Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of
Bangpungtongseong-san Extract-loaded Particles for Tablet Dosage Form - Jinwoo Park, Sung Giu Jin
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):227-232. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.227
- 1,071 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
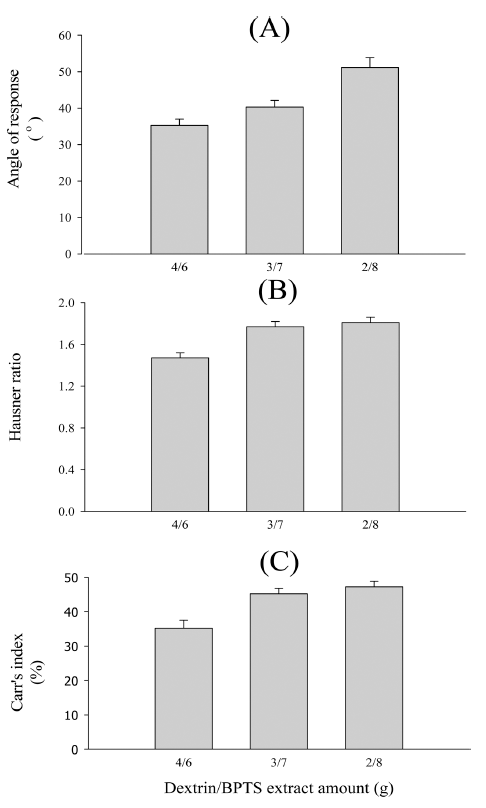
PDF The purpose of this study is to optimize the powder formulation and manufacturing conditions for the solidification of an extract of the herb
Bangpungtongseong-san (BPTS). To develop BPTS-loaded particles for the tablet dosage form, various BPTS-loaded particles composed of BPTS, dextrin, microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), silicon dioxide, ethanol, and water are prepared using spray-drying and high shear granulation (high-speed mixing). Their physical properties are evaluated using scanning electron microscopy and measurements of the angle of repose, Hausner ratio, Carr’s index, hardness, and disintegration time. The optimal BPTS-loaded particles exhibit improved flowability and compressibility. In particular, the BPTS-loaded particles containing silicon dioxide show significantly improved flowability and compressibility (the angle of repose, Hausner ratio, and Carr’s index are 35.27 ± 0.58°, 1.18 ± 0.06, and 15.67 ± 1.68%, respectively), hardness (18.97 ± 1.00 KP), and disintegration time (17.60 ± 1.50 min) compared to those without silicon dioxide. Therefore, this study suggests that particles prepared by high-speed mixing can be used to greatly improve the flowability and compressibility of BPTS using MCC and silicon dioxide.
- [Korean]
- RBSC Prepared by Si Melt Infiltration into the Y2O3 Added Carbon Preform
- Min-Ho Jang, Kyeong-Sik Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(1):51-58. Published online February 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.1.51

- 1,449 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The conversion of carbon preforms to dense SiC by liquid infiltration is a prospectively low-cost and reliable method of forming SiC-Si composites with complex shapes and high densities. Si powder was coated on top of a 2.0wt .% Y2O3-added carbon preform, and reaction bonded silicon carbide (RBSC) was prepared by infiltrating molten Si at 1,450°C for 1-8 h. Reactive sintering of the Y2O3-free carbon preform caused Si to be pushed to one side, thereby forming cracking defects. However, when prepared from the Y2O3-added carbon preform, a SiC-Si composite in which Si is homogeneously distributed in the SiC matrix without cracking can be produced. Using the Si + C → SiC reaction at 1,450°C, 3C and 6H SiC phases, crystalline Si, and Y2O3 were generated based on XRD analysis, without the appearance of graphite. The RBSC prepared from the Y2O3-added carbon preform was densified by increasing the density and decreasing the porosity as the holding time increased at 1,450°C. Dense RBSC, which was reaction sintered at 1,450°C for 4 h from the 2.0wt.% Y2O3-added carbon preform, had an apparent porosity of 0.11% and a relative density of 96.8%.
