Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
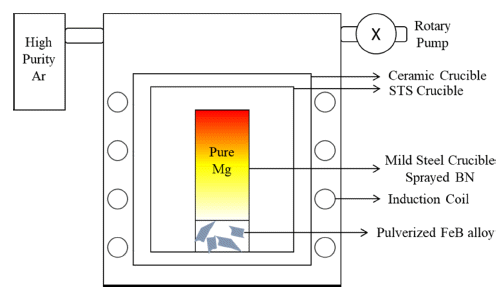
- Study on Reaction Behavior of Mg-FeB Phase for Rare Earth Elements Recovery from End-of-life Magnet
- Sangmin Park, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Rongyu Liu, Jaeyun Jeong, Taek-Soo Kim, Myungsuk Song
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(2):101-106. Published online April 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.2.101
- 1,553 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Liquid metal extraction (LME), a pyrometallurgical recycling method, is popular owing to its negligible environmental impact. LME mainly targets rare-earth permanent magnets having several rare-earth elements. Mg is used as a solvent metal for LME because of its selective and eminent reactivity with rare-earth elements in magnets. Several studies concerning the formation of Dy-Fe intermetallic compounds and their effects on LME using Mg exist. However, methods for reducing these compounds are unavailable. Fe reacts more strongly with B than with Dy; B addition can be a reducing method for Dy-Fe intermetallic compounds owing to the formation of Fe2B, which takes Fe from Dy-Fe intermetallic compounds. The FeB alloy is an adequate additive for the decomposition of Fe2B. To accomplish the former process, Mg must convey B to a permanent magnet during the decomposition of the FeB alloy. Here, the effect of Mg on the transfer of B from FeB to permanent magnet is observed through microstructural and phase analyses. Through microstructural and phase analysis, it is confirmed that FeB is converted to Fe2B upon B transfer, owing to Mg. Finally, the transfer effect of Mg is confirmed, and the possibility of reducing Dy-Fe intermetallic compounds during LME is suggested.
- [Korean]
- Standardization Status of Rare Earth Elements Recycling in ISO TC 298
- Mi Hye Lee, Yosep Song, Ji Sun On, Seung Hwan Yoon, Munhwan Han, Bum Sung Kim, Taek-soo Kim, Bin Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(2):159-165. Published online April 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.2.159

