Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Laser Processing of an Al0.1CoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy + Cu Composite Powders via Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Kwangtae Son, Ji-Woon Lee, Soon-Jik Hong, Somayeh Pasebani
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):277-287. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00101

- 1,131 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study examined process–structure relationships in laser powder bed fusion of Al₀.₁CoCrFeNi + Cu composites, focusing on densification, elemental distribution, and solidification cracking. Mechanically mixed Al₀.₁CoCrFeNi and Cu powders were processed across a range of laser powers (100–250 W) and scan speeds (200–800 mm/s). Increased volumetric energy density (VED) improved densification, with a plateau near 200 J/mm³ yielding ~96% relative density; however, this value was still below application-grade thresholds. At low VED, insufficient thermal input and short melt pool residence times promoted Cu segregation, while higher VED facilitated improved elemental mixing. Elemental mapping showed partial co-segregation of Ni with Cu at low energies. Solidification cracks were observed across all processing conditions. In high VED regimes, cracking exhibited a minimal correlation with segregation behavior and was primarily attributed to steep thermal gradients, solidification shrinkage, and residual stress accumulation. In contrast, at low VED, pronounced Cu segregation appeared to exacerbate cracking through localized thermal and mechanical mismatch.
- [English]
- Investigation on Microstructure and Flowability of Gas Atomized Heat-resistant KHR45A Alloy Powders for Additive Manufacturing
- Geonwoo Baek, Mohsen Saboktakin Rizi, Yeeun Lee, SungJae Jo, Joo-Hyun Choi, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(1):13-21. Published online February 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.1.13

- 2,599 View
- 766 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In additive manufacturing, the flowability of feedstock particles determines the quality of the parts that are affected by different parameters, including the chemistry and morphology of the powders and particle size distribution. In this study, the microstructures and flowabilities of gas-atomized heat-resistant alloys for additive manufacturing applications are investigated. A KHR45A alloy powder with a composition of Fe-30Cr-40Mn-1.8Nb (wt.%) is fabricated using gas atomization process. The microstructure and effect of powder chemistry and morphology on the flow behavior are investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and revolution powder analysis. The results reveal the formation of spherical particles composed of single-phase FCC dendritic structures after gas atomization. SEM observations show variations in the microstructures of the powder particles with different size distributions. Elemental distribution maps, line scans, and high-resolution XPS results indicate the presence of a Si-rich oxide accompanied by Fe, Cr, and Nb metal oxides in the outer layer of the powders. The flowability behavior is found to be induced by the particle size distribution, which can be attributed to the interparticle interactions and friction of particles with different sizes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Engineering heterogeneous microstructure for enhancing mechanical properties of multicomponent alloys via powder metallurgy route
Min Woo Shin, Sung-Jae Jo, Sourabh Kumar Soni, Ji-Woon Lee, Jongun Moon, Hyoung Seop Kim, Soon-Jik Hong
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2025; 941: 148599. CrossRef - Al-based amorphous coatings by warm spraying: Numerical simulation and experimental validation
Deming Wang, Nianchu Wu, Peng Cao
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2024; 1008: 176674. CrossRef
- Engineering heterogeneous microstructure for enhancing mechanical properties of multicomponent alloys via powder metallurgy route
- [Korean]
- Characterization of Classification of Synthesized Ni Nanopowders by Pulsed Wire Evaporation Method
- Joong-Hark Park, Geon-Hong Kim, Dong-Jin Lee, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):389-394. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.389

