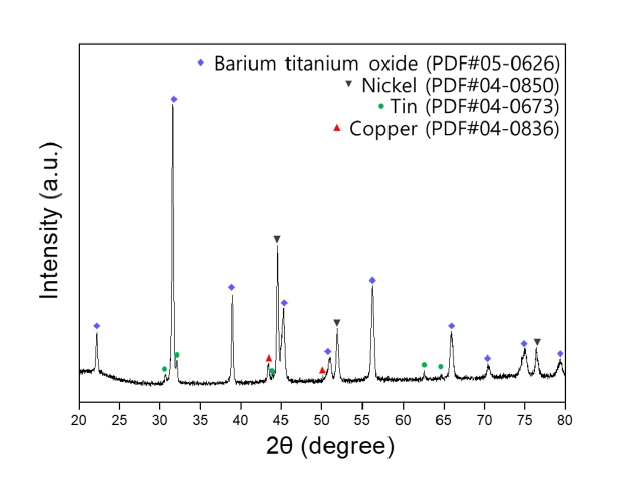
- Recovery of Barium, Nickel, and Titanium Powders from Waste MLCC
- Haein Shin, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):374-381. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00192
- 2,284 View
- 58 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The development of the electronics industry has led to an increased demand for the manufacture of MLCC (Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors), which in turn is expected to result in a rise in MLCC waste. The MLCC contains various metals, notably barium, titanium, and nickel, whose disposal is anticipated to increase correspondingly. Recently, recycling technologies for electronic waste have garnered attention as they address waste management and raw material supply challenges. This paper investigates the recovery of barium, nickel, and titanium from the MLCC by a hydrometallurgical process. Using citric acid, which is an organic acid, the metal inside the MLCC was leached. Additionally, metal materials were recovered through precipitation and complexing processes. As a result, barium and titanium were recovered from the leachate of the waste MLCC, and 93% of the nickel-based powder was recovered. Furthermore, the optimal recovery process conditions for recycling these metal elements were investigated.
- [Korean]
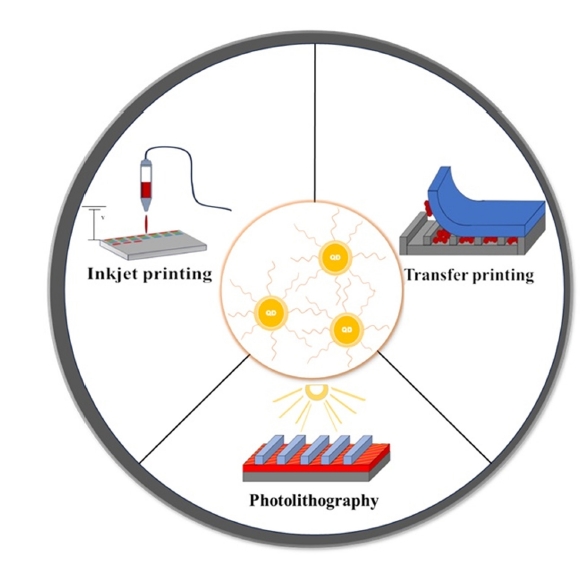
- Recent Developments in Quantum Dot Patterning Technology for Quantum Dot Display
- Yeong Jun Jin, Kyung Jun Jung, Jaehan Jung
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):169-179. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00073
- 7,069 View
- 156 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Colloidal quantum dot (QDs) have emerged as a crucial building block for LEDs due to their size-tunable emission wavelength, narrow spectral line width, and high quantum efficiency. Tremendous efforts have been dedicated to improving the performance of quantum dot light-emitting diodes (QLEDs) in the past decade, primarily focusing on optimization of device architectures and synthetic procedures for high quality QDs. However, despite these efforts, the commercialization of QLEDs has yet to be realized due to the absence of suitable large-scale patterning technologies for high-resolution devices., This review will focus on the development trends associated with transfer printing, photolithography, and inkjet printing, and aims to provide a brief overview of the fabricated QLED devices. The advancement of various quantum dot patterning methods will lead to the development of not only QLED devices but also solar cells, quantum communication, and quantum computers.
- [English]
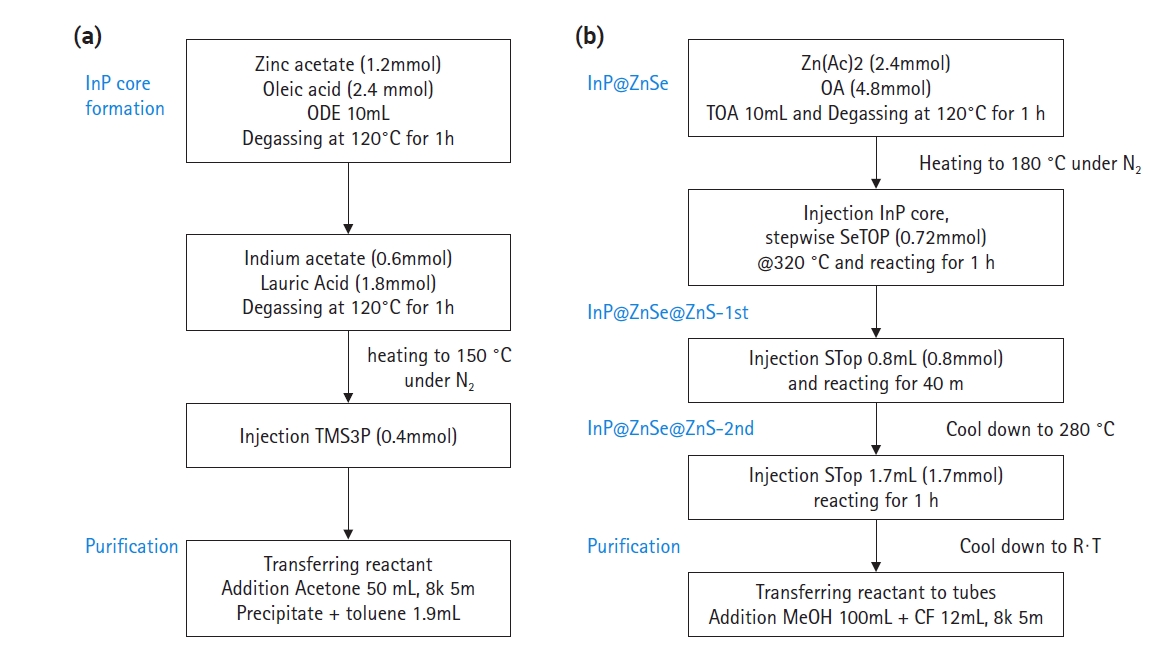
- Bandgap Tuning and Quenching Effects of In(Zn)P@ZnSe@ZnS Quantum Dots
- Sang Yeon Lee, Su Hyun Park, Gyungsu Byun, Chang-Yeoul Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):226-235. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00003
- 3,067 View
- 45 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - InP quantum dot (QDs) have attracted researchers’ interest due to their applicability in quantum dot light-emitting displays (QLED) or biomarkers for detecting cancers or viruses. The surface or interface control of InP QD core/shell has substantially increased quantum efficiency, with a quantum yield of 100% reached by introducing HF to inhibit oxide generation. In this study, we focused on the control of bandgap energy of quantum dots by changing the Zn/(In+Zn) ratio in the In(Zn)P core. Zinc incorporation can change the photoluminescent light colors of green, yellow, orange, and red. Diluting a solution of as-synthesized QDs by more than 100 times did not show any quenching effects by the Förster resonance energy transfer phenomenon between neighboring QDs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing luminescence of QD thin films, polymer composite films, and LED devices by nanostructures
