Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Ultra-Low-Temperature (4.2 K) Tensile Properties and Deformation Mechanism of Stainless Steel 304L Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Seung-Min Jeon, Young-Sang Na, Young-Kyun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):95-103. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00066
- 1,964 View
- 57 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
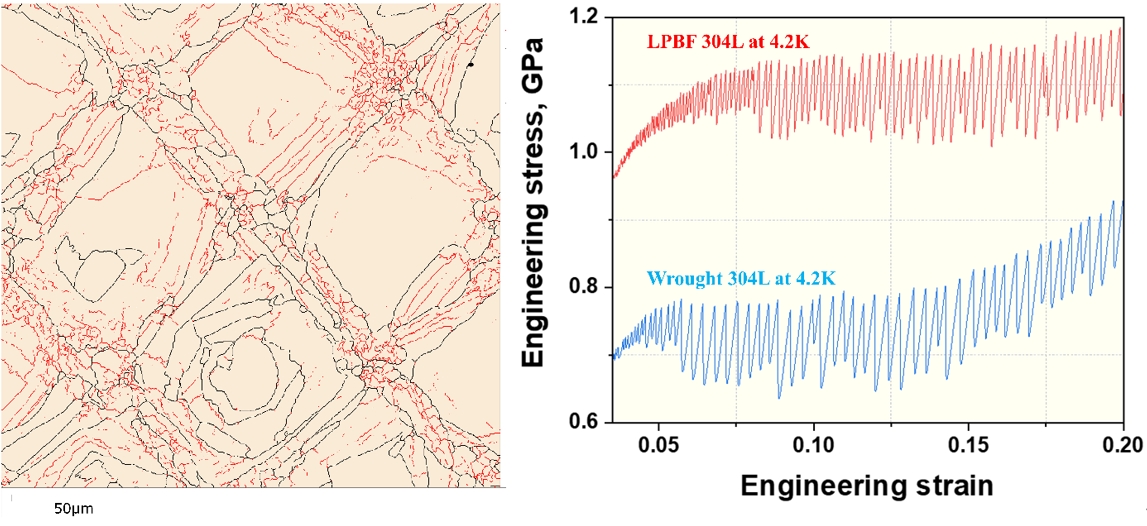
PDF - This study investigated the ultra-low-temperature (4.2 K) tensile properties and deformation mechanisms of stainless steel 304L manufactured via laser powder bed fusion (LPBF). The tensile properties of LPBF 304L were compared to those of conventional 304L to assess its suitability for cryogenic applications. The results revealed that LPBF 304L exhibited a significantly higher yield strength but lower ultimate tensile strength and elongation than conventional 304L at 4.2 K. The temperature dependence of the yield strength also favored LPBF 304L. Microstructural analysis demonstrated that LPBF 304L features a high density of dislocation cells and nano-inclusions, contributing to its greater strength. Furthermore, strain-induced martensitic transformation was observed as a key deformation mechanism at cryogenic temperatures, where austenite transformed into both hexagonal-closed packed (HCP) and body-centered cubic (BCC) martensite. Notably, BCC martensite nucleation occurred within a single HCP band. These findings provide critical insights into the mechanical behavior of LPBF 304L at cryogenic temperatures and its potential for applications in extreme environments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extremely low-temperature tensile behavior of 316L stainless steel additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Haeum Park, Heechan Jung, Min Young Sung, Young-Kyun Kim, Jaimyun Jung, Yoona Lee, Namhyun Kang, Kyung Tae Kim, Young-Sang Na, Seok Su Sohn, Jeong Min Park
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 950: 149460. CrossRef - Twinning- and transformation-induced high cryogenic strength and ductility of the CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy: Experiment and MD simulation
Yuze Wu, Zhide Li, Charlie Kong, M.W. Fu, Hailiang Yu
International Journal of Plasticity.2026; 196: 104553. CrossRef - Understanding the unique appearance behavior of shear bands during tensile deformation of α-brass at 4.2 K
Seon-Keun Oh, Sang-Hun Shim, Young-Kyun Kim, Young-Sang Na
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2025; 945: 148989. CrossRef
- Extremely low-temperature tensile behavior of 316L stainless steel additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
- [English]
- Effect of Calcium Addition on the High-Temperature Recovery of Nd and Dy from Nd-Fe-B Scrap Using Mg-Based Extractants
- Hyoseop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):493-499. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00283

- 1,715 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated whether calcium (Ca) addition improved the recovery of neodymium (Nd) and dysprosium (Dy) from Nd-Fe-B magnet scrap using magnesium (Mg)-based liquid metal extraction (LME). Traditional LME processes are limited to temperatures up to 850 °C due to oxidation issues, reducing the efficiency of rare earth element (REE) recovery, especially for Dy. By adding 10 wt.% Ca to Mg and increasing the processing temperature to 1,000 °C, we achieved nearly 100% Nd and approximately 38% Dy recovery, compared to 91% and 28%, respectively, with pure Mg at 850 °C. However, excessive Ca addition (20 wt.%) decreased the recovery efficiency due to the formation of stable intermetallic compounds. These results highlight the critical role of Ca in optimizing REE recycling from Nd-Fe-B magnet scrap.
- [English]
- The Effect of TiO2 Addition on Low-temperature Sintering Behaviors in a SnO2-CoO-CuO System
- Jae-Sang Lee, Kyung-Sik Oh, Yeong-Kyeun Paek
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):146-151. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00024
- 1,205 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
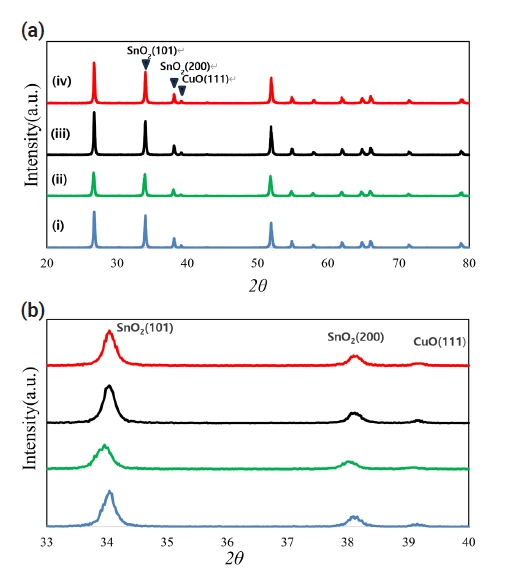
PDF - Pure SnO2 has proven very difficult to densify. This poor densification can be useful for the fabrication of SnO2 with a porous microstructure, which is used in electronic devices such as gas sensors. Most electronic devices based on SnO2 have a porous microstructure, with a porosity of > 40%. In pure SnO2, a high sintering temperature of approximately 1300C is required to obtain > 40% porosity. In an attempt to reduce the required sintering temperature, the present study investigated the low-temperature sinterability of a current system. With the addition of TiO2, the compositions of the samples were Sn1-xTixO2-CoO(0.3wt%)-CuO(2wt%) in the range of x ≤ 0.04. Compared to the samples without added TiO2, densification was shown to be improved when the samples were sintered at 950C. The dominant mass transport mechanism appears to be grain-boundary diffusion during heat treatment at 950C.
- [Korean]
- Development of High-strength, High-temperature Nb-Si-Ti Alloys through Mechanical Alloying
- Jung-Joon Kim, Sang-Min Yoon, Deok-Hyun Han, Jongmin Byun, Young-Kyun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):30-36. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.30
- 2,146 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
Yeon-Joo Lee, Pil-Ryung Cha, Hyoung-Seop Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(1): 144. CrossRef
- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
- [English]
- Cryogenic Tensile Behavior of Ferrous Medium-entropy Alloy Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Seungyeon Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jae Wung Bae, Jeong Min Park
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):8-15. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.8
- 4,542 View
- 139 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The emergence of ferrous-medium entropy alloys (FeMEAs) with excellent tensile properties represents a potential direction for designing alloys based on metastable engineering. In this study, an FeMEA is successfully fabricated using laser powder bed fusion (LPBF), a metal additive manufacturing technology. Tensile tests are conducted on the LPBF-processed FeMEA at room temperature and cryogenic temperatures (77 K). At 77 K, the LPBF-processed FeMEA exhibits high yield strength and excellent ultimate tensile strength through active deformation-induced martensitic transformation. Furthermore, due to the low stability of the face-centered cubic (FCC) phase of the LPBF-processed FeMEA based on nano-scale solute heterogeneity, stress-induced martensitic transformation occurs, accompanied by the appearance of a yield point phenomenon during cryogenic tensile deformation. This study elucidates the origin of the yield point phenomenon and deformation behavior of the FeMEA at 77 K.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Stronger weld than base metal in face-centered cubic alloy through multi-scale heterogeneity
Yoona Lee, Sangwon Park, Dongwon Shin, Marcia Myung Hye Ahn, Wei Xiong, Nokeun Park, Hyoung Seop Kim, Je In Lee, Wookjin Lee, Yoon Suk Choi, Jeong Min Park, Namhyun Kang
Materials Research Letters.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Effect of Building Orientation on Tensile Properties of Hastelloy X alloy Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seong-June Youn, GooWon Noh, Seok Su Sohn, Young-Sang Na, Young-Kyun Kim
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(2): 130. CrossRef - Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang, Oanh, Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 191. CrossRef - Cryogenic tensile behavior of carbon-doped CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloys additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Haeum Park, Hyeonseok Kwon, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Jungho Choe, Hyokyung Sung, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jung Gi Kim, Jeong Min Park
Additive Manufacturing.2024; 86: 104223. CrossRef - Recent progress in high-entropy alloys for laser powder bed fusion: Design, processing, microstructure, and performance
Asker Jarlöv, Zhiguang Zhu, Weiming Ji, Shubo Gao, Zhiheng Hu, Priyanka Vivegananthan, Yujia Tian, Devesh Raju Kripalani, Haiyang Fan, Hang Li Seet, Changjun Han, Liming Tan, Feng Liu, Mui Ling Sharon Nai, Kun Zhou
Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports.2024; 161: 100834. CrossRef
- Stronger weld than base metal in face-centered cubic alloy through multi-scale heterogeneity
- [Korean]
- Effect of Acid Leaching Conditions on the Properties of Cr Powder Produced by Self-propagating High-temperature Synthesis
- YongKwan Lee, YeongWoo Cho, ShinYoung Choi, SungGue Heo, Ju Won, KyoungTae Park, MiHye Lee, JaeJin Sim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):233-241. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.233