- 1,716 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Rare earth elements, which are important components of motors, are in high demand and thus constantly get more expensive. This tendency is driven by the growth of the electric vehicle market, as well as environmental issues associated with rare-earth metal manufacturing. TC 298 of the ISO manages standardization in the areas of rare-earth recycling, measurement, and sustainability. Korea, a resource-poor country, is working on international standardization projects that focus on recycling and encouraging the domestic adoption of international standards. ITU-T has previously issued recommendations regarding the recycling of rare-earth metals from e-waste. ISO TC 298 expands on the previous recommendations and standards for promoting the recycling industry. Recycling-related rare earth standards and drafts covered by ISO TC 298, as well as Korea’s strategies, are reviewed and discussed in this article.
- [English]
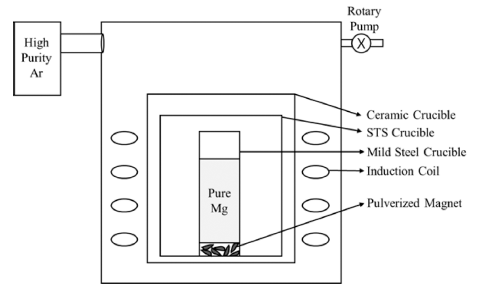
- Effect of Oxidation Behavior of (Nd,Dy)-Fe-B Magnet on Heavy Rare Earth Extraction Process
- Sangmin Park, Sun-Woo Nam, Sang-Hoon Lee, Myung-Suk Song, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):91-96. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.91
- 1,821 View
- 21 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Rare earth magnets with excellent magnetic properties are indispensable in the electric device, wind turbine, and e-mobility industries. The demand for the development of eco-friendly recycling techniques has increased to realize sustainable green technology, and the supply of rare earth resources, which are critical for the production of permanent magnets, are limited. Liquid metal extraction (LME), which is a type of pyrometallurgical recycling, is known to selectively extract the metal forms of rare earth elements. Although several studies have been carried out on the formation of intermetallic compounds and oxides, the effect of oxide formation on the extraction efficiency in the LME process remains unknown. In this study, microstructural and phase analyses are conducted to confirm the oxidation behavior of magnets pulverized by a jaw crusher. The LME process is performed with pulverized scrap, and extraction percentages are calculated to confirm the effect of the oxide phases on the extraction of Dy during the reaction. During the LME p rocess, Nd i s completely e xtracted a fter 6 h, w hile D y remains as D y2Fe17 and Dy-oxide. Because the decomposition rate of Dy2Fe17 is faster than the reduction rate of Dy-oxide, the importance of controlling Dy-oxide on Dy extraction is confirmed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Manipulation of reactivity based on metallic adsorption in magnesium alloy scraps for rare-earth recycling by liquid metal extraction
Sangmin Park, Yoonhyung Keum, Jaeyun Jeong, Seunghun Cha, Ju-Young Cho, Hyunchul Kim, Jiseong Lee, Taek-Soo Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Myungsuk Song
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2025; 1022: 178711. CrossRef - A Review of the Current Progress in High-Temperature Recycling Strategies for Recovery of Rare-Earth Elements from Magnet Waste
Ali Zakeri, Leili Tafaghodi
Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy.2025; 11(1): 88. CrossRef - Selective growth of Nb–Fe–B intermetallic compounds for the direct separation of rare earths based on manipulating liquation
Sangmin Park, Jaeyun Jeong, Seunghun Cha, Yoonhyung Keum, Ju-Young Cho, Hyungbeen Park, Taek-Soo Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Myungsuk Song
Materials Today Sustainability.2024; 28: 101042. CrossRef - Separation and recovery Nd and Dy from Mg-REEs alloy by vacuum distillation
Sangmin Park, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Jaeyun Jeong, Jae Hong Shin, Yujin Kang, Rongyu Liu, Taek-Soo Kim, Myungsuk Song
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2023; 967: 171775. CrossRef - The Supported Boro-Additive Effect for the Selective Recovery of Dy Elements from Rare-Earth-Elements-Based Magnets
Sangmin Park, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Javid Hussain, Myungsuk Song, Taek-Soo Kim
Materials.2022; 15(9): 3032. CrossRef - Influence of Dysprosium Compounds on the Extraction Behavior of Dy from Nd-Dy-Fe-B Magnet Using Liquid Magnesium
Sun-Woo Nam, Sang-Min Park, Mohammad Zarar Rasheed, Myung-Suk Song, Do-Hyang Kim, Taek-Soo Kim
Metals.2021; 11(9): 1345. CrossRef
- Manipulation of reactivity based on metallic adsorption in magnesium alloy scraps for rare-earth recycling by liquid metal extraction
- [Korean]
- Review on Characterization Method and Recent Research Trend about Metal Powder for Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) Process
- Bin Lee, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Young Il Kim, Do Hoon Kim, Yong Son, Kyoung-Tae Park, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):509-519. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.509
- 1,573 View
- 15 Download
- 9 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A well-established characterization method is required in powder bed fusion (PBF) metal additive manufacturing, where metal powder is used. The characterization methods from the traditional powder metallurgy process are still being used. However, it is necessary to develop advanced methods of property evaluation with the advances in additive manufacturing technology. In this article, the characterization methods of powders for metal PBF are reviewed, and the recent research trends are introduced. Standardization status and specifications for metal powder for the PBF process which published by the ISO, ASTM, and MPIF are also covered. The establishment of powder characterization methods are expected to contribute to the metal powder industry and the advancement of additive manufacturing technology through the creation of related databases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent advances in manufacture and application of Mg/Mg alloy powder: A comprehensive review
Yu Cao, Xiaohui Dong, Yulong Zhu, Tao Huang, Bin Jiang, Chenghang Zhang
Journal of Materials Science & Technology.2026; 263: 140. CrossRef -
Enhanced flow properties of SiO
2
nanoparticles coated low-cost hydrogenation-dehydrogenation Ti-6Al-4V powder for powder bed fusion process
Ukju Gim, Sehun Kim, Tae hu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(2): 95. CrossRef -
SiO
2
nanoparticle-coated Ti-6Al-4V spherical powder for powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process
Jongik Lee, Taehoo Kang, Ukju Gim, Sehun Kim, Sanghee Jung, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 333. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef - Cost-effective Fabrication of Near β-Ti Alloy via L-PBF: Process Optimization of In-situ Alloying Ti-3Fe
Sehun Kim, Ukju Gim, Taehu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 288. CrossRef - A Study on Fabrication of PCD Endmill Holder using PBF Additive Manufacturing Technology
Min-Woo Sa, Ho-Min Son, Kyung-Hwan Park, Sang-Geun Lee, Dae-Ho Shin, Dong-Gyu Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2024; 23(6): 124. CrossRef - Rheological Characteristic Analysis Methods and Tests of Metal Powders for PBF Additive Manufacturing
Wan-Sik Woo, Ho-Jin Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2023; 22(10): 1. CrossRef - Residual Stress Analysis of Additive Manufactured A356.2 Aluminum Alloys using X-Ray Diffraction Methods
SangCheol Park, InYeong Kim, Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Soong Ju Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee, Bin Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(7): 534. CrossRef - Enhancing spreadability of hydrogenation-dehydrogenation titanium powder and novel method to characterize powder spreadability for powder bed fusion additive manufacturing
Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, InYeong Kim, Sang Cheol Park, Dongju Lee, Bin Lee
Materials & Design.2022; 223: 111247. CrossRef
- Recent advances in manufacture and application of Mg/Mg alloy powder: A comprehensive review
- [Korean]
- Optimization of Metal Powder Particle Size Distribution for Powder Bed Fusion Process via Simulation
- Hwaseon Lee, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Young Il Kim, Jieun Nam, Yong Son, Taek-Soo Kim, Bin Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):44-51. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.44

- 1,543 View
- 10 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Powder characteristics, such as density, size, shape, thermal properties, and surface area, are of significant importance in the powder bed fusion (PBF) process. The powder required is exclusive for an efficient PBF process. In this study, the particle size distribution suitable for the powder bed fusion process was derived by modeling the PBF product using simulation software (GeoDict). The modeling was carried out by layering sintered powder with a large particle size distribution, with 50 μm being the largest particle size. The results of the simulation showed that the porosity decreased when the mean particle size of the powder was reduced or the standard deviation increased. The particle size distribution of prepared titanium powder by the atomization process was also studied. This study is expected to offer direction for studies related to powder production for additive manufacturing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the International Symposium on Innovation in Materials Processing (ISIMP, 26–29 October 2021)”
Hyunjoo Choi, Jungjoon Kim, Pil-Ryung Cha, Hyoung Seop Kim
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2023; 64(10): 2542. CrossRef
- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the International Symposium on Innovation in Materials Processing (ISIMP, 26–29 October 2021)”
- [Korean]
- Standardization of Rare Earth Elements in ISO TC 298 and Korea's Standardization Strategy
- Nu Si A Eom, Sardar Farhat Abbas, Haq Muhammad Aneeq, Rasheed Mohammad Zarar, Mi Hye Lee, Bum Sung Kim, Taek-Soo Kim, Bin Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):251-257. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.251

- 1,353 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Since the ISO decided to deal with rare-earth elements at the 298th Technical Committee (TC) in 2015, Korea has participated in four plenary meetings and proposed four standards as of June 2019. The status of ISO TC 298, the standards covered by the TC, and the standardization strategies of Korea are summarized. Korean delegations are actively engaged in WG2, which deals with recycling, proposing four standards for fostering the rare-earth recycling industry. However, the participation of domestic experts is still low compared with the increase in the number of working groups and the number of standards in TC 298. The aim of this article is to summarize the current status of ISO international standards related to rare-earth elements, to encourage relevant experts to participate in standardization, and to develop international standards that accurately reflect the realities of the industry.
- [Korean]
- Trends and Implications of International Standardization for Rare Earths
- Sardar Farhat Abbas, Sang-Hyun lee, Bin Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):165-169. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.165