Hongcheng Yang, Junjie Hao, Mingyu Sun, Yujie Song, Kai Wang, Yujie Song, Xiao Wei Sun, Wenda Zhang
The Innovation.2026; 7(2): 101121. CrossRef
- Enhancing luminescence of QD thin films, polymer composite films, and LED devices by nanostructures
- [English]
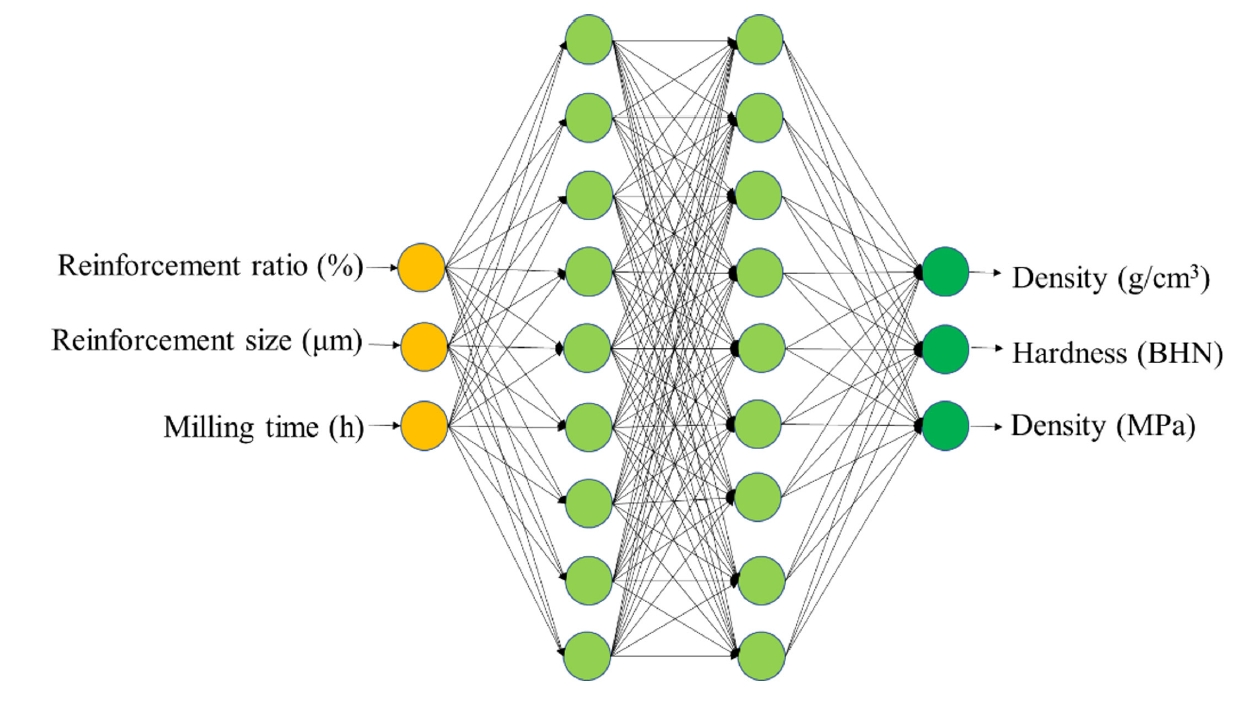
- Machine Learning Modeling of the Mechanical Properties of Al2024-B4C Composites
- Maurya A. K., Narayana P. L., Wang X.-S., Reddy N. S.
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):382-389. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00234
- 1,581 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Aluminum-based composites are in high demand in industrial fields due to their light weight, high electrical conductivity, and corrosion resistance. Due to its unique advantages for composite fabrication, powder metallurgy is a crucial player in meeting this demand. However, the size and weight fraction of the reinforcement significantly influence the components' quality and performance. Understanding the correlation of these variables is crucial for building high-quality components. This study, therefore, investigated the correlations among various parameters—namely, milling time, reinforcement ratio, and size—that affect the composite’s physical and mechanical properties. An artificial neural network model was developed and showed the ability to correlate the processing parameters with the density, hardness, and tensile strength of Al2024-B4C composites. The predicted index of relative importance suggests that the milling time has the most substantial effect on fabricated components. This practical insight can be directly applied in the fabrication of high-quality Al2024-B4C composites.
- [Korean]
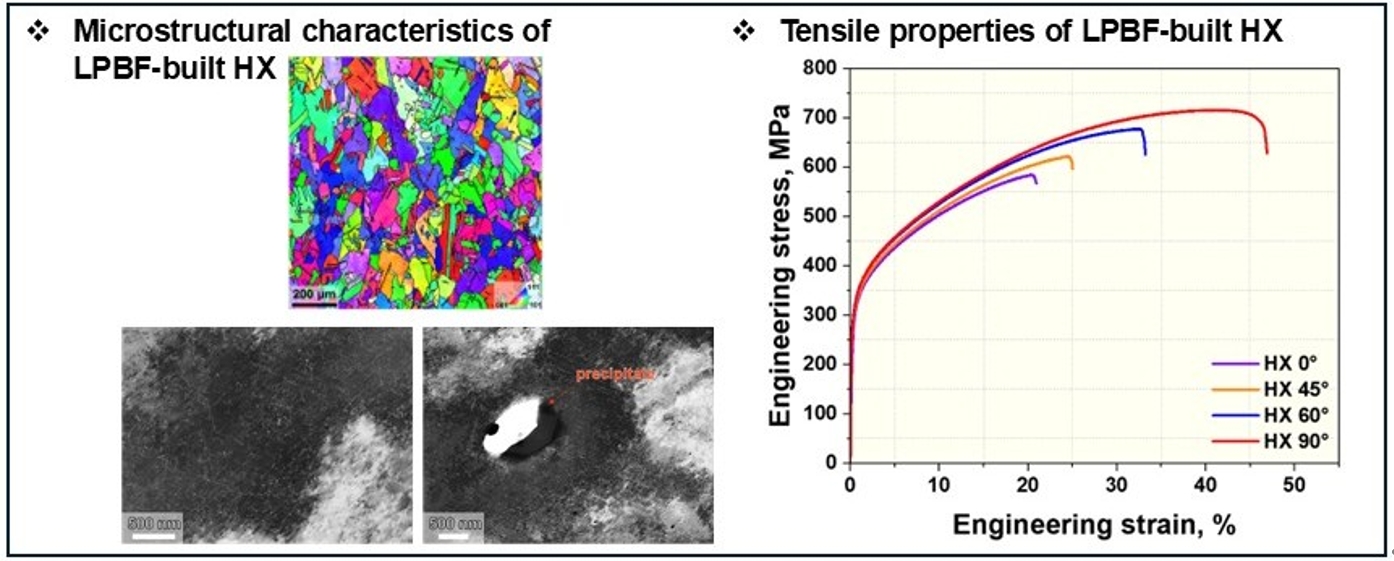
- Effect of Building Orientation on Tensile Properties of Hastelloy X alloy Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Seong-June Youn, GooWon Noh, Seok Su Sohn, Young-Sang Na, Young-Kyun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):131-137. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00080
- 1,149 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, the effect of build orientation on the mechanical properties of Hastelloy X fabricated by laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) process was investigated. Initial microstructural analysis revealed an equiaxed grain structure with random crystallographic orientation and annealing twins. Intragranular precipitates identified as Cr-rich M23C6 and Mo-rich M6C carbides were observed, along with a dense dislocation network and localized dislocation accumulation around the carbides. Mechanical testing showed negligible variation in yield strength with respect to build orientation; however, both ultimate tensile strength and elongation exhibited a clear increasing trend with higher build angles. Notably, the specimen built at 90° exhibited approximately 22% higher tensile strength and more than twice the elongation compared to the 0° specimen.