- 767 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we evaluated the effects of acid leaching on the properties of Cr powder synthesized using self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS). Cr powder was synthesized from a mixture of Cr2O3 and magnesium (Mg) powders using the SHS Process, and the byproducts after the reaction were removed using acid leaching. The properties of the recovered Cr powder were analyzed via X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), particle size analysis (PSA), and oxygen content analysis. The results show that perfect selective leaching of Cr is challenging because of various factors such as incomplete reaction, reaction kinetics, the presence of impurities, and incompatibility between the acid and metal mixture. Therefore, this study provides essential information on the properties under acidic conditions during the production of high-quality Cr powder using a self-propagating high-temperature synthesis method.
- [English]
- The Effect of SnO2 Addition on Sintering Behaviors in a Titanium Oxide-Copper Oxide System
- Ju-Won Lee, Kyung-Sik Oh, Tai-Joo Chung, Yeong-Kyeun Paek
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):357-362. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.357

- 838 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The low-temperature sinterability of TiO2-CuO systems was investigated using a solid solution of SnO2. Sample powders were prepared through conventional ball milling of mixed raw powders. With the SnO2 content, the compositions of the samples were Ti1-xSnxO2-CuO(2 wt.%) in the range of x ≤ 0.08. Compared with the samples without SnO2 addition, the densification was enhanced when the samples were sintered at 900°C. The dominant mass transport mechanism seemed to be grain-boundary diffusion during heat treatment at 900°C, where active grain-boundary diffusion was responsible for the improved densification. The rapid grain growth featured by activated sintering was also obstructed with the addition of SnO2. This suggested that both CuO as an activator and SnO2 dopant synergistically reduced the sintering temperature of TiO2.
- [Korean]
- Recycling of Hardmetal Tool through Alkali Leaching Process and Fabrication Process of Nano-sized Tungsten Carbide Powder using Self-propagation High-temperature Synthesis
- Hee-Nam Kang, Dong Il Jeong, Young Il Kim, In Yeong Kim, Sang Cheol Park, Cheol Woo Nam, Seok-Jun Seo, Jin Yeong Lee, Bin Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):47-55. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.47

- 1,434 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tungsten carbide is widely used in carbide tools. However, its production process generates a significant number of end-of-life products and by-products. Therefore, it is necessary to develop efficient recycling methods and investigate the remanufacturing of tungsten carbide using recycled materials. Herein, we have recovered 99.9% of the tungsten in cemented carbide hard scrap as tungsten oxide via an alkali leaching process. Subsequently, using the recovered tungsten oxide as a starting material, tungsten carbide has been produced by employing a self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) method. SHS is advantageous as it reduces the reaction time and is energy-efficient. Tungsten carbide with a carbon content of 6.18 wt % and a particle size of 116 nm has been successfully synthesized by optimizing the SHS process parameters, pulverization, and mixing. In this study, a series of processes for the highefficiency recycling and quality improvement of tungsten-based materials have been developed.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and High Temperature Mechanical Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steels Manufactured by Combination Milling Process
- Jung-Uk Lee, Young-Kyun Kim, Jeoung Han Kim, Hwi-Jin Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):389-395. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.389
- 818 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
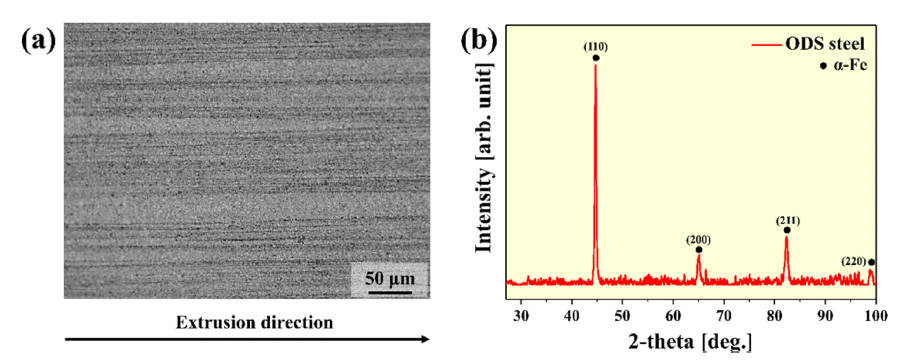
PDF Oxide dispersion-strengthened (ODS) steel has excellent high-temperature properties, corrosion resistance, and oxidation resistance, and is expected to be applicable in various fields. Recently, various studies on mechanical alloying (MA) have been conducted for the dispersion of oxide particles in ODS steel with a high number density. In this study, ODS steel is manufactured by introducing a complex milling process in which planetary ball milling, cryogenic ball milling, and drum ball milling are sequentially performed, and the microstructure and high-temperature mechanical properties of the ODS steel are investigated. The microstructure observation revealed that the structure is stretched in the extrusion direction, even after the heat treatment. In addition, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis confirmed the presence of oxide particles in the range of 5 to 10 nm. As a result of the room-temperature and high-temperature compression tests, the yield strengths were measured as 1430, 1388, 418, and 163 MPa at 25, 500, 700, and 900°C, respectively. Based on these results, the correlation between the microstructure and mechanical properties of ODS steel manufactured using the composite milling process is also discussed.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Freeze Drying Condition of WO3/Tert-Butyl Alcohol Slurry on the Microstructural Characteristics of Porous Body
- Eui Seon Lee, Youn Ji Heo, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(4):331-335. Published online August 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.4.331