- 649 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Ni wires with a diameter and length of 0.4 and 100 mm, respectively, and a purity of 99.9% are electrically exploded at 25 cycles per minute. The Ni nanopowders are successfully synthesized by a pulsed wire evaporation (PWE) method, in which Ar gas is used as the ambient gas. The characterization of the nanopowders is carried out using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and a high-resolution transmission electronmicroscope (HRTEM). The Ni nanopowders are classified for a multilayer ceramic condenser (MLCC) application using a type two Air-Centrifugal classifier (model: CNI, MP-250). The characterization of the classified Ni nanopowders are carried out using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) and particle size analysis (PSA) to observe the distribution and minimum classification point (minimum cutting point) of the nanopowders.
- [English]
- Influence of milling atmosphere on thermoelectric properties of p-type Bi-Sb-Te based alloys by mechanical alloying
- Suk-min Yoon, Cheenepalli Nagarjuna, Dong-won Shin, Chul-hee Lee, Babu Madavali, Soon-jik Hong, Kap-ho Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):357-363. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.357
- 1,289 View
- 4 Download
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
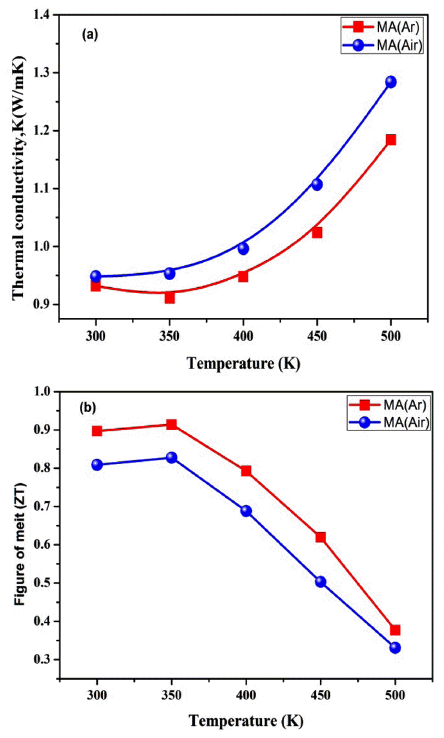
PDF In this study, Bi-Sb-Te thermoelectric materials are produced by mechanical alloying (MA) and spark plasma sintering (SPS). To examine the influence of the milling atmosphere on the microstructure and thermo-electric (TE) properties, a p-type Bi-Sb-Te composite powder is mechanically alloyed in the presence of argon and air atmospheres. The oxygen content increases to 55% when the powder is milled in the air atmosphere, compared with argon. All grains are similar in size and uniformly, distributed in both atmospheric sintered samples. The Seebeck coefficient is higher, while the electrical conductivity is lower in the MA (Air) sample due to a low carrier concentration compared to the MA (Ar) sintered sample. The maximum figure of merit (ZT) is 0.91 and 0.82 at 350 K for the MA (Ar) and MA (Air) sintered samples, respectively. The slight enhancement in the ZT value is due to the decrease in the oxygen content during the MA (Ar) process. Moreover, the combination of mechanical alloying and SPS process shows a higher hardness and density values for the sintered samples.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Grain Size‐Dependent Thermoelectric Performances of Al2O3 Addition into BiSbTe Alloy During Heat Treatment Fabricated by Mechanical Alloying
Ji‐Won Ha, Vasudevan Rathinam, Eun‐Ha Go, Soon‐Jik Hong
Advanced Engineering Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Revealing the improved thermoelectric performances of (BiSb)2Te3 alloy through rapid solidification of cold-water assisted water atomization approach
Eun-Ha Go, Rathinam Vasudevan, Ji-Won Ha, Sung-Jae Jo, GeonWoo Baek, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2025; 1010: 177548. CrossRef - Microstructural and Thermoelectric Properties of Heat-treated Al2O3 Doped BiSbTe Alloy
Jiwon Ha, Vasudevan Rathinam, Eunha Go, Soonjik Hong
Journal of the Japan Society of Powder and Powder Metallurgy.2025; 72(Supplement): S983. CrossRef - Advancement of thermoelectric performances through the dispersion of expanded graphene on p-type BiSbTe alloys
Eun-Ha Go, Rathinam Vasudevan, Babu Madavali, Peyala Dharmaiah, Min-Woo Shin, Sung Ho Song, Soon-Jik Hong
Powder Metallurgy.2023; 66(5): 722. CrossRef - Influence of milling atmosphere on the structure and magnetic properties of mechanically alloyed Fe40Co30Ni30
Alex Abraham Paul, Anuj Rathi, Ganesh Varma Thotakura, Tanjore V. Jayaraman
Materials Chemistry and Physics.2021; 258: 123897. CrossRef - Enhancement of mechanical properties and thermoelectric performance of spark plasma sintered P-type Bismuth Telluride by powder surface oxide reduction
Ahmed A. Abdelnabi, Vickram Lakhian, Joseph R. McDermid, Yu-Chih Tseng, James S. Cotton
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2021; 858: 157657. CrossRef - Solid solution evolution during mechanical alloying in Cu-Nb-Al compounds
Kaouther Zaara, Mahmoud Chemingui, Virgil Optasanu, Mohamed Khitouni
International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials.2019; 26(9): 1129. CrossRef
- Grain Size‐Dependent Thermoelectric Performances of Al2O3 Addition into BiSbTe Alloy During Heat Treatment Fabricated by Mechanical Alloying
- [English]
- Investigation of Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of p-type Bi-Sb-Te alloys
- Jin-Koo Han, Dong-won Shin, Babu Madavali, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):115-121. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.115
- 1,398 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
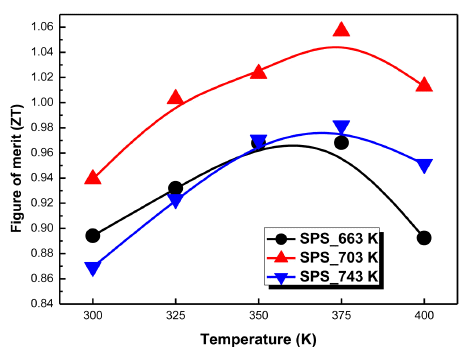
PDF In this work, p-type Bi−Sb−Te alloys powders are prepared using gas atomization, a mass production powder preparation method involving rapid solidification. To study the effect of the sintering temperature on the microstructure and thermoelectric properties, gas-atomized powders are consolidated at different temperatures (623, 703, and 743 K) using spark plasma sintering. The crystal structures of the gas-atomized powders and sintered bulks are identified using an X-ray diffraction technique. Texture analysis by electron backscatter diffraction reveals that the grains are randomly oriented in the entire matrix, and no preferred orientation in any unique direction is observed. The hardness values decrease with increasing sintering temperature owing to a decrease in grain size. The conductivity increases gradually with increasing sintering temperature, whereas the Seebeck coefficient decreases owing to increases in the carrier mobility with grain size. The lowest thermal conductivity is obtained for the bulk sintered at a low temperature (603 K), mainly because of its fine-grained microstructure. A peak ZT of 1.06 is achieved for the sample sintered at 703 K owing to its moderate electrical conductivity and sustainable thermal conductivity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of the SPS heating rate on the optical and mechanical properties of Y2O3-MgO nanocomposites
Seok-Min Yong
Journal of Ceramic Processing Research.2019; 20(1): 59. CrossRef
- Influence of the SPS heating rate on the optical and mechanical properties of Y2O3-MgO nanocomposites
- [English]
- Optimization of Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature Conditions for Enhancement of Thermoelectric Performance in Gas-Atomized Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 Compound
- Kwang-yong Jeong, Chul Hee Lee, Peyala Dharmaiah, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):108-114. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.108

