Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Preparation of Flake-shape Cobalt Powders by High-Energy Ball Milling for rSOC Current Collectors
- Poong-Yeon Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Hyeon Ju Kim, Su-Jin Yun, Si Young Chang, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):383-389. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00241
- 446 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
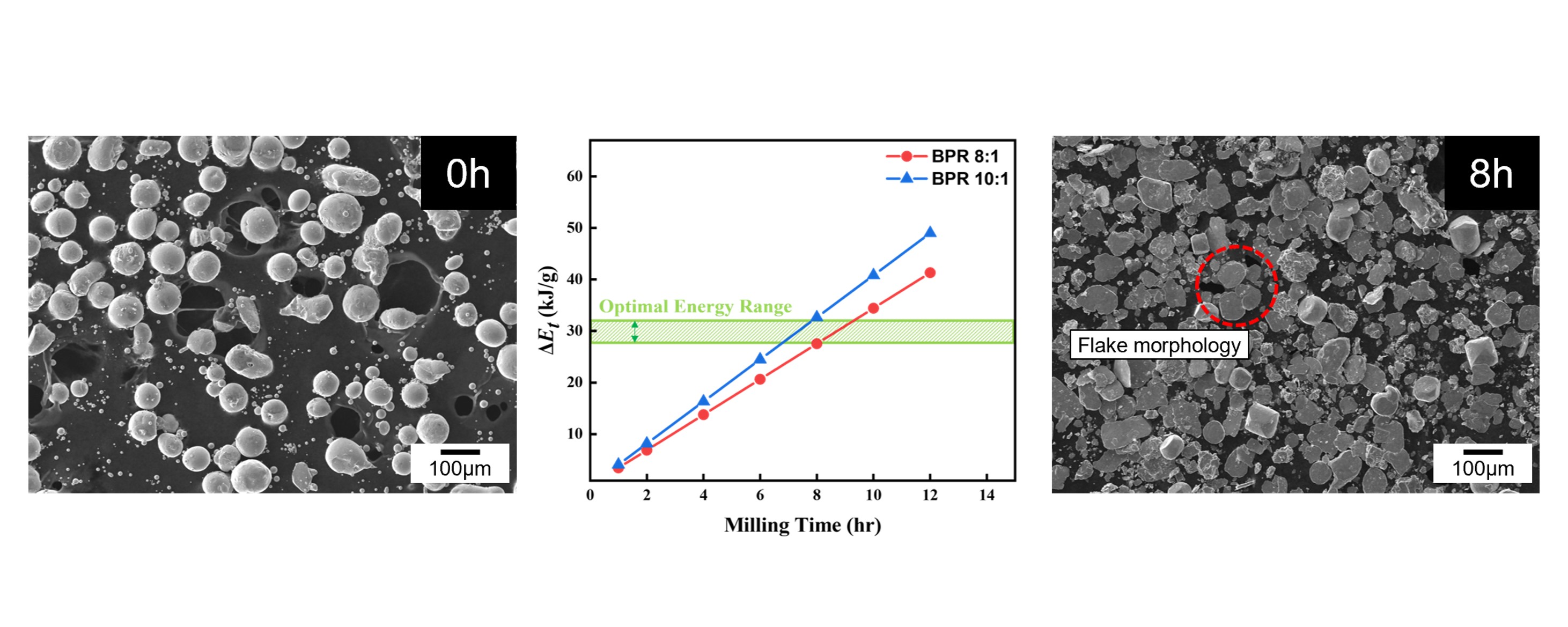
PDF - Reversible solid oxide cells (rSOCs), which enable two-way conversion between electricity and hydrogen, have gained attention with the rise of hydrogen energy. However, foam-type current collectors in rSOC stacks exhibit poor structural controllability and limited electrode contact area. To address these limitations, this study aimed to convert spherical cobalt powders into flake-type morphology via high-energy ball milling, as a preliminary step toward fabricating flake-based current collectors. Milling parameters—specifically, the ball-to-powder ratio (BPR), milling time, and process control agent (PCA) content—were varied. At an 8:1 BPR, over 90% of the powder became flake-shaped after 8 hours, while extended milling caused cold welding. In contrast, a 10:1 BPR resulted in dominant fragmentation. The Burgio–Rojac model quantified energy input and defined the optimal range for flake formation. Increasing the PCA to 4 wt% delayed flake formation to 16 hours and induced cold welding, as shown by bimodal particle size distributions. These results support the development of Co-based current collectors for use in rSOCs.
- [Korean]
- The Effect of Fe and Fe2O3 Powder Mixing Ratios on the Pore Properties of Fe Foam Fabricated by a Slurry Coating Process
- Jin Ho Choi, Eun-Mi Jeong, Dahee Park, Sangsun Yang, Yoo-Dong Hahn, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(4):266-270. Published online August 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.4.266

- 1,355 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metal foams have a cellular structure consisting of a solid metal containing a large volume fraction of pores. In particular, open, penetrating pores are necessary for industrial applications such as in high temperature filters and as a support for catalysts. In this study, Fe foam with above 90% porosity and 2 millimeter pore size was successfully fabricated by a slurry coating process and the pore properties were characterized. The Fe and Fe2O3 powder mixing ratios were controlled to produce Fe foams with different pore size and porosity. First, the slurry was prepared by uniform mixing with powders, distilled water and polyvinyl alcohol(PVA). After slurry coating on the polyurethane( PU) foam, the sample was dried at 80°C. The PVA and PU foams were then removed by heating at 700°C for 3 hours. The debinded samples were subsequently sintered at 1250°C with a holding time of 3 hours under hydrogen atmosphere. The three dimensional geometries of the obtained Fe foams with an open cell structure were investigated using X-ray micro CT(computed tomography) as well as the pore morphology, size and phase. The coated amount of slurry on the PU foam were increased with Fe2O3 mixing powder ratio but the shrinkage and porosity of Fe foams were decreased with Fe2O3 mixing powder ratio.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of STS316L Porous Metal for Vacuum Injection Mold
Se Hoon Kim, Sang Min Kim, Sang Ho Noh, Jin Pyeong Kim, Jae Hyuck Shin, Si-Young Sung, Jin Kwang Jin, Taean Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(3): 197. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of STS316L Porous Metal for Vacuum Injection Mold
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


