Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Effect of Deposition Parameters on the Property of Silicon Carbide Layer in Coated Particle Nuclear Fuels
- Yeon-Ku Kim, Weon-Ju Kim, SungHwan Yeo, Moon Sung Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(5):384-390. Published online October 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.5.384
- 558 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
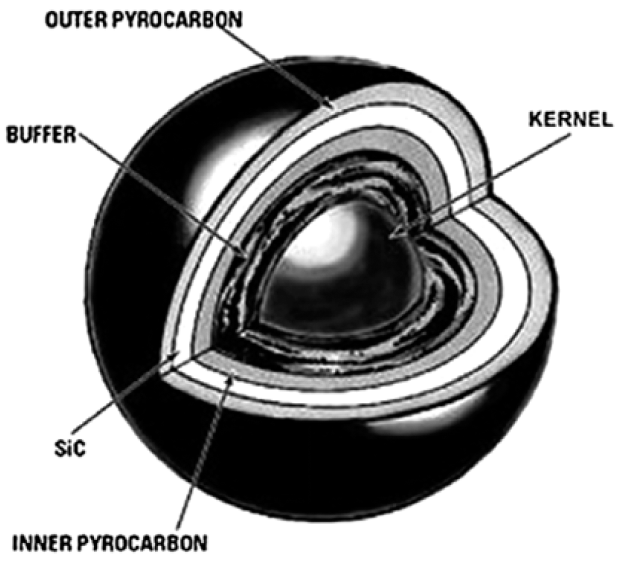
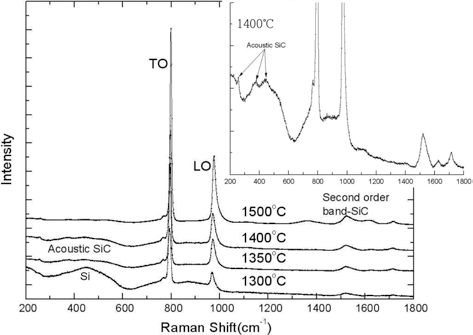
PDF Tri-isotropic (TRISO) coatings on zirconia surrogate beads are deposited using a fluidized-bed vapor deposition (FB-CVD) method. The silicon carbide layer is particularly important among the coated layers because it acts as a miniature pressure vessel and a diffusion barrier to gaseous and metallic fission products in the TRISO-coated particles. In this study, we obtain a nearly stoichiometric composition in the SiC layer coated at 1400°C, 1500°C, and 1400°C with 20 vol.% methyltrichlorosilane (MTS), However, the composition of the SiC layer coated at 1300-1350°C shows a difference from the stoichiometric ratio (1:1). The density decreases remarkably with decreasing SiC deposition temperature because of the nanosized pores. The high density of the SiC layer (≥ 3.19 g/cm2) easily obtained at 1500°C and 1400°C with 20 vol.% MTS did not change at an annealing temperature of 1900°C, simulating the reactor operating temperature. The evaluation of the mechanical properties is limited because of the inaccurate values of hardness and Young’s modulus measured by the nano-indentation method.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Deposition Temperature on the Property of Pyrolytic SiC Fabricated by the FBCVD Method
- Yeon-Ku Kim, Weon-Ju Kim, SungHwan Yeo, Moon-Sung Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(6):434-440. Published online December 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.6.434
- 897 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Silicon carbide(SiC) layer is particularly important tri-isotropic (TRISO) coating layers because it acts as a miniature pressure vessel and a diffusion barrier to gaseous and metallic fission products in the TRISO coated particle. The high temperature deposition of SiC layer normally performed at 1500-1650°C has a negative effect on the property of IPyC layer by increasing its anisotropy. To investigate the feasibility of lower temperature SiC deposition, the influence of deposition temperature on the property of SiC layer are examined in this study. While the SiC layer coated at 1500°C obtains nearly stoichiometric composition, the composition of the SiC layer coated at 1300-1400°C shows discrepancy from stoichiometric ratio(1:1). 3-7 μm grain size of SiC layer coated at 1500°C is decreased to sub-micrometer (<1 μm) -2 μm grain size when coated at 1400°C, and further decreased to nano grain size when coated at 1300- 1350°C. Moreover, the high density of SiC layer (≥3.19 g/cm3) which is easily obtained at 1500°C coating is difficult to achieve at lower temperature owing to nano size pores. the density is remarkably decreased with decreasing SiC deposition temperature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High-temperature thermo-mechanical behavior of functionally graded materials produced by plasma sprayed coating: Experimental and modeling results
Kang Hyun Choi, Hyun-Su Kim, Chang Hyun Park, Gon-Ho Kim, Kyoung Ho Baik, Sung Ho Lee, Taehyung Kim, Hyoung Seop Kim
Metals and Materials International.2016; 22(5): 817. CrossRef
- High-temperature thermo-mechanical behavior of functionally graded materials produced by plasma sprayed coating: Experimental and modeling results
- [Korean]
- Characteristics of the Ammonium Diuranate Powders Prepared with Different Experimental Apparatus in Sol-gel Process
- Yeon-Ku Kim, Kyung-Chai Jeong, Sung-Ho Ueom, Moon Sung Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2012;19(6):398-404.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2012.19.6.398

