Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
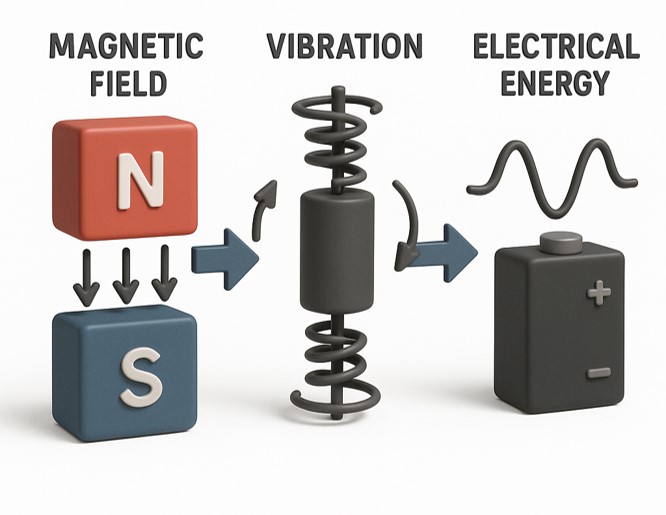
- Research Trends in Magneto-Mechano-Electric (MME) Energy Harvesting Devices
- So Ie Jeong, Geon-Tae Hwang
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):529-541. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00493
- 798 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Magneto-mechano-electric (MME) energy harvesters have emerged as a promising solution for maintenance-free power generation in rapidly expanding Internet of Things (IoT) environments, where replacing or wiring batteries is impractical. MME devices convert weak alternating magnetic fields, ubiquitous around power infrastructures, into useful electrical energy through sequential magnetic, mechanical, and electrical transduction processes. This review summarizes recent advances across triboelectric-, piezoelectric-, and hybrid MME architectures. Triboelectric MME generators employing nano-engineered polymer surfaces, flash-induced surface modification, and nanoscale pattern replication demonstrate low-cost fabrication routes while achieving significantly enhanced voltage and current outputs. Piezoelectric MME systems based on Mn-doped PMN-PZT single crystals highlight strategies for improving mechanical quality factors and resonance-driven power generation. Further, hybrid MME designs that integrate piezoelectric and electromagnetic induction mechanisms enable high-power outputs exceeding tens of milliwatts, sufficient to operate multifunctional IoT platforms and charge practical energy-storage devices. Collectively, these studies illustrate a transition of MME harvesting technologies from laboratory concepts to application-ready self-powered systems. Future opportunities lie in broadband resonance design, modular harvester integration, advanced power management, and multi-source hybridization for robust long-term operation in real environments.
- [Korean]
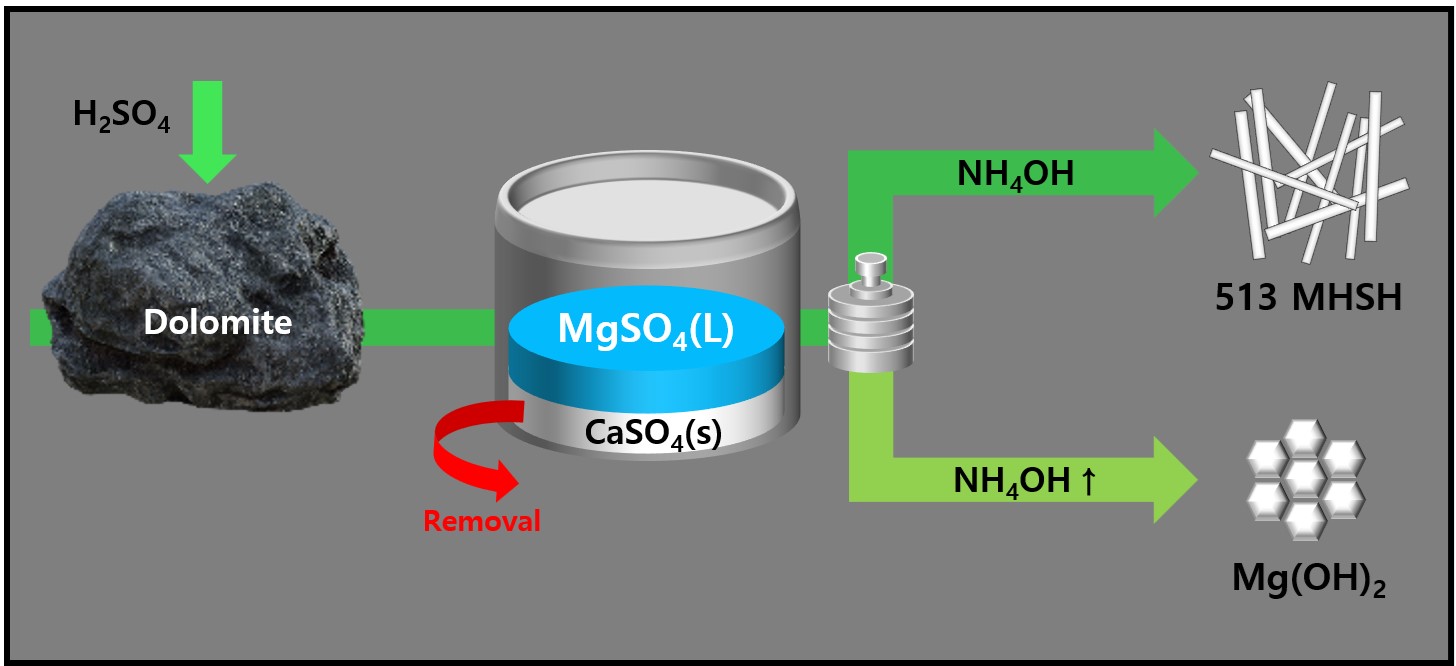
- Synthesis and Morphology Control of Needle Type 513 MHSH and Mg(OH)2 from Dolomite
- Jiyeon Kim, HyunSeung Shim, Seong-Ju Hwang, YooJin Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):399-405. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00227
- 445 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - 513 magnesium hydroxide sulfate hydrate (MHSH) and Mg(OH)₂ were synthesized by controlling the pH and concentration using a domestic resource, dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2), as the raw material. The MgSO₄ was extracted by treating dolomite with sulfuric acid under various conditions. Hexagonal plate-shaped Mg(OH)₂ and needle-like 513 MHSH were synthesized under the hydrothermal condition. The morphology of the synthesized materials was controlled by adjusting the pH (SO42-/OH- ratio) and hydrothermal reaction time. As the pH of the solution increased, the formation of plate-like structures became dominant, whereas lower pH values (higher SO42- concentration) led to needle-like forms. The results of the 513 MHSH, which was synthesized using reagents and sea bittern, are consistent with the synthesis conditions, and we observed changes in the length and aspect ratio of the needle-shaped structure in response to adjusting the hydrothermal reaction time.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Fe and Cr on ω Phase Formation in Metastable β-Ti Alloy
- Sun-Young Park, Young-Bum Chun
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):354-360. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00220

- 1,020 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the effects of Fe and Cr contents on ω phase formation and transformation during solution treatment and the subsequent aging process, for which four model alloys with varying Fe and Cr contents but keeping Mo equivalent of ~ 12.6 were prepared by plasma arc melting and fabricated into plates by hot forging followed by hot-rolling. The atherrmal ω phase was observed in all Ti alloys after solution treatment followed by water quenching through XRD and TEM analysis. The largest volume fraction of athermal ω phase is formed in Ti alloy with only Fe 4 wt.% among all Ti alloys, leading to the highest Vickers value due to hardening effect ω phase. It was found that not only Mo equivalent but also each characteristic of β stabilizing elements should be considered to understand a microstructure evolution and mechanical properties.
- [English]
- Epsilon Iron Oxide (ε-Fe2O3) as an Electromagnetic Functional Material: Properties, Synthesis, and Applications
- Ji Hyeong Jeong, Hwan Hee Kim, Jung-Goo Lee, Youn-Kyoung Baek
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):465-479. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00290

- 3,560 View
- 92 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Iron oxide (ε-Fe₂O₃) is emerging as a promising electromagnetic material due to its unique magnetic and electronic properties. This review focuses on the intrinsic properties of ε-Fe₂O₃, particularly its high coercivity, comparable to that of rare-earth magnets, which is attributed to its significant magnetic anisotropy. These properties render it highly suitable for applications in millimeter wave absorption and high-density magnetic storage media. Furthermore, its semiconducting behavior offers potential applications in photocatalytic hydrogen production. The review also explores various synthesis methods for fabricating ε-Fe₂O₃ as nanoparticles or thin films, emphasizing the optimization of purity and stability. By exploring and harnessing the properties of ε-Fe₂O₃, this study aims to contribute to the advancement of next-generation electromagnetic materials with potential applications in 6G wireless telecommunications, spintronics, high-density data storage, and energy technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Review of GPR Data Analysis for Bridge Deck Evaluation: From Conventional Methods to Emerging Artificial Intelligence Approaches
Babak Enami Alamdari, Yu Tang, Danilo Erricolo, Lesley H. Sneed
Journal of Nondestructive Evaluation.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemical Pressure Induced Strain Control of Magnetic Anisotropy in the Simple Perovskite ϵ-Fe2O3
Subir Roy, Gurleen K. Uppal, Alberto Acosta, Rachel Nickel, Charles A. Roberts, Johan van Lierop
Nano Letters.2026; 26(1): 34. CrossRef - Superparamagnetism of Baked Clays Containing Polymorphs of Iron Oxides: Experimental Study and Theoretical Modeling
Petr Kharitonskii, Andrei Krasilin, Nadezhda Belskaya, Svetlana Yanson, Nikita Bobrov, Andrey Ralin, Kamil Gareev, Nikita Zolotov, Dmitry Zaytsev, Elena Sergienko
Magnetochemistry.2025; 11(12): 103. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Review of GPR Data Analysis for Bridge Deck Evaluation: From Conventional Methods to Emerging Artificial Intelligence Approaches
- [English]
- Effect of Calcium Addition on the High-Temperature Recovery of Nd and Dy from Nd-Fe-B Scrap Using Mg-Based Extractants
- Hyoseop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):493-499. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00283