- [Korean]
- Analysis of Wafer Cleaning Solution Characteristics and Metal Dissolution Behavior according to the Addition of Chelating Agent
- Myungsuk Kim, Keunhyuk Ryu, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(1):25-30. Published online February 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.1.25
- 1,027 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
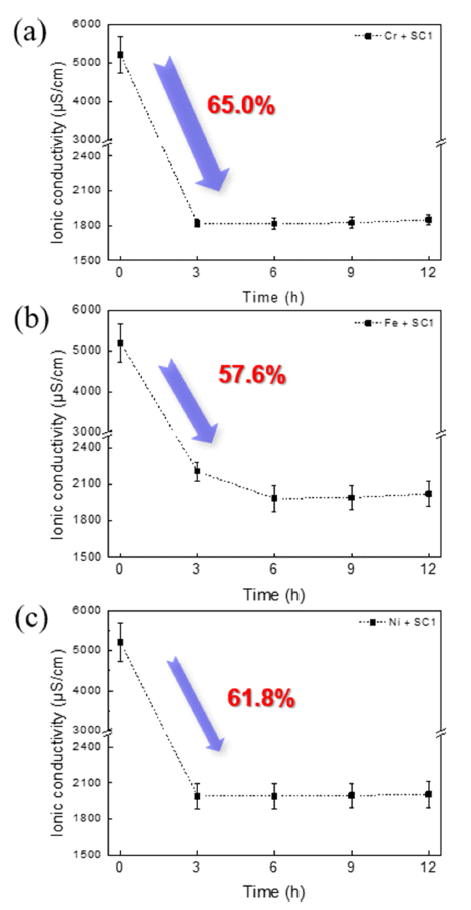
PDF The surface of silicon dummy wafers is contaminated with metallic impurities owing to the reaction with and adhesion of chemicals during the oxidation process. These metallic impurities negatively affect the device performance, reliability, and yield. To solve this problem, a wafer-cleaning process that removes metallic impurities is essential. RCA (Radio Corporation of America) cleaning is commonly used, but there are problems such as increased surface roughness and formation of metal hydroxides. Herein, we attempt to use a chelating agent (EDTA) to reduce the surface roughness, improve the stability of cleaning solutions, and prevent the re-adsorption of impurities. The bonding between the cleaning solution and metal powder is analyzed by referring to the Pourbaix diagram. The changes in the ionic conductivity, H2O2 decomposition behavior, and degree of dissolution are checked with a conductivity meter, and the changes in the absorbance and particle size before and after the reaction are confirmed by ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) analyses. Thus, the addition of a chelating agent prevents the decomposition of H2O2 and improves the life of the silicon wafer cleaning solution, allowing it to react smoothly with metallic impurities.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of
Gastrodia elata -loaded Particles for Increased Moisture Stability - Jae Hwan Jung, Sung Giu Jin
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):241-246. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.241

- 850 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF To develop
Gastrodia elata (GE)-loaded particles for herbal extract dosage forms, various GE-loaded particles containing dextrin, isomalt, maltodextrin, and silicon dioxide as solidifying carriers in the GE water extract are prepared using the spray drying method. Their physical properties are evaluated using the repose angle, Hausner ratio, Carr’s index, weight increase rate at 40°C/75% RH condition, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Particles made of dextrin improve the fluidity, compressibility, and water stability. In addition, 2% silicon dioxide increases the fluidity and moisture stability. The best flowability and compressibility of GE-loaded particles are observed with TP, dextrin, and silicon dioxide amounts in the ratio of 6/4/0.2 (34.29 ± 2.86°, 1.48 ± 0.03, and 38.29 ± 2.39%, repose angle, Hausner Ratio, and Carr’s index, respectively) and moisture stability with a 2% weight increase rate for 14 h at 40°C/75% RH condition. Therefore, our results suggest that the particles prepared by the spray drying method with dextrin and 2% silicon dioxide can be used as powerful particles to improve the flowability, compressibility, and moisture stability of GE.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of
Taraxacum platycarpum Extract-loaded Particles for Tablet Dosage Form - Sung Giu Jin
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):225-230. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.225

- 1,036 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF To develop