- 1,267 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We fabricate fine (<20 μm) powders of Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 alloys using a large-scale production method and subsequently consolidate them at temperatures of 573, 623, and 673 K using a spark plasma sintering process. The microstructure, mechanical properties, and thermoelectric properties are investigated for each sintering temperature. The microstructural features of both the powders and bulks are characterized by scanning electron microscopy, and the crystal structures are analyzed by X-ray diffraction analysis. The grain size increases with increasing sintering temperature from 573 to 673 K. In addition, the mechanical properties increase significantly with decreasing sintering temperature owing to an increase in grain boundaries. The results indicate that the electrical conductivity and Seebeck coefficient (217 μV/K) of the sample sintered at 673 K increase simultaneously owing to decreased carrier concentration and increased mobility. As a result, a high
ZT value of 0.92 at 300 K is achieved. According to the results, a sintering temperature of 673 K is preferable for consolidation of fine (<20 μm) powders.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Complex microstructure induced high thermoelectric performances of p-type Bi–Sb–Te alloys
Eun-Ha Go, Babu Madavali, Min-Woo Shin, Sung Ho Song, Soon-Jik Hong
Materials Chemistry and Physics.2023; 307: 128156. CrossRef - Role of sintering temperature on electronic and mechanical properties of thermoelectric material: A theoretical and experimental study of TiCoSb half-Heusler alloy
Ajay Kumar Verma, Kishor Kumar Johari, Kriti Tyagi, Durgesh Kumar Sharma, Pawan Kumar, Sudhir Kumar, Sivaiah Bathula, S.R. Dhakate, Bhasker Gahtori
Materials Chemistry and Physics.2022; 281: 125854. CrossRef - Enhanced thermoelectric properties of Li and Mg co−substituted Bi2Sr2Co2O fabricated by combined conventional sintering and spark plasma sintering
K. Park, H.Y. Hong, S.Y. Gwon
Inorganic Chemistry Communications.2022; 145: 110005. CrossRef
- Complex microstructure induced high thermoelectric performances of p-type Bi–Sb–Te alloys
- [English]
- Effects of Hydrogen Reduction in Microstructure, Mechanical and Thermoelectric Properties of Gas Atomized
n -type Bi2Te2.7 Se0.3 Material - Pradip Rimal, Sang-Min Yoon, Eun-Bin Kim, Chul-Hee Lee, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):126-131. Published online April 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.126

- 970 View
- 5 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The recent rise in applications of thermoelectric materials has attracted interest in studies toward the fabrication of thermoelectric materials using mass production techniques. In this study, we successfully fabricate
n -type Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 material by a combination of mass production powder metallurgy techniques, gas atomization, and spark plasma sintering. In addition, to examine the effects of hydrogen reduction in the microstructure, the thermoelectric and mechanical properties are measured and analyzed. Here, almost 60% of the oxygen content of the powder are eliminated after hydrogen reduction for 4 h at 360°C. Micrographs of the powder show that the reduced powder had a comparatively clean surface and larger grain sizes than unreduced powder. The density of the consolidated bulk using as-atomized powder and reduced atomized powder exceeds 99%. The thermoelectric power factor of the sample prepared by reduction of powder is 20% better than that of the sample prepared using unreduced powder.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tuning of power factor in bismuth selenide through Sn/Te co doping for low temperature thermoelectric applications
Ganesh Shridhar Hegde, Ashwatha Narayana Prabhu, Ramakrishna Nayak, C. F. Yang, Y. K. Kuo
Applied Physics A.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing thermoelectric performance of K-doped polycrystalline SnSe through band engineering tuning and hydrogen reduction
Nan Xin, Yifei Li, Guihua Tang, Longyun Shen
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2022; 899: 163358. CrossRef - The effect of powder pre-treatment on the mechanical and thermoelectric properties of spark plasma sintered N-type bismuth telluride
Ahmed A. Abdelnabi, Vickram Lakhian, Joseph R. McDermid, James S. Cotton
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2021; 874: 159782. CrossRef - Investigation of Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of p-type Bi-Sb-Te alloys
Jin-Koo Han, Dong-won Shin, Babu Madavali, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 115. CrossRef - The Preparation and Growth Mechanism of the Recovered Bi2Te3 Particles with Respect to Surfactants
Hyeongsub So, Eunpil Song, Yong-Ho Choa, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 141. CrossRef - Enhanced thermoelectric cooling properties of Bi2Te3−xSex alloys fabricated by combining casting, milling and spark plasma sintering
Seung Tek Han, Pradip Rimal, Chul Hee Lee, Hyo-Seob Kim, Yongho Sohn, Soon-Jik Hong
Intermetallics.2016; 78: 42. CrossRef
- Tuning of power factor in bismuth selenide through Sn/Te co doping for low temperature thermoelectric applications
- [English]
- Investigation of Ball Size Effect on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of
p -type BiSbTe by Mechanical Alloying - May Likha Lwin, Sang-min Yoon, Babu Madavali, Chul-Hee Lee, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):120-125. Published online April 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.120