- 1,716 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated whether calcium (Ca) addition improved the recovery of neodymium (Nd) and dysprosium (Dy) from Nd-Fe-B magnet scrap using magnesium (Mg)-based liquid metal extraction (LME). Traditional LME processes are limited to temperatures up to 850 °C due to oxidation issues, reducing the efficiency of rare earth element (REE) recovery, especially for Dy. By adding 10 wt.% Ca to Mg and increasing the processing temperature to 1,000 °C, we achieved nearly 100% Nd and approximately 38% Dy recovery, compared to 91% and 28%, respectively, with pure Mg at 850 °C. However, excessive Ca addition (20 wt.%) decreased the recovery efficiency due to the formation of stable intermetallic compounds. These results highlight the critical role of Ca in optimizing REE recycling from Nd-Fe-B magnet scrap.
- [Korean]
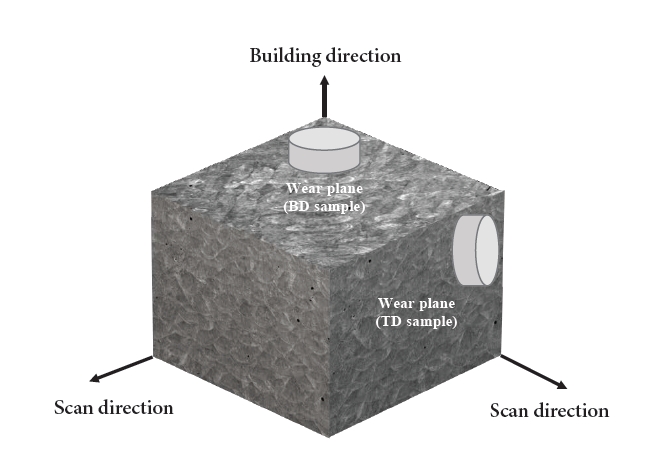
- Effect of Anisotropy on the Wear Behavior of Age-Treated Maraging Steel Manufactured by LPBF
- Seung On Lim, Se-Eun Shin
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):308-317. Published online August 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00171
- 2,141 View
- 38 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Maraging steel has excellent mechanical properties resulting from the formation of precipitates within the matrix through aging treatment. Maraging steel fabricated by the laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) process is suitable for applications including precise components and optimized design. The anisotropic characteristic, which depends on the stacking direction, affects the mechanical properties. This study aimed to analyze the influence of anisotropy on the wear behavior of maraging steel after aging treatment. The features of additive manufacturing tended to disappear after heat treatment. However, some residual cellular and dendrite structures were observed. In the wear tests, a high wear rate was observed on the building direction plane for all counter materials. This is believed to be because the oxides formed on the wear track positively affected the wear characteristics; meanwhile, the bead shape in the stacking direction surface was vulnerable to wear, leading to significant wear.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unveiling age-hardening mechanisms: first-principles carbide insights and enhanced thermomechanical fatigue in niobium-bearing austenitic stainless steels
Godwin Kwame Ahiale, Jin Woong Park, Raj Narayan Hajra, Yong-Jun Oh, Won Doo Choi, Tae-Wook Na, Gi Yong Kim, Hyun-Ju Choi, Jeoung Han Kim
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 949: 149397. CrossRef - A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 390. CrossRef
- Unveiling age-hardening mechanisms: first-principles carbide insights and enhanced thermomechanical fatigue in niobium-bearing austenitic stainless steels
- [Korean]
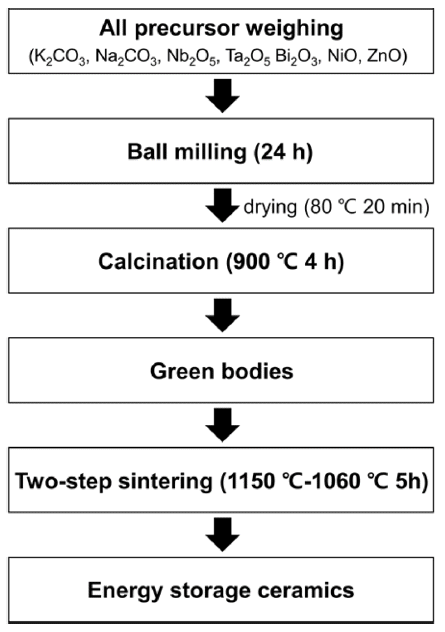
- Modulation of Microstructure and Energy Storage Performance in (K,Na)NbO3-Bi(Ni,Ta)O3 Ceramics through Zn Doping
- Jueun Kim, Seonhwa Park, Yuho Min
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):509-515. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.509
- 917 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Lead-free perovskite ceramics, which have excellent energy storage capabilities, are attracting attention owing to their high power density and rapid charge-discharge speed. Given that the energy-storage properties of perovskite ceramic capacitors are significantly improved by doping with various elements, modifying their chemical compositions is a fundamental strategy. This study investigated the effect of Zn doping on the microstructure and energy storage performance of potassium sodium niobate (KNN)-based ceramics. Two types of powders and their corresponding ceramics with compositions of (1-x)(K,Na)NbO3-xBi(Ni2/3Ta1/3)O3 (KNN-BNT) and (1-x)(K,Na)NbO3-xBi(Ni1/3Zn1/3Ta1/3) O3 (KNN-BNZT) were prepared via solid-state reactions. The results indicate that Zn doping retards grain growth, resulting in smaller grain sizes in Zn-doped KNN-BNZT than in KNN-BNT ceramics. Moreover, the Zn-doped KNNBNZT ceramics exhibited superior energy storage density and efficiency across all x values. Notably, 0.9KNN-0.1BNZT ceramics demonstrate an energy storage density and efficiency of 0.24 J/cm3 and 96%, respectively. These ceramics also exhibited excellent temperature and frequency stability. This study provides valuable insights into the design of KNNbased ceramic capacitors with enhanced energy storage capabilities through doping strategies.
- [Korean]
- Formation of Phases and Mechanical Properties of YSZ-Based Thermal Barrier Coating Materials Doped with Rare Earth Oxides
- Yong Seok Choi, Gye Won Lee, Sahn Nahm, Yoon suk Oh
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(5):402-408. Published online October 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.5.402
- 1,818 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
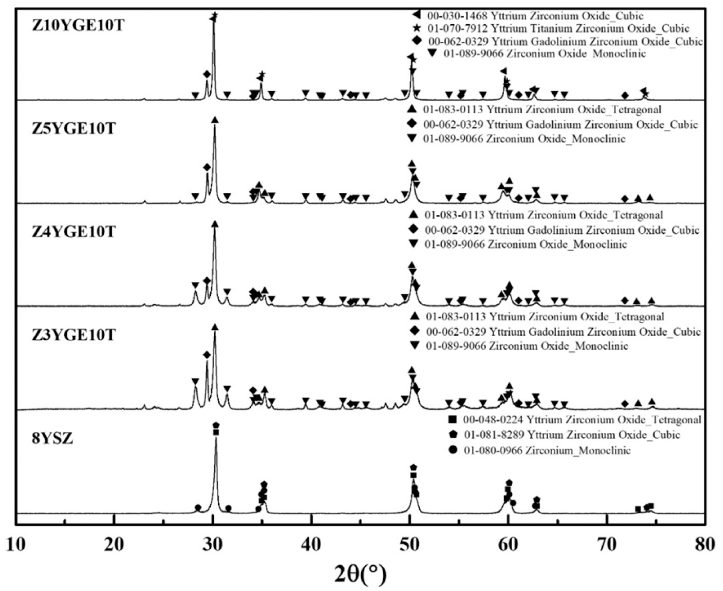
PDF This study focused on improving the phase stability and mechanical properties of yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ), commonly utilized in gas turbine engine thermal barrier coatings, by incorporating Gd2O3, Er2O3, and TiO2. The addition of 3-valent rare earth elements to YSZ can reduce thermal conductivity and enhance phase stability while adding the 4-valent element TiO2 can improve phase stability and mechanical properties. Sintered specimens were prepared with hot-press equipment. Phase analysis was conducted with X-ray diffraction (XRD), and mechanical properties were assessed with Vickers hardness equipment. The research results revealed that, except for Z10YGE10T, most compositions predominantly exhibited the t-phase. Increasing the content of 3-valent rare earth oxides resulted in a decrease in the monoclinic phase and an increase in the tetragonal phase. In addition, the t(400) angle decreased while the t(004) angle increased. The addition of 10 mol% of 3-valent rare-earth oxides discarded the t-phase and led to the complete development of the c-phase. Adding 10 mol% TiO2 increased hardness than YSZ.
- [Korean]
- Size Control of Iron Oxide (Fe3O4) Nanoclusters according to Reaction Factors and Consequent Change in Their Magnetic Attraction
- Sanghoon Lee, Arim Byun, Jin-sil Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):297-304. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.297
- 1,075 View
- 13 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
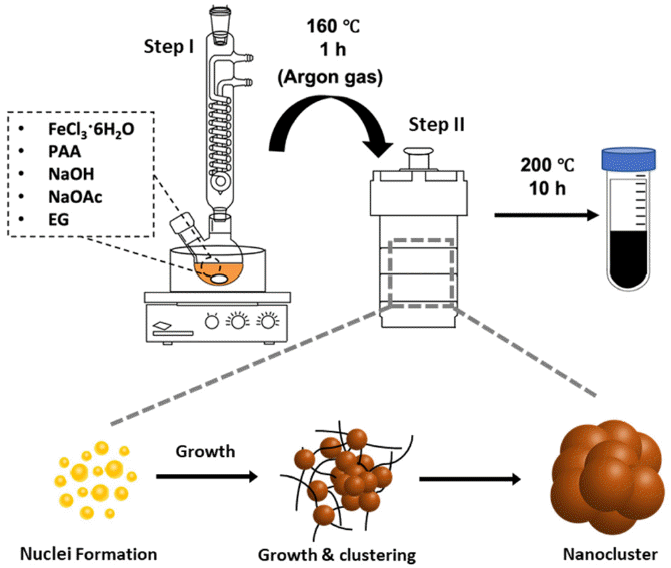
PDF Iron oxide (Fe2O3) nanoclusters exhibit significant potential in the biomedical and pharmaceutical fields due to their strong magnetic properties, stability in solutions, and compatibility with living systems. They excel in magnetic separation processes, displaying high responsiveness to external magnetic fields. In contrast to conventional Fe2O3 nanoparticles that can aggregate in aqueous solutions due to their ferrimagnetic properties, these nanoclusters, composed of multiple nanoparticles, maintain their magnetic traits even when scaled to hundreds of nanometers. In this study, we develop a simple method using solvothermal synthesis to precisely control the size of nanoclusters. By adjusting precursor materials and reducing agents, we successfully control the particle sizes within the range of 90 to 420 nm. Our study not only enhances the understanding of nanocluster creation but also offers ways to improve their properties for applications such as magnetic separation. This is supported by our experimental results highlighting their size-dependent magnetic response in water. This study has the potential to advance both the knowledge and practical utilization of Fe2O3 nanoclusters in various applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enzymatic properties of iron oxide nanoclusters and their application as a colorimetric glucose detection probe
Dahyun Bae, Minhee Kim, Jin-sil Choi
RSC Advances.2025; 15(6): 4573. CrossRef
- Enzymatic properties of iron oxide nanoclusters and their application as a colorimetric glucose detection probe
- [Korean]
- Effect of WC Particle Size on the Microstructure, Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Ag/WC Sintered Electrical Contact Material
- Soobin Kim, So-Yeon Park, Jong-Bin Lim, Soon Ho Kwon, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):242-248. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.242
- 967 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
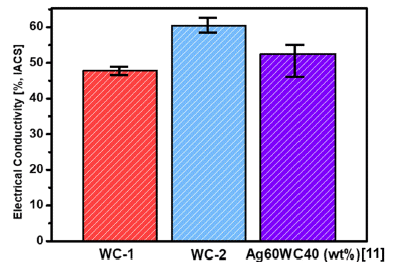
PDF The Ag/WC electrical contacts were prepared via powder metallurgy using 60 wt% Ag, 40 wt% WC, and small amounts of Co3O4 with varying WC particle sizes. After the fabrication of the contact materials, microstructure observations confirmed that WC-1 had an average grain size (AGS) of 0.27 μm, and WC-2 had an AGS of 0.35 μm. The Ag matrix in WC-1 formed fine grains, whereas a significantly larger and continuous growth of the Ag matrix was observed in WC-2. This indicates the different flow behaviors of liquid Ag during the sintering process owing to the different WC sizes. The electrical conductivities of WC-1 and WC-2 were 47.8% and 60.4%, respectively, and had a significant influence on the Ag matrix. In particular, WC-2 exhibited extremely high electrical conductivity owing to its large and continuous Ag-grain matrix. The yield strengths of WC-1 and WC-2 after compression tests were 349.9 MPa and 280.7 MPa, respectively. The high yield strength of WC-1 can be attributed to the Hall–Petch effect, whereas the low yield strength of WC-2 can be explained by the high fraction of high-angle boundaries (HAB) between the WC grains. Furthermore, the relationships between the microstructure, electrical/mechanical properties, and deformation mechanisms were evaluated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhanced Epoxy Composites Reinforced by 3D-Aligned Aluminum Borate Nanowhiskers
Hyunseung Song, Kiho Song, Haejin Hwang, Changui Ahn
Materials.2024; 17(19): 4727. CrossRef
- Enhanced Epoxy Composites Reinforced by 3D-Aligned Aluminum Borate Nanowhiskers
- [Korean]
- Effect of Acid Leaching Conditions on the Properties of Cr Powder Produced by Self-propagating High-temperature Synthesis
- YongKwan Lee, YeongWoo Cho, ShinYoung Choi, SungGue Heo, Ju Won, KyoungTae Park, MiHye Lee, JaeJin Sim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):233-241. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.233

