Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Study on the Elemental Diffusion Distance of a Pure Nickel Layer Additively Manufactured on 316H Stainless Steel
- UiJun Ko, Won Chan Lee, Gi Seung Shin, Ji-Hyun Yoon, Jeoung Han Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):220-225. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00164
- 1,593 View
- 53 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Molten salt reactors represent a promising advancement in nuclear technology due to their potential for enhanced safety, higher efficiency, and reduced nuclear waste. However, the development of structural materials that can survive under severe corrosion environments is crucial. In the present work, pure Ni was deposited on the surface of 316H stainless steel using a directed energy deposition (DED) process. This study aimed to fabricate pure Ni alloy layers on an STS316H alloy substrate. It was observed that low laser power during the deposition of pure Ni on the STS316H substrate could induce stacking defects such as surface irregularities and internal voids, which were confirmed through photographic and SEM analyses. Additionally, the diffusion of Fe and Cr elements from the STS316H substrate into the Ni layers was observed to decrease with increasing Ni deposition height. Analysis of the composition of Cr and Fe components within the Ni deposition structures allows for the prediction of properties such as the corrosion resistance of Ni.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructural analysis and characterization of nickel deposition on 316H stainless steel via gas tungsten arc welding and powder laser cladding
Won Chan Lee, Jin Woong Park, Seung Ju Nam, Ji-Hyun Yoon, Jeoung Han Kim
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 342. CrossRef - Effect of oxygen content in feedstock powders on microstructure and mechanical properties of ELI Ti-6Al-4V fabricated via laser powder bed fusion
Woo Hyeok Kim, Sang Woo Kim, Raj Narayan Hajra, Gargi Roy, Jeoung Han Kim
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 307. CrossRef - Development of Aluminum Alloys for Additive Manufacturing Using Machine Learning
Sungbin An, Juyeon Han, Seoyeon Jeon, Dowon Kim, Jae Bok Seol, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 202. CrossRef - Evaluation of Mechanical Properties of Pure Ni Coatings on a Type 316H Stainless Steel Substrate via High-Velocity Oxy-fuel and Directed Energy Deposition Processes
Won Chan Lee, Seung Ju Nam, Ji-Hyun Yoon, Jeoung Han Kim
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 309. CrossRef
- Microstructural analysis and characterization of nickel deposition on 316H stainless steel via gas tungsten arc welding and powder laser cladding
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Characterization of Brilliant Yellow Color Pigments using α-FeOOH Nanorods
- JiYeon Yun, Ri Yu, YooJin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(6):453-457. Published online December 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.6.453

- 644 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this work, we synthesize brilliant yellow color α-FeOOH by controlling the rod length and core-shell structure. The characteristics of α-FeOOH nanorods are controlled by the reaction conditions. In particular, the length of the α-FeOOH rods depends on the concentration of the raw materials, such as the alkali solution. The length of the nanorods is adjusted from 68 nm to 1435 nm. Their yellowness gradually increases, with the highest b* value of 57 based on the International Commission on Illumination (CIE)
Lab system, by controlling the nanorod length. A high quality yellow color is obtained after formation of a silica coating on the α-FeOOH structure. The morphology and the coloration of the nal products are investigated in detail by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, UV-vis spectroscopy, and the CIELab color parameter measurements.
- [Korean]
- Coloration Study of Red/Yellow β-FeOOH Nanorod using NH4OH Solution
- Ri Yu, IllJoo Kim, JiYeon Yun, Eun-Young Choi, Jae-Hwan Pee, YooJin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(5):343-347. Published online October 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.5.343
- 597 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
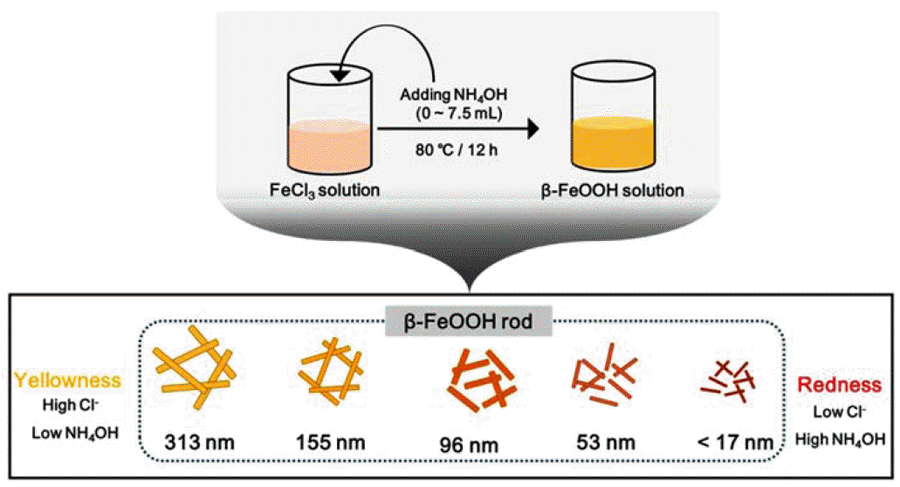
PDF Fe-based pigments have attracted much interest owing to their eco-friendliness. In particular, the color of nanosized pigments can be tuned by controlling their size and morphology. This study reports on the effect of length on the coloration of β-FeOOH pigments prepared using an NH4OH solution. First, rod-type β-FeOOH is prepared by the hydrolysis of FeCl3·6H2O and NH4OH. When the amount of NH4OH is increased, the length of the rods decreases. Thus, the length of the nanorods can be adjusted from 10 nm to 300 nm. The color of β-FeOOH changes from orangered to yellow depending on the length of β-FeOOH. The color and phase structure of β-FeOOH is characterized by UVvis spectroscopy, CIE Lab color parameter measurements, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and powder X-ray diffraction (XRD).
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


