Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Stretch-Flangeability of Laser Powder Bed Fusion-Processed 316L Stainless Steel
- Rae Eon Kim, Yeon Taek Choi, Sang Guk Jeong, Do Won Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):87-94. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00017
- 2,286 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
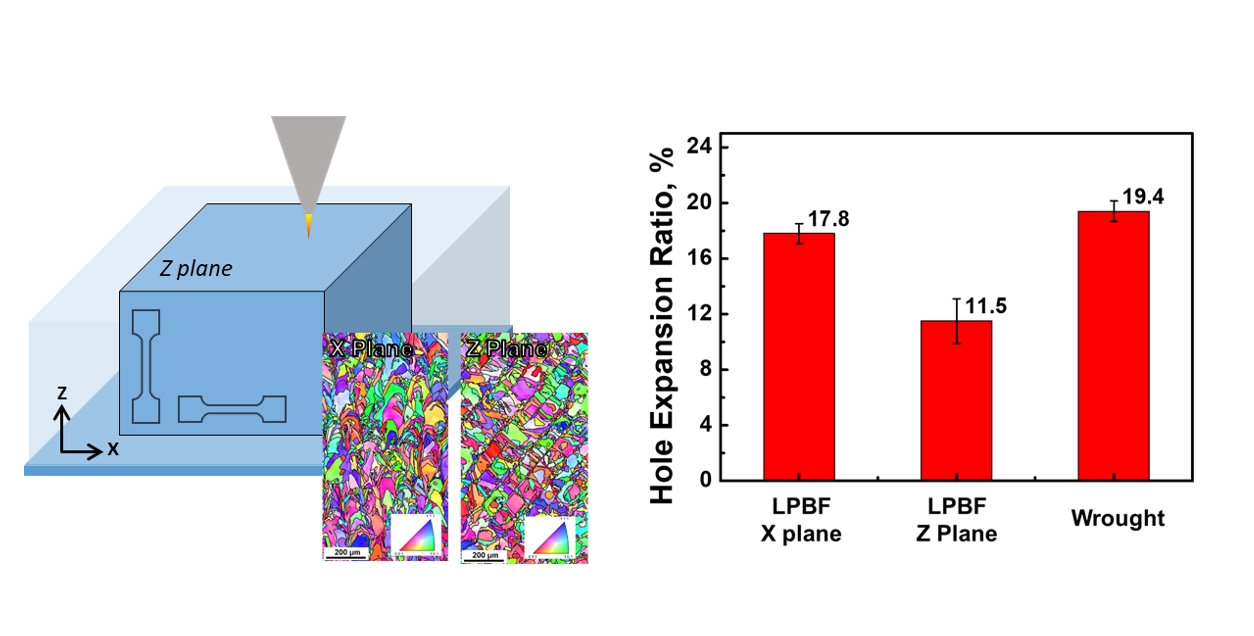
Supplementary Material - Metal additive manufacturing (AM) facilitates the production of complex geometries with enhanced functionality. Among various AM techniques, laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) is distinguished by its precision and exceptional mechanical properties achieved via laser fusion deposition. Recent advancements in AM have focused on combining LPBF with post-processing methods such as cold rolling, high-pressure torsion, and forming processes. Therefore, understanding the forming behavior of LPBF-processed materials is essential for industrial adoption. This study investigates the stretch-flangeability of LPBF-fabricated 316L stainless steel, emphasizing its anisotropic microstructure and mechanical properties. Hole expansion tests were employed to assess stretch-flangeability in comparison to wrought 316L stainless steel. The results demonstrate that LPBF-processed samples exhibit significant anisotropic behavior, demonstrating the influence of microstructural evolution on formability. These findings contribute valuable insights into optimizing LPBF materials for industrial forming applications.
- [Korean]
- Stretch-Flangeability of Harmonic Structure Material Manufactured by Powder Metallurgy Method
- Jae Ik Yoon, Hak Hyeon Lee, Hyung Keun Park, Kei Ameyama, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):128-132. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.128

- 871 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Harmonic structure materials are materials with a core–shell structure having a shell with a small grain size and a core with a relatively large grain size. They are in the spotlight because their mechanical properties reportedly feature strength similar to that of a sintered powder with a fine grain size and elongation similar to that of a sintered powder with a coarse grain size at the same time. In this study, the tensile properties, microstructure, and stretchflangeability of harmonic structure SUS304L made using powder metallurgy are investigated to check its suitability for automotive applications. The harmonic powders are made by mechanical milling and sintered using a spark plasma sintering method at 1173 K and a pressure of 50 MPa in a cylindrical die. The sintered powders of SUS304L having harmonic structure (harmonic SUS304L) exhibit excellent tensile properties compared with sintered powders of SUS304L having homogeneous microstructure. In addition, the harmonic SUS304L has excellent stretch-flangeability compared with commercial advanced high-strength steels (AHSSs) at a similar strength grade. Thus, the harmonic SUS304L is more suitable for automotive applications than conventional AHSSs because it exhibits both excellent tensile properties and stretch-flangeability.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI

 First
First Prev
Prev