- 768 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we evaluated the effects of acid leaching on the properties of Cr powder synthesized using self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS). Cr powder was synthesized from a mixture of Cr2O3 and magnesium (Mg) powders using the SHS Process, and the byproducts after the reaction were removed using acid leaching. The properties of the recovered Cr powder were analyzed via X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), particle size analysis (PSA), and oxygen content analysis. The results show that perfect selective leaching of Cr is challenging because of various factors such as incomplete reaction, reaction kinetics, the presence of impurities, and incompatibility between the acid and metal mixture. Therefore, this study provides essential information on the properties under acidic conditions during the production of high-quality Cr powder using a self-propagating high-temperature synthesis method.
- [Korean]
- Prediction of Crack Density in additive manufactured AA7075 Alloy Reinforced with ZrH2 inoculant via Response Surface Method
- Jeong Ah Lee, Jungho Choe, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):203-209. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.203
- 2,141 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
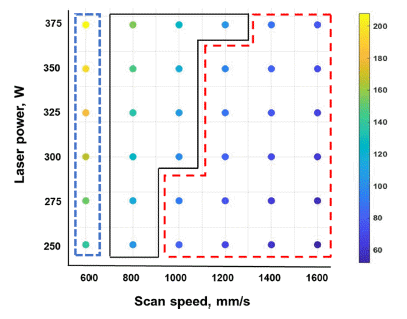
PDF Aluminum alloy-based additive manufacturing (AM) has emerged as a popular manufacturing process for the fabrication of complex parts in the automotive and aerospace industries. The addition of an inoculant to aluminum alloy powder has been demonstrated to effectively reduce cracking by promoting the formation of equiaxed grains. However, the optimization of the AM process parameters remains challenging owing to their variability. In this study, the response surface methodology (RSM) was used to predict the crack density of AM-processed Al alloy samples. RSM was performed by setting the process parameters and equiaxed grain ratio, which influence crack propagation, as independent variables and designating crack density as a response variable. The RSM-based quadratic polynomial models for crack-density prediction were found to be highly accurate. The relationship among the process parameters, crack density, and equiaxed grain fraction was also investigated using RSM. The findings of this study highlight the efficacy of RSM as a reliable approach for optimizing the properties of AM-processed parts with limited experimental data. These results can contribute to the development of robust AM processing strategies for the fabrication of highquality Al alloy components for various applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synergistic strengthening of crack-free Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys with hierarchical microstructures achieved via laser powder bed fusion
Jungho Choe, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park, Hyomoon Joo, Sang Guk Jeong, Eun Seong Kim, Soung Yeoul Ahn, Gang Hee Gu, Hyoung Seop Kim
Materials Research Letters.2024; 12(8): 598. CrossRef
- Synergistic strengthening of crack-free Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys with hierarchical microstructures achieved via laser powder bed fusion
- [Korean]
- Effect of Substrate Pre-heating on Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Nd-Fe-B Permanent Magnet Manufactured by L-PBF
- Yeon Woo Kim, Haeum Park, Tae-Hoon Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Yoon Suk Choi, Jeong Min Park
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(2):116-122. Published online April 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.2.116

- 1,170 View
- 17 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Because magnets fabricated using Nd-Fe-B exhibit excellent magnetic properties, this novel material is used in various high-tech industries. However, because of the brittleness and low formability of Nd-Fe-B magnets, the design freedom of shapes for improving the performance is limited based on conventional tooling and postprocessing. Laserpowder bed fusion (L-PBF), the most famous additive manufacturing (AM) technique, has recently emerged as a novel process for producing geometrically complex shapes of Nd-Fe-B parts owing to its high precision and good spatial resolution. However, because of the repeated thermal shock applied to the materials during L-PBF, it is difficult to fabricate a dense Nd-Fe-B magnet. In this study, a high-density (>96%) Nd-Fe-B magnet is successfully fabricated by minimizing the thermal residual stress caused by substrate heating during L-PBF.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef - Linkage between process-induced microstructure and magnetic property of Nd-Fe-B permanent magnets additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Yeon Woo Kim, Sujin Lee, Yoona Lee, Jae Bok Seol, Namhyun Kang, Yoon Suk Choi, Ji-Hun Yu, Jung-Goo Lee, Tae-Hoon Kim, Jeong Min Park
Materials & Design.2025; 259: 114929. CrossRef
- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- [Korean]
- Effect of Post Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal Coating Layers Fabricated by High Velocity Oxygen Fuel Thermal Spray Process on Ag Substrate
- So-Yeon Park, Seong-June Youn, Jae-Sung Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(4):283-290. Published online August 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.4.283

- 1,174 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A Cu-15Ag-5P filler metal (BCuP-5) is fabricated on a Ag substrate using a high-velocity oxygen fuel (HVOF) thermal spray process, followed by post-heat treatment (300°C for 1 h and 400°C for 1 h) of the HVOF coating layers to control its microstructure and mechanical properties. Additionally, the microstructure and mechanical properties are evaluated according to the post-heat treatment conditions. The porosity of the heat-treated coating layers are significantly reduced to less than half those of the as-sprayed coating layer, and the pore shape changes to a spherical shape. The constituent phases of the coating layers are Cu, Ag, and Cu-Ag-Cu3P eutectic, which is identical to the initial powder feedstock. A more uniform microstructure is obtained as the heat-treatment temperature increases. The hardness of the coating layer is 154.6 Hv (as-sprayed), 161.2 Hv (300°C for 1 h), and 167.0 Hv (400°C for 1 h), which increases with increasing heat-treatment temperature, and is 2.35 times higher than that of the conventional cast alloy. As a result of the pull-out test, loss or separation of the coating layer rarely occurs in the heat-treated coating layer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation and Prediction of Mechanical Properties According to Welding Methods of Ni 825/A516-70N Clad Plates
Cheolhong Hwang, Jeongseok Oh, Jini Park, Myungwoo Joe, Sunhwan Kim, Kyunghoon Yoo, Sungwoong Kim, Youngjoo Kim, Sangyeob Lee, Joonsik Park
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2024; 62(11): 844. CrossRef
- Evaluation and Prediction of Mechanical Properties According to Welding Methods of Ni 825/A516-70N Clad Plates
- [Korean]
- Fabrication, Microstructure and Adhesion Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal/Ag Plate Clad Material by Using High Velocity Oxygen Fuel Thermal Spray Process
- Yeun A Joo, Yong-Hoon Cho, Jae-Sung Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(3):226-232. Published online June 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.3.226

- 941 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, a new manufacturing process for a multilayer-clad electrical contact material is suggested. A thin and dense BCuP-5 (Cu-15Ag-5P filler metal) coating layer is fabricated on a Ag plate using a high-velocity oxygen-fuel (HVOF) process. Subsequently, the microstructure and bonding properties of the HVOF BCuP-5 coating layer are evaluated. The thickness of the HVOF BCuP-5 coating layer is determined as 34.8 μm, and the surface fluctuation is measured as approximately 3.2 μm. The microstructure of the coating layer is composed of Cu, Ag, and Cu-Ag-Cu3P ternary eutectic phases, similar to the initial BCuP-5 powder feedstock. The average hardness of the coating layer is 154.6 HV, which is confirmed to be higher than that of the conventional BCuP-5 alloy. The pull-off strength of the Ag/BCup-5 layer is determined as 21.6 MPa. Thus, the possibility of manufacturing a multilayer-clad electrical contact material using the HVOF process is also discussed.
- [Korean]
- Recycling of Hardmetal Tool through Alkali Leaching Process and Fabrication Process of Nano-sized Tungsten Carbide Powder using Self-propagation High-temperature Synthesis
- Hee-Nam Kang, Dong Il Jeong, Young Il Kim, In Yeong Kim, Sang Cheol Park, Cheol Woo Nam, Seok-Jun Seo, Jin Yeong Lee, Bin Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):47-55. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.47

- 1,434 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tungsten carbide is widely used in carbide tools. However, its production process generates a significant number of end-of-life products and by-products. Therefore, it is necessary to develop efficient recycling methods and investigate the remanufacturing of tungsten carbide using recycled materials. Herein, we have recovered 99.9% of the tungsten in cemented carbide hard scrap as tungsten oxide via an alkali leaching process. Subsequently, using the recovered tungsten oxide as a starting material, tungsten carbide has been produced by employing a self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) method. SHS is advantageous as it reduces the reaction time and is energy-efficient. Tungsten carbide with a carbon content of 6.18 wt % and a particle size of 116 nm has been successfully synthesized by optimizing the SHS process parameters, pulverization, and mixing. In this study, a series of processes for the highefficiency recycling and quality improvement of tungsten-based materials have been developed.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Characteristics of Ag-SnO2-Bi2O3 Contact Materials by Powder Compaction
- Jin Kyu Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):41-46. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.41
- 545 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we report the microstructure and characteristics of Ag-SnO2-Bi2O3 contact materials using a controlled milling process with a subsequent compaction process. Using magnetic pulsed compaction (MPC), the milled Ag-SnO2-Bi2O3 powders have been consolidated into bulk samples. The effects of the compaction conditions on the microstructure and characteristics have been investigated in detail. The nanoscale SnO2 phase and microscale Bi2O3 phase are well-distributed homogeneously in the Ag matrix after the consolidation process. The successful consolidation of Ag-SnO2-Bi2O3 contact materials was achieved by an MPC process with subsequent atmospheric sintering, after which the hardness and electrical conductivity of the Ag-SnO2-Bi2O3 contact materials were found to be 62–75 HV and 52–63% IACS, respectively, which is related to the interfacial stability between the Ag matrix, the SnO2 phase, and the Bi2O3 phase.
- [Korean]
- Recent Advances in Soft Magnetic Actuators and Sensors using Magnetic Particles
- Hyeonseo Song, Hajun Lee, Junghyo Kim, Jiyun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):509-517. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.509

