Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Enhancing the Dispersion Stability of Exfoliated MoS2 Nanoflakes for Na⁺ Intercalation
- Jae Min Sung, Dong-Won Kyung, Ammad Ali, Kee-Ryung Park, Mi Hye Lee, Da-Woon Jeong, Bum Sung Kim, Haejin Hwang, Leeseung Kang, Yoseb Song
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):390-398. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00255
- 520 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
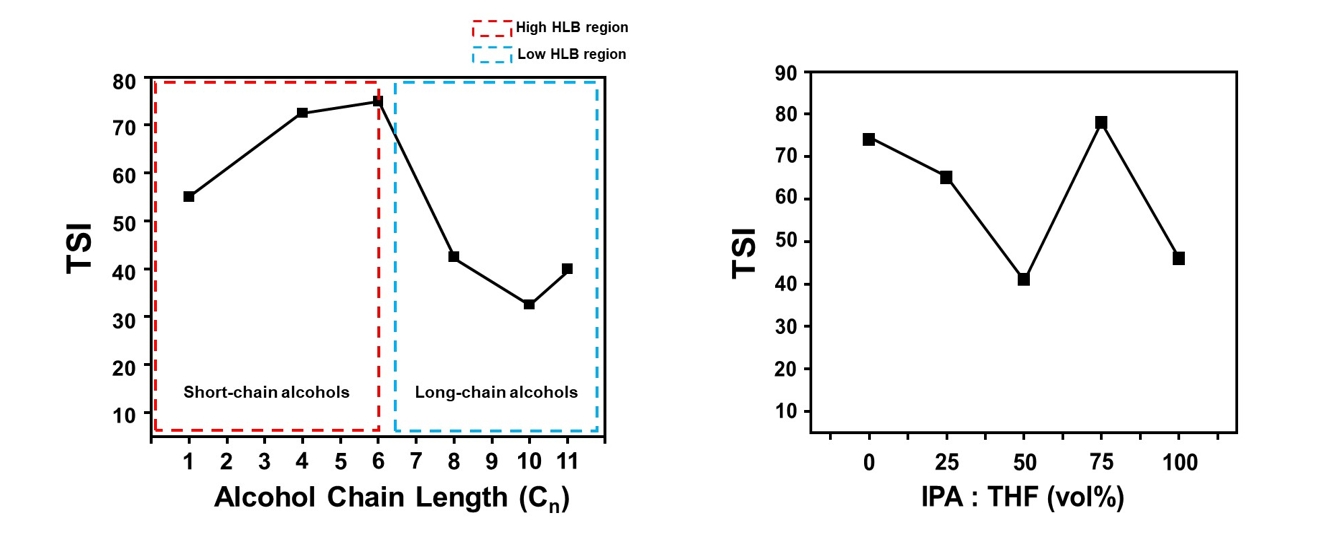
PDF - This study investigated the dispersion stability of exfoliated MoS₂ nanoflakes in various organic solvents and binary mixtures using a Turbiscan optical analyzer. Sedimentation behavior was quantitatively evaluated via transmittance variation (ΔT), backscattering variation (ΔBS), and the Turbiscan stability index (TSI). Alcohol-based solvents were categorized by hydrophilic-lipophilic balance values. Long-chain alcohols, such as 1-undecanol, showed increased stability due to high viscosity and strong hydrophobic affinity with MoS2 basal planes, while short-chain alcohols exhibited poor stabilization. Binary mixtures of isopropanol (IPA) and tetrahydrofuran (THF) were also assessed, with the 5:5 volume ratio showing the best stability profile, including the lowest TSI and minimal ΔT and ΔBS values. This improvement is attributed to synergistic interactions, as IPA stabilizes hydrophilic edge sites, while THF engages with hydrophobic basal surfaces. These findings highlight the importance of balancing physicochemical properties when selecting solvents to improve MoS2 dispersion for structural modification and electrocatalytic applications.
- [Korean]
- The Effects of MoS2 Addition on the Mechanical Properties of Fe-Cr-Mn-C-V P/M Alloy
- Geon-Hong Kim, Hyun Seok Yang, Man-Sik Kong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(4):294-300. Published online August 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.4.294

- 819 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The connecting rod is one of the most important parts in automotive engines, transforming the reciprocal motion of a piston generated by internal combustion into the rotational motion of a crankshaft. Recent advances in high performance automobile engines demand corresponding technological breakthroughs in the materials for engine parts. In the present research, the powder metallurgy (P/M) process was used to replace conventional quenching and/or tempering processes for mass production and ultimately for more cost-efficient manufacturing of high strength connecting rods. The development of P/M alloy powder was undertaken not only to achieve the improvement in mechanical properties, but also to enhance the machinability of the P/M processed connecting rods. Specifically MoS2 powders were added as lubricants to non-normalizing Fe-Cr-Mn-V-C alloy powder to improve the post-sintering machinability. The effects of MoS2 addition on the microstructure, mechanical properties, and machining characteristics were investigated.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI

 First
First Prev
Prev