- 619 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The effects of drying temperature on the microstructure of porous W fabricated by the freeze-casting process of tert-butyl alcohol slurry with WO3 powder was investigated. Green bodies were hydrogen-reduced at 800°C for 1 h and sintered at 1000°C for 6 h. X-ray diffraction analysis revealed that WO3 powders were completely converted to W without any reaction phases by hydrogen reduction. The sintered body showed pores aligned in the direction of tertbutyl alcohol growth, and the porosity and pore size decreased as the amount of WO3 increased from 5 to 10v ol%. As the drying temperature of the frozen body increased from -25°C to -10°C, the pore size and thickness of the struts increased. The change in microstructural characteristics based on the amount of powder added and the drying temperature was explained by the growth behavior of the freezing agent and the degree of rearrangement of the solid powder during the solidification of the slurry.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation of Porous W-Cu by Freeze Casting of Tert-butyl Alcohol Slurry Mixed with WO3-CuO Powder
Youngmin Kim, Ji Young Kim, Minju Son, Wonyong Kwon, Eui Seon Lee, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 466. CrossRef
- Preparation of Porous W-Cu by Freeze Casting of Tert-butyl Alcohol Slurry Mixed with WO3-CuO Powder
- [Korean]
- High Temperature Oxidation Behavior of 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process
- Yu-Jin Hwang, Dong-Yeol Wi, Kyu-Sik Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):110-119. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.110
- 1,212 View
- 26 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
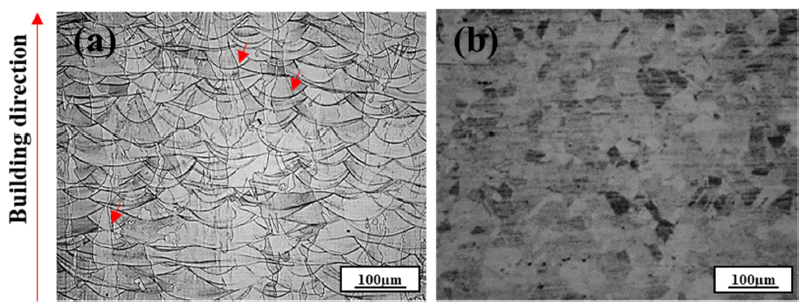
PDF In this study, the high-temperature oxidation properties of austenitic 316L stainless steel manufactured by laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) is investigated and compared with conventional 316L manufactured by hot rolling (HR). The initial microstructure of LPBF-SS316L exhibits a molten pool ~100 μm in size and grains grown along the building direction. Isotropic grains (~35 μm) are detected in the HR-SS316L. In high-temperature oxidation tests performed at 700°C and 900°C, LPBF-SS316L demonstrates slightly superior high-temperature oxidation resistance compared to HR-SS316L. After the initial oxidation at 700°C, shown as an increase in weight, almost no further oxidation is observed for both materials. At 900°C, the oxidation weight displays a parabolic trend and both materials exhibit similar behavior. However, at 1100°C, LPBF-SS316L oxidizes in a parabolic manner, but HR-SS316L shows a breakaway oxidation behavior. The oxide layers of LPBF-SS316L and HR-SS316L are mainly composed of Cr2O3, Febased oxides, and spinel phases. In LPBF-SS316L, a uniform Cr depletion region is observed, whereas a Cr depletion region appears at the grain boundary in HR-SS316L. It is evident from the results that the microstructure and the hightemperature oxidation characteristics and behavior are related.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Retention factor-based constitutive model of high-strength austenitic A4–80 bolts after fire exposure
Hui Wang, Bo Yang, Tao Sun, Weilai Yao, Wei Jiang
Journal of Constructional Steel Research.2025; 235: 109930. CrossRef - Study of structural stability at high temperature of pseudo-single tube with double layer as an alternative method for accident-tolerant fuel cladding
Jong Woo Kim, Hyeong Woo Min, Jaehwan Ko, Yonghee Kim, Young Soo Yoon
Journal of Nuclear Materials.2022; 566: 153800. CrossRef
- Retention factor-based constitutive model of high-strength austenitic A4–80 bolts after fire exposure
- [Korean]
- Effects of Synthesis Conditions on Luminescence Characteristics of Glutathione Capped ZnSe Nano particles
- Geum Ji Back, Ha Yeon Song, Min Seo Lee, Hyun Seon Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(1):44-50. Published online February 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.1.44

- 1,214 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Zinc selenide (ZnSe) nanoparticles were synthesized in aqueous solution using glutathione (GSH) as a ligand. The influence of the ligand content, reaction temperature, and hydroxyl ion concentration (pH) on the fabrication of the ZnSe particles was investigated. The optical properties of the synthesized ZnSe particles were characterized using various analytical techniques. The nanoparticles absorbed UV-vis light in the range of 350-400 nm, which is shorter than the absorption wavelength of bulk ZnSe particles (460 nm). The lowest ligand concentration for achieving good light absorption and emission properties was 0.6 mmol. The reaction temperature had an impact on the emission properties; photoluminescence spectroscopic analysis showed that the photo-discharge characteristics were greatly enhanced at high temperatures. These discharge characteristics were also affected by the hydroxyl ion concentration in solution; at pH 13, sound emission characteristics were observed, even at a low temperature of 25°C. The manufactured nanoparticles showed excellent light absorption and emission properties, suggesting the possibility of fabricating ZnSe QDs in aqueous solutions at low temperatures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Green synthesis and luminescence characteristics of ZnSe-ZnS core-shell quantum dots
Geum Ji Back, Ha Yeon Song, Min Seo Lee, Jaesik Yoon, Hyun Seon Hong
Journal of Crystal Growth.2024; 626: 127475. CrossRef - Effect of UV Irradiation on Optical Properties of Water-Based Synthetic Zinc Selenide Quantum Dots
Geum Ji Back, Yu Jin Kang, I Ju Kang, Jeong Hyeon Lim, Hyun Seon Hong
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2022; 60(2): 160. CrossRef
- Green synthesis and luminescence characteristics of ZnSe-ZnS core-shell quantum dots
- [Korean]
- Austenite Stability of Sintered Fe-based Alloy
- Seunggyu Choi, Namhyuk Seo, Junhyub Jun, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(5):414-419. Published online October 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.5.414
- 1,316 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In the present study, we investigated the austenite stability of a sintered Fe-based nanocrystalline alloy. The volume fraction of austenite was measured based on the X-ray diffraction data of sintered Fe-based nanocrystalline alloys, which were prepared by high-energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering. The sintered alloy samples showed a higher volume fraction of austenite at room temperature as compared to the equilibrium volume fraction of austenite obtained using thermodynamic calculations, which resulted from the nanosized crystalline structure of the sintered alloy. It was proved that the austenite stability of the sintered Fe-based alloy increased with a rise in the amount of austenite stabilizing elements such as Mn, Ni, and C; however, it increased more effectively with a decrease in the actual grain size. Furthermore, we proposed a new equation to predict the martensite starting temperature for sintered Fe-based alloys.
- [Korean]
- Influence of Reducing Agents and Additives on the Synthesis of ZnSe Nanoparticles
- Geum Ji Back, Da Gyeong Lee, Min Seo Lee, Ha Yeon Song, Hyun Seon Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):233-240. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.233

- 632 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Nano-sized ZnSe particles are successfully synthesized in an aqueous solution at room temperature using sodium borohydride (NaBH4) and thioglycolic acid (TGA) as the reducing agent and stabilizer, respectively. The effects of the mass ratio of the reducing agent to Se, stabilizer concentration, and stirring time on the synthesis of the ZnSe nanoparticles are evaluated. The light absorption/emission properties of the synthesized nanoparticles are characterized using ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy, photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy, and particle size analyzer (PSA) techniques. At least one mass ratio (NaBH4/Se) of the reducing agent should be added to produce ZnSe nanoparticles finer than 10 nm and to absorb UV–vis light shorter than the ZnSe bulk absorption wavelength of 460 nm. As the ratio of the reducing agent increases, the absorption wavelengths in the UV-vis curves are blue-shifted. Stirring in the atmosphere acts as a deterrent to the reduction reaction and formation of nanoparticles, but if not stirred in the atmosphere, the result is on par with synthesis in a nitrogen atmosphere. The stabilizer, TGA, has an impact on the Zn precursor synthesis. The fabricated nanoparticles exhibit excellent photo-absorption/discharge characteristics, suggesting that ZnSe nanoparticles can be alloyed without the need for organic solutions or high-temperature environments.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Calcination Temperature on the Microstructure and Photocatalytic Activity of Electrospun BiVO4 Nanofiber
- Myeongjun Ji, Jeong Hyun Kim, Cheol-Hui Ryu, Yun Taek Ko, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):226-232. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.226

- 1,227 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Bismuth vanadate (BiVO4) is considered a potentially attractive candidate for the visible-light-driven photodegradation of organic pollutants. In an effort to enhance their photocatalytic activities, BiVO4 nanofibers with controlled microstructures, grain sizes, and crystallinities are successfully prepared by electrospinning followed by a precisely controlled heat treatment. The structural features, morphologies, and photo-absorption performances of the asprepared samples are systematically investigated and can be readily controlled by varying the calcination temperature. From the physicochemical analysis results of the synthesized nanofiber, it is found that the nanofiber calcines at a lower temperature, shows a smaller crystallite size, and lower crystallinity. The photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine-B (RhB) reveals that the photocatalytic activity of the BiVO4 nanofibers can be improved by a thermal treatment at a relatively low temperature because of the optimization of the conflicting characteristics, crystallinity, crystallite size, and microstructure. The photocatalytic activity of the nanofiber calcined at 350°C for the degradation of RhB under visible-light irradiation exhibits a greater photocatalytic activity than the nanofibers synthesized at 400°C and 450°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Design, synthesis, and characterization of a porous ceramic-supported CeO2 nanocatalyst for CO -free H2 evolution
Jimin Lee, Minseob Lim, Tae Sung Kim, Kee-Ryung Park, Jong-Sik Lee, Hong-Baek Cho, Joo Hyun Park, Yong-Ho Choa
Applied Surface Science.2021; 548: 149198. CrossRef
- Design, synthesis, and characterization of a porous ceramic-supported CeO2 nanocatalyst for CO -free H2 evolution
- [English]
- Effect of SiC and WC additon on Oxidation Behavior of Spark-Plasma-Sintered ZrB2
- Chang-Yeoul Kim, Jae-Seok Choi, Sung-Churl Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(6):455-462. Published online December 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.6.455