- 1,491 View
- 5 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF P -type ternary Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 alloys are fabricated via mechanical alloying (MA) and spark plasma sintering (SPS). Different ball sizes are used in the MA process, and their effect on the microstructure; hardness, and thermoelectric properties of thep -type BiSbTe alloys are investigated. The phases of milled powders and bulks are identified using an X-ray diffraction technique. The morphology of milled powders and fracture surface of compacted samples are examined using scanning electron microscopy. The morphology, phase, and grain structures of the samples are not altered by the use of different ball sizes in the MA process. Measurements of the thermoelectric (TE) transport properties including the electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and power factor are measured at temperatures of 300- 400 K for samples treated by SPS. The TE properties do not depend on the ball size used in the MA process.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigation of Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of p-type Bi-Sb-Te alloys
Jin-Koo Han, Dong-won Shin, Babu Madavali, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 115. CrossRef - Flexible Thermoelectric Device Using Thick Films for Energy Harvesting from the Human Body
Han Ki Cho, Da Hye Kim, Hye Sun Sin, Churl-Hee Cho, Seungwoo Han
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2017; 54(6): 518. CrossRef - Investigation of the Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of P-Type BiSbTe Alloys by Usage of Different Revolutions Per Minute (RPM) During Mechanical Milling
S.-M. Yoon, B. Madavali, Y.-N. Yoon, S.-J. Hong
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1167. CrossRef - Mechanical and thermoelectric properties of Bi2−xSbxTe3 prepared by using encapsulated melting and hot pressing
Woo-Jin Jung, Il-Ho Kim
Journal of the Korean Physical Society.2016; 69(8): 1328. CrossRef
- Investigation of Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of p-type Bi-Sb-Te alloys
- [Korean]
- Technology Trend Analysis of CO2 Capture and Storage by Patent Information
- Su-Jin Lee, Yun-Seock Lee, Jeong-Gu Lee, Soon-Jik Hong, Joong-Beom Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(4):289-297. Published online August 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.4.289

- 714 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF As recognized by all scientific and industrial groups, carbon dioxide(CO2) capture and storage(CCS) could play an important role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Especially carbon capture technology by dry sorbent is considered as a most energy-efficient method among the existing CCS technologies. Patent analysis has been considered to be a necessary step for identifying technological trend and planning technology strategies. This paper is aimed at identifying evolving technology trend and key indicators of dry sorbent from the objective information of patents. And technology map of key patents is also presented. In this study the patents applied in korea, japan, china, canada, US, EU from 1993 to 2013 are analyzed. The result of patent analysis could be used for R&D and policy making of domestic CCS industry.
- [Korean]
- Electromagnetic Wave Shielding Effect of Nano-powder Dispersed Epoxy Resin Composite
- Jun-Young Han, Chul-Hee Lee, Min-Gyu Choi, Soon-Jik Hong, Joong-Hark Park, Dong-Jin Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(4):234-239. Published online August 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.4.234

- 581 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Electronic products are a major part of evolving industry and human life style; however most of them are known to emit electromagnetic waves that have severe health hazards. Therefore, different materials and fabrication techniques are understudy to control or limit transfer of such waves to human body. In this study, nanocomposite powder is dispersed into epoxy resin and shielding effects such as absorption, reflection, penetration and multiple reflections are investigated. In addition, nano size powder (Ni, Fe2O3, Fe-85Ni, C-Ni) is fabricated by pulsed wire evaporation method and dispersed manually into epoxy. Characterization techniques such as X-ray diffraction, Scanning electron microscopy and Transmission electron microscopy are used to investigate the phase analysis, size and shape as well as dispersion trend of a nano powder on epoxy matrix. Shielding effect is measured by standard test method to investigate the electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of planar materials, ASTM D4935. At lower frequency, sample consisting nano-powder of Fe-85%Wt Ni shows better electromagnetic shielding effect compared to only epoxy, only Ni, Fe2O3 and C-Ni samples.
- [Korean]
- Importance and Utilization Strategy for Company & Research Institute
- Yun-Seock Lee, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(5):388-395.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.5.388

- 413 View
- 0 Download
- [Korean]
- Investigation of Material Flow and Industrial Trend of Domestic Europium
- Han-Jin Ko, Jeong-Gon Kim, Il-Seuk Lee, Hong-Yoon Kang, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(5):382-387.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.5.382

- 709 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
- [Korean]
- The Effect of Milling Conditions for Dissolution Efficiency of Valuable Metals from PDP Waste Panels
- Hyo-Seob Kim, Chan-Mi Kim, Chul-Hee Lee, Sung-Kyu Lee, Hyun-Seon Hong, Jar-Myung Koo, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(2):107-113.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.2.107