- [Korean]
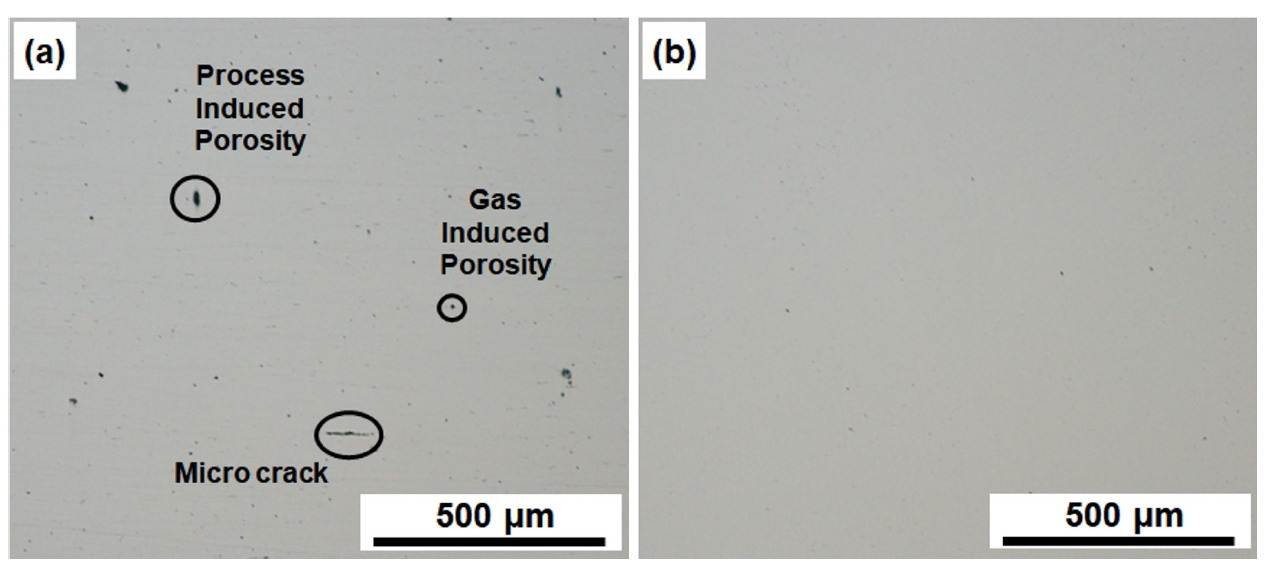
- Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing on the Stellite 6 Alloy prepared by Directed Energy Deposition
- Joowon Suh, Jae Hyeon Koh, Young-Bum Chun, Young Do Kim, Jinsung Jang, Suk Hoon Kang, Heung Nam Han
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):152-162. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00066
- 1,758 View
- 39 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The directed energy deposited (DED) alloys show higher hardness values than the welded alloys due to the finer microstructure following the high cooling rate. However, defects such as microcracks, pores, and the residual stress are remained within the DED alloy. These defects deteriorate the wear behavior so post-processing such as heat treatment and hot isostatic pressing (HIP) are applied to DED alloys to reduce the defects. HIP was chosen in this study because the high pressure and temperature uniformly reduced the defects. The HIP is processed at 1150oC under 100 MPa for 4 hours. After HIP, microcracks are disappeared and porosity is reduced by 86.9%. Carbides are spherodized due to the interdiffusion of Cr and C between the dendrite and interdendrite region. After HIP, the nanohardness (GPa) of carbides increased from 11.1 to 12, and the Co matrix decreased from 8.8 to 7.9. Vickers hardness (HV) decreased by 18.9 % after HIP. The dislocation density (10-2/m2) decreased from 7.34 to 0.34 and the residual stress (MPa) changed from tensile 79 to a compressive -246 by HIP. This study indicates that HIP is effective in reducing defects, and the HIP DED Stellite 6 exhibits a higher HV than welded Stellite 6.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Recycling Process and Powderization Technology of Stellite 6 Scrap: A Thermodynamic and Heat Transfer Analysis
YongKwan Lee, Hyun-chul Kim, Myungsuk Kim, Soong Ju Oh, Kyoungtae Park, JaeJin Sim
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 330. CrossRef
- The Recycling Process and Powderization Technology of Stellite 6 Scrap: A Thermodynamic and Heat Transfer Analysis
- [English]
- Characterization of the Manufacturing Process and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloys via Metal Injection Molding and Hot Isostatic Pressing
- Eun Seong Kim, Jae Man Park, Do Won Lee, Hyojeong Ha, Jungho Choe, Jaemin Wang, Seong Jin Park, Byeong-Joo Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):243-254. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00059

- 2,244 View
- 56 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - High-entropy alloys (HEAs) have been reported to have better properties than conventional materials; however, they are more expensive due to the high cost of their main components. Therefore, research is needed to reduce manufacturing costs. In this study, CoCrFeMnNi HEAs were prepared using metal injection molding (MIM), which is a powder metallurgy process that involves less material waste than machining process. Although the MIM-processed samples were in the face-centered cubic (FCC) phase, porosity remained after sintering at 1200°C, 1250°C, and 1275°C. In this study, the hot isostatic pressing (HIP) process, which considers both temperature (1150°C) and pressure (150 MPa), was adopted to improve the quality of the MIM samples. Although the hardness of the HIP-treated samples decreased slightly and the Mn composition was significantly reduced, the process effectively eliminated many pores that remained after the 1275°C MIM process. The HIP process can improve the quality of the alloy.
- [English]
- Effect of Calcium Addition on the High-Temperature Recovery of Nd and Dy from Nd-Fe-B Scrap Using Mg-Based Extractants
- Hyoseop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):493-499. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00283

- 1,708 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated whether calcium (Ca) addition improved the recovery of neodymium (Nd) and dysprosium (Dy) from Nd-Fe-B magnet scrap using magnesium (Mg)-based liquid metal extraction (LME). Traditional LME processes are limited to temperatures up to 850 °C due to oxidation issues, reducing the efficiency of rare earth element (REE) recovery, especially for Dy. By adding 10 wt.% Ca to Mg and increasing the processing temperature to 1,000 °C, we achieved nearly 100% Nd and approximately 38% Dy recovery, compared to 91% and 28%, respectively, with pure Mg at 850 °C. However, excessive Ca addition (20 wt.%) decreased the recovery efficiency due to the formation of stable intermetallic compounds. These results highlight the critical role of Ca in optimizing REE recycling from Nd-Fe-B magnet scrap.
- [Korean]
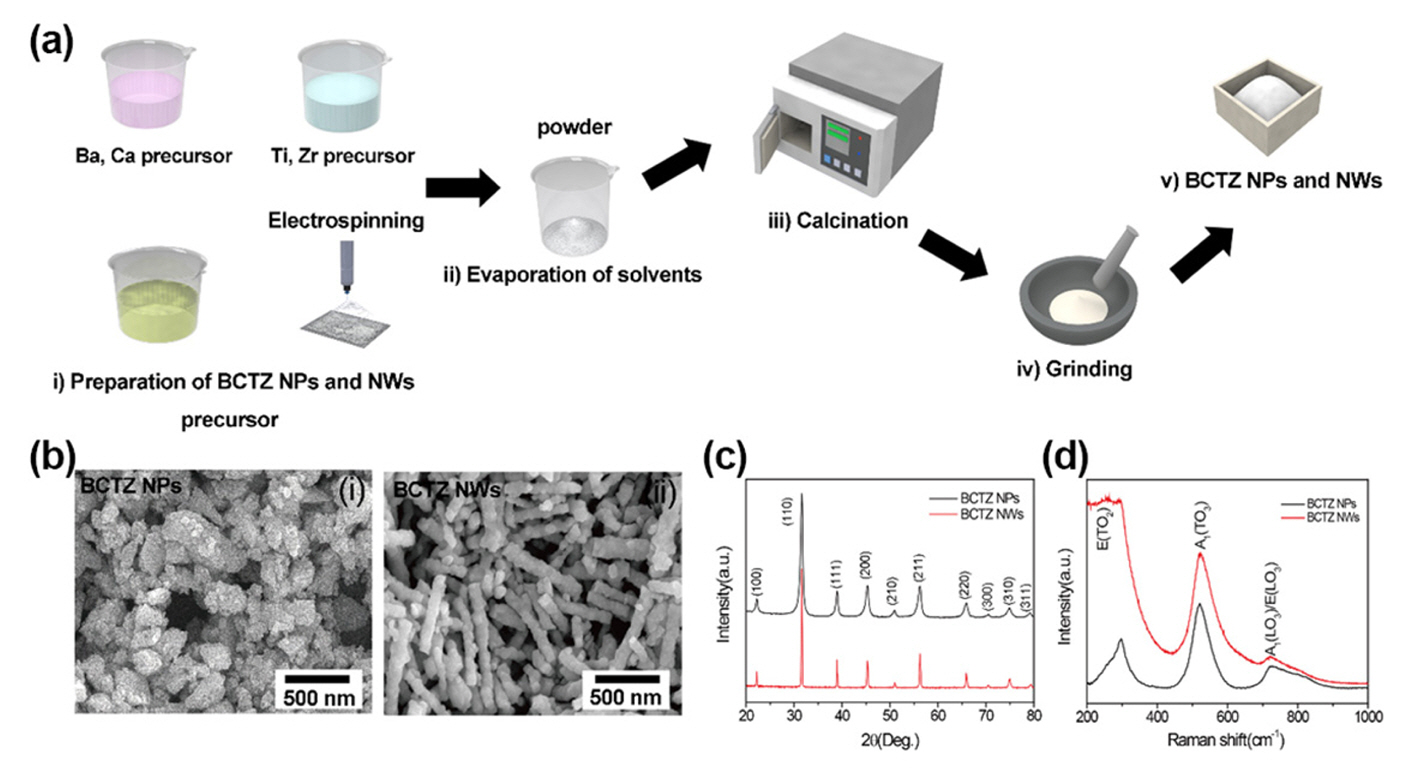
- Development of Composite-film-based Flexible Energy Harvester using Lead-free BCTZ Piezoelectric Nanomaterials
- Gwang Hyeon Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Bitna Bae, Haksu Jang, Cheol Min Kim, Donghun Lee, Kwi-Il Park
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):16-22. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.16
- 1,853 View
- 33 Download