- 1,015 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Rare earth elements (REEs) are considered to be vital to modern industry due to their important roles in applications such as permanent magnets, automobile production, displays, and many more. The imbalance between demand and supply of REEs can be solved by recycling processes. Regarding the needs of industry and society, the International Organization for Standardization, Technical Committee 298 (ISO/TC298) Rare Earths has been recently launched for developing international standards on rare earth elements. In accordance with the suggestion of its constituents, it is tentatively working to develop the appropriate standards under five working groups (WG) on terms and definitions (WG1), element recycling (WG2), environmental stewardship (WG3), packaging, labelling, marking, transport, and storage (WG4), and testing analysis (WG5). The scope and structure of ISO/TC298 on the topic of rare earths is discussed in this document.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and magnetic properties of Sm2Co17 particles using salt-assisted spray pyrolysis and a reduction-diffusion process
Tae-Yeon Hwang, Jimin Lee, Min Kyu Kang, Gyutae Lee, Jongryoul Kim, Yong-Ho Choa
Applied Surface Science.2019; 475: 986. CrossRef - Worker Safety in the Rare Earth Elements Recycling Process From the Review of Toxicity and Issues
Seo-Ho Shin, Hyun-Ock Kim, Kyung-Taek Rim
Safety and Health at Work.2019; 10(4): 409. CrossRef
- Synthesis and magnetic properties of Sm2Co17 particles using salt-assisted spray pyrolysis and a reduction-diffusion process
- [English]
- Microstructural Characterization of Gas Atomized Copper-Iron Alloys with Composition and Powder Size
- Sardar Farhat Abbas, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(1):19-24. Published online February 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.25.1.19

- 694 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Cu-Fe alloys (CFAs) are much anticipated for use in electrical contacts, magnetic recorders, and sensors. The low cost of Fe has inspired the investigation of these alloys as possible replacements for high-cost Cu-Nb and Cu-Ag alloys. Here, alloys of Cu and Fe having compositions of Cu100-xFex (x = 10, 30, and 50 wt.%) are prepared by gas atomization and characterized microstructurally and structurally based on composition and powder size with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Grain sizes and Fe-rich particle sizes are measured and relationships among composition, powder size, and grain size are established. Same-sized powders of different compositions yield different microstructures, as do differently sized powders of equal composition. No atomic-level alloying is observed in the CFAs under the experimental conditions.
- [Korean]
- Supply and Demand Strategy of Rare Metal in Korea − Focusing on the Stocking pile −
- Taek-Soo Kim, Bum-Sung Kim, Min-Ha Lee, Kyoung-Tae Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(4):313-317. Published online August 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.4.313

- 977 View
- 4 Download
- [English]
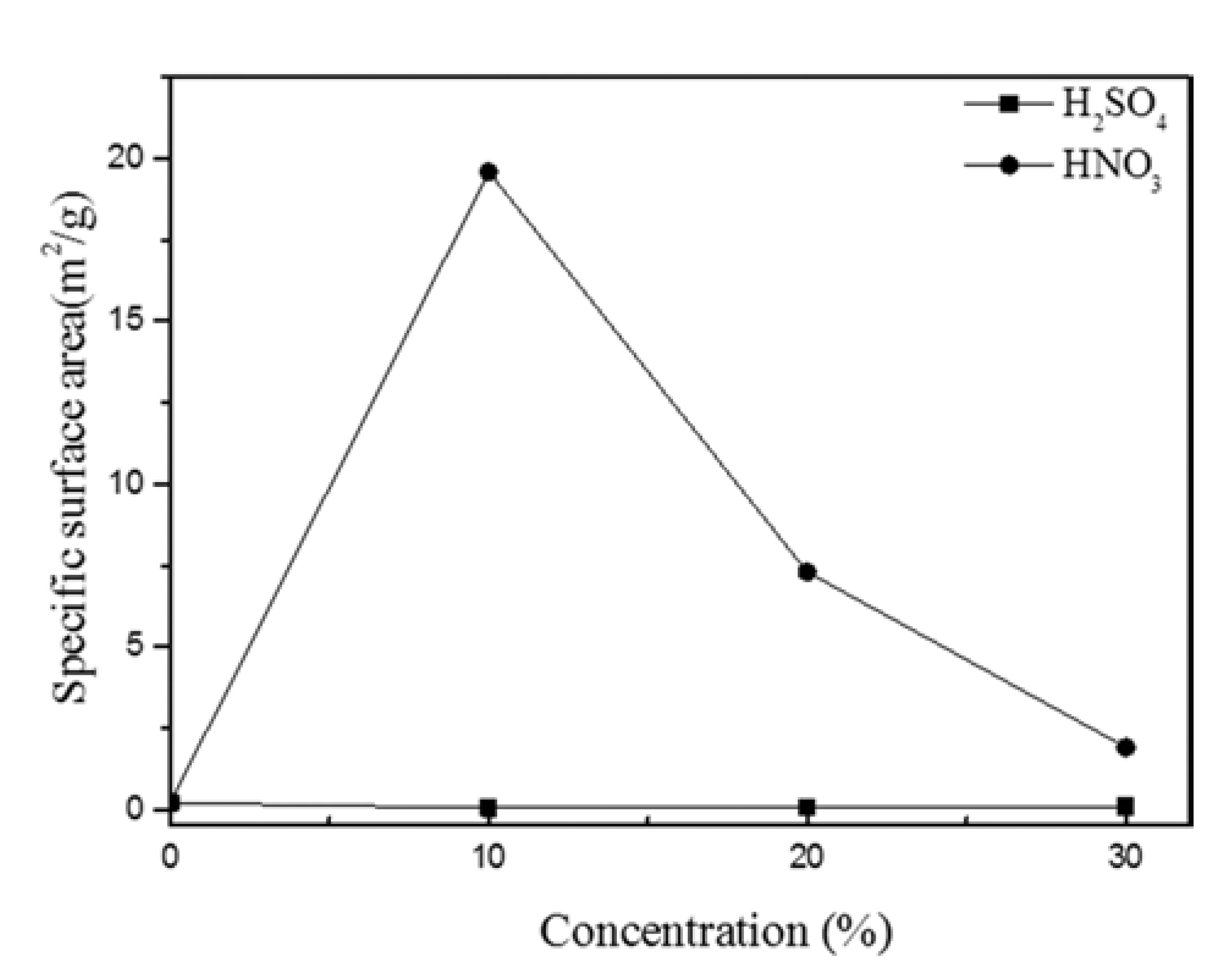
- Production of Porous Metallic Glass Granule by Optimizing Chemical Processing
- Song-Yi Kim, Bo-Kyung Guem, Min-Ha Lee, Taek-Soo Kim, Jurgen Eckert, Bum-Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(4):251-255. Published online August 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.4.251
- 1,137 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we optimized dissolution the dissolution conditions of porous amorphous powder to have high specific surface area. Porous metallic glass(MG) granules were fabricated by selective phase dissolution, in which brass is removed from a composite powder consisting of MG and 40 vol.% brass. Dissolution was achieved through various concentrations of H2SO4 and HNO3, with HNO3 proving to have the faster reaction kinetics. Porous powders were analyzed by differential scanning calorimetry to observe crystallization behavior. The Microstructure of milled powder and dissolved powder was analyzed by scanning electron microscope. To check for residual in the dissolved powder after dissolution, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscory and elemental mapping was conducted. It was confirmed that the MG/brass composite powder dissolved in 10% HNO3 produced a porous MG granule with a relatively high specific surface area of 19.60 m2/g. This proved to be the optimum dissolution condition in which both a porous internal granule structure and amorphous phase were maintained. Consequently, porous MG granules were effectively fabricated and applications of such structures can be expanded.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhanced wear resistivity of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass processed by high-pressure torsion under reciprocating dry conditions
Soo-Hyun Joo, Dong-Hai Pi, Jing Guo, Hidemi Kato, Sunghak Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
Metals and Materials International.2016; 22(3): 383. CrossRef
- Enhanced wear resistivity of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass processed by high-pressure torsion under reciprocating dry conditions
- [Korean]
- Patent Analysis for the Preparation of Rare Metals
- Kee-Ahn Lee, Jae-Sung Oh, Jae-Yeon Kim, Bum-Sung Kim, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(2):147-154. Published online April 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.2.147