- 867 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, the microstructure and valuable metals dissolution properties of PDP waste panel powders were investigated as a function of milling parameters such as ball diameter size, milling time, and rotational speed during high-energy milling process. The complete refinement of powder could achieved at the ball diameter size of 5 mm due to sufficient impact energy and the number of collisions. With increasing milling time, the average particle size was rapidly decreased until the first 30 seconds, then decreased gradually about 3µm at 3 minutes and finally, increased with presence of agglomerated particles of 35µm at 5 minutes. Although there was no significant difference on the size of the particle according to the rotational speed from 900 to 1,100 rpm, the total valuable metals dissolution amount was most excellent at 1,100 rpm. As a result, the best milling conditions for maximum dissolving amount of valuable metals (Mg: 375 ppm, Ag 135 ppm, In: 17 ppm) in this research were achieved with 5 mm of ball diameter size, 3min of milling time, and 1,100 rpm of rotational speed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison Of Mercury Distribution Between The Types Of Spent Fluorescent Lamp
S.W. Rhee, H.-S. Park, H.H. Choi
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2015; 60(2): 1297. CrossRef
- Comparison Of Mercury Distribution Between The Types Of Spent Fluorescent Lamp
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Ceramic Dental Block by Magnetic Pulsed Compaction
- Hyo-Young Park, Hyo-Seob Kim, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2012;19(5):373-378.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2012.19.5.373

- 564 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Sintered bulks of ZrO_2 nanopowders were fabricated by magnetic pulsed compaction (MPC) and subsequent two-step sintering employed in this study and the formability effects of nanopowder on mixing condition, pressure and sintering temperature were investigated. The addition of PVA induced and increase in the formability of the sintered bulk. But cracked bulks were obtained on sintering with addition of over 10 wt% PVA due to generation of crack during sintering. The optimum compaction pressure during MPC was 1.0 GPa and mixing conditions included using 5.0 wt% PVA. The optimum processing condition included MPC process, followed by two-step sintering (first at 1000 and then at 1450°C). The sintered bulks with the diameter of 30 mm under these conditions were found to have non crack, ~99% density.
- [Korean]
- Recycling Technology and Status of Tellurium Materials
- Hyo-Seob Kim, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2012;19(3):232-238.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2012.19.3.232

- 448 View
- 2 Download
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Fe coated Mg Based Desulfurization Powder by Mechanical Alloying Process
- Joon-Woo Song, Otaduy Guillermo, Byong-Sun Chun, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2012;19(3):226-231.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2012.19.3.226

- 456 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this research, the coating behavior of Mg and Fe desulfurization powder fabricated by low energy and conventional planetary mill equipment was investigated as a function of milling time, which produces uniform Fe coated powders due to milling energy. Since high energy ball milling results in breaking the Fe coated Mg powders into coarse particles, low energy ball milling was considered appropriate for this study, and can be implemented in desulfurization industry widely. XRD and FE-SEM analyses were carried out to investigate the microstructure and distribution of the coating material. The thickness of the Fe coating layer reaches a maximum of 14 µm at 20 milling hours. The BCC structures of Fe particles are deformed due to the slip system of Fe coated Mg particles.
- [Korean]
- Industrial Supply Chain Trend of Domestic Tungsten
- Joon-Woo Song, Sang-Hyun Lee, Hyun-Seon Hong, Hong-Yoon Kang, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2012;19(1):79-86.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2012.19.1.079

- 874 View
- 7 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extraction Factor Of Tungsten Sources From Tungsten Scraps By Zinc Decomposition Process
J.-H. Pee, G.H. Kim, H.Y. Lee, Y.J. Kim
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2015; 60(2): 1311. CrossRef - Microstructure and Elevated Temperature Strength of W-ZrC Composites with Micrometric and Nanosized ZrC Particles
Yoon Soo Han, Sung-Soo Ryu
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2014; 21(6): 415. CrossRef - Investigation of Material Flow and Industrial Trend of Domestic Europium
Han-Jin Ko, Jeong-Gon Kim, Il-Seuk Lee, Hong-Yoon Kang, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2013; 20(5): 382. CrossRef
- Extraction Factor Of Tungsten Sources From Tungsten Scraps By Zinc Decomposition Process
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Characterization of (AgSbTe2)15(GeTe)85 Thermoelectric Powder by Gas Atomization Process
- Hyo-Seob Kim, Jin-Kyu Lee, Jar-Myung Koo, Byong-Sun Chun, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2011;18(5):449-455.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2011.18.5.449

- 758 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, p-type (AgSbTe_2)_15(GeTe)_85: TAGS-85 compound powders were prepared by gas atomization process, and then their microstructures and mechanical properties were investigated. The fabricated powders were of spherical shape, had clean surface, and illustrated fine microstructure and homogeneous AgSbTe_2 + GeTe solid solution. Powder X-ray diffraction results revealed that the crystal structure of the TAGS-85 sample was single rhombohedral GeTe phase, which with a space group R_3m. The grain size of the powder particles increased while the micro Vickers hardness decreased with increasing annealing temperature within the range of 573 K and 723 K due to grain growth and loss of Te. In addition, the crystal structure of the powder went through a phase transformation from rhombohedral (R_3m) at low-temperature to cubic (F_m-3m) at high-temperature with increasing annealing temperature. The micro Vickers hardness of the as-atomized powder was around 165 Hv, while it decreased gradually to 130 Hv after annealing at 673K, which is still higher than most other fabrication processes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thermoelectric properties of n-type Bi2Te3 alloys produced by a combined process of magnetic pulsed compaction (MPC) and spark plasma sintering (SPS)
Chul-Hee Lee, M. Fatih Kilicaslan, Babu Madavali, Soon-Jik Hong
Research on Chemical Intermediates.2014; 40(7): 2543. CrossRef
- Thermoelectric properties of n-type Bi2Te3 alloys produced by a combined process of magnetic pulsed compaction (MPC) and spark plasma sintering (SPS)
- [Korean]
- Characteristics of Indium Dissolution of Waste LCD Panel Powders Fabricated by High Energy Ball Milling (HEBM) Process with Milling Time
- Hyo-Seob Kim, Jun-Je Sung, Cheol-Hee Lee, Hyun-Seon Hong, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2011;18(4):378-384.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2011.18.4.378