- 10 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Composite-based piezoelectric devices are extensively studied to develop sustainable power supply and selfpowered devices owing to their excellent mechanical durability and output performance. In this study, we design a leadfree piezoelectric nanocomposite utilizing (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.9Zr0.1)O3 (BCTZ) nanomaterials for realizing highly flexible energy harvesters. To improve the output performance of the devices, we incorporate porous BCTZ nanowires (NWs) into the nanoparticle (NP)-based piezoelectric nanocomposite. BCTZ NPs and NWs are synthesized through the solidstate reaction and sol-gel-based electrospinning, respectively; subsequently, they are dispersed inside a polyimide matrix. The output performance of the energy harvesters is measured using an optimized measurement system during repetitive mechanical deformation by varying the composition of the NPs and NWs. A nanocomposite-based energy harvester with 4:1 weight ratio generates the maximum open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current of 0.83 V and 0.28 A, respectively. In this study, self-powered devices are constructed with enhanced output performance by using piezoelectric energy harvesting for application in flexible and wearable devices.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unidirectional porous PVDF Piezoelectrets fabricated via gradient ice-templating for enhanced energy harvesting performance
HyoMin Jeon, Seo Young Yoon, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Momanyi Amos Okirigiti, HakSu Jang, Changyeon Baek, Tiandong Zhang, Geon-Tae Hwang, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Sustainable Materials and Technologies.2026; 47: e01888. CrossRef - In Situ Amidation‐Derived Interfacial Modulation for Homogeneous Ultra‐High Nanoparticle Loading Toward Robust and Flexible Piezoelectric Composites
HakSu Jang, In Beom Heo, Changyeon Baek, Dong Won Jeon, Donghun Lee, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Hyejeong Choi, HyoMin Jeon, SungHoon Kim, Hyunseung Kim, Jihun Choi, Hyun‐Soo Chang, Chang Kyu Jeong, Min‐Ku Lee, Jun Mo Koo, Tiandong Zhang, Geon‐Tae Hwang, S
Advanced Functional Materials.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Long‐Lasting, Steady and Enhanced Energy Harvesting by Inserting a Conductive Layer into the Piezoelectric Polymer
HakSu Jang, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Dong Won Jeon, Hyeon Jun Park, BitNa Bae, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Cheol Min Kim, Changyeon Baek, Min‐Ku Lee, Sung Beom Cho, Gyoung‐Ja Lee, Kwi‐Il Park
Advanced Functional Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Flexible hybrid thermoelectric films made of bismuth telluride-PEDOT:PSS composites enabled by freezing-thawing process and simple chemical treatment
Cheol Min Kim, Seoha Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Bitna Bae, Momanyi Amos Okirigiti, Gwang Hyun Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Haksu Jang, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Materials Today Chemistry.2025; 44: 102532. CrossRef - Dual-controlled piezoelectric composite film with enhanced crystallinity and defect-free via solvent vapor treatment
HakSu Jang, Hyeon Jun Park, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Cheol Min Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, BitNa Bae, HyoMin Jeon, DongHun Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Nano Energy.2025; 136: 110705. CrossRef - Optimized Process and Mechanical and Electrical Analysis of Polyimide/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Composites
Junki Lee, Sang-il Yoon, Hyunseung Kim, Chang Kyu Jeong
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(1): 16. CrossRef - Flexible Hybrid Energy Harvester based on Thermoelectric Composite Film and Electrospun Piezopolymer Membranes
Hyomin Jeon, Cheol Min Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Bitna Bae, Hyejeong Choi, HakSu Jang, Kwi-Il Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(2): 104. CrossRef - Flexible Thermoelectric Energy Harvester with Stacked Structure of Thermoelectric Composite Films Made of PVDF and Bi2Te3-Based Particles
Da Eun Shin, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Kwi-Il Park
ACS Applied Energy Materials.2024; 7(19): 8288. CrossRef - Enhanced energy harvesting of fibrous composite membranes via plasma-piezopolymer interaction
Hyeon Jun Park, Bitna Bae, HakSu Jang, Dong Yeol Hyeon, Dong Hun Lee, Gwang Hyun Kim, Cheol Min Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Nano Energy.2024; 131: 110299. CrossRef - CoFe2O4-BaTiO3 core-shell-embedded flexible polymer composite as an efficient magnetoelectric energy harvester
Bitna Bae, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Cheol Min Kim, Jungho Ryu, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Geon-Tae Hwang, Kwi-Il Park
Materials Today Physics.2024; 48: 101567. CrossRef
- Unidirectional porous PVDF Piezoelectrets fabricated via gradient ice-templating for enhanced energy harvesting performance
- [English]
- A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
- Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):390-398. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00325

- 2,206 View
- 65 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The AlSi10Mg alloy has garnered significant attention for its application in laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF), due to its lightweight properties and good printability using L-PBF. However, the low production speed of the L-PBF process is the main bottleneck in the industrial commercialization of L-PBF AlSi10Mg alloy parts. Furthermore, while L-PBF AlSi10Mg alloy exhibits excellent mechanical properties, the properties are often over-specified compared to the target properties of parts traditionally fabricated by casting. To accelerate production speed in L-PBF, this study investigated the effects of process parameters on the build rate and mechanical properties of the AlSi10Mg alloy. Guidelines are proposed for high-speed additive manufacturing of the AlSi10Mg alloy for use in automotive parts. The results show a significant increase in the build rate, exceeding the conventional build rate by a factor of 3.6 times or more, while the L-PBF AlSi10Mg alloy met the specifications for automotive prototype parts. This strategy can be expected to offer significant cost advantages while maintaining acceptable mechanical properties of topology-optimized parts used in the automobile industry.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Data-Driven analysis relates mechanical properties to pore morphology in laser powder bed fusion
