Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [Korean]
- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):244-253. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00087
- 1,112 View
- 46 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
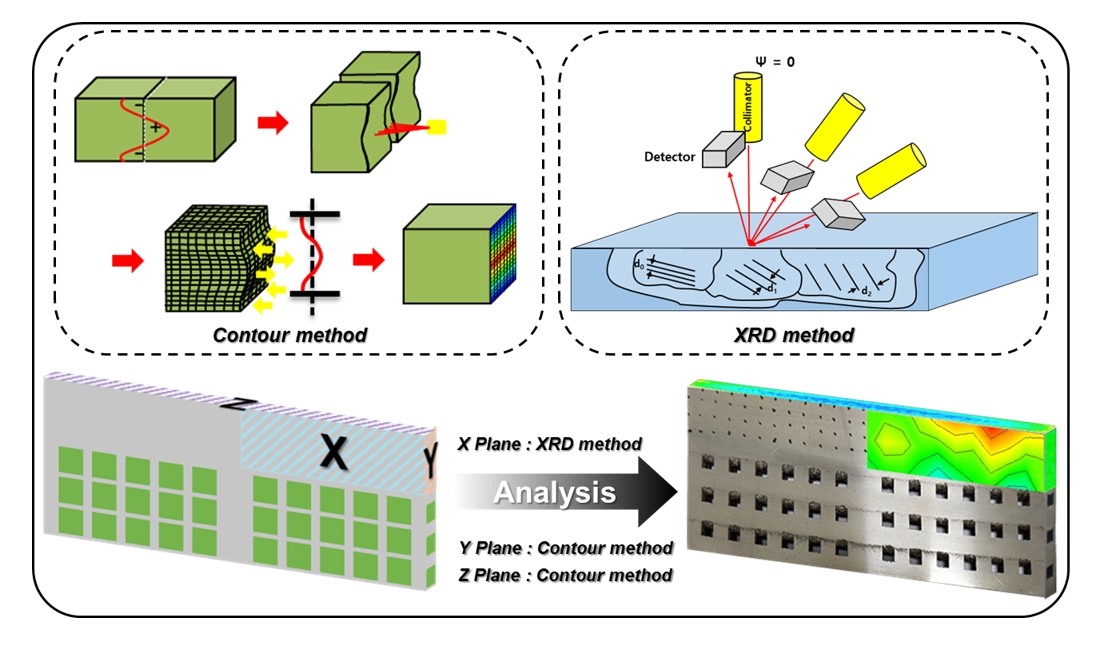
PDF - Ti-6Al-4V alloy is widely utilized in aerospace and medical sectors due to its high specific strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. However, its low machinability makes it difficult to manufacture complex-shaped products. Advancements in additive manufacturing have focused on producing high-performance, complex components using the laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) process, which is a specialized technique for customized geometries. The LPBF process exposes materials to extreme thermal conditions and rapid cooling rates, leading to residual stresses within the parts. These stresses are intensified by variations in the thermal history across regions of the component. These variations result in differences in microstructure and mechanical properties, causing distortion. Although support structure design has been researched to minimize residual stress, few studies have conducted quantitative analyses of stress variations due to different support designs. This study investigated changes in the residual stress and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy fabricated using LPBF, focusing on support structure design.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI

 First
First Prev
Prev