- 566 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This paper describes the spherical ammonium diuranate gel particles which are the intermediated material of the UO_2 microsphere for an VHTR(very high temperature reactor) nuclear fuel. The characteristics of the intermediate-ADU gel particles prepared by AWD(ageing, washing, and drying) and FB(fluidized-bed) apparatus were examined and compared in a sol-gel fabrication process. The electrical conductivity of washing filtrate from the FB treating and the surface area of dried-ADU gel particles were higher than those of AWD treating. Also, an internal pore volume in dried-ADU gel particles showed a more decrease in AWD treatment than FB treatment because of decomposition of PVA affected by the washing time. However, the internal microstructures of ADU gel particles were similar regardless of the process variation.
- [Korean]
- Effects of Process Parameters on the Powder Characteristics of Uranium Oxide Kernel Prepared by Sol-gel Process
- Yeon-Ku Kim, Kyung-Chai Jeong, Seung-Chul Oh, Dong-Soo Suhr, Moon-Sung Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(4):254-261.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.4.254

- 486 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, we investigated the unit process parameters in spherical UO_2 kernel preparation. Nearly perfect spherical UO_3 microspheres were obtained from the 0.6M of U-concentration in the broth solution, and the microstructure of the UO_2 kernel appeared the good results in the calcining, reducing, and sintering processes. For good sphericity, high density, suitable microstructure, and no-crack final UO_2 microspheres, the temperature control range in calcination process was 300sim450°C, and the microstructure, the pore structure, and the density of UO_2 kernel could be controlled in this temperature range. Also, the concentration changes of the ageing solution in aging step were not effective factor in the gelation of the liquid droplets, but the temperature change of the ageing solution was very sensitive for the final ADU gel particles.
- [Korean]
- Effects of Thermal Treatment Conditions on the Powder Characteristics of Uranium Oxide in HTGR Fuel Preparation
- Yeon-Ku Kim, Kyung-Chai Jeong, Seung-Chul Oh, Dong-Soo Suhr, Moon-Sung Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(2):115-121.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.2.115

- 719 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The effects of thermal treatment conditions on ADU (ammonium diuranate) prepared by SOL-GEL method, so-called GSP (Gel supported precipitation) process, were investigated for UO_2 kernel preparation. In this study, ADU compound particles were calcined to UO_3 particles in air and Ar atmospheres, and these UO_3 particles were reduced and sintered in 4%-H_2/Ar. During the thermal calcining treatment in air, ADU compound was slightly decomposed, and then converted to UO_3 phases at 500°C. At 600°C, the U_3O_8 phase appeared together with UO_3. After sintering of theses particles, the uranium oxide phases were reduced to a stoichiometric UO_2. As a result of the calcining treatment in Ar, more reduced-form of uranium oxide was observed than that treated in air atmosphere by XRD analysis. The final phases of these particles were estimated as a mixture of U_3O_7 and U_4O_9.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- UO2 Spheres Produce by External Gelation Process
Yeon-Ku Kim, Injin Sah, Eung Seon Kim
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2020; 30(10): 533. CrossRef - Effects of Process Parameters on the Powder Characteristics of Uranium Oxide Kernel Prepared by Sol-gel Process
Yeon-Ku Kim, Kyung-Chai Jeong, Seung-Chul Oh, Dong-Soo Suhr, Moon-Sung Cho
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2009; 16(4): 254. CrossRef
- UO2 Spheres Produce by External Gelation Process
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