Jaemin Wang, Seungyeon Lee, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park, Dierk Raabe
Acta Materialia.2026; 304: 121751. CrossRef - Lightweight Design of a Connecting Rod Using Lattice-Structure Parameter Optimisation: A Test Case for L-PBF
Michele Amicarelli, Michele Trovato, Paolo Cicconi
Machines.2025; 13(3): 171. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef
- Data-Driven analysis relates mechanical properties to pore morphology in laser powder bed fusion
- [Korean]
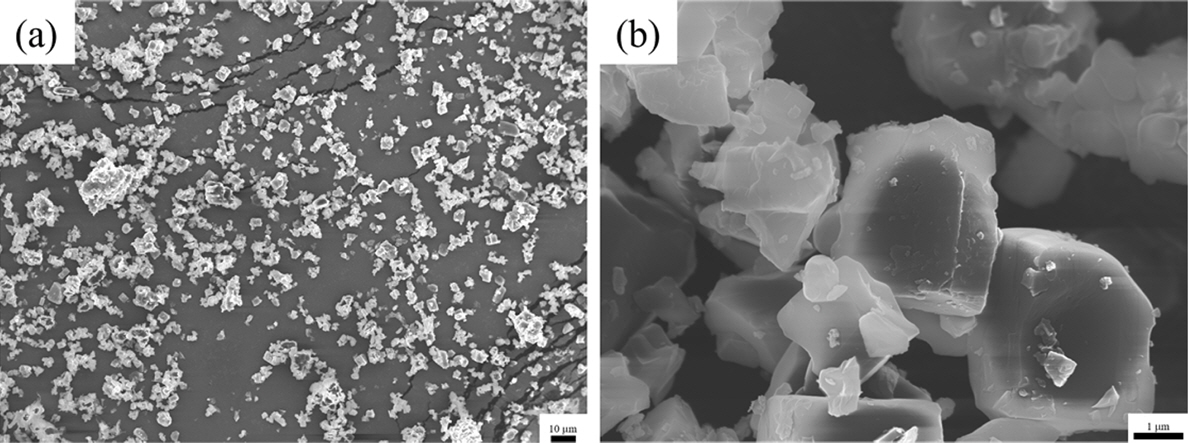
- Effect of Abnormal Grain Growth on Ionic Conductivity in LATP
- Hyungik Choi, Yoonsoo Han
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):23-29. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.23
- 2,986 View
- 66 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Temperature-dependent microstructural evolution in a compositionally complex solid electrolyte: The role of a grain boundary transition
Shu-Ting Ko, Chaojie Du, Huiming Guo, Hasti Vahidi, Jenna L. Wardini, Tom Lee, Yi Liu, Jingjing Yang, Francisco Guzman, Timothy J. Rupert, William J. Bowman, Shen J. Dillon, Xiaoqing Pan, Jian Luo
Journal of Advanced Ceramics.2025; 14(3): 9221047. CrossRef - Effect of bimodal particle size distribution on Li1.5Al0.5Ti1.5(PO4)3 solid electrolytes: Microstructures and electrochemical properties
Gi Jeong Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Seul Ki Choi, Jong Won Bae, Kun-Jae Lee, Minho Yang
Powder Technology.2025; 466: 121407. CrossRef
- Temperature-dependent microstructural evolution in a compositionally complex solid electrolyte: The role of a grain boundary transition
- [English]
- The Effect of Aluminum Powder Size on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of Foam
- Seunghyeok Choi, Sungjin Kim, Tae-Young Ahn, Yu-Song Choi, Jae-Gil Jung, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):232-243. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00157
- 1,392 View
- 55 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, we analyzed the structural and mechanical properties of aluminum foams fabricated using aluminum powders of varying sizes and mixtures. The effects of sintering and pore structure at each size on the integrity and mechanical properties of the foams were investigated. Structural characteristics were examined using scanning electron microscopy and micro–computed tomography, while mechanical properties were evaluated through compression testing. The experimental results demonstrated that smaller powder sizes improved foam integrity, reduced porosity and pore size, and resulted in thinner cell walls. In combination, these effects increased compressive strength as the powder size decreased. The findings of this study contribute to the understanding and improvement of the mechanical properties of aluminum foams and highlight their potential for use in a wide range of applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sustainable Manufacturing of Graphene–Aluminum Composites: A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment
Xinwei Yang, Qian Peng, Changke Chen, Qingcui Liu, Yudai Huang
Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy.2026; 12(1): 727. CrossRef
- Sustainable Manufacturing of Graphene–Aluminum Composites: A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment
- [English]
- Comparative Study of Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogels and Films for Supercapacitor Electrodes
- Sunghee Choi, Seulgi Kim, Seojin Woo, Dongju Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):23-29. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00472
- 1,792 View
- 34 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Supercapacitors, renowned for their high power density and rapid charge-discharge rates, are limited by their low energy density. This limitation has prompted the need for advanced electrode materials. The present study investigated reduced graphene oxide (rGO) in two distinct structures, as a film and as an aerogel, for use as supercapacitor electrodes. The rGO film, prepared by vacuum filtration and thermal reduction, exhibited a compact, lamellar structure, while the aerogel, synthesized through hydrothermal treatment, was a highly porous three-dimensional network. Electrochemical analyses demonstrated the aerogel’s superior performance, as shown by a specific capacitance of 121.2 F/g at 5 mV/s, with 94% capacitance retention after 10,000 cycles. These findings emphasize the importance of structural design in optimizing ion accessibility and charge transfer. They also demonstrate the potential of rGO aerogels for increasing the energy storage efficiency of advanced supercapacitor systems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
Min Gi An, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 492. CrossRef
- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
- [English]
- Investigation of the Thermal-to-Electrical Properties of Transition Metal-Sb Alloys Synthesized for Thermoelectric Applications
- Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Sooho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Kwi-Il Park, Kyung Tae Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):236-242. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00031
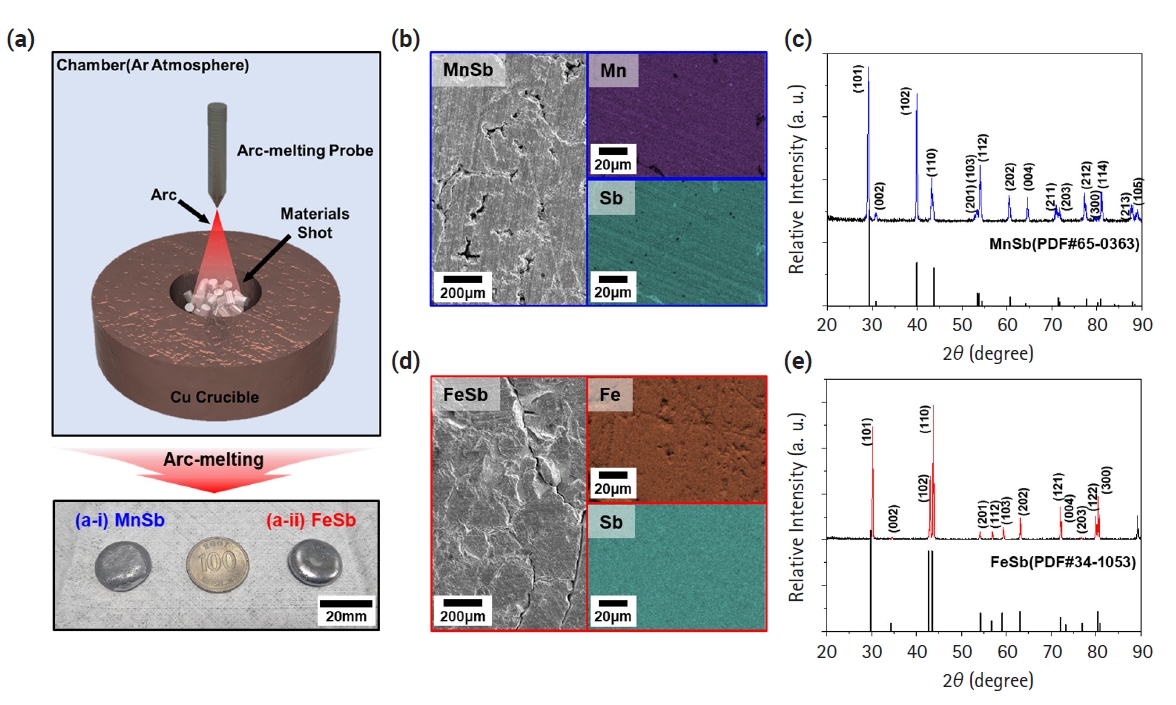
- 1,826 View