- 831 View
- 2 Download
- [Korean]
- Luminescent Characteristics of CdSe Quantum Dot Phosphor Depending on Se Precursor Ratio
- Nu Si A Eom, Taek-Soo Kim, Yong-Ho Choa, Bum Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2012;19(6):442-445.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2012.19.6.442

- 729 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The quantum dots (QD) have unique electrical and optical properties due to quantum dot confinement effect. The optical properties of QDs are decided by various synthesis conditions. In a prior QDs study, a study on the QDs size with synthesis condition such as synthesis time and temperature is being extensively researched. However, the research on QDs size with composition ratio has hitherto received scant attention. In order to evaluate the ratio dependence of CdSe crystal, synthesis ratio of Se precursor is changed from 16.7 mol%Se to 44 mol%Se. As the increasing Se ratio, the band gap was increased. This is caused by red shift of emission. We confirmed optical property of CdSe QDs with composition ratio.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and analysis CdSe/ZnS quantum dot with a Core/shell Continuous Synthesis System Using a Microfluidic Reactor
Myung Hwan Hong, So Young Joo, Lee-Seung Kang, Chan Gi Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(2): 132. CrossRef - Multimodal luminescence properties of surface-treated ZnSe quantum dots by Eu
Ji Young Park, Da-Woon Jeong, Kyoung-Mook Lim, Yong-Ho Choa, Woo-Byoung Kim, Bum Sung Kim
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 8. CrossRef - Optical Characteristics of CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dot with Precursor Flow Rate Synthesized by using Microreactor
Ji Young Park, Da-Woon Jeong, Won Ju, Han Wook Seo, Yong-Ho Choa, Bum Sung Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(2): 91. CrossRef
- Synthesis and analysis CdSe/ZnS quantum dot with a Core/shell Continuous Synthesis System Using a Microfluidic Reactor
- [Korean]
- Ultrafine Grained Cu-diamond Composites using High Pressure Torsion
- Eun-Yoo Yoon, Dong-Jun Lee, Taek-Soo Kim, Hyoung-Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2012;19(3):204-209.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2012.19.3.204

- 815 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this work, powder metallurgy and severe plastic deformation by high-pressure torsion (HPT) approaches were combined to achieve both full density and grain refinement at the same time. Pure Cu powders were mixed with 5 and 10 vol% diamonds and consolidated into disc-shaped samples at room temperature by HPT at 1.25 GPa and 1 turn, resulting in ultrafine grained metallic matrices embedded with diamonds. Neither heating nor additional sintering was required with the HPT process so that in situ consolidation was successfully achieved at ambient temperature. Significantly refined grain structures of Cu metallic matrices with increasing diamond volume fractions were observed by electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD), which enhanced the microhardness of the Cu-diamond composites.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of a nano-sized TiC particle addition on the flow-assisted corrosion resistance of SA 106B carbon steel
Jin-Ju Park, Eun-Kwang Park, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Chang-Kyu Rhee, Min-Ku Lee
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 143. CrossRef - Analyses of Densification and Consolidation of Copper Powders during High-Pressure Torsion Process Using Finite Element Method
Dong Jun Lee, Eun Yoo Yoon
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(1): 6. CrossRef - Trend in Research of Powder Consolidation Using Severe Plastic Deformation
Eun Yoo Yoon, Dong Jun Lee, Dong-Hyun Ahn, Hyuk Jae Jeong, Hyoung Seop Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2013; 20(2): 148. CrossRef - Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Al-1080 Processed by a Combination of Equal Channel Angular Pressing and High Pressure Torsion
Mohamed Ibrahim Abd El Aal, Eun Yoo Yoon, Hyoung Seop Kim
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A.2013; 44(6): 2581. CrossRef - Grinding Behaviour of Aluminum Powder for Al/CNTs Nano Composites Fabrication by Dry Grinding Process Using a High Speed Planetary Ball Mill
Heekyu Choi, Jehyun Lee, Seongsoo Kim, Gyungpil Choi, Daehyung Bae, Sungbak Lee, Woong Lee
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2013; 23(2): 89. CrossRef - Densification of Copper Powders using High-pressure Torsion Process
Dong-Jun Lee, Eun-Yoo Yoon, Soo-Young Kang, Jung-Hwan Lee, Hyoung-Seop Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2012; 19(5): 333. CrossRef
- Effect of a nano-sized TiC particle addition on the flow-assisted corrosion resistance of SA 106B carbon steel
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Dynamic Consolidation Behaviors of Rapidly Solidified Mg Alloy Powders
- Hong-Jun Chae, Young-Do Kim, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2011;18(4):340-346.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2011.18.4.340