- 948 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Smart materials capable of changing their characteristics in response to stimuli such as light, heat, pH, and electric and magnetic fields are promising for application to flexible electronics, soft robotics, and biomedicine. Compared with conventional rigid materials, these materials are typically composed of soft materials that improve the biocompatibility and allow for large and dynamic deformations in response to external environmental stimuli. Among them, smart magnetic materials are attracting immense attention owing to their fast response, remote actuation, and wide penetration range under various conditions. In this review, we report the material design and fabrication of smart magnetic materials. Furthermore, we focus on recent advances in their typical applications, namely, soft magnetic actuators, sensors for self-assembly, object manipulation, shape transformation, multimodal robot actuation, and tactile sensing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advanced Magnetic Actuation: Harnessing the Dynamics of Sm2Fe17–xCuxN3 Composites
Kangmo Koo, Young-Tae Kwon, Ji Young Park, Yong-Ho Choa
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.2024; 16(9): 11872. CrossRef
- Advanced Magnetic Actuation: Harnessing the Dynamics of Sm2Fe17–xCuxN3 Composites
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Application of Magnetoplasmonic Nanoparticles
- Sejeong Park, Siyeong Hwang, Seonghwan Jung, Juyong Gwak, Jaebeom Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):429-434. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.429

- 749 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Magnetic nanoparticles have a significant impact on the development of basic sciences and nanomedical, electronic, optical, and biotech industries. The development of magnetic structures with size homogeneity, magnetization, and particle dispersibility due to high-quality process development can broaden their utilization for separation analysis, structural color optics using surface modification, and energy/catalysts. In addition, magnetic nanoparticles simultaneously exhibit two properties: magnetic and plasmon resonance, which can be self-assembled and can improve signal sensitivity through plasmon resonance. This paper reports typical examples of the synthesis and properties of various magnetic nanoparticles, especially magnetoplasmonic nanoparticles developed in our laboratory over the past decade, and their optical, electrochemical, energy/catalytic, and bio-applications. In addition, the future value of magnetoplasmonic nanoparticles can be reevaluated by comparing them with that reported in the literature.
- [Korean]
- A Study on the Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Fe83.2Si5.33-0.33
x B10.67-0.67x Px Cu0.8 Nanocrystalline Soft Magnetic Alloys with varying P Content - Hyun Ah Im, Kyoung-Hoon Bae, Yeong gyun Nam, Subong An, Sangsun Yang, Yong-Jin Kim, Jung Woo Lee, Jae Won Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(4):293-300. Published online August 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.4.293

- 890 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We investigate the effect of phosphorous content on the microstructure and magnetic properties of Fe83.2Si5.33-0.33
x B10.67-0.67x Px Cu0.8 (x = 1–4 at.%) nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloys. The simultaneous addition of Cu and P to nanocrystalline alloys reportedly decreases the nanocrystalline size significantly, to 10–20 nm. In the P-containing nanocrystalline alloy, P atoms are distributed in an amorphous residual matrix, which suppresses grain growth, increases permeability, and decreases coercivity. In this study, nanocrystalline ribbons with a composition of Fe83.2Si5.33-0.33x B10.67- 0.67x Px Cu0.8 (x = 1–4 at.%) are fabricated by rapid quenching melt-spinning and thermal annealing. It is demonstrated that the addition of a small amount of P to the alloy improves the glass-forming ability and increases the resistance to undesirable Fex(B,P) crystallization. Among the alloys investigated in this work, an Fe83.2Si5B10P1Cu0.8 nanocrystalline ribbon annealed at 460°C exhibits excellent soft-magnetic properties including low coercivity, low core loss, and high saturation magnetization. The uniform nanocrystallization of the Fe83.2Si5B10P1Cu0.8 alloy is confirmed by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy analysis.
- [Korean]
- Development of Hybrid Insulating Coating for Fe-based Soft Magnetic Powder
- Jungjoon Kim, Sungyeom Kim, Youngkyun Kim, Taesuk Jang, Hwi-jun Kim, Youngjin Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):233-238. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.233

- 634 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Iron-based amorphous powder attracts increasing attention because of its excellent soft magnetic properties and low iron loss at high frequencies. The development of an insulating layer on the surface of the amorphous soft magnetic powder is important for minimizing the eddy current loss and enhancing the energy efficiency of highfrequency devices by further increasing the electrical resistivity of the cores. In this study, a hybrid insulating coating layer is investigated to compensate for the limitations of monolithic organic or inorganic coating layers. Fe2O3 nanoparticles are added to the flexible silicon-based epoxy layer to prevent magnetic dilution; in addition TiO2 nanoparticles are added to enhance the mechanical durability of the coating layer. In the hybrid coating layer with optimal composition, the decrease in magnetic permeability and saturation magnetization is suppressed.
- [Korean]
- Analysis of Wafer Cleaning Solution Characteristics and Metal Dissolution Behavior according to the Addition of Chelating Agent
- Myungsuk Kim, Keunhyuk Ryu, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(1):25-30. Published online February 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.1.25
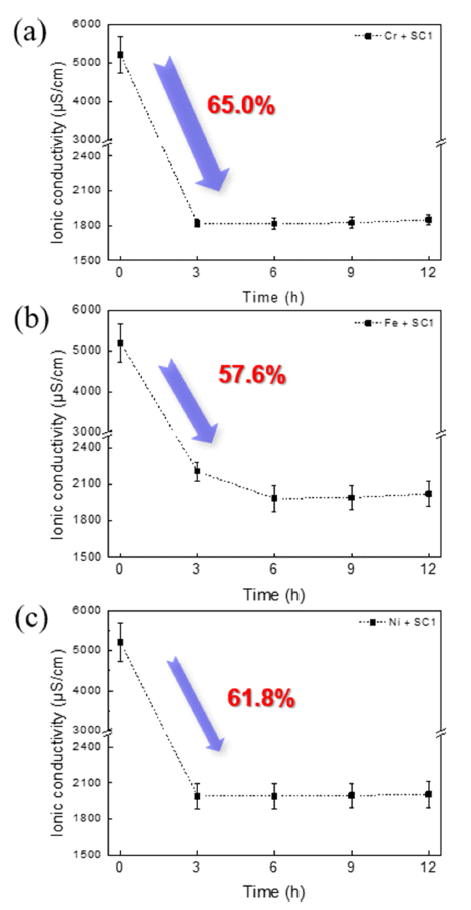
- 1,027 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The surface of silicon dummy wafers is contaminated with metallic impurities owing to the reaction with and adhesion of chemicals during the oxidation process. These metallic impurities negatively affect the device performance, reliability, and yield. To solve this problem, a wafer-cleaning process that removes metallic impurities is essential. RCA (Radio Corporation of America) cleaning is commonly used, but there are problems such as increased surface roughness and formation of metal hydroxides. Herein, we attempt to use a chelating agent (EDTA) to reduce the surface roughness, improve the stability of cleaning solutions, and prevent the re-adsorption of impurities. The bonding between the cleaning solution and metal powder is analyzed by referring to the Pourbaix diagram. The changes in the ionic conductivity, H2O2 decomposition behavior, and degree of dissolution are checked with a conductivity meter, and the changes in the absorbance and particle size before and after the reaction are confirmed by ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) analyses. Thus, the addition of a chelating agent prevents the decomposition of H2O2 and improves the life of the silicon wafer cleaning solution, allowing it to react smoothly with metallic impurities.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Ti-Mn-Cu Alloys with Magnetic Pulsed Compaction
- Ye Jun Yun, Chun Woong Park, Won June Choi, Jongmin Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(1):20-24. Published online February 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.1.20
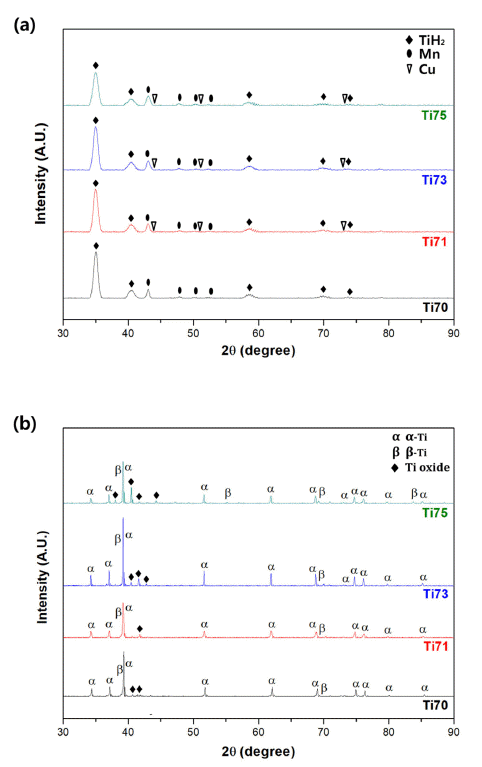
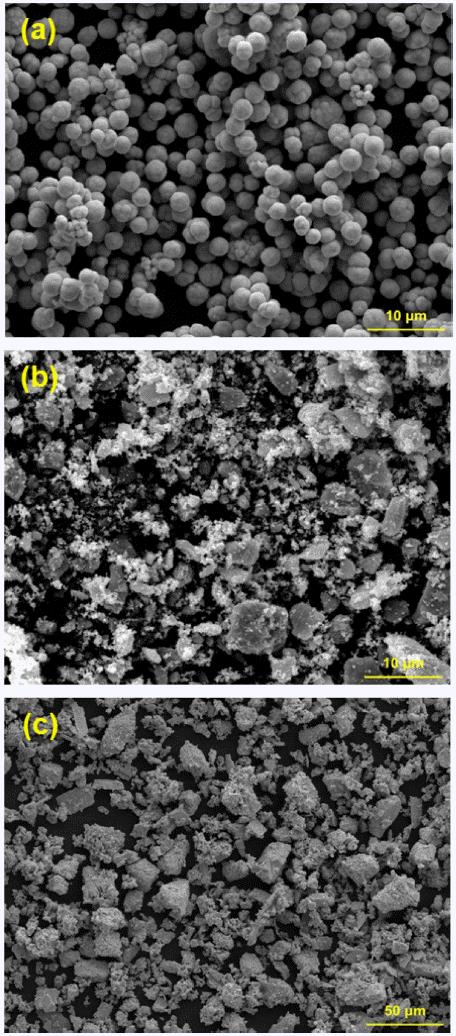
- 830 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Ti-based alloys are widely used in biomaterials owing to their excellent biocompatibility. In this study, Ti- Mn-Cu alloys are prepared by high-energy ball milling, magnetic pulsed compaction, and pressureless sintering. The microstructure and microhardness of the Ti-Mn-Cu alloys with variation of the Cu addition and compaction pressure are analyzed. The correlation between the composition, compaction pressure, and density is investigated by measuring the green density and sintered density for samples with different compositions, subjected to various compaction pressures. For all compositions, it is confirmed that the green density increases proportionally as the compaction pressure increases, but the sintered density decreases owing to gas formation from the pyrolysis of TiH2 powders and reduction of oxides on the surface of the starting powders during the sintering process. In addition, an increase in the amount of Cu addition changes the volume fractions of the α-Ti and β-Ti phases, and the microstructure of the alloys with different compositions also changes. It is demonstrated that these changes in the phase volume fraction and microstructure are closely related to the mechanical properties of the Ti-Mn-Cu alloys.
- [Korean]
- Experimental Study on Improving Compressive Strength of Hexagonal Boron Nitride Reinforced Cement Composite
- Yomin Choi, Hyun‐Gyoo Shin
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):503-508. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.503

