Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [English]
- Preparation of Flake-shape Cobalt Powders by High-Energy Ball Milling for rSOC Current Collectors
- Poong-Yeon Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Hyeon Ju Kim, Su-Jin Yun, Si Young Chang, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):383-389. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00241
- 446 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
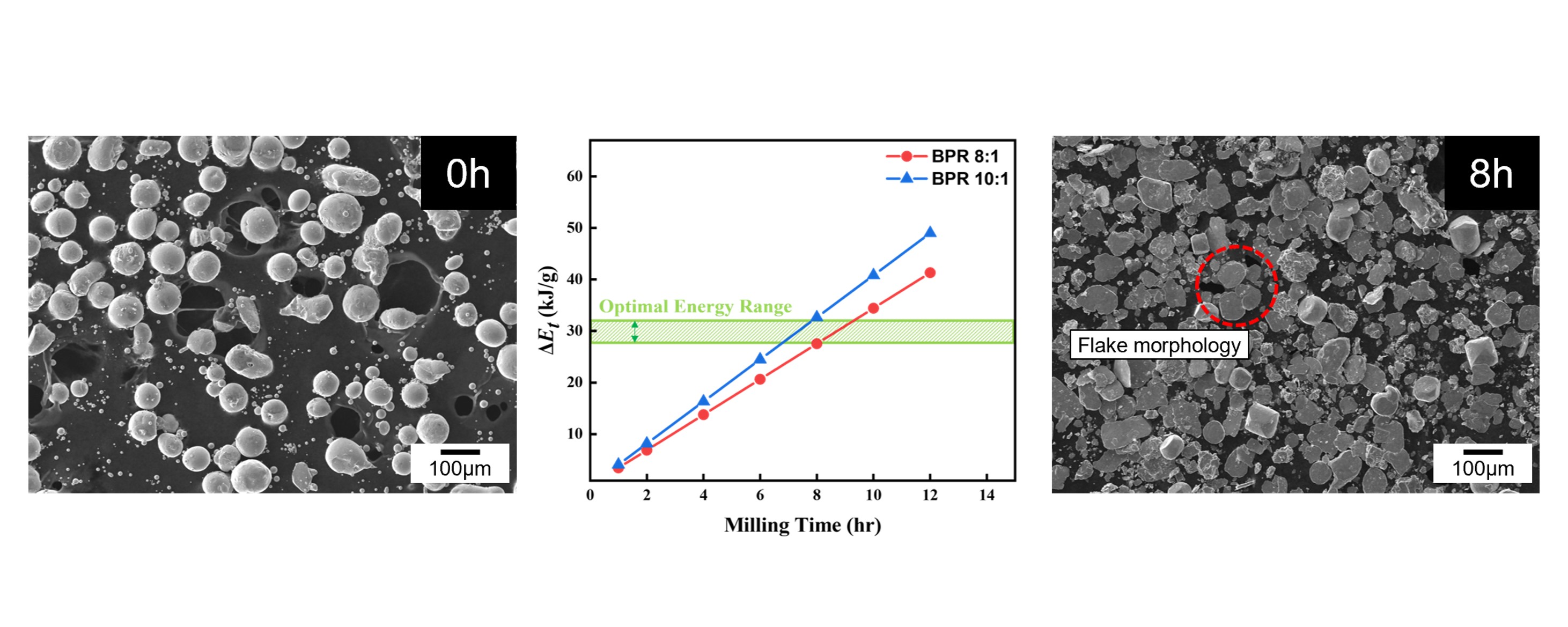
PDF - Reversible solid oxide cells (rSOCs), which enable two-way conversion between electricity and hydrogen, have gained attention with the rise of hydrogen energy. However, foam-type current collectors in rSOC stacks exhibit poor structural controllability and limited electrode contact area. To address these limitations, this study aimed to convert spherical cobalt powders into flake-type morphology via high-energy ball milling, as a preliminary step toward fabricating flake-based current collectors. Milling parameters—specifically, the ball-to-powder ratio (BPR), milling time, and process control agent (PCA) content—were varied. At an 8:1 BPR, over 90% of the powder became flake-shaped after 8 hours, while extended milling caused cold welding. In contrast, a 10:1 BPR resulted in dominant fragmentation. The Burgio–Rojac model quantified energy input and defined the optimal range for flake formation. Increasing the PCA to 4 wt% delayed flake formation to 16 hours and induced cold welding, as shown by bimodal particle size distributions. These results support the development of Co-based current collectors for use in rSOCs.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI

 First
First Prev
Prev