- 415 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In order to improve the weak mechanical properties of cast Mg alloys, Mg-Zn_1Y_2 (at%) alloy powders were synthesized using gas atomization, a typical rapid solidification process. The powders consist of fine dendrite structures less than 3 µm in arm spacing. In order to fabricate a bulk form, the Mg powders were compacted using magnetic pulse compaction (MPC) under various processing parameters of pressure and temperature. The effects of the processing parameters on the microstructure and mechanical properties were systematically investigated.
- [Korean]
- Thermoelectric Properties of Rapid Solidified p-type Bi2Te3 Alloy Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering(SPS) Process
- Chul-Dong Moon, Soon-Jik Hong, Do-Hyang Kim, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(6):494-498.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.6.494

- 912 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The p-type thermoelectric compounds of Bi_2Te_3 based doped with 3wt% Te were fabricated by a combination of rapid solidification and spark plasma sintering (SPS) process. The effect of holding time during spark plasma sintering (SPS) on the microstructure and thermoelectric properties were investigated using scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and thermoelectric properties. The powders as solidified consisted of homogeneous thermoelectric phases. The thermoelectric figure of merit measured to be maximum (3.41times10-3/K) at the SPS temperature of 430°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Sintering Temperature on the Thermoelectric Properties of Bismuth Antimony Telluride Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering
경석 이, 영근 정, 성호 서, 상현 진, 봉영 유
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2012; 22(6): 280~284. CrossRef
- Effect of Sintering Temperature on the Thermoelectric Properties of Bismuth Antimony Telluride Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering
- [Korean]
- Refinement Behavior of Coarse Magnesium Powder by High Energy Ball Milling (HEBM)
- Joon-Woo Song, Hyo-Seob Kim, Hong-Moule Kim, Taek-Soo Kim, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(4):302-311.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.4.302

- 932 View
- 3 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this research, the refinement behavior of the coarse magnesium powders fabricated by gas atomization was investigated as a function of milling time using a short duration high-energy ball milling equipment, which produces fine powders by means of an ultra high-energy within a short duration. The microstructure, hardness, and formability of the powders were investigated as a function of milling time using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, Vickers micro-hardness tester and magnetic pulsed compaction. The particle morphology of Mg powders changed from spherical particles of feed metals to irregular oval particles, then platetype particles, with increasing milling time. Due to having HCP structure, deformation occurs due to the existence of the easily breakable C-axis perpendicular to the base, resulting in producing plate-type powders. With increasing milling time, the particle size increased until 5 minutes, then decreased gradually reaching a uniform size of about 50 micrometer after 20 minutes. The relative density of the initial power was 98% before milling, and mechanically milled powder was 92~94% with increase milling time (1~5 min) then it increased to 99% after milling for 20 minutes because of the change in particle shapes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quantitative Study on the Refinement Behaviors of TiC Powders Produced by Mechanical Milling Under Different Impact Energy
Sung-Mo Hong, Eun-Kwang Park, Kyeong-Yeol Kim, Jin-Ju Park, Min-Ku Lee, Chang-Kyu Rhee, Jin-Kyu Lee, Young-Soon Kwon
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2012; 19(1): 32. CrossRef - Fabrication of Fe coated Mg Based Desulfurization Powder by Mechanical Alloying Process
Joon-Woo Song, Otaduy Guillermo, Byong-Sun Chun, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2012; 19(3): 226. CrossRef - Characteristics of Indium Dissolution of Waste LCD Panel Powders Fabricated by High Energy Ball Milling (HEBM) Process with Milling Time
Hyo-Seob Kim, Jun-Je Sung, Cheol-Hee Lee, Hyun-Seon Hong, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2011; 18(4): 378. CrossRef - Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Nano-sized Ti-35%Nb-7%Zr-10%CPP Composite Fabricated by Pulse Current Activated Sintering
Kee-Do Woo, Duck-Soo Kang, Sang-Hyuk Kim, Sang-Hoon Park, Ji-Young Kim, Hye-Rim Ko
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2011; 18(2): 188. CrossRef
- Quantitative Study on the Refinement Behaviors of TiC Powders Produced by Mechanical Milling Under Different Impact Energy
- [Korean]
- Consolidation and Mechanical Behavior of Gas Atomized MgZn4.3Y0.7 Alloy Powders using High Pressure Torsion
- Eun-Yoo Yoon, Hong-Jun Chae, Taek-Soo Kim, Chong-Soo Lee, Hyoung-Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(3):190-196.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.3.190

- 749 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this paper, rapid solidified Mg-4.3Zn-0.7Y (at.%) alloy powders were prepared using an inert gas atomizer, followed by a severe plastic deformation technique of high pressure torsion (HPT) for consolidation of the powders. The gas atomized powders were almost spherical in shape, and grain size was as fine as less than 5;µm due to rapid solidification. Plastic deformation responses during HPT were simulated using the finite element method, which shows in good agreement with the analytical solutions of a strain expression in torsion. Varying the HPT processing temperature from ambient to 473 K, the behavior of powder consolidation, matrix microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of the compacts was investigated. The gas atomized powders were deformed plastically as well as fully densified, resulting in effective grain size refinements and enhanced microhardness values.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trend in Research of Powder Consolidation Using Severe Plastic Deformation
Eun Yoo Yoon, Dong Jun Lee, Dong-Hyun Ahn, Hyuk Jae Jeong, Hyoung Seop Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2013; 20(2): 148. CrossRef - Densification of Copper Powders using High-pressure Torsion Process
Dong-Jun Lee, Eun-Yoo Yoon, Soo-Young Kang, Jung-Hwan Lee, Hyoung-Seop Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2012; 19(5): 333. CrossRef - Ultrafine Grained Cu-diamond Composites using High Pressure Torsion
Eun-Yoo Yoon, Dong-Jun Lee, Taek-Soo Kim, Hyoung-Seop Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2012; 19(3): 204. CrossRef - Densification and Nanocrystallization of Water-Atomized Pure Iron Powder Using High Pressure Torsion
Eun-Yoo Yoon, Dong-Jun Lee, Ha-Neul Kim, Hee-Soo Kang, Eon-Sik Lee, Hyoung-Seop Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2011; 18(5): 411. CrossRef
- Trend in Research of Powder Consolidation Using Severe Plastic Deformation
- [Korean]
- Microstructure Control of Mg Alloy Powder Using a Repeated Extrusion Process
- Jeong-Gon Kim, Han-Shin Choi, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(6):438-441.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.6.438