- 44 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The development of thermoelectric (TE) materials to replace Bi2Te3 alloys is emerging as a hot issue with the potential for wider practical applications. In particular, layered Zintl-phase materials, which can appropriately control carrier and phonon transport behaviors, are being considered as promising candidates. However, limited data have been reported on the thermoelectric properties of metal-Sb materials that can be transformed into layered materials through the insertion of cations. In this study, we synthesized FeSb and MnSb, which are used as base materials for advanced thermoelectric materials. They were confirmed as single-phase materials by analyzing X-ray diffraction patterns. Based on electrical conductivity, the Seebeck coefficient, and thermal conductivity of both materials characterized as a function of temperature, the zT values of MnSb and FeSb were calculated to be 0.00119 and 0.00026, respectively. These properties provide a fundamental data for developing layered Zintl-phase materials with alkali/alkaline earth metal insertions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Jihun Yu, Kyung Tae Kim
Materials Letters.2025; 381: 137796. CrossRef - Highly deformable and hierarchical 3D composite sponge for versatile thermoelectric energy conversion
Jong Min Park, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Kwi-Il Park
Applied Surface Science.2025; 692: 162730. CrossRef
- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
- [English]
- SnF2-Induced LiF Interphase for Stable Lithium Metal Anodes with Suppressed Dendrite Growth
- Yeong Hoon Jeon, Seul Ki Choi, Yun Seung Nah, Wonil Shin, Yong-Ho Choa, Minho Yang
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):212-221. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00164
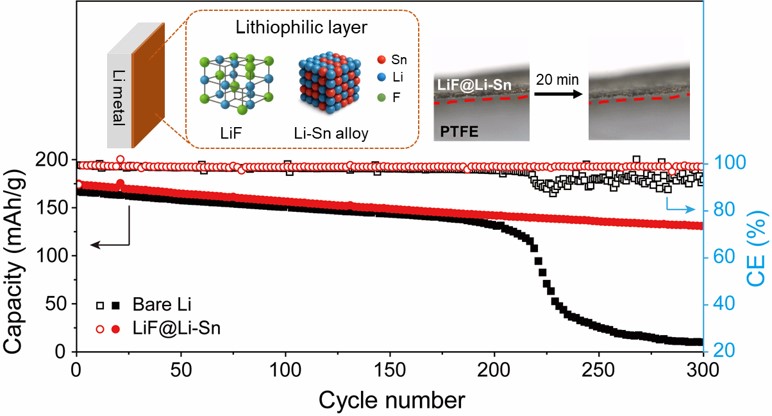
- 1,773 View
- 53 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Lithium (Li) metal is a promising anode for next-generation batteries due to its high capacity, low redox potential, and low density. However, dendrite growth and interfacial instability limit its use. In this study, an artificial solid electrolyte interphase layer of LiF and Li-Sn (LiF@Li-Sn) was fabricated by spray-coating SnF2 onto Li. The LiF@Li-Sn anode exhibited improved air stability and electrochemical performance. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy indicated a charge transfer resistance of 25.2 Ω after the first cycle. In symmetric cells, it maintained a low overpotential of 27 mV after 250 cycles at 2 mA/cm2, outperforming bare Li. In situ microscopy confirmed dendrite suppression during plating. Full cells with NMC622 cathodes and LiF@Li-Sn anodes delivered 130.8 mAh/g with 79.4% retention after 300 cycles at 1 C and 98.8% coulombic efficiency. This coating effectively stabilized the interface and suppressed dendrites, with promising implications for practical lithium metal batteries.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser Powder Bed Fusion 3D-Printed Cu-10Sn Alloy
- Jonggyu Kim, Junghoon Won, Wookjin Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):422-430. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00276
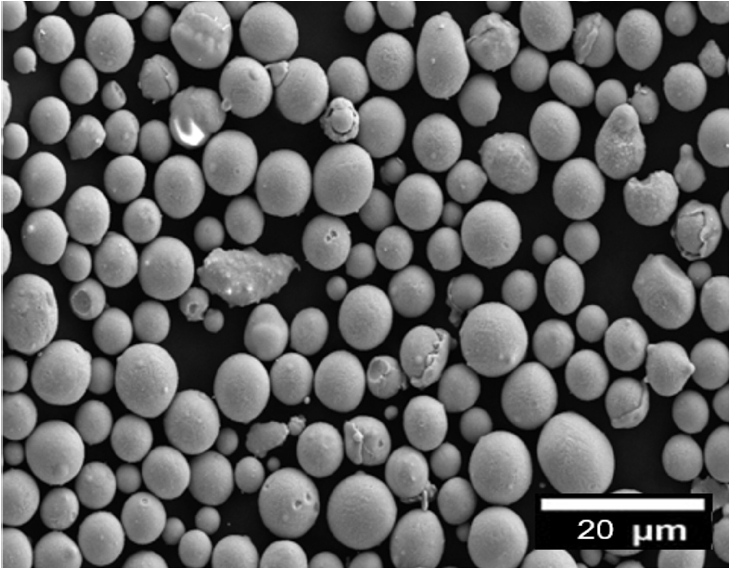
- 1,166 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the optimal process conditions and mechanical properties of Cu-10Sn alloys produced by the powder bed fusion (PBF) method. The optimal PBF conditions were explored by producing samples with various laser scanning speeds and laser power. It was found that under optimized conditions, samples with a density close to the theoretical density could be fabricated using PBF without any serious defects. The microstructure and mechanical properties of samples produced under optimized conditions were investigated and compared with a commercial alloy produced by the conventional method. The hardness, maximum tensile strength, and elongation of the samples were significantly higher than those of the commercially available cast alloy with the same chemical composition. Based on these results, it is expected to be possible to use the PBF technique to manufacture Cu-10Sn products with complex 3D shapes that could not be made using the conventional manufacturing method.
- [English]
- Morphological Control and Surface Modification Characteristics of Nickel Oxalate Synthesized via Oxalic Acid Precipitation
- Eunbi Park, Jongwon Bae, Sera Kang, Minsu Kang, Suseong Lee, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):375-382. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00248
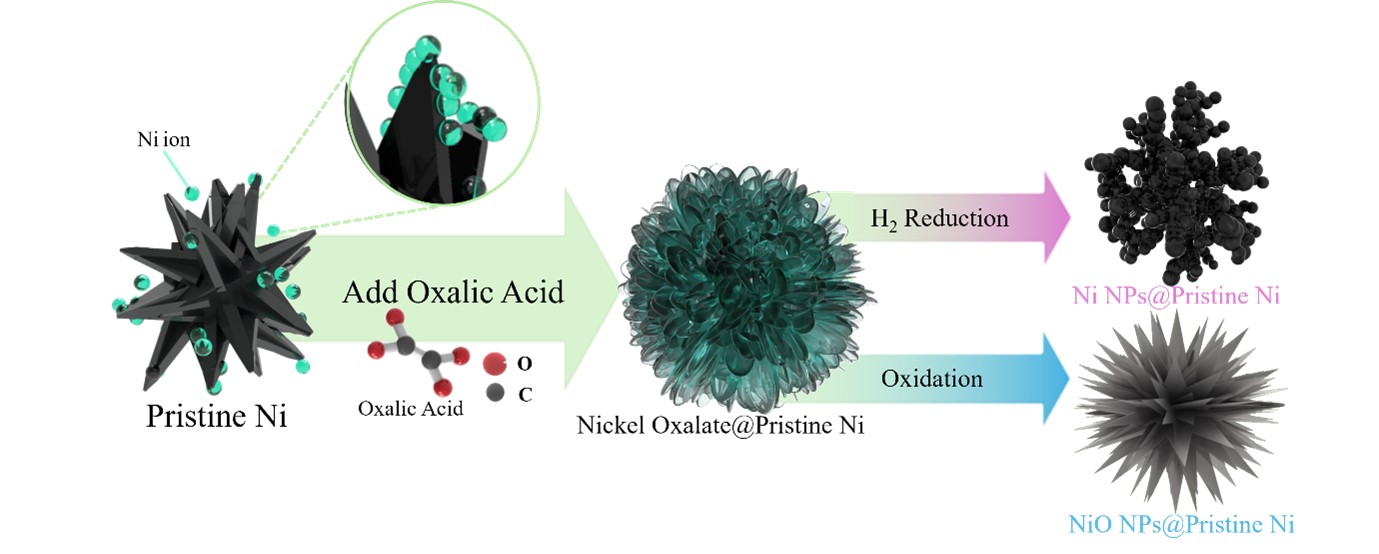
- 1,120 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Nickel is widely used in industrial fields such as electrocatalysis and energy storage devices. Although micron-sized nickel particles exhibit excellent mechanical durability, their low specific surface area limits their reactivity. We modified the surface of micron-sized nickel particles with nanostructured nickel oxalate and investigated the effects of the solvent dielectric constant, surfactant, and thermal treatment atmosphere on the resulting particle morphology and phase transformation. Rietveld refinement analysis confirmed that changes in the solvent dielectric constant led to increased or diminished crystallinity of specific planes in nickel oxalate, resulting in diffraction patterns distinct from standard JCPDS data. These structural changes were also found to influence the morphology of the synthesized nickel oxalate. The results demonstrate that nickel oxalate serves as an effective precursor for producing Ni and NiO phases, and shape control of the final product can increase the surface reactivity of micron-sized nickel materials.