- 1,172 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ZrB2 ceramic and ZrB2 ceramic composites with the addition of SiC, WC, and SiC/WC are successfully synthesized by a spark plasma sintering method. During high-temperature oxidation, SiC additive form a SiO2 amorphous outer scale layer and SiC-deplete ZrO2 scale layer, which decrease the oxidation rate. WC addition forms WO3 during the oxidation process to result in a ZrO2/WO3 liquid sintering layer, which is known to improve the antioxidation effect. The addition of SiC and WC to ZrB2 reduces the oxygen effective diffusivity by one-fifth of that of ZrB2. The addition of both SiC and WC shows the formation of a SiO2 outer dense glass layer and ZrO2/WO3 layer so that the anti-oxidation effect is improved three times as much as that of ZrB2. Therefore, SiC- and WC-added ZrB2 has a lower two-order oxygen effective diffusivity than ZrB2; it improves the anti-oxidation performance 3 times as much as that of ZrB2.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Role of TiC and WC Addition on the Mechanism and Kinetics of Isothermal Oxidation and High-Temperature Stability of ZrB2–SiC Composites
Pradyut Sengupta, Indranil Manna
High Temperature Corrosion of Materials.2024; 101(S1): 57. CrossRef
- Role of TiC and WC Addition on the Mechanism and Kinetics of Isothermal Oxidation and High-Temperature Stability of ZrB2–SiC Composites
- [Korean]
- Effect of Li2O-Bi2O3 Addition on the Piezoelectric Properties of Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)0.65Ti0.35O3 Ceramics
- Jae Hyuk Kim, Shi Yeon Kim, Jeoung Sik Choi, Dong-Hun Yeo, Hyo-Soon Shin, Sahn Nahm
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):405-409. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.405
- 738 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
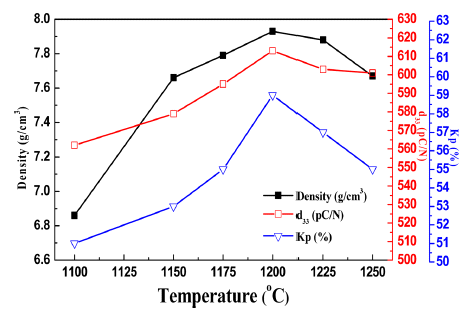
PDF Piezoelectric ceramic specimens with the Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)0.65Ti0.35O3 (PMN-PT) composition are prepared by the solid state reaction method known as the “columbite precursor” method. Moreover, the effects of the Li2O-Bi2O3 additive on the microstructure, crystal structure, and piezoelectric properties of sintered PMN-PT ceramic samples are investigated. The addition of Li2O-Bi2O3 lowers the sintering temperature from 1,200°C to 950°C. Moreover, with the addition of >5 wt.% additive, the crystal structure changes from tetragonal to rhombohedral. Notably, the sample with 3 wt.% additive exhibits excellent piezoelectric properties (d33 = 596 pC/N and Kp = 57%) and a sintered density of 7.92 g/cm3 after sintering at 950°C. In addition, the sample exhibits a curie temperature of 138.6°C at 1 kHz. Finally, the compatibility of the sample with a Cu electrode is examined, because the energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy data indicate the absence of interdiffusion between Cu and the ceramic material.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Pyrolysis temperature on TiO2 Nanoparticles Synthesized by a Salt-assisted Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process
- Jae-Hyun Yoo, Myeong-Jun Ji, Woo-Young Park, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):237-242. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.237

- 847 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, ultrasonic spray pyrolysis combined with salt-assisted decomposition, a process that adds sodium nitrate (NaNO3) into a titanium precursor solution, is used to synthesize nanosized titanium dioxide (TiO2) particles. The added NaNO3 prevents the agglomeration of the primary nanoparticles in the pyrolysis process. The nanoparticles are obtained after a washing process, removing NaNO3 and NaF from the secondary particles, which consist of the salts and TiO2 nanoparticles. The effects of pyrolysis temperature on the size, crystallographic characteristics, and bandgap energy of the synthesized nanoparticles are systematically investigated. The synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles have a size of approximately 2–10 nm a bandgap energy of 3.1–3.25 eV, depending on the synthetic temperature. These differences in properties affect the photocatalytic activities of the synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructure and Sintering Behavior of Fine Tungsten Powders Synthesized by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis
Hyeonhui Jo, Jeong Hyun Kim, Young-In Lee, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2021; 59(5): 289. CrossRef
- Microstructure and Sintering Behavior of Fine Tungsten Powders Synthesized by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis
- [Korean]
- Research Trends of the Mo-Si-B Alloys as Next Generation Ultra-high-temperature Alloys
- Won June Choi, Chun Woong Park, Jung Hyo Park, Young Do Kim, Jong Min Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):156-165. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.156
- 1,522 View
- 26 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
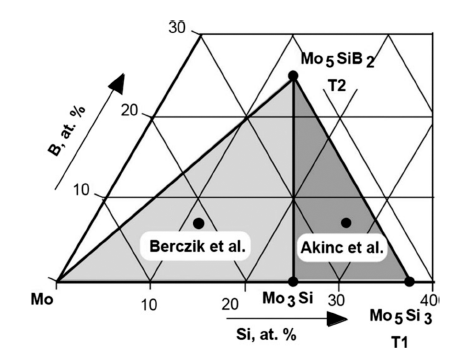
PDF Over the last decade, the next generation’s ultra-high-temperature materials as an alternative to Nickel-based superalloys have been highlighted. Ultra-high-temperature materials based on refractory metals are one of several potential candidates. In particular, molybdenum alloys with small amounts of silicon and boron (Mo-Si-B alloys) have superior properties at high temperature. However, research related to Mo-Si-B alloys were mainly conducted by several developed countries but garnered little interest in Korea. Therefore, in this review paper, we introduce the development history of Mo-Si-B alloys briefly and discuss the properties, particularly the mechanical and oxidation properties of Mo-Si-B alloys. We also introduce the latest research trends of Mo-Si-B alloys based on the research paper. Finally, for domestic research related to this field, we explain why Mo-Si-B alloys should be developed and suggest the potential directions for Mo-Si-B alloys research.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thermal Stability and Weight Reduction of Al0.75V2.82CrZr Refractory High Entropy Alloy Prepared Via Mechanical Alloying
Minsu Kim, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(6): 478. CrossRef - Preparation and Structure of Chromium Coatings Doped with Diamond Nanoparticles Deposited Directly on a Monolithic Composite of Molybdenum and Aluminum
V. P. Petkov, M. K. Aleksandrova, R. V. Valov, V. P. Korzhov, V. M. Kiiko, I. S. Zheltyakova
Protection of Metals and Physical Chemistry of Surfaces.2023; 59(3): 396. CrossRef - A Review of Mo-Si Intermetallic Compounds as Ultrahigh-Temperature Materials
Liang Jiang, Bin Zheng, Changsong Wu, Pengxiang Li, Tong Xue, Jiandong Wu, Fenglan Han, Yuhong Chen
Processes.2022; 10(9): 1772. CrossRef - Heat-Resistant Molybdenum Borosilicate Alloys Hardened with Titanium Carbides: Mo–Si–B–TiC (Survey)
I. L. Svetlov, O. G. Ospennikova, M. I. Karpov, Yu. V. Artemenko
Inorganic Materials: Applied Research.2021; 12(4): 866. CrossRef
- Thermal Stability and Weight Reduction of Al0.75V2.82CrZr Refractory High Entropy Alloy Prepared Via Mechanical Alloying
- [Korean]
- Effects of the Mixing Method and Sintering Temperature on the Characteristics of PZNN-PZT Piezoelectric Ceramic Materials
- So Won Kim, Yong Jeong Jeong, Hee Chul Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):487-493. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.487
- 986 View
- 6 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The impact of different mixing methods and sintering temperatures on the microstructure and piezoelectric properties of PZNN-PZT ceramics is investigated. To improve the sinterability and piezoelectric properties of these ceramics, the composition of 0.13Pb((Zn0.8Ni0.2)1/3Nb2/3)O3-0.87Pb(Zr0.5Ti0.5)O3 (PZNN-PZT) containing a Pb-based relaxor component is selected. Two methods are used to create the powder for the PZNN-PZT ceramics. The first involves blending all source powders at once, followed by calcination. The second involves the preferential creation of columbite as a precursor, by reacting NiO with Nb2O5 powder. Subsequently, PZNN-PZT powder can be prepared by mixing the columbite powder, PbO, and other components, followed by an additional calcination step. All the PZNNPZT powder samples in this study show a nearly-pure perovskite phase. High-density PZNN-PZT ceramics can be fabricated using powders prepared by a two-step calcination process, with the addition of 0.3 wt% MnO2 at even relatively low sintering temperatures from 800°C to 1000°C. The grain size of the ceramics at sintering temperatures above 900°C is increased to approximately 3 μm. The optimized PZNN-PZT piezoelectric ceramics show a piezoelectric constant (d33) of 360 pC/N, an electromechanical coupling factor (kp) of 0.61, and a quality factor (Qm) of 275.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Analysis of Edge Chipping in LiTaO3 Wafer Grinding Using a Scratch Test and FEA Simulation
Haeseong Hwang, Seungho Han, Hyunseop Lee
Lubricants.2023; 11(7): 297. CrossRef - A generalized rule for phase transition generated by additives in piezoelectric ceramics
Jae-Min Cha, Young-Kook Moon, Jung-hwan Kim, Hyun-Ae Cha, Jong-Jin Choi, Byung-Dong Hahn, Seog-Young Yoon, Cheol-Woo Ahn
Materials Today Communications.2023; 37: 107290. CrossRef - Low-Temperature Sintering Properties of Bi2O3 Doped PZT-5H Piezoelectric Ceramics
Wanzi Mao, Qing Xu, Duanping Huang, Huajun Sun, Feng Zhang, Xiaobin Xie
Journal of Electronic Materials.2023; 52(5): 3334. CrossRef - Effect of LiBiO2 on low-temperature sintering of PZT-PZNN ceramics
Sung Cheul Hong, Shi Yeon Kim, Dong-Hun Yeo, Hyo-Soon Shin, Zee Hoon Park, Sahn Nahm
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2022; 59(5): 638. CrossRef - Two-Stage De-binding for Cu Electrode Application to PZT-PZNN Multilayer Actuator
Sung Cheul Hong, Zeehoon Park, Dong-Hun Yeo, Hyo-Soon Shin, Sahn Nahm
Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Materials.2022; 23(4): 348. CrossRef
- An Analysis of Edge Chipping in LiTaO3 Wafer Grinding Using a Scratch Test and FEA Simulation
- [Korean]
- Pre-treatments of initial materials for controlling synthesized TaC characteristics in the SHS process
- Jae Jin Sim, Sang Hoon Choi, Ji Hwan Park, Il Kyu Park, Jae Hong Lim, Kyoung Tae Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(3):251-256. Published online June 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.3.251