- 811 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Mg-Cu composites were successively fabricated using a combination of rapid solidification and extrusion processes. In addition, the microstructural variation of the composite was investigated by performing the extrusion repeatedly. It resulted that the composite formed an uniform and dense structure by the extrusion, and the microstructure became fine as the extrusion conducted repeatedly. The microstructural variation was known to be dependent on the number of extrusion and the area reduction ratio. The tensile strength was also measured as a function of the microstructural variation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High Temperature Deformation Flow Of A ZK60A Magnesium Alloy After Extrusion
M. Kawasaki, H.-J. Lee, M.C. Oh, B. Ahn
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2015; 60(2): 1327. CrossRef
- High Temperature Deformation Flow Of A ZK60A Magnesium Alloy After Extrusion
- [Korean]
- Effects of Phase Fraction and Metallic Glass-Diamond Size Ratio on the Densification of Metallic Glass/Diamond Composite
- Su-Min Shin, Taek-Soo Kim, Seung-Koo Kang, Jeong-Gon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(3):173-179.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.3.173

- 447 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In the present study, Zr-base metallic glass(MG)/diamond composites are fabricated using a combination of gas-atomization and spark plasma sintering (SPS). The densification behaviors of mixtures of soft MG and hard diamond powders during consolidation process are investigated. The influence of mixture characteristics on the densification is discussed and several mechanism explaining the influence of diamond particles on consolidation behaviour are proposed. The experimental results show that consolidation is enhanced with increasing diamond/Metallic Glass(MG) size ratio, while the diamond fraction is fixed.
- [Korean]
- Rare Metal as a National Strategic Material
- Soo-Young Lee, Yul-Kwon Ji, Han-Shin Choi, Hwan-Yong Kim, Jin-Kyu Lee, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(3):161-166.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.3.161

- 487 View
- 1 Download
- [Korean]
- Finite Element Analysis of Densification of Mg Powders during Equal Channel Angular Pressing: Effect of Sheath
- Seung-Chae Yoon, Taek-Soo Kim, Hyoung-Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(2):85-90.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.2.085

- 475 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Magnesium and its alloys are attractive as light weight structural/functional materials for high performance application in automobile and electronics industries due to their superior physical properties. In order to obtain high quality products manufactured by the magnesium powders, it is important to control and understand the densification behavior of the powders. The effect of the sheath surrounding the magnesium powders on the plastic deformation and densification behavior during equal channel angular pressing was investigated in the study by experimental and the finite element methods. A modified version of Lee-Kim's plastic yield criterion, notably known as the critical relative density model, was applied to simulate the densification behavior of magnesium powders. In addition, a new approach that extracts the mechanical characteristics of both the powder and the matrix was developed. The model was implemented into the finite element method, with which powder compaction under equal channel angular pressing was simulated.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Spark Plasma Sintering on the Materials Properties of Water Atomized Al-Zn-Mg Alloy
- Sun-Mi Kim, Taek-Soo Kim, Young-Do Kim, Jeong-Gon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(1):63-67.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.1.063

- 829 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In order to investigate the effect of rapid solidification on the microstructure and the mechanical properties of Al-Zn-Mg system alloys, water atomization was carried out, since the water atomization beared the highest solidification rate among the atomization processes. The as atomized alloy powders consisted of fine grains less than 4 µm in diameter, and the second particles were not detected on XRD. The microstructure as solidified was maintained even after the spark plasma sintering at the heating rate of 50 K/min. On the other hand, lower rate of 20 K/min induced a formation of MgZn_2 particles, resulting in strengthening of the matrix. The density was almost constant at the temperature above 698K. The sintering temperature above 698K had no effect on the strength of the sintered materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Ultra Fine Grained Molybdenum and Mechanical Properties
Se-Hoon Kim, Young-Ik Seo, Dae-Gun Kim, Myung-Jin Suk, Young-Do Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2010; 17(3): 235. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Ultra Fine Grained Molybdenum and Mechanical Properties
- [Korean]
- Analysis of Densification Behavior of Magnesium Powders in Extrusion using the Critical Relative Density Model
- Seung-Chae Yoon, Hong-Jun Chae, Taek-Soo Kim, Hyoung-Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(1):50-55.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.1.050

- 595 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Numerical simulations of the powder extrusion need an appropriate pressure-dependent constitutive model for densification modeling of the magnesium powders. The present research investigated the effect of representative powder yield function of the critical relative density model. We could obtain reasonable physical properties of pure magnesium powders using cold isostatic pressing. The proposed densification model was implemented into the finite element code. The finite element analysis was applied to simulation of powder extrusion of pure magnesium powder in order to investigate the densification and processing load at room temperature.
- [Korean]
- Analysis of Densification Behavior during Powder Equal Channel Angular Pressing using Critical Relative Density Model
- Cheon-Hee Bok, Ji-Hoon Yoo, Seung-Chae Yoon, Taek-Soo Kim, Byong-Sun Chun, Hyoung-Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2008;15(5):365-370.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2008.15.5.365