- 797 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this research, the indium dissolution properties of the waste LCD panel powders were investigated as a function of milling time fabricated by high-energy ball milling (HEBM) process. The particle morphology of waste LCD panel powders changed from sharp and irregular shape of initial cullet to spherical shape with an increase in milling time. The particle size quickly decreased to 15 µm until the first minute, then decreased gradually about 6 µm with presence of agglomerated particles after 5 minutes, which increased gradually reaching a uniform size of 13 µm consist of agglomerated particles after 30 minutes. The glass recovery, after dissolution, was over 99% at initial cullet, which decreased to 90.1 and 78.6% with increasing milling time of 1 and 30 minute respectively, due to a loss in remaining powder of the surface ball and jar, as well as the filter paper. The dissolution amount of indium out of the initial cullet was 208 ppm before milling, turning into 223 ppm for the mechanically milled powder after 1 minute, and nearly 146~125 ppm with further increase in milling time because of the reaction surface decrease of powders due to agglomeration. With this process, maximum dissolving indium amount (223 ppm) could be achieved at a particle size of 15 µm with 1 minute of milling.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Indium ion cementation onto aluminum plates in hydrochloric acid solutions: a kinetic perspective
Hyun Seon Hong, Geon Hong Kim, Myung Hwan Hong, Sungkyu Lee, Jae-Chun Lee
International Journal of Materials Research.2014; 105(2): 177. CrossRef - The Effect of Milling Conditions for Dissolution Efficiency of Valuable Metals from PDP Waste Panels
Hyo-Seob Kim, Chan-Mi Kim, Chul-Hee Lee, Sung-Kyu Lee, Hyun-Seon Hong, Jar-Myung Koo, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2013; 20(2): 107. CrossRef
- Indium ion cementation onto aluminum plates in hydrochloric acid solutions: a kinetic perspective
- [Korean]
- Thermoelectric Properties of Rapid Solidified p-type Bi2Te3 Alloy Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering(SPS) Process
- Chul-Dong Moon, Soon-Jik Hong, Do-Hyang Kim, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(6):494-498.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.6.494

- 913 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The p-type thermoelectric compounds of Bi_2Te_3 based doped with 3wt% Te were fabricated by a combination of rapid solidification and spark plasma sintering (SPS) process. The effect of holding time during spark plasma sintering (SPS) on the microstructure and thermoelectric properties were investigated using scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and thermoelectric properties. The powders as solidified consisted of homogeneous thermoelectric phases. The thermoelectric figure of merit measured to be maximum (3.41times10-3/K) at the SPS temperature of 430°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Sintering Temperature on the Thermoelectric Properties of Bismuth Antimony Telluride Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering
경석 이, 영근 정, 성호 서, 상현 진, 봉영 유
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2012; 22(6): 280~284. CrossRef
- Effect of Sintering Temperature on the Thermoelectric Properties of Bismuth Antimony Telluride Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering
- [Korean]
- Phase Transformation and Microstructure of FeSi2 Thermoelectric Compounds Manufactured by Powder Metallurgy
- Kyoung-Tae Park, Jin-Gyo Shin, Soon-Jik Hong, Byong-Sun Chun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(6):482-488.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.6.482

- 481 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, FeSi_2 as high temperature performance capable thermoelectric materials was manufactured by powder metallurgy.The as-casted Fe-Si alloy was annealed for homogenization below 1200°C for 3 h. Due to its high brittleness, the cast alloy transformed to fine powders by ball-milling, followed by subsequent compaction (hydraulic pressure; 2 GPa) and sintering (1200°C, 12 h). In order to precipitate beta-FeSi_2, heat treatment was performed at 850°C with varying dwell time (7, 15 and 55 h). As a result of this experiment thermoelectric phase beta-FeSi_2 was quickly transformed by powder metallurgical process. There was not much change in powder factor between 7h and 55h specimens.
- [Korean]
- Refinement Behavior of Coarse Magnesium Powder by High Energy Ball Milling (HEBM)
- Joon-Woo Song, Hyo-Seob Kim, Hong-Moule Kim, Taek-Soo Kim, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(4):302-311.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.4.302