Taraxacum platycarpum extract (TP)-loaded particles for tablet dosage form, various TP-loaded particles composed of TP, dextrin, microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), silicon dioxide, ethanol, and water are prepared using a spray-drying method and fluid-bed-drying method. Their physical properties are evaluated using angle of repose, Hausner ratio, Carr’s index, hardness, disintegrant time, and scanning electron microscopy. Optimal TP-loaded particles improve flowability and compressibility. Furthermore, 2% silicon dioxide gives increased flowability and compressibility. The formula of TP-loaded fluid-bed-drying particles at a TP/MCC/silicon-dioxide amount of 5/5/0.2 improves the angle of repose, Hausner ratio, Carr’s index, hardness, and disintegrant time as compared with the TP-loaded spray-drying particles. The TP-loaded fluid-bed-drying particles considerably improve flowability and compressibility (35.10° vs. 40.3°, 0.97 vs. 1.17, and 18.97% vs. 28.97% for the angle of repose, Hausner ratio, and Carr’s index, respectively), hardness (11.34 vs. 4.7 KP), and disintegrant time (7.4 vs. 10.4 min) as compared with the TP-loaded spray-drying particles. Thus, the results suggest that these fluid-bed-drying particles with MCC and silicon dioxide can be used as powerful particles to improve the flowability and compressibility of the TP.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Characterization of Gastrodia elata-loaded Particles for Increased Moisture Stability
Jae Hwan Jung, Sung Giu Jin
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 241. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Characterization of Gastrodia elata-loaded Particles for Increased Moisture Stability
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Molybdenum Silicide-based Composites with Uniformly Dispersed Silicon Carbide
- Won June Choi, Chun Woong Park, Young Do Kim, Jong Min Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):402-407. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.402

- 488 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Molybdenum silicide has gained interest for high temperature structural applications. However, poor fracture toughness at room temperatures and low creep resistance at elevated temperatures have hindered its practical applications. This study uses a novel powder metallurgical approach applied to uniformly mixed molybdenum silicidebased composites with silicon carbide. The degree of powder mixing with different ball milling time is also demonstrated by Voronoi diagrams. Core-shell composite powder with Mo nanoparticles as the shell and β-SiC as the core is prepared via chemical vapor transport. Using this prepared core-shell composite powder, the molybdenum silicide-based composites with uniformly dispersed β-SiC are fabricated using pressureless sintering. The relative density of the specimens sintered at 1500°C for 10 h is 97.1%, which is similar to pressure sintering owing to improved sinterability using Mo nanoparticles.
- [English]
- Microwave Absorbance of Polymer Composites Containing SiC Fibers Coated with Ni-Fe Thin Films
- Tian Liu, Sung-Soo Kim, Woo-cheal Choi, Byungil Yoon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):375-378. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.375