- 756 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, bottom-up powder processing and top-down severe plastic deformation processing approaches were combined in order to achieve both full density and grain refinement with least grain growth. The numerical modeling of the powder process requires the appropriate constitutive model for densification of the powder materials. The present research investigates the effect of representative powder yield function of the Shima-Oyane model and the critical relative density model. It was found that the critical relative density model is better than the Shima-Oyane model for powder densification behavior, especially for initial stage.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Densification Behavior of Magnesium Powders in Extrusion using the Critical Relative Density Model
Seung-Chae Yoon, Hong-Jun Chae, Taek-Soo Kim, Hyoung-Seop Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2009; 16(1): 50. CrossRef
- Analysis of Densification Behavior of Magnesium Powders in Extrusion using the Critical Relative Density Model
- [Korean]
- Consolidation and Characterization of Cu-based Bulk Metallic Glass Composites
- Jin-Kyu Lee, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2007;14(6):399-404.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2007.14.6.399

- 473 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The Cu-based bulk metallic glass (BMG) composite was fabricated by spark plasma sintering (SPS) using of gas-atomized metallic glass powders and ductile brass powders. No defect such as pores and cavities was observed at the interface between the brass powder and the metallic glass matrix, suggesting that the SPS process caused a severe viscous flow of the metallic glass and brass phases in the supercooled liquid region, resulting in a full densification. The BMG composites shows some macroscopic plasticity after yielding, although the levels of strength decreased.
- [Korean]
- Characteristics of Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Coatings on Mg-Zn-Y Alloys Prepared by Gas Atomization
- Si-Young Chang, Han-Gyoung Cho, Du-Hyung Lee, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2007;14(6):372-379.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2007.14.6.372

- 697 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The microstructure, mechanical and electrochemical properties of plasma electrolytic coatings (PEO) coatings on Mg-4.3 wt%Zn-1.0 wt%Y and Mg-1.0 wt%Zn-2.0 wt%Y alloys prepared by gas atomization, followed by compaction at 320 for 10 min under the pressure of 700 MPa and sintering at 380 and 420 respectively for 24 h, were investigated, which was compared with the cast Mg-1.0 wt%Zn alloy. All coatings consisting of MgO and Mg_2SiO_4 oxides showed porous and coarse surface features with some volcano top-like pores distributed disorderly and cracks between pores. In particular, the surface of coatings on Mg-1.0 wt%Zn-2.0 wt%Y alloy showed smaller area of pores and cracks compared to the Mg-4.3 wt%Zn-1.0 wt%Y and Mg-1.0 wt%Zn alloys. The cross section micro-hardness of coatings on the gas atomized Mg-Zn-Y alloys was higher than that on the cast Mg-1.0 wt%Zn alloy. Additionally, the coated Mg-1.0 wt%Zn-2.0 wt%Y alloy exhibited the best corrosion resistance in 3.5%NaCl solution. It could be concluded that the addition of Y has a beneficial effect on the formation of protective and hard coatings on Mg alloys by plasma electrolytic oxidation treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Aging Characteristics of Mg-6 wt.% Al-1 wt.% Zn Alloy Prepared by Gas Atomization
Du-Hyung Lee, Bo-Sik Kim, Si-Young Chang
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2009; 16(4): 275. CrossRef
- The Aging Characteristics of Mg-6 wt.% Al-1 wt.% Zn Alloy Prepared by Gas Atomization
- [Korean]
- Densification Behaviour of Magnesium Powders during Cold Isostatic Pressing using the Finite Element Method
- Seung-Chae Yoon, Eun-Jeong Kwak, Won-Hyoung Choi, Hyoung-Kun Kim, Taek-Soo Kim, Hyoung-Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2007;14(6):362-366.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2007.14.6.362

- 881 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Magnesium and magnesium alloys are promising materials for light weight and high strength applications. In order to obtain homogeneous and high quality products in powder compaction and powder forging processes, it is very important to control density and density distributions in powder compacts. In this study, a model for densification of metallic powder is proposed for pure magnesium. The mode] considers the effect of powder characteristics using a pressure-dependent critical density yield criterion. Also with the new model, it was possible to obtain reasonable physical properties of pure magnesium powder using cold iso-state pressing. The proposed densification model was implemented into the finite element method code. The finite element analysis was applied to simulating die compaction of pure magnesium powders in order to investigate the density and effective strain distributions at room temperature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Densification Behavior of Magnesium Powders in Extrusion using the Critical Relative Density Model
Seung-Chae Yoon, Hong-Jun Chae, Taek-Soo Kim, Hyoung-Seop Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2009; 16(1): 50. CrossRef - Finite element analysis of the bending behavior of a workpiece in equal channel angular pressing
Seung Chae Yoon, Anumalasetty Venkata Nagasekhar, Hyoung Seop Kim
Metals and Materials International.2009; 15(2): 215. CrossRef
- Analysis of Densification Behavior of Magnesium Powders in Extrusion using the Critical Relative Density Model
- [Korean]
- Application of PM to the Consolidation of Metallic Glassy Powder and its Composites
- Su-Min Shin, Taek-Soo Kim, Jin-Kyu Lee, Min-Seok Song, Jeong-Gon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2007;14(6):348-353.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2007.14.6.348

- 503 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In the present study, Zr-base metallic glass (MG) and Zr-base BMG/diamond composites were fabricated using a combination of gas atomization and spark plasma sintering (SPS). The microstructure, thermal stability and mechanical property of both the specimens as atomized and sintered were investigated. The experimental results showed that the SPSed specimens could be densified into nearly 100% and maintained the initial thermal stability at the sintering temperature of 630K. In addition, MG/diamond powder composites were successfully synthesised using SPS process. The composites, even a very low diamond volume fraction, generated a significant increase in compressive strength. With increasing the diamond volume fraction, the compressive strength was also increased due to the addition of hardest diamonds. It suggests that these composites would be potential candidates for a new cutting tool material.
- [Korean]
- Extrusion Behavior of Gas Atomized Mg Alloy Powders
- Hong-Jun Chae, Young-Do Kim, Jin-Kyu Lee, Jeong-Gon Kim, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2007;14(4):251-255.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2007.14.4.251