- 651 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The mechanical properties and microstructures of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN)-reinforced cement composites are experimentally studied for three and seven curing days. Various sizes (5, 10, and 18 μm) and concentrations (0.1%, 0.25%, 0.5%, and 1.0%) of h-BN are dispersed by the tip ultrasonication method in water and incorporated into the cement composite. The compressive strength of the h-BN reinforced cements increases by 40.9%, when 0.5 wt% of 18 μm-sized h-BN is added. However, the compressive strength decreases when the 1.0 wt% cement composite is added, owing to the aggregation of the h-BNs in the cement composite. The microstructural characterization of the h-BN-reinforced cement composite indicates that the h-BNs act as bridges connecting the cracks, resulting in improved mechanical properties for the reinforced cement composite.
- [Korean]
- Effect of H2SO4 and Reaction Time on Synthesis of 5Mg(OH)2∙MgSO4∙3H2O Whiskers using Hydrothermal Reaction
- Areum Choi, Nuri Oh, YooJin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(5):401-405. Published online October 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.5.401
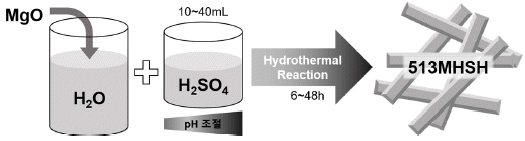
- 1,059 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Magnesium hydroxide sulfate hydrate (MHSH) whiskers were synthesized via a hydrothermal reaction by using MgO as the reactant as well as the acid solution. The effects of the H2SO4 amount and reaction time at the same temperature were studied. In general, MHSH whiskers were prepared using MgSO4 in aqueous ammonia. In this work, to reduce the formation of impurities and increase the purity of MHSH, we employed a synthesis technique that did not require the addition of a basic solution. Furthermore, the pH value, which was controlled by the H2SO4 amount, acted as an important factor for the formation of high-purity MHSH. MgO was used as the raw material because it easily reacts in water and forms Mg+ and MgOH+ ions that bind with SO4 2- ions to produce MHSH. Their morphologies and structures were determined using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and Morphology Control of Needle Type 513 MHSH and Mg(OH)2 from Dolomite
Jiyeon Kim, HyunSeung Shim, Seong-Ju Hwang, YooJin Kim
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(5): 399. CrossRef - Study of SiO2 coating and carboxylic surface-modification on Mg-based inorganic fiber by one-step reflux reaction
Minsol Park, Areum Choi, Seiki Kim, Wooyoung Shim, YooJin Kim
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2022; 59(6): 869. CrossRef - Effect of sulfate ion on synthesis of 5 Mg(OH)2·MgSO4·3H2O whiskers using non-hydrothermal method with acid catalyst
Areum Choi, Nuri Oh, YooJin Kim
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2022; 59(2): 224. CrossRef
- Synthesis and Morphology Control of Needle Type 513 MHSH and Mg(OH)2 from Dolomite
- [Korean]
- Fabrication, Microstructure and Adhesive Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal/Ag Plate Composite by using Plasma Spray Process
- Seong-June Youn, Young-Kyun Kim, Jae-Sung Park, Joo-Hyun Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(4):333-338. Published online August 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.4.333
- 741 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
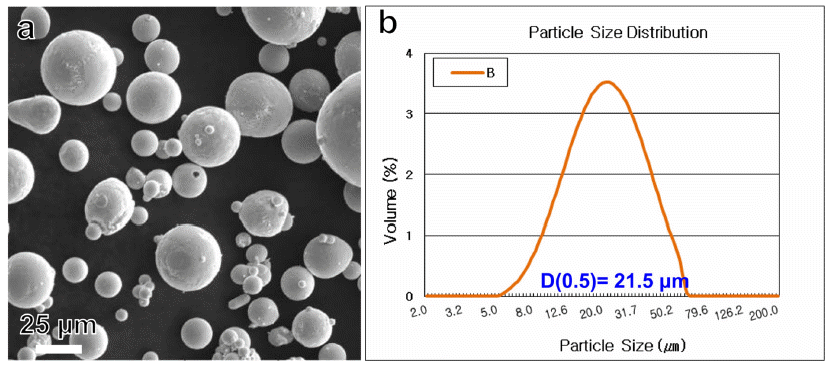
PDF In this study, we fabricate a thin- and dense-BCuP-5 coating layer, one of the switching device multilayers, through a plasma spray process. In addition, the microstructure and macroscopic properties of the coating layer, such as hardness and bond strength, are investigated. Both the initial powder feedstock and plasma-sprayed BCuP-5 coating layer show the main Cu phase, Cu-Ag-Cu3P ternary phases, and Ag phase. This means that microstructural degradation does not occur during plasma spraying. The Vickers hardness of the coating layer was measured as 117.0 HV, indicating that the fine distribution of the three phases enables the excellent mechanical properties of the plasma-sprayed BCuP-5 coating layer. The pull-off strength of the plasma-sprayed BCuP-5 coating layer is measured as 16.5 kg/cm2. Based on the above findings, the applicability of plasma spray for the fabrication process of low-cost multi-layered electronic contact materials is discussed and suggested.
- [Korean]
- Influence of Reducing Agents and Additives on the Synthesis of ZnSe Nanoparticles
- Geum Ji Back, Da Gyeong Lee, Min Seo Lee, Ha Yeon Song, Hyun Seon Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):233-240. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.233

- 632 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Nano-sized ZnSe particles are successfully synthesized in an aqueous solution at room temperature using sodium borohydride (NaBH4) and thioglycolic acid (TGA) as the reducing agent and stabilizer, respectively. The effects of the mass ratio of the reducing agent to Se, stabilizer concentration, and stirring time on the synthesis of the ZnSe nanoparticles are evaluated. The light absorption/emission properties of the synthesized nanoparticles are characterized using ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy, photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy, and particle size analyzer (PSA) techniques. At least one mass ratio (NaBH4/Se) of the reducing agent should be added to produce ZnSe nanoparticles finer than 10 nm and to absorb UV–vis light shorter than the ZnSe bulk absorption wavelength of 460 nm. As the ratio of the reducing agent increases, the absorption wavelengths in the UV-vis curves are blue-shifted. Stirring in the atmosphere acts as a deterrent to the reduction reaction and formation of nanoparticles, but if not stirred in the atmosphere, the result is on par with synthesis in a nitrogen atmosphere. The stabilizer, TGA, has an impact on the Zn precursor synthesis. The fabricated nanoparticles exhibit excellent photo-absorption/discharge characteristics, suggesting that ZnSe nanoparticles can be alloyed without the need for organic solutions or high-temperature environments.
- [Korean]
- Sintering Behavior of M-type Sr-Hexaferrite by MnCO3 Addition
- MinSeok Jeong, Changjae You, Jung Young Cho, Kyoung-Seok Moon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(2):126-131. Published online April 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.2.126

- 594 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The grain growth behavior of M-type Sr hexaferrite (SrM) grains is investigated with the addition of MnCO3. First, the SrM powder is synthesized by a conventional solid-state reaction. The powder compacts of SrM are sintered at 1250°C for 2 h with various amounts of MnCO3 (0, 0.5, 1.0, and 4.0 mol%). There is no secondary solid phase in any of the sintered samples. Relative density increases when MnCO3 is added to the SrM. Obvious abnormal grain growth does not appear in any of the SrM samples with MnCO3. The average grain size increases when 0.5 mol% MnCO3 is added to the SrM. However, as the amount of MnCO3 increase to over 0.5 mol%, the average grain size decreases. These observations allow us to conclude that the growth of SrM grains is governed by the two-dimensional nucleation grain growth mechanism, and the critical driving force for the growth of a grain decreases as the amount of MnCO3 increases.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of C3S, C2S, C3A Powders using Ultra-fine Calcium Oxide Powder Synthesized from Eggshell and Effect of C3A Content on Hardened Mixed Aggregates
- Heon Kong, Ki-Beom Kwon, Sang-Jin Park, Whyo-Sub Noh, Sang-Jin Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(6):493-501. Published online December 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.6.493
- 1,038 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
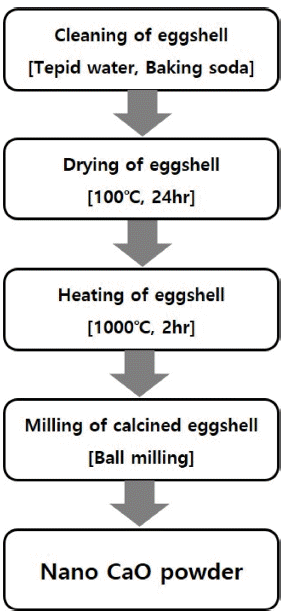
PDF In this work, ultra-fine calcium oxide (CaO) powder derived from eggshells is used as the starting material to synthesize mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA). The prepared CaO powder is confirmed to have an average particle size of 500 nm. MTAs are synthesized with three types of fine CaO-based powders, namely, tricalcium silicate (C3S), dicalcium silicate (C2S), and tricalcium aluminate (C3A). The synthesis behavior of C3S, C2S and C3A with ultra-fine CaO powder and the effects of C3A content and curing time on the properties of MTA are investigated. The characteristics of the synthesized MTA powders are examined by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission-scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), and a universal testing machine (UTM). The microstructure and compressive strength characteristics of the synthesized MTA powders are strongly dependent on the C3A wt.% and curing time. Furthermore, MTA with 5 wt.% C3A is found to increase the compressive strength and shorten the curing time.
- [Korean]
- Magnetic Properties of Micron Sized Fe3O4 Crystals Synthesized by Hydrothermal Methods
- Ki-Bum Lee, Chunghee Nam
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(6):481-486. Published online December 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.6.481