- 1,003 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We report the feasibility of TaC production via self-propagating high temperature synthesis, and the influence of the initial green compact density on the final composite particle size. Experiments are carried out from a minimum pressure of 0.3 MPa, the pressure at which the initial green body becomes self-standing, up to 3 MPa, the point at which no further combustion occurs. The green density of the pellets varies from 29.99% to 42.97%, as compared with the theoretical density. The increase in green density decreases the powder size of TaC, and the smallest particle size is observed with 1.5 MPa, at 10.36 μm. Phase analysis results confirm the presence of the TaC phase only. In the range of 0.3-0.5 MPa, traces of unreacted Ta and C residues are detected. However, results also show the presence of only C residue in the matrix within the pressure range of 0.6-3.0 MPa.
- [Korean]
- Manufacturing of Ni-Cr-B-Si + WC/12Co Composite Coating Layer Using Laser Cladding Process and its Mechanical Properties
- Gi-Su Ham, Chul-O Kim, Soon-Hong Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):370-376. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.370
- 750 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study we manufacture a Ni-Cr-B-Si +WC/12Co composite coating layer on a Cu base material using a laser cladding (LC) process, and investigate the microstructural and mechanical properties of the LC coating and Ni electroplating layers (reference material). The initial powder used for the LC coating layer is a powder feedstock with an average particle size of 125 μm. To identify the microstructural and mechanical properties, OM, SEM, XRD, room and high temperature hardness, and wear tests are implemented. Microstructural observation of the initial powder and LC coating layer confirm the layer is composed mainly of γ-Ni phases and WC and Cr23C6 carbides. The measured hardness of the LC coating and Ni electroplating layers are 653 and 154 Hv, respectively. The hardness measurement from room up to high temperatures of 700°C result in a hardness decrease as the temperature increases, but the hardness of the LC coating layer is higher for all temperature conditions. Room temperature wear results show that the wear loss of the LC coating layer is 1/12 of the wear level of the Ni electroplating layer. The measured bond strength is also greater in the LC coating than the Ni electroplating.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructure and Room Temperature Wear Properties of a Ni-Cr-B-Si-C Coating Layer Manufactured by the Laser Cladding Process
Tae-Hoon Kang, Kyu-Sik Kim, Soon-Hong Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2018; 56(6): 423. CrossRef - Microstructural and Wear Properties of WC-based and Cr3C2-based Cermet Coating Materials Manufactured with High Velocity Oxygen Fuel Process
Yeon-Ji Kang, Gi-Su Ham, Hyung-Jun Kim, Sang-Hoon Yoon, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(5): 408. CrossRef
- Microstructure and Room Temperature Wear Properties of a Ni-Cr-B-Si-C Coating Layer Manufactured by the Laser Cladding Process
- [English]
- Dispersion Behavior and Size Analysis of Thermally Purified High Pressure-high Temperature Synthesized Nanodiamond Particles
- Hansang Kwon, Jehong Park, Marc Leparoux
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(3):216-222. Published online June 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.3.216

- 1,400 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Synthesized monocrystalline nanodiamond (nD) particles are heat-treated at various temperatures to produce highly structured diamond crystals. The heat-treated nDs show different weight loss ratios during thermogravimetric analysis. The crystallinities of the heat-treated nDs are analyzed using Raman spectroscopy. The average particle sizes of the heat-treated nDs are measured by a dynamic light scattering (DLS) system and direct imaging observation methods. Moreover, individual dispersion behaviors of the heat-treated nD particles are investigated based on ultrasonic dispersion methods. The average particle sizes of the dispersed nDs according to the two different measurement methods show very similar size distributions. Thus, it is possible to produce highly crystallized nD powder particles by a heattreatment process, and the nD particles are relatively easy to disperse individually without any dispersant. The heattreated nDs can lead to potential applications such as in nanocomposites, quantum dots, and biomedical materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Two extreme crystal size scales of diamonds, large single crystal and nanocrystal diamonds: Synthesis, properties and their mutual transformation
Yang Wang, Wei-hua Wang, Shi-lin Yang, Guo-yang Shu, Bing Dai, Jia-qi Zhu
New Carbon Materials.2021; 36(3): 512. CrossRef
- Two extreme crystal size scales of diamonds, large single crystal and nanocrystal diamonds: Synthesis, properties and their mutual transformation
- [Korean]
- High Temperature Oxidation Behavior of Fe-14Cr Ferritic Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steels Manufactured by Mechanical Alloying Process
- Young-Kyun Kim, Jong-Kwan Park, Hwi-Jun Kim, Man-Sik Kong, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):133-140. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.133