- 932 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this research, the refinement behavior of the coarse magnesium powders fabricated by gas atomization was investigated as a function of milling time using a short duration high-energy ball milling equipment, which produces fine powders by means of an ultra high-energy within a short duration. The microstructure, hardness, and formability of the powders were investigated as a function of milling time using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, Vickers micro-hardness tester and magnetic pulsed compaction. The particle morphology of Mg powders changed from spherical particles of feed metals to irregular oval particles, then platetype particles, with increasing milling time. Due to having HCP structure, deformation occurs due to the existence of the easily breakable C-axis perpendicular to the base, resulting in producing plate-type powders. With increasing milling time, the particle size increased until 5 minutes, then decreased gradually reaching a uniform size of about 50 micrometer after 20 minutes. The relative density of the initial power was 98% before milling, and mechanically milled powder was 92~94% with increase milling time (1~5 min) then it increased to 99% after milling for 20 minutes because of the change in particle shapes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quantitative Study on the Refinement Behaviors of TiC Powders Produced by Mechanical Milling Under Different Impact Energy
Sung-Mo Hong, Eun-Kwang Park, Kyeong-Yeol Kim, Jin-Ju Park, Min-Ku Lee, Chang-Kyu Rhee, Jin-Kyu Lee, Young-Soon Kwon
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2012; 19(1): 32. CrossRef - Fabrication of Fe coated Mg Based Desulfurization Powder by Mechanical Alloying Process
Joon-Woo Song, Otaduy Guillermo, Byong-Sun Chun, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2012; 19(3): 226. CrossRef - Characteristics of Indium Dissolution of Waste LCD Panel Powders Fabricated by High Energy Ball Milling (HEBM) Process with Milling Time
Hyo-Seob Kim, Jun-Je Sung, Cheol-Hee Lee, Hyun-Seon Hong, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2011; 18(4): 378. CrossRef - Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Nano-sized Ti-35%Nb-7%Zr-10%CPP Composite Fabricated by Pulse Current Activated Sintering
Kee-Do Woo, Duck-Soo Kang, Sang-Hyuk Kim, Sang-Hoon Park, Ji-Young Kim, Hye-Rim Ko
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2011; 18(2): 188. CrossRef
- Quantitative Study on the Refinement Behaviors of TiC Powders Produced by Mechanical Milling Under Different Impact Energy
- [Korean]
- Effect of Initial Silicon Scrap Size on Powder Refining Process During High Energy Ball Milling (HEBM)
- Joon-Woo Song, Hyo-Seob Kim, Sung-Shin Kim, Jar-Myung Koo, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(3):242-250.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.3.242

- 928 View
- 4 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this research, the optimal manufacturing conditions of fine Si powders from Si scrap were investigated as a function of different initial powder size using the high-energy ball milling equipment, which produces the fine powder by means of an ultra high-energy within a short duration. The morphological change of the powders according to the milling time was observed by Scanning electron microscopy (SEM). With the increasing milling time, the size of Si powder was decreased. In addition, more energy and stress for milling were required with the decreasing initial powder size. The refinement of Si scrap was rapidly carried out at 10min ball milling time. However, the refined powder started to agglomerate at 30 min milling time, while the powder size became uniform at 60 min milling time.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mechanical Properties and Biocompatibility of Ti-Nb-Zr-Mo-CPP Biomaterial Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering
기도 우, 상미 김, 동건 김, 대영 김, 동수 강
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2013; 23(2): 135~142. CrossRef - The Effect of Milling Conditions for Dissolution Efficiency of Valuable Metals from PDP Waste Panels
Hyo-Seob Kim, Chan-Mi Kim, Chul-Hee Lee, Sung-Kyu Lee, Hyun-Seon Hong, Jar-Myung Koo, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2013; 20(2): 107. CrossRef - Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Nano-sized Ti-35%Nb-7%Zr-10%CPP Composite Fabricated by Pulse Current Activated Sintering
Kee-Do Woo, Duck-Soo Kang, Sang-Hyuk Kim, Sang-Hoon Park, Ji-Young Kim, Hye-Rim Ko
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2011; 18(2): 188. CrossRef - Effect of Milling Time on the Microstructure and Phase Transformation Behaviors of Ni-B Powder During Mechanical Alloying Process
Jung-Geun Kim, Wook-Jin Lee, Sung-Kyun Park, Ik-Min Park, Yong-Ho Park
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2011; 18(6): 496. CrossRef - Refinement Behavior of Coarse Magnesium Powder by High Energy Ball Milling (HEBM)
Joon-Woo Song, Hyo-Seob Kim, Hong-Moule Kim, Taek-Soo Kim, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2010; 17(4): 302. CrossRef
- Mechanical Properties and Biocompatibility of Ti-Nb-Zr-Mo-CPP Biomaterial Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering
- [Korean]
- Recycling Technology for End-of-Life LCD Units
- Hi-Min Lee, Hyun-Seon Hong, Hang-Chul Jung, Hong-Yoon Kang, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(2):88-100.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.2.088

- 899 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Milling Conditions for Dissolution Efficiency of Valuable Metals from PDP Waste Panels
Hyo-Seob Kim, Chan-Mi Kim, Chul-Hee Lee, Sung-Kyu Lee, Hyun-Seon Hong, Jar-Myung Koo, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2013; 20(2): 107. CrossRef - Characteristics of Indium Dissolution of Waste LCD Panel Powders Fabricated by High Energy Ball Milling (HEBM) Process with Milling Time
Hyo-Seob Kim, Jun-Je Sung, Cheol-Hee Lee, Hyun-Seon Hong, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2011; 18(4): 378. CrossRef
- The Effect of Milling Conditions for Dissolution Efficiency of Valuable Metals from PDP Waste Panels
- [Korean]
- The Effect of Ti Powder addition on Compaction Behavior of TiO2 Nano Powder
- Jin-Sub Park, Hyo-Seob Kim, Ki-Seok Lee, Jeong-Goo Lee, Chang-Kyu Rhee, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(3):223-230.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.3.223