- 1,169 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Iron oxides currently attract considerable attention due to their potential applications in the fields of lithiumion batteries, bio-medical sensors, and hyperthermia therapy materials. Magnetite (Fe3O4) is a particularly interesting research target due to its low cost, good biocompatibility, outstanding stability in physiological conditions. Hydrothermal synthesis is one of several liquid-phase synthesis methods with water or an aqueous solution under high pressure and high temperature. This paper reports the growth of magnetic Fe3O4 particles from iron powder (spherical, <10 μm) through an alkaline hydrothermal process under the following conditions: (1) Different KOH molar concentrations and (2) different synthesis time for each KOH molar concentrations. The optimal condition for the synthesis of Fe3O4 using Fe powders is hydrothermal oxidation with 6.25 M KOH for 48 h, resulting in 89.2 emu/g of saturation magnetization at room temperature. The structure and morphologies of the synthesized particles are characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD, 2θ = 20°–80°) with Cu-kα radiation and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), respectively. The magnetic properties of magnetite samples are investigated using a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). The role of KOH in the formation of magnetite octahedron is observed.
- [Korean]
- Synthesize of Nd2Fe14B Powders from 1-D Nd2Fe14B Wires using Electrospinning Process
- Nu Si A Eom, Su Noh, Muhammad Aneeq Haq, Bum Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(6):477-480. Published online December 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.6.477
- 907 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
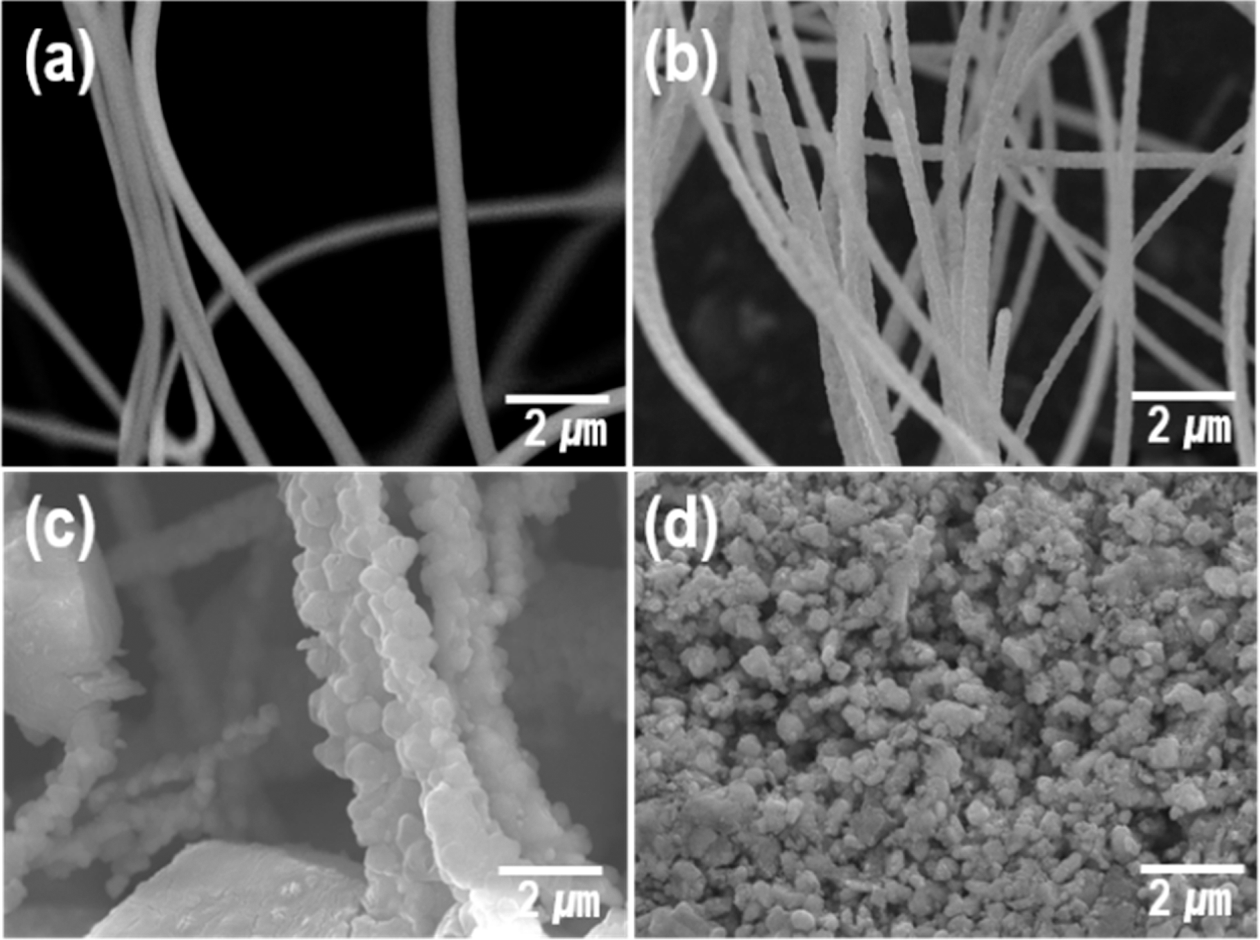
PDF Magnetic 0-D Nd2Fe14B powders are successfully fabricated using 1-D Nd2Fe14B nanowire formed by an efficient and facile electrospinning process approach. The synthesized Nd-Fe-B fibers and powders are investigated for their microstructural, crystallographic, and magnetic properties according to a series of subsequent heat treatments. Each heat-treatment process leads to the removal of organic impurities and the formation of the respective oxides/composites of Nd, Fe, and B, resulting in the formation of Nd2Fe14B powders. Nd-Fe-B fibers exhibit the following magnetic properties: The coercivity (Hci) of 3260 Oe, a maximum magnetization at 3T of 109.44 emu/g, and a magnetization remanence (Mr) of 44.11 emu/g. This process easily mass produces hard magnetic Nd2Fe14B powders using a 1-D synthesis process and can be extended to the experimental design of other magnetic materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nd2Fe14B/FeCo Core–Shell Nanoparticle Synthesis Using Galvanic Substitution Based Electroless Plating
Muhammad Aneeq Haq, Han-Saem Lee, Mi Hye Lee, Da-Woon Jeong, Eom Nu Si A, Bin Lee, Yoseb Song, Bum Sung Kim
Coatings.2022; 12(3): 389. CrossRef
- Nd2Fe14B/FeCo Core–Shell Nanoparticle Synthesis Using Galvanic Substitution Based Electroless Plating
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of the Multifunctional Core/Intermediate/Shell Nanoparticles: Tunable Magnetic and Photoluminescence Properties
- Mun-Kyoung Kim, Seyun Kim, Kyoung-Seok Moon, Weon Ho Shin, Hyung Mo Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(6):463-470. Published online December 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.6.463
- 757 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
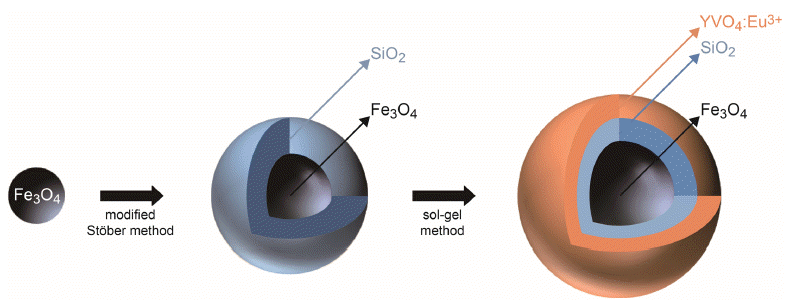
PDF Fe3O4/SiO2/YVO4:Eu3+ multifunctional nanoparticles are successfully synthesized by facile stepwise sol-gel processes. The multifunctional nanoparticles show a spherical shape with narrow size distribution (approximately 40 nm) and the phosphor shells are well crystallized. The Eu3+ shows strong photoluminescence (red emission at 619 nm, absorbance at 290 nm) due to an effective energy transfer from the vanadate group to Eu. Core-shell structured multifunctional nanoparticles have superparamagnetic properties at 300 K. Furthermore, the core-shell nanoparticles have a quick response time for the external magnetic field. These results suggest that the photoluminescence and magnetic properties could be easily tuned by either varying the number of coating processes or changing the phosphor elements. The nanoparticles may have potential applications for appropriate fields such as laser systems, optical amplifiers, security systems, and drug delivery materials.
- [Korean]
- Study on the Optimization of Reduction Conditions for Samarium-Cobalt Nanofiber Preparation
- Jimin Lee, Jongryoul Kim, Yong-Ho Choa
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(4):334-339. Published online August 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.4.334

- 567 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF To meet the current demand in the fields of permanent magnets for achieving a high energy density, it is imperative to prepare nano-to-microscale rare-earth-based magnets with well-defined microstructures, controlled homogeneity, and magnetic characteristics via a bottom-up approach. Here, on the basis of a microstructural study and qualitative magnetic measurements, optimized reduction conditions for the preparation of nanostructured Sm-Co magnets are proposed, and the elucidation of the reduction-diffusion behavior in the binary phase system is clearly manifested. In addition, we have investigated the microstructural, crystallographic, and magnetic properties of the Sm-Co magnets prepared under different reduction conditions, that is, H2 gas, calcium, and calcium hydride. This work provides a potential approach to prepare high-quality Sm-Co-based nanofibers, and moreover, it can be extended to the experimental design of other magnetic alloys.
- [Korean]
- Study on the Optimization of Reduction Conditions for Samarium-Cobalt Nanofiber Preparation
- Jimin Lee, Jongryoul Kim, Yong-Ho Choa
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(4):334-339. Published online August 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.4.334

- 519 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF To meet the current demand in the fields of permanent magnets for achieving a high energy density, it is imperative to prepare nano-to-microscale rare-earth-based magnets with well-defined microstructures, controlled homogeneity, and magnetic characteristics via a bottom-up approach. Here, on the basis of a microstructural study and qualitative magnetic measurements, optimized reduction conditions for the preparation of nanostructured Sm-Co magnets are proposed, and the elucidation of the reduction-diffusion behavior in the binary phase system is clearly manifested. In addition, we have investigated the microstructural, crystallographic, and magnetic properties of the Sm-Co magnets prepared under different reduction conditions, that is, H2 gas, calcium, and calcium hydride. This work provides a potential approach to prepare high-quality Sm-Co-based nanofibers, and moreover, it can be extended to the experimental design of other magnetic alloys.
- [Korean]
- Research trend in Fabrication of Metastable-phase Iron Nitrides for Hard Magnetic Applications
- Kyung Min Kim, Jung-Goo Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Youn-Kyoung Baek
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):146-155. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.146

- 1,734 View
- 23 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Rare earth magnets are the strongest type of permanent magnets and are integral to the high tech industry, particularly in clean energies, such as electric vehicle motors and wind turbine generators. However, the cost of rare earth materials and the imbalance in supply and demand still remain big problems to solve for permanent magnet related industries. Thus, a magnet with abundant elements and moderate magnetic performance is required to replace rare-earth magnets. Recently, a”-Fe16N2 has attracted considerable attention as a promising candidate for next-generation non-rare-earth permanent magnets due to its gigantic magnetization (3.23 T). Also, metastable a”-Fe16N2 exhibits high tetragonality (c/a = 1.1) by interstitial introduction of N atoms, leading to a high magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant (K1 = 1.0MJ/m3). In addition, Fe has a large amount of reserves on the Earth compared to other magnetic materials, leading to low cost of raw materials and manufacturing for industrial production. In this paper, we review the synthetic methods of metastable a”-Fe16N2 with film, powder and bulk form and discuss the approaches to enhance magnetocrystalline anisotropy of a”-Fe16N2. Future research prospects are also offered with patent trends observed thus far.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Failure Cases according to Photocuring-Based Alumina 3D Printing
So-Young Ko, Shin-Il Go, Kyoung-Jun Jang, Sang-Jin Lee
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2024; 34(10): 457. CrossRef
- Failure Cases according to Photocuring-Based Alumina 3D Printing
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Molybdenum Silicide-based Composites with Uniformly Dispersed Silicon Carbide
- Won June Choi, Chun Woong Park, Young Do Kim, Jong Min Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):402-407. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.402