- 690 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study investigates the oxidation properties of Fe-14Cr ferritic oxide-dispersion-strengthened (ODS) steel at various high temperatures (900, 1000, and 1100°C for 24 h). The initial microstructure shows that no clear structural change occurs even under high-temperature heat treatment, and the average measured grain size is 0.4 and 1.1 μm for the as-fabricated and heat-treated specimens, respectively. Y–Ti–O nanoclusters 10–50 nm in size are observed. High-temperature oxidation results show that the weight increases by 0.27 and 0.29 mg/cm2 for the asfabricated and heat-treated (900°C) specimens, and by 0.47 and 0.50 mg/cm2 for the as-fabricated and heat-treated (1000°C) specimens, respectively. Further, after 24 h oxidation tests, the weight increases by 56.50 and 100.60 mg/cm2 for the as-fabricated and heat-treated (1100°C) specimens, respectively; the latter increase is approximately 100 times higher than that at 1000°C. Observation of the surface after the oxidation test shows that Cr2O3 is the main oxide on a specimen tested at 1000°C, whereas Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 phases also form on a specimen tested at 1100°C, where the weight increases rapidly. The high-temperature oxidation behavior of Fe-14Cr ODS steel is confirmed to be dominated by changes in the Cr2O3 layer and generation of Fe-based oxides through evaporation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructure and Wear Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steel Powder Added Steel-Based Composite Material for Automotive Part
Young-Kyun Kim, Jong-Kwan Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(1): 36. CrossRef
- Microstructure and Wear Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steel Powder Added Steel-Based Composite Material for Automotive Part
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and High Temperature Oxidation Behaviors of Fe-Ni Alloys by Spark Plasma Sintering
- Chae Hong Lim, Jong Seok Park, Sangsun Yang, Jung-Yeul Yun, Jin Kyu Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):53-57. Published online February 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.53

- 526 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we report the microstructure and the high-temperature oxidation behavior of Fe-Ni alloys by spark plasma sintering. Structural characterization is performed by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. The oxidation behavior of Fe-Ni alloys is studied by means of a high-temperature oxidation test at 1000°C in air. The effect of Ni content of Fe-Ni alloys on the microstructure and on the oxidation characteristics is investigated in detail. In the case of Fe-2Ni and Fe-5Ni alloys, the microstructure is a ferrite (α) phase with body centered cubic (BCC) structure, and the microstructure of Fe-10Ni and Fe-20Ni alloys is considered to be a massive martensite (α’) phase with the same BCC structure as that of the ferrite phase. As the Ni content increases, the micro-Vickers hardness of the alloys also increases. It can also be seen that the oxidation resistance is improved by decreasing the thickness of the oxide film.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Diamond Particle Size on the Thermal Shock Property of High Pressure High Temperature Sintered Polycrystalline Diamond Compact
- Ji-Won Kim, Min-Seok Baek, Hee-Sub Park, Jin-Hyeon Cho, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(5):364-371. Published online October 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.5.364

- 1,210 View
- 13 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study investigates the thermal shock property of a polycrystalline diamond compact (PDC) produced by a high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) sintering process. Three kinds of PDCs are manufactured by the HPHT sintering process using different particle sizes of the initial diamond powders: 8-16 μm (D50 = 4.3 μm), 10-20 μm (D50 = 6.92 μm), and 12-22 μm (D50 = 8.94 μm). The microstructure observation results for the manufactured PDCs reveal that elemental Co and W are present along the interface of the diamond particles. The fractions of Co and WC in the PDC increase as the initial particle size decreases. The manufactured PDCs are subjected to thermal shock tests at two temperatures of 780°C and 830°C. The results reveal that the PDC with a smaller particle size of diamond easily produces microscale thermal cracks. This is mainly because of the abundant presence of Co and WC phases along the diamond interface and the easy formation of Co-based (CoO, Co3O4) and W-based (WO2) oxides in the PDC using smaller diamond particles. The microstructural factors for controlling the thermal shock property of PDC material are also discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- From abrasion to spallation: Stress-dependent transition of wear mechanisms in polycrystalline diamond governed by grain architecture
Di Xu, Lifen Deng, Xiwei Cui, Shuai Hou, Jialin Li, Xiaoling Li, Nan Jiang
Diamond and Related Materials.2026; 163: 113417. CrossRef - Effects of initial diamond particle size on the comprehensive mechanical properties of PDC
Xueqi Wang, Jianbo Tu, Baochang Liu
Ceramics International.2025; 51(8): 10433. CrossRef - High-impact-resistant polycrystalline diamond compact cutters with double working layers
Xueqi Wang, Jianbo Tu, Baochang Liu
Diamond and Related Materials.2025; 152: 111906. CrossRef - The Influence of the Binder Phase on the Properties of High-Pressure Sintered Diamond Polycrystals or Composites for Cutting Tool Applications
Lucyna Jaworska
Materials.2025; 18(3): 634. CrossRef - HPHT sintering and performance investigation of PDC with different interfacial geometry substrates for trimodal diamond particle size
Jianbo Tu, Xueqi Wang, Haibo Zhang, Baochang Liu
Ceramics International.2024; 50(11): 19074. CrossRef - HPHT sintering and performance investigation of PDC with high stacking density by dual particle size diamond formulations
Jianbo Tu, Xueqi Wang, Baochang Liu
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2024; 124: 106802. CrossRef
- From abrasion to spallation: Stress-dependent transition of wear mechanisms in polycrystalline diamond governed by grain architecture
- [Korean]
- The Effect of Diffusion Barrier and thin Film Deposition Temperature on Change of Carbon Nanotubes Length
- Soon-kyu Hong, Hyung Woo Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;24(3):248-253. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.3.248

- 584 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we investigate the effect of the diffusion barrier and substrate temperature on the length of carbon nanotubes. For synthesizing vertically aligned carbon nanotubes, thermal chemical vapor deposition is used and a substrate with a catalytic layer and a buffer layer is prepared using an e-beam evaporator. The length of the carbon nanotubes synthesized on the catalytic layer/diffusion barrier on the silicon substrate is longer than that without a diffusion barrier because the diffusion barrier prevents generation of silicon carbide from the diffusion of carbon atoms into the silicon substrate. The deposition temperature of the catalyst and alumina are varied from room temperature to 150°C, 200°C, and 250°C. On increasing the substrate temperature on depositing the buffer layer on the silicon substrate, shorter carbon nanotubes are obtained owing to the increased bonding force between the buffer layer and silicon substrate. The reason why different lengths of carbon nanotubes are obtained is that the higher bonding force between the buffer layer and the substrate layer prevents uniformity of catalytic islands for synthesizing carbon nanotubes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study on Residual Powder Removing Technique of Multi-Layered Graphene Based on Graphene One-Step Transfer Process
Chae-young Woo, Yeongsu Jo, Soon-kyu Hong, Hyung Woo Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(1): 11. CrossRef - Fabrication of robust, ultrathin and light weight, hydrophilic, PVDF-CNT membrane composite for salt rejection
Vivek Dhand, Soon Kyu Hong, Luhe Li, Jong-Man Kim, Soo Hyung Kim, Kyong Yop Rhee, Hyung Woo Lee
Composites Part B: Engineering.2019; 160: 632. CrossRef
- A Study on Residual Powder Removing Technique of Multi-Layered Graphene Based on Graphene One-Step Transfer Process
- [Korean]
- The Preparation of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell Paste Used the Peroxo Titanium Complex and Characteristics by Annealing Temperature
- Hyunsu Park, Soyeong Joo, Joon-Phil Choi, Woo-Byoung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(6):396-402. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.6.396