- 810 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The compaction response of TiO_2 nano powders with an addition of Ti powders prepared by magnetic pulsed compaction and subsequent sintering processes was investigated. All kinds of different bulk exhibited an average shrinkage of about 12% for different MPCed pressure and sintering temperature, which were approximately 50% lower than those fabricated by general process (20%) and a maximum density of around 92.7% was obtained for 0.8GPa MPCed pressure and 1400°C sintering temperature. The addition of Ti powder induced an increase in the formability and hardness of the sintered TiO_2. But the lower densities were obtained on sintering with addition of over 10 (wt%) Ti powder due to generation of crack during sintering. Subsequently it was verified that the optimum compaction pressure in MPC and sintering temperature were 0.8GPa and 1400°C, respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Ceramic Dental Block by Magnetic Pulsed Compaction
Hyo-Young Park, Hyo-Seob Kim, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2012; 19(5): 373. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Ceramic Dental Block by Magnetic Pulsed Compaction
- [Korean]
- Effect of Ball milling Time on Graphite Dispersion and Mechanical Properties in Rapidly Solidified 6061 Al Composite
- Hyeon-Taek Son, Jae-Seol Lee, Soon-Jik Hong, Byong-Sun Chun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(3):209-216.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.3.209

- 830 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A composite of rapidly solidified Al-6061 alloy powder with graphite particle reinforcements was prepared by ball milling and subsequent hot extrusion. The microstructure and mechanical properties of these composites were investigated as a function of milling time. With increasing milling time, the gas atomized initially and spherical powders became elongated with a maximum aspect ratio after milling for 30 h. Then, refinement and spheroidization were achieved by further milling to 70 h with a homogeneous and fine dispersion of graphite particles forming between the matrix alloy layers. The best compression and wear properties were obtained in the powder milled for 70 h, associated with the increased fine and homogeneous distribution of graphite particles in the aluminum alloy matrix.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Fe coated Mg Based Desulfurization Powder by Mechanical Alloying Process
Joon-Woo Song, Otaduy Guillermo, Byong-Sun Chun, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2012; 19(3): 226. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Fe coated Mg Based Desulfurization Powder by Mechanical Alloying Process
- [Korean]
- Consolidation and Mechanical Property of Rapidly Solidified Al-20 wt% Si Alloy Powders by Continuous Equal Channel Multi-Angular Pressing
- Seung-Chae Yoon, Cheon-Hee Bok, Min-Hong Seo, Soon-Jik Hong, Hyoung-Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2008;15(1):31-36.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2008.15.1.031

- 823 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, the bottom-up powder metallurgy and the top-down severe plastic deformation (SPD) techniques for manufacturing bulk nanomaterials were combined in order to achieve both full density and grain refinement without grain growth of rapidly solidified Al-20 wt% Si alloy powders during consolidation processing. Continuous equal channel multi-angular processing (C-ECMAP) was proposed to improve low productivity of conventional ECAP, one of the most promising method in SPD. As a powder consolidation method, C-ECMAP was employed. A wide range of experimental studies were carried out for characterizing mechanical properties and microstructures of the ECMAP processed materials. It was found that effective properties of high strength and full density maintaining nanoscale microstructure are achieved. The proposed SPD processing of powder materials can be a good method to achieve fully density and nanostructured materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- X-ray diffraction study on the microstructure of a Mg–Zn–Y alloy consolidated by high-pressure torsion
Péter Jenei, Jenő Gubicza, Eun Yoo Yoon, Hyoung Seop Kim
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2012; 539: 32. CrossRef - Microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Y alloy consolidated from gas-atomized powders using high-pressure torsion
Eun Yoo Yoon, Dong Jun Lee, Taek-Soo Kim, Hong Jun Chae, P. Jenei, Jeno Gubicza, Tamas Ungár, Milos Janecek, Jitka Vratna, Sunghak Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
Journal of Materials Science.2012; 47(20): 7117. CrossRef - Synthesis and microstructure control of Mg alloy powder composites by multi-extrusion
Taek-Soo Kim, Hong Jun Chae, Sun-Mi Kim, Hanshin Choi, Hye Sung Kim
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2011; 509: S247. CrossRef
- X-ray diffraction study on the microstructure of a Mg–Zn–Y alloy consolidated by high-pressure torsion
- [Korean]
- Equal Channel Angular Pressing of Rapidly Solidified Al-20 wt % Si Alloy Powder Extrudates
- Seung-Chae Yoon, Soon-Jik Hong, Min-Hong Seo, Pham Quang, Hyoung-Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2004;11(2):97-104.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2004.11.2.097

- 694 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this paper processing and mechanical properties of Al-20 wt% Si alloy was studied. A bulk form of Al-20Si alloy was prepared by gas atomizing powders having the powder size of 106-145 µm and powder extrusion. The powder extrudate was subsequently equal channel angular pressed up to 8 passes in order to refine grain and Si particle. The microstructure of the gas atomized powders, powder extrudates and equal channel angular pressed samples were investigated using a scanning electron microscope and X-ray diffraction. The mechanical properties of the bulk sample were measured by compressive tests and a micro Victors hardness test. Equal channel angular pressing was found to be effective in matrix grain and Si particle refinement, which enhanced the strength and hardness of the Al-2OSi alloy without deteriorating ductility in the range of experimental strain of 30%.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Consolidation of Rapidly Solidified Al-20 wt% Si Alloy Powders Using Equal Channel Angular Pressing
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2004; 11(3): 233. CrossRef
- Consolidation of Rapidly Solidified Al-20 wt% Si Alloy Powders Using Equal Channel Angular Pressing
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