- 488 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Molybdenum silicide has gained interest for high temperature structural applications. However, poor fracture toughness at room temperatures and low creep resistance at elevated temperatures have hindered its practical applications. This study uses a novel powder metallurgical approach applied to uniformly mixed molybdenum silicidebased composites with silicon carbide. The degree of powder mixing with different ball milling time is also demonstrated by Voronoi diagrams. Core-shell composite powder with Mo nanoparticles as the shell and β-SiC as the core is prepared via chemical vapor transport. Using this prepared core-shell composite powder, the molybdenum silicide-based composites with uniformly dispersed β-SiC are fabricated using pressureless sintering. The relative density of the specimens sintered at 1500°C for 10 h is 97.1%, which is similar to pressure sintering owing to improved sinterability using Mo nanoparticles.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Metallic Tantalum Powder by Magnesium-gas Reduction of Tantalum Oxide
- Dong-Won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):390-394. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.390

- 861 View
- 14 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metallic tantalum powder is manufactured by reducing tantalum oxide (Ta2O5) with magnesium gas at 1,073–1,223 K in a reactor under argon gas. The high thermodynamic stability of magnesium oxide makes the reduction reaction from tantalum oxide into tantalum powder possible. The microstructure after the reduction reaction has the form of a mixture of tantalum and magnesium oxide, and the latter could be entirely eliminated by dissolving in weak hydrochloric acid. The powder size in SEM microstructure for the tantalum powder increases after acid leaching in the range of 50–300 nm, and its internal crystallite sizes are observed to be 11.5 to 24.7 nm with increasing reduction temperatures. Moreover, the optimized reduction temperature is found to be 1,173 K as the minimum oxygen concentration is approximately 1.3 wt.%.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A review of tantalum resources and its production
Xue WEI, Long-gong XIA, Zhi-hong LIU, Le-ru ZHANG, Qi-hou LI
Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China.2023; 33(10): 3132. CrossRef - Valuable metal recovery from waste tantalum capacitors via cryogenic crushing-alkaline calcination-leaching process
Longgong Xia, Xue Wei, Hongjun Wang, Fengchun Ye, Zhihong Liu
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2022; 16: 1637. CrossRef
- A review of tantalum resources and its production
- [Korean]
- Pre-treatments of initial materials for controlling synthesized TaC characteristics in the SHS process
- Jae Jin Sim, Sang Hoon Choi, Ji Hwan Park, Il Kyu Park, Jae Hong Lim, Kyoung Tae Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(3):251-256. Published online June 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.3.251

- 1,004 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We report the feasibility of TaC production via self-propagating high temperature synthesis, and the influence of the initial green compact density on the final composite particle size. Experiments are carried out from a minimum pressure of 0.3 MPa, the pressure at which the initial green body becomes self-standing, up to 3 MPa, the point at which no further combustion occurs. The green density of the pellets varies from 29.99% to 42.97%, as compared with the theoretical density. The increase in green density decreases the powder size of TaC, and the smallest particle size is observed with 1.5 MPa, at 10.36 μm. Phase analysis results confirm the presence of the TaC phase only. In the range of 0.3-0.5 MPa, traces of unreacted Ta and C residues are detected. However, results also show the presence of only C residue in the matrix within the pressure range of 0.6-3.0 MPa.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of CNT dispersed Cu matrix composites by wet mixing and spark plasma sintering process
- Seungchan Cho, Ilguk Jo, Sang-Bok Lee, Sang-Kwan Lee, Moonhee Choi, Jehong Park, Hansang Kwon, Yangdo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):158-164. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.158

- 974 View
- 18 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT)–copper (Cu) composites are successfully fabricated by a combination of a binder-free wet mixing and spark plasma sintering (SPS) process. The SPS is performed under various conditions to investigate optimized processing conditions for minimizing the structural defects of CNTs and densifying the MWCNT–Cu composites. The electrical conductivities of MWCNT–Cu composites are slightly increased for compositions containing up to 1 vol.% CNT and remain above the value for sintered Cu up to 2 vol.% CNT. Uniformly dispersed CNTs in the Cu matrix with clean interfaces between the treated MWCNT and Cu leading to effective electrical transfer from the treated MWCNT to the Cu is believed to be the origin of the improved electrical conductivity of the treated MWCNT–Cu composites. The results indicate the possibility of exploiting CNTs as a contributing reinforcement phase for improving the electrical conductivity and mechanical properties in the Cu matrix composites.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Proposing Machine Learning Models Suitable for Predicting Open Data Utilization
Junyoung Jeong, Keuntae Cho
Sustainability.2024; 16(14): 5880. CrossRef
- Proposing Machine Learning Models Suitable for Predicting Open Data Utilization
- [Korean]
- Effect of Milling Time and Addition of PCA on Austenite Stability of Fe-7%Mn Alloy
- Seung-Jin Oh, In-Jin Shon, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):126-131. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.126

- 786 View
- 9 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In the present study, we investigate the effects of milling time and the addition of a process control agent (PCA) on the austenite stability of a nanocrystalline Fe-7%Mn alloy by XRD analysis and micrograph observation. Nanocrystalline Fe-7%Mn alloys samples are successfully fabricated by spark plasma sintering. The crystallite size of ball-milled powder and the volume fraction of austenite in the sintered sample are calculated using XRD analysis. Changes in the shape and structure of alloyed powder according to milling conditions are observed through FE-SEM. It is found that the crystallite size is reduced with increasing milling time and amount of PCA addition due to the variation in the balance between the cold-welding and fracturing processes. As a result, the austenite stability increased, resulting in an exceptionally high volume fraction of austenite retained at room temperature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of mechanical milling on microstructure and mechanical properties of CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy fabricated via spark plasma sintering
Seonghyun Park, Sang-Hwa Lee, Eunjoo Shin, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2025; 39: 4854. CrossRef - Effect of Cooling Rate on Microstructure and Hardness during Solution Treatment and Aging Process of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy for Aerospace Components
Seongji Seo, Hojoon Choi, Geeyoung Lee, Kee-Ahn Lee, Jeongho Han, Minsu Jung
Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance.2021; 30(5): 3406. CrossRef - Development of Fe-Mn-based Hybrid Materials Containing Nano-scale Oxides by a Powder Metallurgical Route
Jonggyu Jeon, Jungjoon Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 203. CrossRef - Austenite Stability of Sintered Fe-based Alloy
Seunggyu Choi, Namhyuk Seo, Junhyub Jun, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(5): 414. CrossRef - Austenite Stability of Nanocrystalline FeMnNiC Alloy
Seung-Jin Oh, Junhyub Jeon, In-Jin Shon, Seok-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(5): 389. CrossRef
- Effects of mechanical milling on microstructure and mechanical properties of CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy fabricated via spark plasma sintering
- [Korean]
- A Study on the Improvement of Storage Stability of Solder Paste Using Multiple size of solder Powder
- Chan-Kyu Lim, Bo-Suk Gyun, Min-Jung Son, Inyoung Kim, Sangsun Yang, Su-Yong Nam
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):395-399. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.395
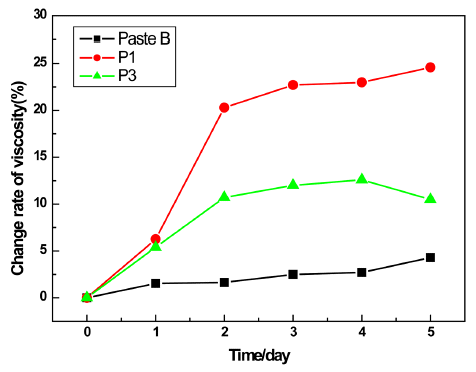
- 1,216 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Solder paste is widely used as a conductive adhesive in the electronics industry. In this paper, nano and microsized mixed lead-free solder powder (Sn-Ag-Cu) is used to manufacture solder paste. The purpose of this paper is to improve the storage stability using different types of solvents that are used in fabricating the solder paste. If a solvent of sole acetate is used, the nano sized solder powder and organic acid react and form a Sn-Ag-Cu malonate. These formed malonates create fatty acid soaps. The fatty acid soaps absorb the solvents and while the viscosity of the solder paste rises, the storage stability and reliability decrease. When ethylene glycol, a dihydric alcohol, is used the fatty acid soaps and ethylene glycol react, preventing the further creation of the fatty acid soaps. The prevention of gelation results in an improvement in the solder paste storage ability.
- [Korean]
- Recovery and Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Leaching Solution of LTCC Electrode By-Products
- Juyeon Yoo, Yubin Kang, Jinju Park, Hojin Ryu, Jin-Ho Yoon, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):315-320. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.315

- 513 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF There has been much interest in recycling electronic wastes in order to mitigate environmental problems and to recover the large amount of constituent metals. Silver recovery from electronic waste is extensively studied because of environmental and economic benefits and the use of silver in fabricating nanodevices. Hydrometallurgical processing is often used for silver recovery because it has the advantages of low cost and ease of control. Research on synthesis recovered silver into nanoparticles is needed for application to transistors and solar cells. In this study, silver is selectively recovered from the by-product of electrodes. Silver precursors are prepared using the dissolution characteristics of the leaching solution. In the liquid reduction process, silver nanoparticles are synthesized under various surfactant conditions and then analyzed. The purity of the recovered silver is 99.24%, and the average particle size of the silver nanoparticles is 68 nm.
- [English]
- Development of Dark Field image Processing Technique for the Investigation of Nanostructures
- Jongchul Jeon, Kyou-Hyun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):285-291. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.285

- 1,083 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We propose a custom analysis technique for the dark field (DF) image based on transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The custom analysis technique is developed based on the DigitalMicrograph® (DM) script language embedded in the Gatan digital microscopy software, which is used as the operational software for most TEM instruments. The developed software automatically scans an electron beam across a TEM sample and records a series of electron diffraction patterns. The recorded electron diffraction patterns provide DF and ADF images based on digital image processing. An experimental electron diffraction pattern is recorded from a IrMn polycrystal consisting of fine nanograins in order to test the proposed software. We demonstrate that the developed image processing technique well resolves nanograins of ~ 5 nm in diameter.
- [English]
- Magnetically Driven Assemblies of γ-Fe3O4 Nanoparticles into Well-Ordered Permanent Structures
- Myunghwan Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(3):229-234. Published online June 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.3.229