- 1,018 View
- 6 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The organic binder-free paste for dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC) has been investigated using peroxo titanium complex. The crystal structure of TiO2 nanoparticles, morphology of TiO2 film and electrical properties are analyzed by X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Electrochemical Impedance Spectra (EIS), and solar simulator. The synthesized TiO2 nanopowders by the peroxo titanium complex at 150, 300, 400°C, and 450°C have anatase phase and average crystal sizes are calculated to be 4.2, 13.7, 16.9, and 20.9 nm, respectively. The DSSC prepared by the peroxo titanium complex binder have higher Voc and lower Jsc values than that of the organic binder. It can be attributed to improvement of sintering properties of TCO/TiO2 and TiO2/TiO2 interface and to formation of agglomerate by the nanoparticles. As a result, we have investigated the organic binder-free paste and 3.178% conversion efficiency of the DSSC at 450°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Eco-Friendly Ag Embedded Peroxo Titanium Complex Solution Based Thin Film and Electrical Behaviors of Resistive Random Access Memory
Won Jin Kim, Jinho Lee, Ryun Na Kim, Donghee Lee, Woo-Byoung Kim
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2024; 34(3): 152. CrossRef - Development of eco-friendly thin film manufacturing process using poeroxo titanium complex solution and potential for resistive random access memory
Jinho Lee, Ryun Na Kim, Kee-Ryung Park, Woo-Byoung Kim
Applied Surface Science.2021; 562: 150170. CrossRef - Preparation of ultra-thin TiO2 shell by peroxo titanium complex (PTC) solution-based green surface modification, and photocatalytic activity of homo-core/shell TiO2
Jinho Lee, Jiyong Hwang, Hyunsu Park, Tohru Sekino, Woo-Byoung Kim
Applied Surface Science.2021; 540: 148399. CrossRef - Effects of Annealing Temperature on the Crystal Structure, Morphology, and Optical Properties of Peroxo-Titanate Nanotubes Prepared by Peroxo-Titanium Complex Ion
Hyunsu Park, Tomoyo Goto, Sunghun Cho, Soo Wohn Lee, Masato Kakihana, Tohru Sekino
Nanomaterials.2020; 10(7): 1331. CrossRef - Study on thermal behavior of Ammonium Hexafluofide Titanate for Synthesis of TiO2 Powders
Duk-Hee Lee, Jae-Ryang Park, Chan-Gi Lee, Kyung-Soo Park, Hyeon-Mo Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(5): 353. CrossRef
- Development of Eco-Friendly Ag Embedded Peroxo Titanium Complex Solution Based Thin Film and Electrical Behaviors of Resistive Random Access Memory
- [Korean]
- Superconducting Properties and Phase Formation of MgB2 Superconductors Prepared by the Solid State Reaction Method using MgB4 and Mg Powder
- Hyeondeok Jeonga, Chan-Joong Kim, Byung-Hyuk Jun, Seolhyang Kim, Hai-Woong Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(5):344-349. Published online October 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.5.344
- 688 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
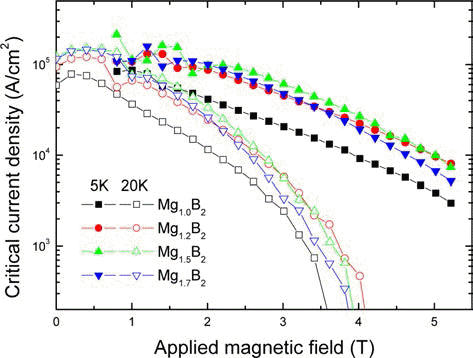
PDF MgB2 bulk superconductors are synthesized by the solid state reaction of (MgB4+xMg) precursors with excessive Mg compositions (x=1.0, 1.4, 2.0 and 2.4). The MgB4 precursors are synthesized using (Mg+B) powders. The secondary phases (MgB4 and MgO) present in the synthesized MgB4 are removed by HNO3 leaching. It is found that the formation reaction of MgB2 is accelerated when Mg excessive compositions are used. The magnetization curves of Mg1+xB2 samples show that the transition from the normal state to the superconducting state of the Mg excessive samples with x=0.5 and x=0.7 are sharper than that of MgB2. The highest
J c-B curve at 5 K and 20 K is achieved for x=0.5. Further addition of Mg decreases theJ c owing to the formation of more pores in the MgB2 matrix and smaller volume fraction of MgB2.
- [Korean]
- Influence of Oxidation Temperatures on the Structure and the Microstructure of GaN MOCVD Scraps
- Hyun Seon Hong, Joong Woo Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(4):278-282. Published online August 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.4.278

- 1,029 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The GaN-powder scrap generated in the manufacturing process of LED contains significant amounts of gallium. This waste can be an important resource for gallium through recycling of scraps. In the present study, the influence of annealing temperatures on the structural properties of GaN powder was investigated when the waste was recycled through the mechanochemical oxidation process. The annealing temperature varied from 200°C to 1100°C and the changes in crystal structure and microstructure were studied. The annealed powder was characterized using various analytical tools such as TGA, XRD, SEM, and XRF. The results indicate that GaN structure was fully changed to Ga2O3 structure when annealed above 900°C for 2 h. And, as the annealing temperature increased, crystallinity and particle size were enhanced. The increase in particle size of gallium oxide was possibly promoted by powder-sintering which merged particles to larger than 50 nm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High-temperature thermo-mechanical behavior of functionally graded materials produced by plasma sprayed coating: Experimental and modeling results
Kang Hyun Choi, Hyun-Su Kim, Chang Hyun Park, Gon-Ho Kim, Kyoung Ho Baik, Sung Ho Lee, Taehyung Kim, Hyoung Seop Kim
Metals and Materials International.2016; 22(5): 817. CrossRef
- High-temperature thermo-mechanical behavior of functionally graded materials produced by plasma sprayed coating: Experimental and modeling results
- [Korean]
- Evaluation of Material Characteristics with Sintering Temperature in Ti2AlC MAX Phase Material using Spark Plasma Sintering Method
- Chang-Hun Lee, Gyung Rae Baek, Hee Sang Jung, Young-Keun Jeong, Myung Chang Kang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(3):175-180. Published online June 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.3.175

