Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [English]
- The Effect of Aluminum Powder Size on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of Foam
- Seunghyeok Choi, Sungjin Kim, Tae-Young Ahn, Yu-Song Choi, Jae-Gil Jung, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):232-243. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00157
- 1,397 View
- 55 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
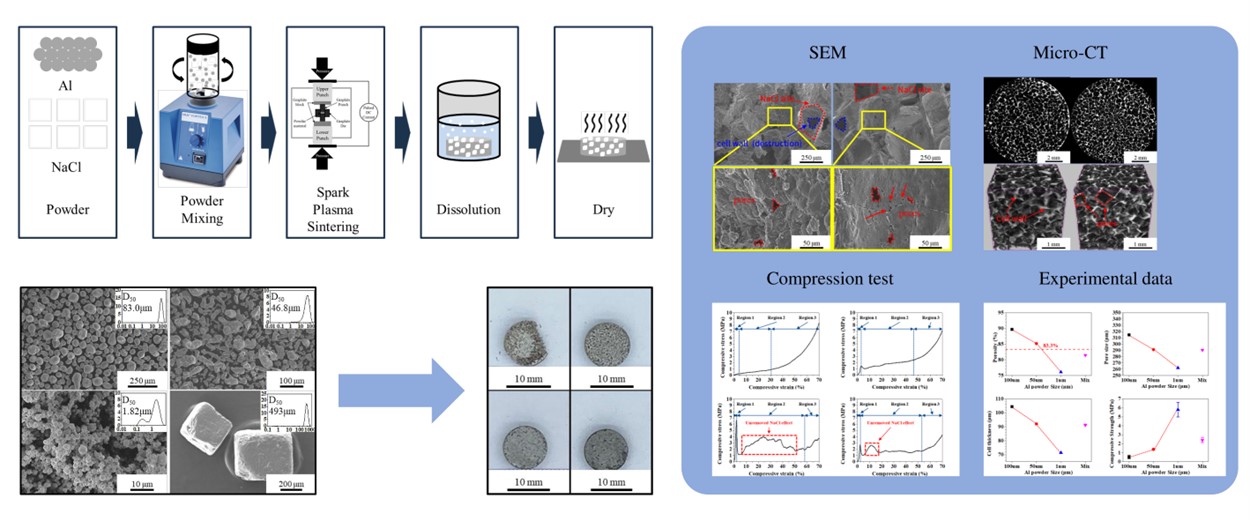
PDF - In this study, we analyzed the structural and mechanical properties of aluminum foams fabricated using aluminum powders of varying sizes and mixtures. The effects of sintering and pore structure at each size on the integrity and mechanical properties of the foams were investigated. Structural characteristics were examined using scanning electron microscopy and micro–computed tomography, while mechanical properties were evaluated through compression testing. The experimental results demonstrated that smaller powder sizes improved foam integrity, reduced porosity and pore size, and resulted in thinner cell walls. In combination, these effects increased compressive strength as the powder size decreased. The findings of this study contribute to the understanding and improvement of the mechanical properties of aluminum foams and highlight their potential for use in a wide range of applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sustainable Manufacturing of Graphene–Aluminum Composites: A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment
Xinwei Yang, Qian Peng, Changke Chen, Qingcui Liu, Yudai Huang
Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy.2026; 12(1): 727. CrossRef
- Sustainable Manufacturing of Graphene–Aluminum Composites: A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment
- [English]
- Synthesis, Characterization and Functionalization of the Coated Iron Oxide Nanostructures
- Oybek Tursunkulov, Bunyod Allabergenov, Amir Abidov, Soon-Wook Jeong, Sungjin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(3):180-185.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.3.180
- 786 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The iron oxides nanoparticles and iron oxide with other compounds are of importance in fields including biomedicine, clinical and bio-sensing applications, corrosion resistance, and magnetic properties of materials, catalyst, and geochemical processes etc. In this work we describe the preparation and investigation of the properties of coated magnetic nanoparticles consisting of the iron oxide core and organic modification of the residue. These fine iron oxide nanoparticles were prepared in air environment by the co-precipitation method using of Fe2+: Fe3+ where chemical precipitation was achieved by adding ammonia aqueous solution with vigorous stirring. During the synthesis of nanoparticles with a narrow size distribution, the techniques of separation and powdering of nanoparticles into rather monodisperse fractions are observed. This is done using controlled precipitation of particles from surfactant stabilized solutions in the form organic components. It is desirable to maintain the particle size within pH range, temperature, solution ratio wherein the particle growth is held at a minimum. The iron oxide nanoparticles can be well dispersed in an aqueous solution were prepared by the mentioned co-precipitation method. Besides the iron oxide nanowires were prepared by using similar method. These iron oxide nanoparticles and nanowires have controlled average size and the obtained products were investigated by X-ray diffraction, FESEM and other methods.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diacerein-loaded surface modified iron oxide microparticles (SMIOMPs): an emerging magnetic system for management of osteoarthritis via intra-articular injection
Nouran Abdelmageed Ali, Nadia M. Morsi, Shaimaa M. Badr-Eldin, Rehab N. Shamma
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Facile Fabrication of Flexible Electrodes and Immobilization of Silver Nanoparticles on Nanoscale Silicate Platelets to Form Highly Conductive Nanohybrid Films for Wearable Electronic Devices
Peng-Yang Huang, Chih-Wei Chiu, Chen-Yang Huang, Sheng-Yen Shen, Yen-Chen Lee, Chih-Chia Cheng, Ru-Jong Jeng, Jiang-Jen Lin
Nanomaterials.2019; 10(1): 65. CrossRef
- Diacerein-loaded surface modified iron oxide microparticles (SMIOMPs): an emerging magnetic system for management of osteoarthritis via intra-articular injection
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