- 862 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We report on a simple and robust route to the spontaneous assembly of well-ordered magnetic nanoparticle superstructures by irreversible evaporation of a sessile single droplet of a mixture of a ferrofluid (FF) and a nonmagnetic fluid (NF). The resulting assembled superstructures are seen to form well-packed, vertically arranged columns with diameters of 5~0.7 μm, interparticle spacings of 9~2 μm, and heights of 1.3~3 μm. The assembled superstructures are strongly dependent on both the magnitude of magnetic field and the mixing ratio of the mixture. As the magnitude of the externally applied magnetic field and the mixing ratio of the mixture increase gradually, the size and interspacing of the magnetic nanoparticle aggregations decrease. Without an externally applied magnetic field, featureless patterns are observed for the γ-Fe3O4 nanoparticle aggregations. The proposed approach may lead to a versatile, cost-effective, fast, and scalable fabrication process based on the field-induced self-assembly of magnetic nanoparticles.
- [English]
- Microstructure and Soft Magnetic Properties of Fe-6.5 wt.%Si Sheets Fabricated by Powder Hot Rolling
- Myung Shin Kim, Do Hun Kwon, Won Sik Hong, Hwi Jun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):122-127. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.122

- 952 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Fe-6.5 wt.% Si alloys are widely known to have excellent soft magnetic properties such as high magnetic flux density, low coercivity, and low core loss at high frequency. In this work, disc-shaped preforms are prepared by spark plasma sintering at 1223 K after inert gas atomization of Fe-6.5 wt.% Si powders. Fe-6.5 wt.% Si sheets are rolled by a powder hot-rolling process without cracking, and their microstructure and soft magnetic properties are investigated. The microstructure and magnetic properties (saturation magnetization and core loss) of the hot-rolled Fe-6.5 wt.% Si sheets are examined by scanning electron microscopy, electron backscatter diffraction, vibration sample magnetometry, and AC
B–H analysis. The Fe-6.5 wt.% Si sheet rolled at a total reduction ratio of 80% exhibits good soft magnetic properties such as a saturation magnetization of 1.74 T and core loss (W5/1000) of 30.7 W/kg. This result is caused by an increase in the electrical resistivity resulting from an increased particle boundary density and the oxide layers between the primary particle boundaries.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Nd-Fe-B Sintered Magnet with the Variation of Particle Size
- Dongwon Shin, Dong-Hwan Kim, Young-Cheol Park, Jeong-Gon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(6):447-452. Published online December 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.6.447
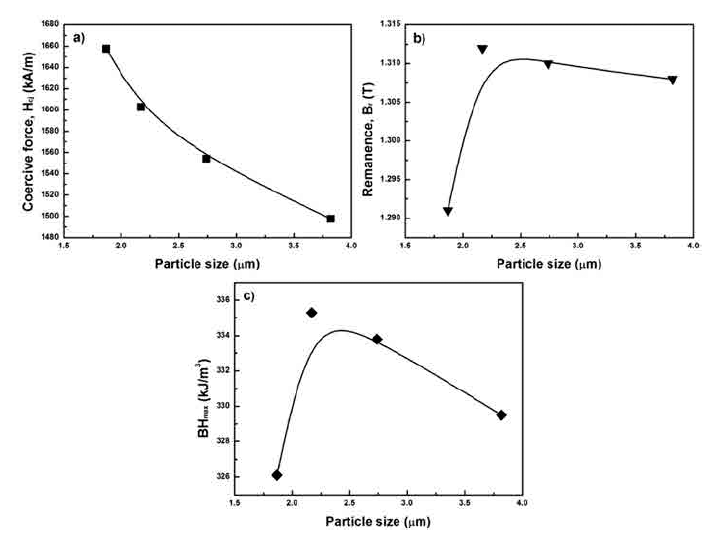
- 634 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Neodymium-iron-boron (Nd-Fe-B) sintered magnets have excellent magnetic properties such as the remanence, coercive force, and the maximum energy product compared to other hard magnetic materials. The coercive force of Nd-Fe-B sintered magnets is improved by the addition of heavy rare earth elements such as dysprosium and terbium instead of neodymium. Then, the magnetocrystalline anisotropy of Nd-Fe-B sintered magnets increases. However, additional elements have increased the production cost of Nd-Fe-B sintered magnets. Hence, a study on the control of the microstructure of Nd-Fe-B magnets is being conducted. As the coercive force of magnets improves, the grain size of the Nd2Fe14B grain is close to 300 nm because they are nucleation-type magnets. In this study, fine particles of Nd-Fe-B are prepared with various grinding energies in the pulverization process used for preparing sintered magnets, and the microstructure and magnetic properties of the magnets are investigated.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Cu/Al powder mixing on Dy diffusion in Nd-Fe-B sintered magnets treated with a grain boundary diffusion process
- Min Woo Lee, Tae Suk Jang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(6):432-436. Published online December 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.6.432

- 800 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We investigate the microstructural and magnetic property changes of DyH2, Cu + DyH2, and Al + DyH2 diffusion-treated NdFeB sintered magnets with the post annealing (PA) temperature. The coercivity of all the diffusiontreated magnets increases with increasing heat treatment temperature except at 910°C, where it decreases slightly. Moreover, at 880°C, the coercivity increases by 3.8 kOe in Cu and 4.7 kOe in Al-mixed DyH2-coated magnets, whereas this increase is relatively low (3.0 kOe) in the magnet coated with only DyH2. Both Cu and Al have an almost similar effect on the coercivity improvement, particularly over the heat treatment temperature range of 790-880°C. The diffusivity and diffusion depth of Dy increases in those magnets that are treated with Cu or Al-mixed DyH2, mainly because of the comparatively easy diffusion path provided by Cu and Al owing to their solubility in the Nd-rich grain boundary phase. The formation of a highly anisotropic (Nd, Dy)2Fe14B phase layer, which acts as the shell in the core-shell-type structure so as to prevent the reverse domain movement, is the cause of enhanced coercivity of diffusion-treated Nd-Fe-B magnets.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesize of Nd2Fe14B Powders from 1-D Nd2Fe14B Wires using Electrospinning Process
Nu Si A Eom, Su Noh, Muhammad Aneeq Haq, Bum Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(6): 477. CrossRef
- Synthesize of Nd2Fe14B Powders from 1-D Nd2Fe14B Wires using Electrospinning Process
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Hexagonal Boron Nitride Nanocrystals and Their Application to Thermally Conductive Composites
- Jae-Yong Jung, Yang-Do Kim, Pyung-Woo Shin, Young-Kuk Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(6):414-419. Published online December 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.6.414

- 1,516 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Much attention has been paid to thermally conductive materials for efficient heat dissipation of electronic devices to maintain their functionality and to support lifetime span. Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), which has a high thermal conductivity, is one of the most suitable materials for thermally conductive composites. In this study, we synthesize h-BN nanocrystals by pyrolysis of cost-effective precursors, boric acid, and melamine. Through pyrolysis at 900°C and subsequent annealing at 1500°C, h-BN nanoparticles with diameters of ~80 nm are synthesized. We demonstrate that the addition of small amounts of Eu-containing salts during the preparation of melamine borate precursors significantly enhanced the crystallinity of h-BN. In particular, addition of Eu assists the growth of h-BN nanoplatelets with diameters up to ~200 nm. Polymer composites containing both spherical Al2O3 (70 vol%) and Eu-doped h-BN nanoparticles (4 vol%) show an enhanced thermal conductivity (λ ~ 1.72W/mK), which is larger than the thermal conductivity of polymer composites containing spherical Al2O3 (70 vol%) as the sole fillers (λ ~ 1.48W/mK).
- [Korean]
- Investigation on Fe-Hf-B-Nb-P-C Soft Magnetic Powders Prepared by High-Pressure Gas Atomization
- Jae Won Jeong, Dong-Yeol Yang, Ki Bong Kim, Junhong Lee, Young Ja Kim, Tae-Soo Lim, Sangsun Yang, Min Ha Lee, Hwi Jun Kim, Yong-Jin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(5):391-396. Published online October 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.5.391

- 842 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, ultra-fine soft-magnetic micro-powders are prepared by high-pressure gas atomization of an Fe-based alloy, Fe-Hf-B-Nb-P-C. Spherical powders are successfully obtained by disintegration of the alloy melts under high-pressure He or N2 gas. The mean particle diameter of the obtained powders is 25.7 μm and 42.1 μm for He and N2 gas, respectively. Their crystallographic structure is confirmed to be amorphous throughout the interior when the particle diameter is less than 45 μm. The prepared powders show excellent soft magnetic properties with a saturation magnetization of 164.5 emu/g and a coercivity of 9.0 Oe. Finally, a toroidal core is fabricated for measuring the magnetic permeability, and a μr of up to 78.5 is obtained. It is strongly believed that soft magnetic powders prepared by gas atomization will be beneficial in the fabrication of high-performance devices, including inductors and motors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimization of Densification Behavior of a Soft Magnetic Powder by Discrete Element Method and Machine Learning
Jungjoon Kim, Dongchan Min, Suwon Park, Junhyub Jeon, Seok-Jae Lee, Youngkyun Kim, Hwi-Jun Kim, Youngjin Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2022; 63(10): 1304. CrossRef - Optimizing the magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous powder by adjusting atomic structures from vitrification at different temperatures
Song-Yi Kim, Hye-Ryeong Oh, Hyeon-Ah Kim, A-Young Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim, Sang-Sun Yang, Yong-Jin Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi, Il-Hyun Kim, Hyun-Gil Kim, Jürgen Eckert, Jong-Ryoul Kim, Min-Ha Lee
Journal of Applied Physics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Soft magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous/nanocrystalline hybrid materials
Yeonjoo Lee, Jonggyu Jeon, Seungjin Nam, Teasuk Jang, Hwijun Kim, Minwoo Lee, Yongjin Kim, Dongyeol Yang, Kyeongsik Min, Hyunjoo Choi
Powder Technology.2018; 339: 440. CrossRef
- Optimization of Densification Behavior of a Soft Magnetic Powder by Discrete Element Method and Machine Learning
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of Ag Particles by Polyol Process and Wet Chemical Process
- Juyeon Yoo, Hyosung Jang, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):297-302. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.297

- 818 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Ag nanoparticles are extensively studied and utilized due to their excellent catalysis, antibiosis and optical properties. They can be easily synthesized by chemical reduction methods and it is possible to prepare particles of uniform size and high purity. These methods are divided into vapor methods and liquid phase reduction methods. In the present study, Ag particles are prepared and analyzed through two chemical reduction methods using solvents containing a silver nitrate precursor. When Ag ions are reduced using a reductant in the aqueous solution, it is possible to control the Ag particle size by controlling the formic acid ratio. In addition, in the Polyol process, Ag nanoparticles prepared at various temperatures and reaction time conditions have multiple twinned and anisotropic structures, and the particle size variation can be confirmed using field emissions scanning electron microscopy and by analyzing the UV-vis spectrum.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recovery and Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Leaching Solution of LTCC Electrode By-Products
Juyeon Yoo, Yubin Kang, Jinju Park, Hojin Ryu, Jin-Ho Yoon, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(4): 315. CrossRef
- Recovery and Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Leaching Solution of LTCC Electrode By-Products
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