- 1,097 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, ternary compound Max Phase Ti2AlC material was mixed by 3D ball milling as a function of ball milling time. More than 99.5 wt% pure Ti2AlC was synthesized by using spark plasma sintering method at 1000, 1100, 1200, and 1300°C for 60 min. The material characteristics of synthesized samples were examined with relative density, hardness, and electrical conductivity as a function of sintering temperature. The phase composition of bulk was identified by X-ray diffraction. On the basis of FE-SEM result, a terraced structures which consists of several laminated layers were observed. And Ti2AlC bulk material obtained a vickers hardness of 5.1 GPa at the sintering temperature of 1100°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and reaction path of Ti‐Al‐C MAX phases by reaction with Ti‐Al intermetallic compounds and TiC
Hojun Lee, Si Yeon Kim, Young‐In Lee, Jongmin Byun
Journal of the American Ceramic Society.2023; 106(12): 7230. CrossRef
- Synthesis and reaction path of Ti‐Al‐C MAX phases by reaction with Ti‐Al intermetallic compounds and TiC
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Fe-Cr-Al Porous Metal with Sintering Temperature and Times
- Bon-Uk Koo, Su-in Lee, Dahee Park, Jung-Yeul Yun, Byoung-Kee Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(2):100-104. Published online April 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.2.100
- 819 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
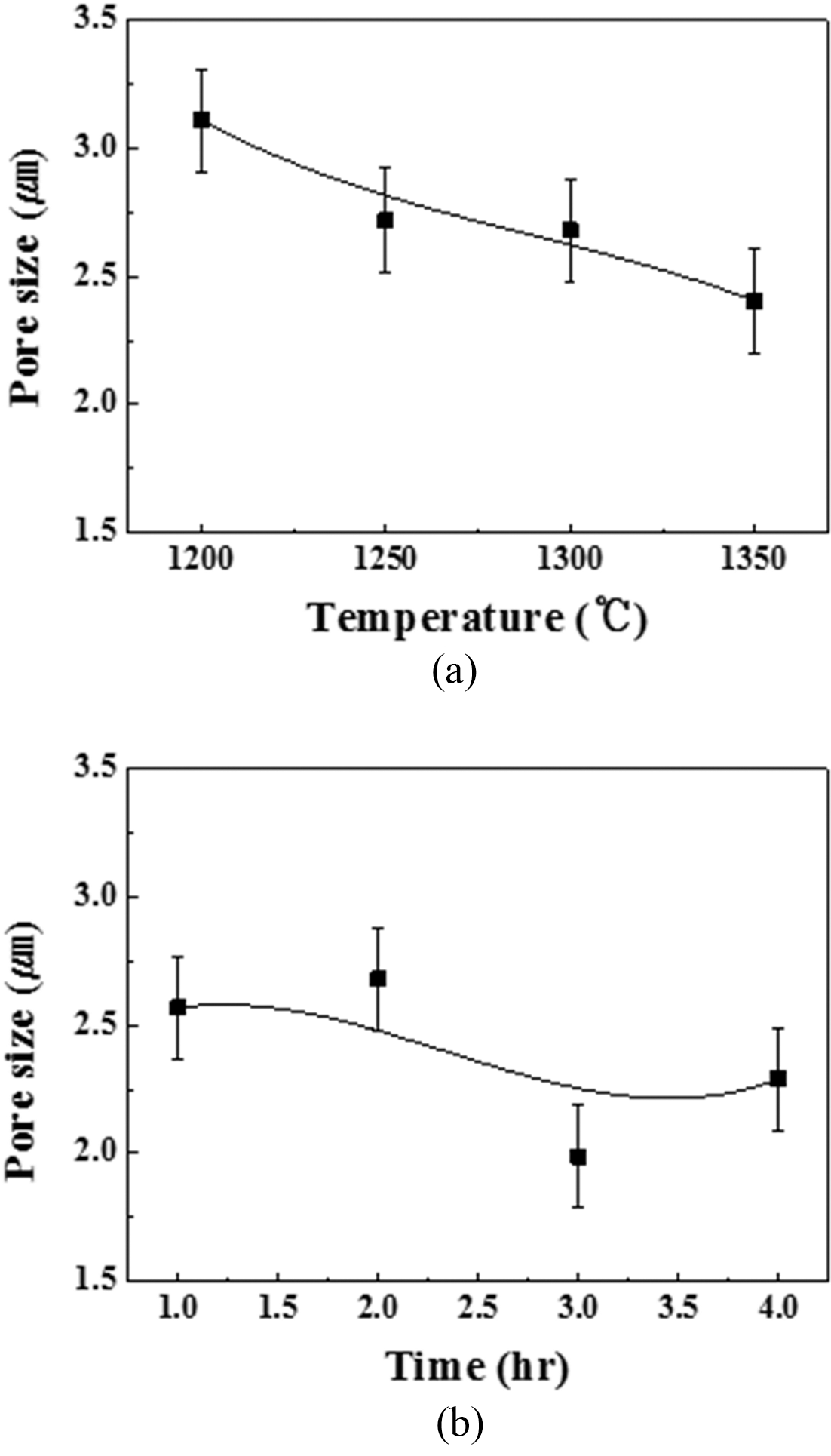
PDF The porous metals are known as relatively excellent characteristic such as large surface area, light, lower heat capacity, high toughness and permeability. The Fe-Cr-Al alloys have high corrosion resistance, heat resistance and chemical stability for high temperature applications. And then many researches are developed the Fe-Cr-Al porous metals for exhaust gas filter, hydrogen reformer catalyst support and chemical filter. In this study, the Fe-Cr-Al porous metals are developed with Fe-22Cr-6Al(wt) powder using powder compaction method. The mean size of Fe-22Cr-6Al(wt) powders is about 42.69 μm. In order to control pore size and porosity, Fe-Cr-Al powders are sintered at 1200~1450°C and different sintering maintenance as 1~4 hours. The powders are pressed on disk shapes of 3 mm thickness using uniaxial press machine and sintered in high vacuum condition. The pore properties are evaluated using capillary flow porometer. As sintering temperature increased, relative density is increased from 73% to 96% and porosity, pore size are decreased from 27 to 3.3%, from 3.1 to 1.8 μm respectively. When the sintering time is increased, the relative density is also increased from 76.5% to 84.7% and porosity, pore size are decreased from 23.5% to 15.3%, from 2.7 to 2.08 μm respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and Magnetic Hysteresis Properties of an Aluminum-Doped Isotropic Hard-Magnetic Fe–Cr–Co Powder Alloy
A. S. Ustyukhin, V. A. Zelensky, I. M. Milyaev, M. I. Alymov, A. A. Ashmarin, A. B. Ankudinov, K. V. Sergienko
Inorganic Materials: Applied Research.2024; 15(2): 480. CrossRef - Fabrication of a Porous Ni-Based Metal with a Multi-pore Structure by a Screen Printing Process
Yu-Jeong Yi, Min-Jeong Lee, Jung-Yeul Yun, Byoung-Kee Kim
Metals and Materials International.2019; 25(5): 1272. CrossRef
- Synthesis and Magnetic Hysteresis Properties of an Aluminum-Doped Isotropic Hard-Magnetic Fe–Cr–Co Powder Alloy
- [Korean]
- Effect of Deposition Temperature on the Property of Pyrolytic SiC Fabricated by the FBCVD Method
- Yeon-Ku Kim, Weon-Ju Kim, SungHwan Yeo, Moon-Sung Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(6):434-440. Published online December 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.6.434
- 892 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
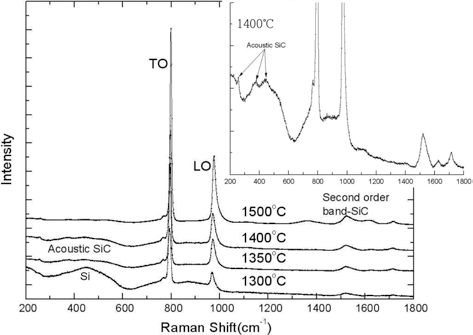
PDF Silicon carbide(SiC) layer is particularly important tri-isotropic (TRISO) coating layers because it acts as a miniature pressure vessel and a diffusion barrier to gaseous and metallic fission products in the TRISO coated particle. The high temperature deposition of SiC layer normally performed at 1500-1650°C has a negative effect on the property of IPyC layer by increasing its anisotropy. To investigate the feasibility of lower temperature SiC deposition, the influence of deposition temperature on the property of SiC layer are examined in this study. While the SiC layer coated at 1500°C obtains nearly stoichiometric composition, the composition of the SiC layer coated at 1300-1400°C shows discrepancy from stoichiometric ratio(1:1). 3-7 μm grain size of SiC layer coated at 1500°C is decreased to sub-micrometer (<1 μm) -2 μm grain size when coated at 1400°C, and further decreased to nano grain size when coated at 1300- 1350°C. Moreover, the high density of SiC layer (≥3.19 g/cm3) which is easily obtained at 1500°C coating is difficult to achieve at lower temperature owing to nano size pores. the density is remarkably decreased with decreasing SiC deposition temperature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High-temperature thermo-mechanical behavior of functionally graded materials produced by plasma sprayed coating: Experimental and modeling results
Kang Hyun Choi, Hyun-Su Kim, Chang Hyun Park, Gon-Ho Kim, Kyoung Ho Baik, Sung Ho Lee, Taehyung Kim, Hyoung Seop Kim
Metals and Materials International.2016; 22(5): 817. CrossRef
- High-temperature thermo-mechanical behavior of functionally graded materials produced by plasma sprayed coating: Experimental and modeling results
- [Korean]
- A Study of the Sintering Behavior of Boron Carbide using In-situ High Temperature Dilatometer
- Hyukjae Lee, Bum-Sup Kim, Tai-Joo Chung
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(2):102-107. Published online April 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.2.102

- 854 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A high temperature dilatometer attached to a graphite furnace is built and used to study the sintering behavior of B4C. Pristine and carbon doped B4C compacts are sintered at various soaking temperatures and their shrinkage profiles are detected simultaneously using the dilatometer. Carbon additions enhance the sinterability of B4C with sintering to more than 97% of the theoretical density, while pristine B4C compacts could not be sintered above 91% due to particle coarsening. The shrinkage profiles of B4C reveal that the effect of carbon on the sinterability of B4C can be seen mostly below 1950°C. The high temperature dilatometer delivers very useful information which is impossible to obtain with conventional furnaces.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Application of rate-controlled sintering into the study of sintering behavior of boron carbide
Hyukjae Lee
Journal of the Korean Crystal Growth and Crystal Technology.2015; 25(1): 6. CrossRef
- Application of rate-controlled sintering into the study of sintering behavior of boron carbide
- [Korean]
- Effect of Cell Size on the High Temperature Oxidation Properties of Fe-Cr-Al Powder Porous Metal Manufactured by Electro-spray Process
- Jae-Sung Oh, Young-Min Kong, Byoung-Kee Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(1):55-61. Published online February 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.1.55

- 999 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Fe-Cr-Al powder porous metal was manufactured by using new electro-spray process. First, ultra-fine fecralloy powders were produced by using the submerged electric wire explosion process. Evenly distributed colloid (0.05~0.5% powders) was dispersed on Polyurethane foam through the electro-spray process. And then degreasing and sintering processes were conduced. In order to examine the effect of cell size (200 μm, 450 μm, 500 μm) in process, pre-samples were sintered for two hours at temperature of 1450°C, in H2 atmospheres. A 24-hour thermo gravimetric analysis test was conducted at 1000°C in a 79% N2 + 21% O2 to investigate the high temperature oxidation behavior of powder porous metal. The results of the high temperature oxidation tests showed that oxidation resistance increased with increasing cell size. In the 200 μm porous metal with a thinner strut and larger specific surface area, the depletion of the stabilizing elements such as Al and Cr occurred more quickly during the high-temperature oxidation compared with the 450, 500 μm porous metals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of Open‐Cell Austenitic Stainless Steel Foam by Electrostatic Powder Spraying Process
Tae-Hoon Kang, Kyu-Sik Kim, Jung-Yeul Yun, Min-Jeong Lee, Kee-Ahn Lee
Advanced Engineering Materials.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Microstructure and High Temperature Oxidation Behaviors of Fe-Ni Alloys by Spark Plasma Sintering
Chae Hong Lim, Jong Seok Park, Sangsun Yang, Jung-Yeul Yun, Jin Kyu Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(1): 53. CrossRef - Effect of Al2O3 Inter-Layer Grown on FeCrAl Alloy Foam to Improve the Dispersion and Stability of NiO Catalysts
유진 이, 본율 구, 성호 백, 만호 박, 효진 안
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2015; 25(8): 391~397. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of Open‐Cell Austenitic Stainless Steel Foam by Electrostatic Powder Spraying Process
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


