Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [English]
- SnF2-Induced LiF Interphase for Stable Lithium Metal Anodes with Suppressed Dendrite Growth
- Yeong Hoon Jeon, Seul Ki Choi, Yun Seung Nah, Wonil Shin, Yong-Ho Choa, Minho Yang
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):212-221. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00164
- 1,785 View
- 55 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
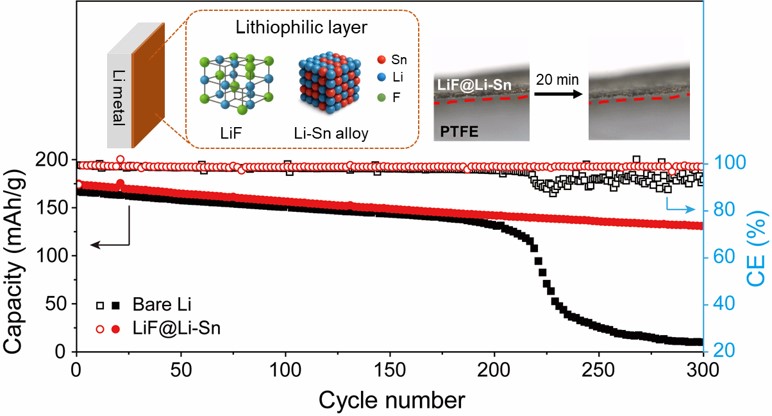
PDF - Lithium (Li) metal is a promising anode for next-generation batteries due to its high capacity, low redox potential, and low density. However, dendrite growth and interfacial instability limit its use. In this study, an artificial solid electrolyte interphase layer of LiF and Li-Sn (LiF@Li-Sn) was fabricated by spray-coating SnF2 onto Li. The LiF@Li-Sn anode exhibited improved air stability and electrochemical performance. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy indicated a charge transfer resistance of 25.2 Ω after the first cycle. In symmetric cells, it maintained a low overpotential of 27 mV after 250 cycles at 2 mA/cm2, outperforming bare Li. In situ microscopy confirmed dendrite suppression during plating. Full cells with NMC622 cathodes and LiF@Li-Sn anodes delivered 130.8 mAh/g with 79.4% retention after 300 cycles at 1 C and 98.8% coulombic efficiency. This coating effectively stabilized the interface and suppressed dendrites, with promising implications for practical lithium metal batteries.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI

 First
First Prev
Prev