- 785 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This work is to report not only the effect of rapid solidification of MgZn_4.3Y_0.7 alloys on the micro-structure, but also the extrusion behavior on the materials properties. The average grain size of the atomized powders was about 3-4µm. The alloy powders of Mg_97Zn_4.3Y_0.7, consisted of I-Phase (Icosahedral, Mg_3Zn_6Y_1) as well as Cubic structured W-Phase (Mg_3Zn_3Y_2), which was finely distributed within alpha-Mg matrix. The oxide layer formed along the Mg surface was about 48 nm in thickness. In order to study the consolidation behavior of Mg alloy powders, extrusion was carried out with the area reduction ratio of 10:1 to 20:1. As the ratio increased, fully deformed and homogeneous microstructure could be obtained, and the mechanical properties such as tensile strength and elongation were simultaneously increased.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Dynamic Consolidation Behaviors of Rapidly Solidified Mg Alloy Powders
Hong-Jun Chae, Young-Do Kim, Taek-Soo Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2011; 18(4): 340. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Dynamic Consolidation Behaviors of Rapidly Solidified Mg Alloy Powders
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Bulk Metallic Glass Composites by Mechanical Milling with Subsequent Spark Plasma Sintering Process
- Jin-Kyu Lee, Taek-Soo Kim, Jeong-Gon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2007;14(3):197-201.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2007.14.3.197

- 730 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Bulk metallic glass (BMG) composite was fabricated by consolidation of milled metallic glass composite powders. The metallic glass composite powder was synthesized by a controlled milling process using the Cu-based metallic glass powder blended with 30 vol% Zr-based metallic glass powders. The milled composite powders showed a layered structure with three metallic phases, which is formed as a result of mechanical milling. By spark plasma sintering of milled metallic glass powders in the supercooled liquid region, a fully dense BMG composite was successfully synthesized.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Powder Sintering Characteristics of Carbon Nanotubes Reinforced SKD11 Tool Steel Sintered by Spark Plasma Sintering
Je-Se Moon, Sung-Sil Jung, Dae-Yeol Lee, Young-Keun Jeong, Myung Chang Kang, Chun-Dal Park, Kook-Tae Youn
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(3): 157. CrossRef
- Powder Sintering Characteristics of Carbon Nanotubes Reinforced SKD11 Tool Steel Sintered by Spark Plasma Sintering
- [Korean]
- Consolidation Behavior of Gas Atomized Mg-Zn-Y Alloy Powders by Spark Plasma Sintering
- Jin-Kyu Lee, Taek-Soo Kim, Jung-Chan Bae
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2007;14(2):140-144.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2007.14.2.140

- 946 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Using Spark Plasma Sintering process (SPS), consolidation behavior of gas atomized Mg_97Zn_1Y_2 alloys were investigated via examining the microstructure and evaluating the mechanical properties. In the atomized ahoy powders, fine Mg_12YZn particles were homogeneously distributed in the alpha-Mg matrix. The phase distribution was maintained even after SPS at 723 K, although Mg_24Y_5 particles were newly precipitated by consolidating at 748 K. The density of the consolidated bulk Mg-Zn-Y alloy was 1.86g/cm3. The ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and elongation were varied with the consolidation temperature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High Temperature Deformation Flow Of A ZK60A Magnesium Alloy After Extrusion
M. Kawasaki, H.-J. Lee, M.C. Oh, B. Ahn
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2015; 60(2): 1327. CrossRef
- High Temperature Deformation Flow Of A ZK60A Magnesium Alloy After Extrusion
- [Korean]
- Materials Properties of Gas Atomized and Extruded Mg-Zn-Y Alloys
- Hong-Jun Chae, Jin-Kyu Lee, Jung-Chan Bae, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2006;13(6):427-431.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2006.13.6.427

- 715 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Mg-4.3Zn-0.7Y (at%) alloy powders were prepared using an industrial scale gas atomizer, followed by warm extrusion. The powders were almost spherical in shape. The microstructure of atomized powders and those extruded bars was examined using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscope (EDS) and X-ray Diffractometer (XRD). The grain size of the powders was coarsen as the initial powder size increased. After the extrusion, the grain size became fine due to the severe plastic deformation during the extrusion with the ratio of 10:1. Both the ultimate strength and elongation were enhanced with the decrease of initial particle size.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Dynamic Consolidation Behaviors of Rapidly Solidified Mg Alloy Powders
Hong-Jun Chae, Young-Do Kim, Taek-Soo Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2011; 18(4): 340. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Dynamic Consolidation Behaviors of Rapidly Solidified Mg Alloy Powders
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Properties of Amorphous Matrix Composites using Cu-based/Ni-based Amorphous Powders
- Taek-Soo Kim, Jin-Kyu Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim, Jung-Chan Bae
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2005;12(6):406-412.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2005.12.6.406

- 915 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This work is to present a new synthesis of metallic glass (MG)/metallic glass (MG) composites using gas atomization and spark plasma sintering (SPS) processes. The MG powders of Cu_54Ni_6Zr_22Ti_18 (CuA) and Ni_59Zr_15Ti_13Nb_7Si_3Sn_2Al_1(NiA) as atomized consist of fully amorphous phases and present a different thermal behavior; T_g (glass transition temperature) and T_x (crystallization temperature) are 716K and 765K for the Cu base powder, but 836K and 890K for the Ni base ones, respectively. SPS process was used to consolidate the mixture of each amorphous powder, being CuA/10%NiA;and;NiA/10%CuA in weight. The resultant phases were Cu crystalline dispersed NiA matrix composites as well as NiA phase dispersed CuA matrix composites, depending on the SPS temperatures. Effect of the second phases embedded in the MG matrix was discussed on the micro-structure and mechanical properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Micro-deformation behavior of Brittle Hf-based Metallic Glass during Mechanical Milling
Song-Yi Kim, A-Young Lee, Eun-Ji Cha, Do-Hun Kwon, Sung-Uk Hong, Min-Woo Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim, Min-Ha Lee
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(3): 246. CrossRef - Synthesis of Ni-based Metallic Glass Composite Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering
Song Yi Kim, Bo Kyeong Guem, Min Ha Lee, Bum Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2013; 20(1): 33. CrossRef
- Micro-deformation behavior of Brittle Hf-based Metallic Glass during Mechanical Milling
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