- [English]
- High-Temperature Steam Oxidation Behavior of Silicide- or Aluminide- Coated Mo and Nb Refractory Metals
- Woojin Lim, Je-Kyun Baek, JaeJoon Kim, Hyun Gil Kim, Ho Jin Ryu
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):546-555. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00381

- 1,495 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Refractory materials, such as molybdenum and niobium, are potential candidates for cladding material due to their high melting temperatures and desirable mechanical properties at higher temperatures than those of zirconium alloys. However, refractory materials have low resistance to oxidation at elevated temperatures. Therefore, this study examined silicide or aluminide surface coatings as protection against rapid oxidation of refractory materials at elevated temperatures for a potential accident-tolerant fuel cladding. Silicide or aluminide layers were formed on refractory metal substrates by using the pack cementation method. The steam oxidation behavior of both coated and uncoated samples was compared by thermogravimetric analysis at 1200°C. The weight changes of the coated samples were greatly reduced than those of uncoated samples. Microstructural analyses demonstrated that the silicide and aluminide layers were oxidized to form a protective surface oxide that prevented rapid oxidation of the refractory substrate at elevated temperatures.
- [Korean]
- Hydrogen Reduction Behavior of NCM-based Lithium-ion Battery Cathode Materials
- So-Yeong Lee, So-Yeon Lee, Dae-Hyeon Lee, Ho-Sang Sohn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):163-168. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00017
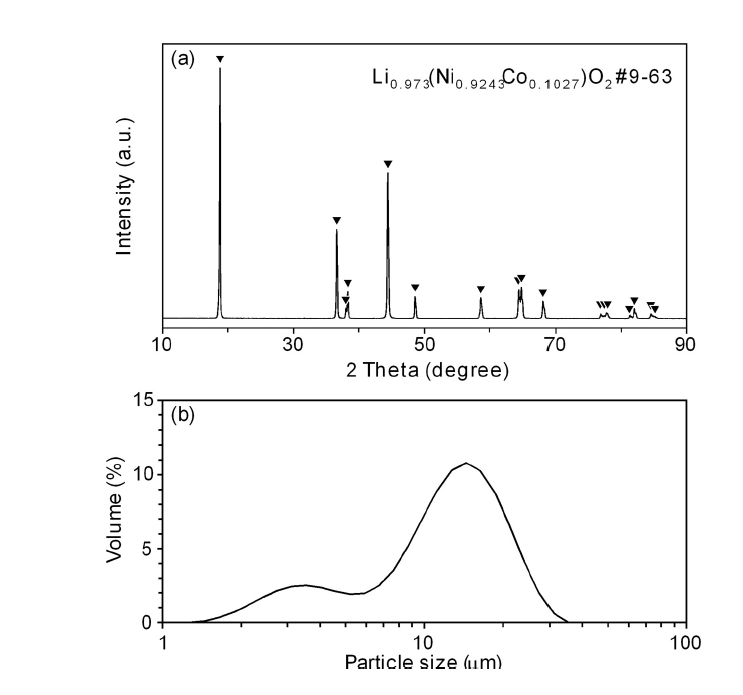
- 1,675 View
- 43 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - As the demand for lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles is increasing, it is important to recover valuable metals from waste lithium-ion batteries. In this study, the effects of gas flow rate and hydrogen partial pressure on hydrogen reduction of NCM-based lithium-ion battery cathode materials were investigated. As the gas flow rate and hydrogen partial pressure increased, the weight loss rate increased significantly from the beginning of the reaction due to the reduction of NiO and CoO by hydrogen. At 700 °C and hydrogen partial pressure above 0.5 atm, Ni and Li2O were produced by hydrogen reduction. From the reduction product and Li recovery rate, the hydrogen reduction of NCM-based cathode materials was significantly affected by hydrogen partial pressure. The Li compounds recovered from the solution after water leaching of the reduction products were LiOH, LiOH·H2O, and Li2CO3, with about 0.02 wt% Al as an impurity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reduction Roasting of Black Mass Recovered from NCM-based Spent Lithium-ion Batteries Using CH4 Gas
Sang-Yeop Lee, Jae-Ho Hwang, Ho-Sang Sohn
Resources Recycling.2025; 34(5): 93. CrossRef
- Reduction Roasting of Black Mass Recovered from NCM-based Spent Lithium-ion Batteries Using CH4 Gas
- [English]
- Stretch-Flangeability of Laser Powder Bed Fusion-Processed 316L Stainless Steel
- Rae Eon Kim, Yeon Taek Choi, Sang Guk Jeong, Do Won Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):87-94. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00017
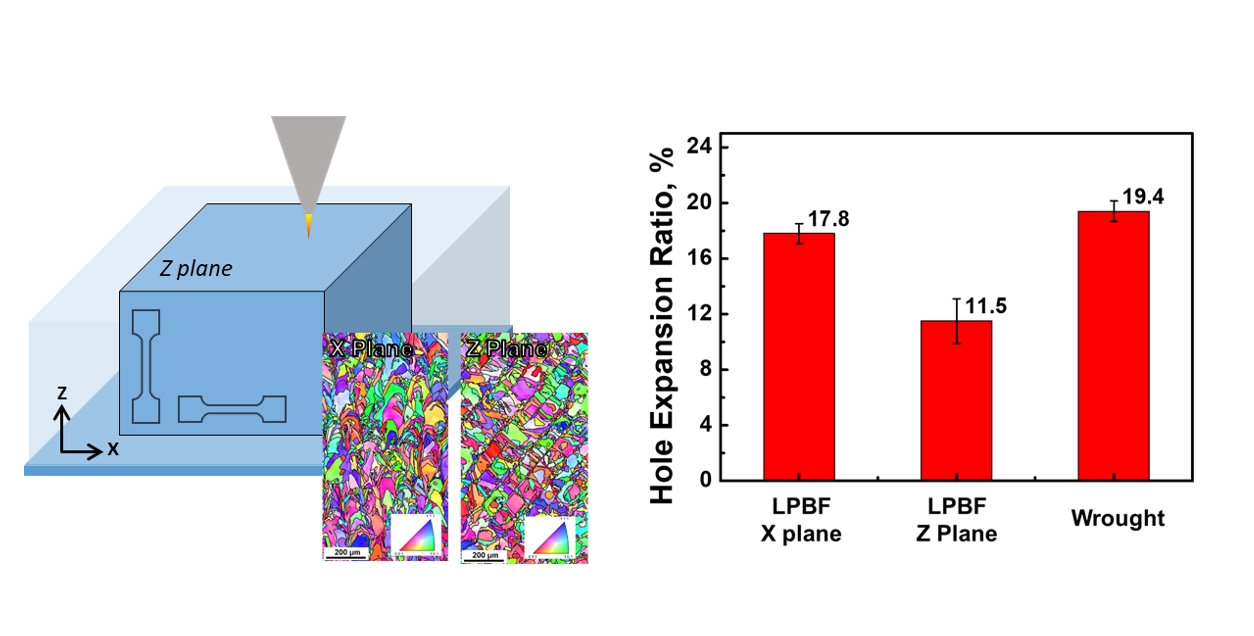
- 2,277 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Metal additive manufacturing (AM) facilitates the production of complex geometries with enhanced functionality. Among various AM techniques, laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) is distinguished by its precision and exceptional mechanical properties achieved via laser fusion deposition. Recent advancements in AM have focused on combining LPBF with post-processing methods such as cold rolling, high-pressure torsion, and forming processes. Therefore, understanding the forming behavior of LPBF-processed materials is essential for industrial adoption. This study investigates the stretch-flangeability of LPBF-fabricated 316L stainless steel, emphasizing its anisotropic microstructure and mechanical properties. Hole expansion tests were employed to assess stretch-flangeability in comparison to wrought 316L stainless steel. The results demonstrate that LPBF-processed samples exhibit significant anisotropic behavior, demonstrating the influence of microstructural evolution on formability. These findings contribute valuable insights into optimizing LPBF materials for industrial forming applications.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Anisotropy on the Wear Behavior of Age-Treated Maraging Steel Manufactured by LPBF
- Seung On Lim, Se-Eun Shin
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):308-317. Published online August 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00171
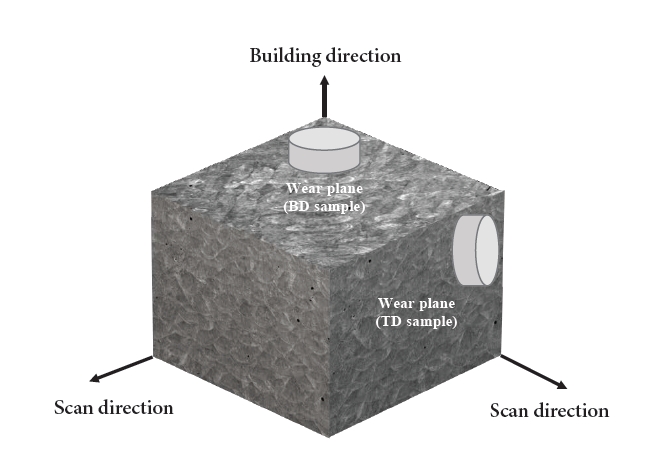
- 2,137 View
- 38 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Maraging steel has excellent mechanical properties resulting from the formation of precipitates within the matrix through aging treatment. Maraging steel fabricated by the laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) process is suitable for applications including precise components and optimized design. The anisotropic characteristic, which depends on the stacking direction, affects the mechanical properties. This study aimed to analyze the influence of anisotropy on the wear behavior of maraging steel after aging treatment. The features of additive manufacturing tended to disappear after heat treatment. However, some residual cellular and dendrite structures were observed. In the wear tests, a high wear rate was observed on the building direction plane for all counter materials. This is believed to be because the oxides formed on the wear track positively affected the wear characteristics; meanwhile, the bead shape in the stacking direction surface was vulnerable to wear, leading to significant wear.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unveiling age-hardening mechanisms: first-principles carbide insights and enhanced thermomechanical fatigue in niobium-bearing austenitic stainless steels
Godwin Kwame Ahiale, Jin Woong Park, Raj Narayan Hajra, Yong-Jun Oh, Won Doo Choi, Tae-Wook Na, Gi Yong Kim, Hyun-Ju Choi, Jeoung Han Kim
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 949: 149397. CrossRef - A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 390. CrossRef