- 1,125 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Conductive and dielectric SiC are fabricated using electroless plating of Ni–Fe films on SiC chopped fibers to obtain lightweight and high-strength microwave absorbers. The electroless plating of Ni–Fe films is achieved using a two-step process of surface sensitizing and metal plating. The complex permeability and permittivity are measured for the composite specimens with the metalized SiC chopped fibers dispersed in a silicone rubber matrix. The original noncoated SiC fibers exhibit considerable dielectric losses. The complex permeability spectrum does not change significantly with the Ni–Fe coating. Moreover, dielectric constant is sensitively increased with Ni–Fe coating, owing to the increase of the space charge polarization. The improvements in absorption capability (lower reflection loss and small matching thickness) are evident with Ni–Fe coating on SiC fibers. For the composite SiC fibers coated with Ni–Fe thin films, a -35 dB reflection loss is predicted at 7.6 GHz with a matching thickness of 4 mm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Magnetic sputtering of FeNi/C bilayer film on SiC fibers for effective microwave absorption in the low-frequency region
Tong Guo, Ben Huang, Changgeng Li, Yumin Lou, Xiu-Zhi Tang, Xiaozhong Huang, Jianling Yue
Ceramics International.2021; 47(4): 5221. CrossRef
- Magnetic sputtering of FeNi/C bilayer film on SiC fibers for effective microwave absorption in the low-frequency region
- [Korean]
- Mechanical Strength Values of Reaction-Bonded-Silicon-Carbide Tubes with Different Sample Size
- Seongwon Kim, Soyul Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh, Sung-Min Lee, Yoonsoo Han, Hyun-Ick Shin, Youngseok Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):450-456. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.450
- 529 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
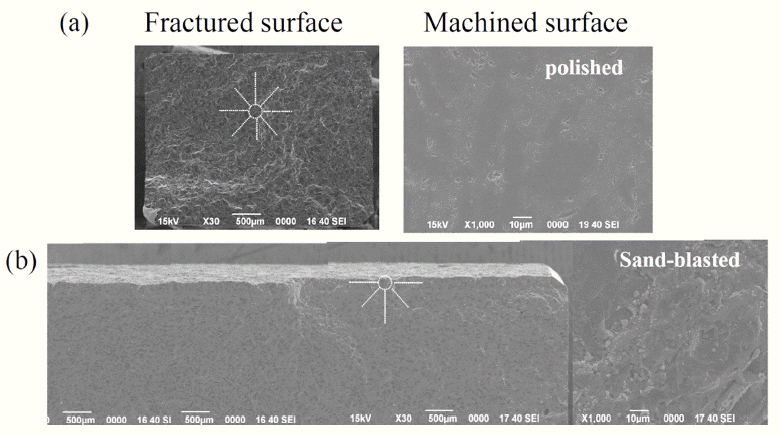
PDF Reaction-bonded silicon carbide (RBSC) is a SiC-based composite ceramic fabricated by the infiltration of molten silicon into a skeleton of SiC particles and carbon, in order to manufacture a ceramic body with full density. RBSC has been widely used and studied for many years in the SiC field, because of its relatively low processing temperature for fabrication, easy use in forming components with a near-net shape, and high density, compared with other sintering methods for SiC. A radiant tube is one of the most commonly employed ceramics components when using RBSC materials in industrial fields. In this study, the mechanical strengths of commercial RBSC tubes with different sizes are evaluated using 3-point flexural and C-ring tests. The size scaling law is applied to the obtained mechanical strength values for specimens with different sizes. The discrepancy between the flexural and C-ring strengths is also discussed.
- [Korean]
- Briquetting of Waste Silicon Carbide Obtained from Silicon Wafer Sludges
- Seong Mo Koo, Su Jong Yoon, Hye Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(1):43-48. Published online February 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.1.43
- 792 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
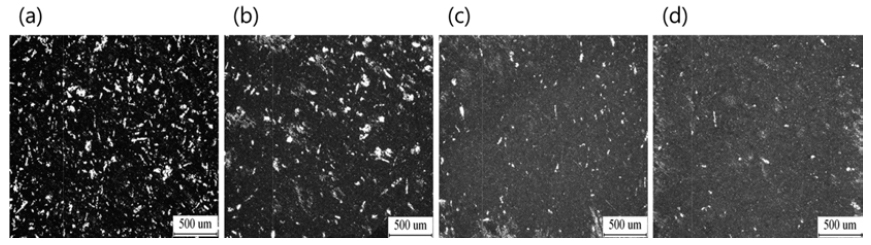
PDF Waste SiC powders obtained from silicon wafer sludge have very low density and a narrow particle size distribution of 10-20 μm. A scarce yield of C and Si is expected when SiC powders are incorporated into the Fe melt without briquetting. Here, the briquetting variables of the SiC powders are studied as a function of the sintering temperature, pressure, and type and contents of the binders to improve the yield. It is experimentally confirmed that Si and C from the sintered briquette can be incorporated effectively into the Fe melt when the waste SiC powders milled for 30 min with 20 wt.% Fe binder are sintered at 1100°C upon compaction using a pressure of 250 MPa. XRF-WDS analysis shows that an yield of about 90% is obtained when the SiC briquette is kept in the Fe melt at 1650°C for more than 1 h.