- Unveiling age-hardening mechanisms: first-principles carbide insights and enhanced thermomechanical fatigue in niobium-bearing austenitic stainless steels
- [Korean]
- Preparation and Microstructural Characteristics of Ti Nanopowder by Ball Milling and Dehydrogenation of TiH2 Powder
- Ji Young Kim, Eui Seon Lee, Ji Won Choi, Youngmin Kim, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):324-328. Published online August 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00199
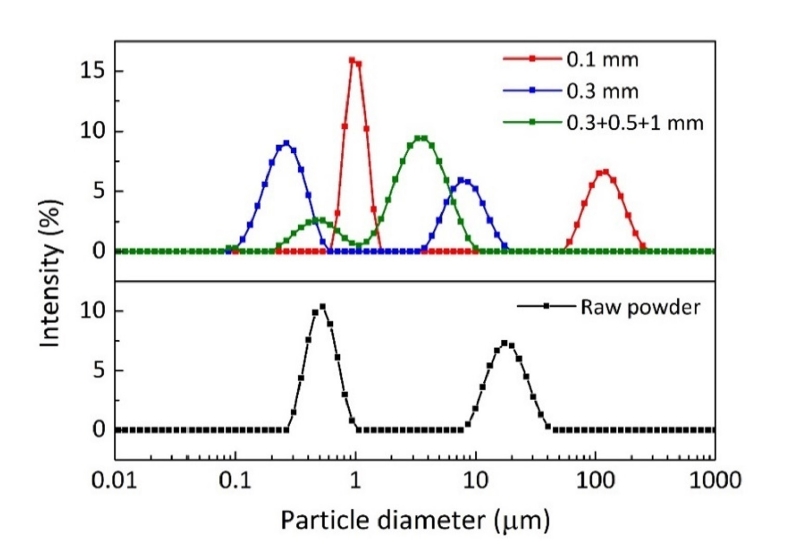
- 1,179 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study analyzed the influence of ball size and process control agents on the refinement and dehydrogenation behavior of TiH2 powder. Powders milled using ZrO2 balls with diameters of 0.1 mm, 0.3 mm, and 0.3+0.5+1 mm exhibited a bimodal particle size distribution, of which the first mode had the smallest size of 0.23 μm for the 0.3 mm balls. Using ethanol and/or stearic acid as process control agents was effective in particle refinement. Thermogravimetric analysis showed that dehydrogenation of the milled powder started at a relatively low temperature compared to the raw powder, which is interpreted to have resulted from a decrease in particle size and an increase in defects. The dehydrogenation kinetics of the TiH2 powder were evaluated by the magnitude of peak shift with heating rates using thermogravimetric analysis. The activation energy of the dehydrogenation reaction, calculated from the slope of the Kissinger plot, was measured to be 228.6 kJ/mol for the raw powder and 194.5 kJ/mol for the milled powder. TEM analysis revealed that both the milled and dehydrogenated powders showed an angular shape with a size of about 200 nm.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Optimization of Al2O3 Microchannels Using DLP-Based 3D Printing
- Jun-Min Cho, Yong-Jun Seo, Yoon-Soo Han
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):59-66. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00346

- 1,126 View
- 33 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study focused on optimizing the digital light processing (DLP) 3D printing process for high-precision ceramic components using alumina-based slurries. Key challenges, such as cracking during debinding and precision loss due to slurry sedimentation, were addressed by evaluating the exposure time and the nano-to-micro alumina powder ratios. The optimal conditions—exposure time of 15 seconds and a 1:9 mixing ratio—minimized cracking, improved gas flow during debinding, and increased structural precision. Microchannels with diameters above 1.2 mm were successfully fabricated, but channels below 0.8 mm faced challenges due to slurry accumulation and over-curing. These results establish a reliable process for fabricating complex ceramic components with improved precision and structural stability. The findings have significant potential for applications in high-value industries, including aerospace, energy, and healthcare, by providing a foundation for the efficient and accurate production of advanced ceramic structures.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Ball Milling Conditions on the Microstructure and Dehydrogenation Behavior of TiH2 Powder
- Ji Young Kim, Eui Seon Lee, Ji Won Choi, Youngmin Kim, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):132-136. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00001
- 2,195 View
- 38 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the effects of revolution speed and ball size in planetary milling on the microstructure and dehydrogenation behavior of TiH2 powder. The particle size analysis showed that the large particles present in the raw powder were effectively refined as the revolution speed increased, and when milled at 500 rpm, the median particle size was 1.47 m. Milling with a mixture of balls of two or three sizes was more effective in refining the raw powder than milling with balls of a single size. A mixture of 3-mm and 5-mm-diameter balls was the optimal condition for particle refinement, and the measured median particle size was 0.71 m. The dependence of particle size on revolution speed and ball size was explained by changes in input energy and the number of contact points of the balls. In the milled powder, the endothermic peak measured using differential thermal analysis was observed at a relatively low temperature. This finding was interpreted as the activation of a dehydrogenation reaction, mainly due to the increase in the specific surface area and the concentration of lattice defects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation and Microstructural Characteristics of Ti Nanopowder by Ball Milling and Dehydrogenation of TiH2 Powder
Ji Young Kim, Eui Seon Lee, Ji Won Choi, Youngmin Kim, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(4): 324. CrossRef
- Preparation and Microstructural Characteristics of Ti Nanopowder by Ball Milling and Dehydrogenation of TiH2 Powder
- [Korean]
- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):244-253. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00087
- 1,102 View
- 46 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ti-6Al-4V alloy is widely utilized in aerospace and medical sectors due to its high specific strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. However, its low machinability makes it difficult to manufacture complex-shaped products. Advancements in additive manufacturing have focused on producing high-performance, complex components using the laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) process, which is a specialized technique for customized geometries. The LPBF process exposes materials to extreme thermal conditions and rapid cooling rates, leading to residual stresses within the parts. These stresses are intensified by variations in the thermal history across regions of the component. These variations result in differences in microstructure and mechanical properties, causing distortion. Although support structure design has been researched to minimize residual stress, few studies have conducted quantitative analyses of stress variations due to different support designs. This study investigated changes in the residual stress and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy fabricated using LPBF, focusing on support structure design.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