- [Korean]
- Shape Control of Anodic Aluminum Oxide and Effect as Support of Silicon Powder Electrode
- Ju-Seok Song, Jong-Keun Ha, Yoo-Young Kim, Dong-Kyu Park, In-Shup Ahn, Jou-Hyeon Ahn, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(4):240-246. Published online August 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.4.240

- 758 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) has been widely used for the development and fabrication of nano-powder with various morphologies such as particle, wire, rod, and tube. So far, many researchers have reported about shape control and fabrication of AAO films. However, they have reported on the shape control with different diameter and length of anodic aluminum oxide mainly. We present a combined mild-hard (or hard-mild) anodization to prepare shape-controlled AAO films. Two main parameters which are combination mild-hard (or hard-mild) anodization and run-time of voltage control are applied in this work. The voltages of mild and hard anodization are respectively 40 and 80 V. Anodization was conducted on the aluminum sheet in 0.3 mole oxalic acid at 4°C. AAO films with morphologies of varying interpore distance, branch-shaped pore, diameter-modulated pore and long funnel-shaped pore were fabricated. Those shapes will be able to apply to fabricate novel nano-materials with potential application which is especially a support to prevent volume expansion of inserted active materials, such as metal silicon or tin powder, in lithium ion battery. The silicon powder electrode using an AAO as a support shows outstanding cycle performance as 1003 mAh/g up to 200 cycles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nano silicon encapsulated in modified copper as an anode for high performance lithium ion battery
Jong-Keun Ha, Anupriya K. Haridas, Gyu-Bong Cho, Hyo-Jun Ahn, Jou-Hyeon Ahn, Kwon-Koo Cho
Applied Surface Science.2019; 481: 307. CrossRef
- Nano silicon encapsulated in modified copper as an anode for high performance lithium ion battery
- [English]
- Preparation and Characterization of Porous Silicon and Carbon Composite as an Anode Material for Lithium Rechargeable Batteries
- Junsoo Park, Jae-won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(1):15-20. Published online February 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.1.15
- 801 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The composite of porous silicon (Si) and amorphous carbon (C) is prepared by pyrolysis of a nano-porous Si + pitch mixture. The nano-porous Si is prepared by mechanical milling of magnesium powder with silicon monoxide (SiO) followed by removal of MgO with hydrochloric acid (etching process). The Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface area of porous Si (64.52 m2g−1) is much higher than that before etching Si/MgO (4.28 m2g−1) which indicates pores are formed in Si after the etching process. Cycling stability is examined for the nano-porous Si + C composite and the result is compared with the composite of nonporous Si + C. The capacity retention of the former composite is 59.6% after 50 charge/discharge cycles while the latter shows only 28.0%. The pores of Si formed after the etching process is believed to accommodate large volumetric change of Si during charging and discharging process.
- [Korean]
- Effect of the SiC Size on the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Reaction-bonded Silicon Carbide Ceramics
- Chang-Sup Kwon, Yoon-Suk Oh, Sung-Min Lee, Yoonsoo Han, Hyun-Ick Shin, Youngseok Kim, Seongwon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(6):467-472. Published online December 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.6.467

- 1,485 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF RBSC (reaction-bonded silicon carbide) represents a family of composite ceramics processed by infiltrating with molten silicon into a skeleton of SiC particles and carbon in order to fabricate a fully dense body of silicon carbide. RBSC has been commercially used and widely studied for many years, because of its advantages, such as relatively low temperature for fabrication and easier to form components with near-net-shape and high relative density, compared with other sintering methods. In this study, RBSC was fabricated with different size of SiC in the raw material. Microstructure, thermal and mechanical properties were characterized with the reaction-sintered samples in order to examine the effect of SiC size on the thermal and mechanical properties of RBSC ceramics. Especially, phase volume fraction of each component phase, such as Si, SiC, and C, was evaluated by using an image analyzer. The relationship between microstructures and physical properties was also discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Structural and Mechanical Properties of SiC-Rich By-Products of the Metal Grade Si Process
Thomas Hafner, Jonas Hafner, Frank Kimm, Vira Bovda, Oleksandr Bovda, Oleksandr Kuprin, Anatoliy Pikalov, Kostiantyn Lentsov, Pavlo Schikhaylo, Yriy Onyschuk, Andriy Tarasuk, Viktoriya Podhurska, Bogdan Vasyliv, Oleksandr Shcheretsky, Ihor Vorona, Roman Y
Materials Science Forum.2024; 1113: 87. CrossRef - Effect of Y2O3 Additive Amount on Densification of Reaction Bonded Silicon Carbides Prepared by Si Melt Infiltration into All Carbon Preform
Kyeong-Sik Cho, Min-Ho Jang
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2021; 31(5): 301. CrossRef - Mechanical Strength Values of Reaction-Bonded-Silicon-Carbide Tubes with Different Sample Size
Seongwon Kim, Soyul Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh, Sung-Min Lee, Yoonsoo Han, Hyun-Ick Shin, Youngseok Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(6): 450. CrossRef
- Structural and Mechanical Properties of SiC-Rich By-Products of the Metal Grade Si Process
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


