Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Preparation of Flake-shape Cobalt Powders by High-Energy Ball Milling for rSOC Current Collectors
- Poong-Yeon Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Hyeon Ju Kim, Su-Jin Yun, Si Young Chang, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):383-389. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00241
- 446 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
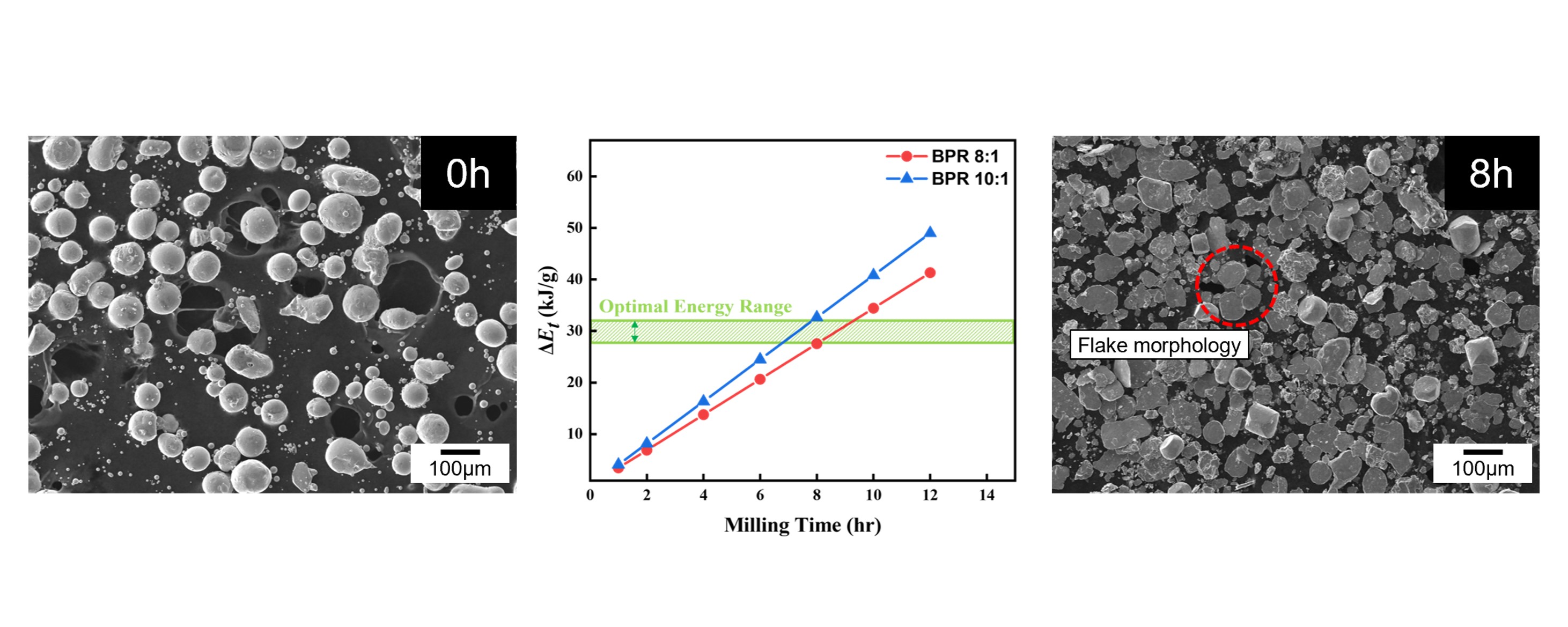
PDF - Reversible solid oxide cells (rSOCs), which enable two-way conversion between electricity and hydrogen, have gained attention with the rise of hydrogen energy. However, foam-type current collectors in rSOC stacks exhibit poor structural controllability and limited electrode contact area. To address these limitations, this study aimed to convert spherical cobalt powders into flake-type morphology via high-energy ball milling, as a preliminary step toward fabricating flake-based current collectors. Milling parameters—specifically, the ball-to-powder ratio (BPR), milling time, and process control agent (PCA) content—were varied. At an 8:1 BPR, over 90% of the powder became flake-shaped after 8 hours, while extended milling caused cold welding. In contrast, a 10:1 BPR resulted in dominant fragmentation. The Burgio–Rojac model quantified energy input and defined the optimal range for flake formation. Increasing the PCA to 4 wt% delayed flake formation to 16 hours and induced cold welding, as shown by bimodal particle size distributions. These results support the development of Co-based current collectors for use in rSOCs.
- [Korean]
- Preparation and Microstructural Characteristics of Ti Nanopowder by Ball Milling and Dehydrogenation of TiH2 Powder
- Ji Young Kim, Eui Seon Lee, Ji Won Choi, Youngmin Kim, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):324-328. Published online August 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00199
- 1,180 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
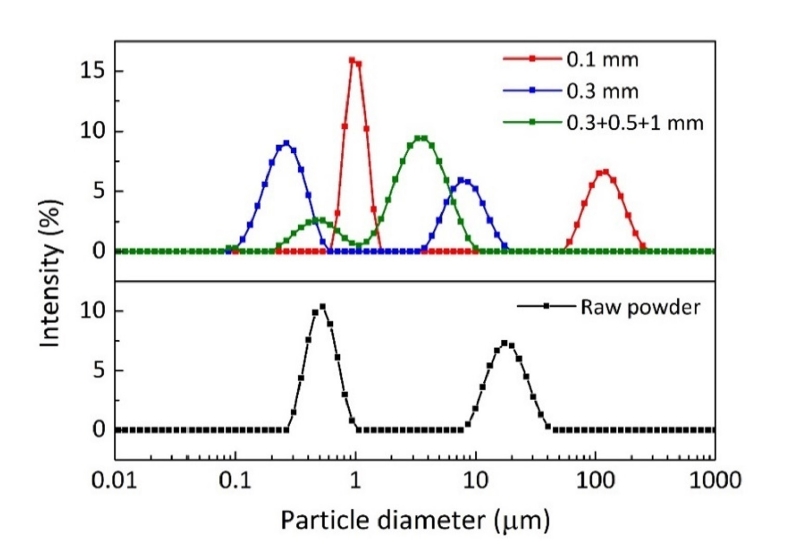
PDF - This study analyzed the influence of ball size and process control agents on the refinement and dehydrogenation behavior of TiH2 powder. Powders milled using ZrO2 balls with diameters of 0.1 mm, 0.3 mm, and 0.3+0.5+1 mm exhibited a bimodal particle size distribution, of which the first mode had the smallest size of 0.23 μm for the 0.3 mm balls. Using ethanol and/or stearic acid as process control agents was effective in particle refinement. Thermogravimetric analysis showed that dehydrogenation of the milled powder started at a relatively low temperature compared to the raw powder, which is interpreted to have resulted from a decrease in particle size and an increase in defects. The dehydrogenation kinetics of the TiH2 powder were evaluated by the magnitude of peak shift with heating rates using thermogravimetric analysis. The activation energy of the dehydrogenation reaction, calculated from the slope of the Kissinger plot, was measured to be 228.6 kJ/mol for the raw powder and 194.5 kJ/mol for the milled powder. TEM analysis revealed that both the milled and dehydrogenated powders showed an angular shape with a size of about 200 nm.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Ball Milling Conditions on the Microstructure and Dehydrogenation Behavior of TiH2 Powder
- Ji Young Kim, Eui Seon Lee, Ji Won Choi, Youngmin Kim, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):132-136. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00001
- 2,201 View
- 38 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
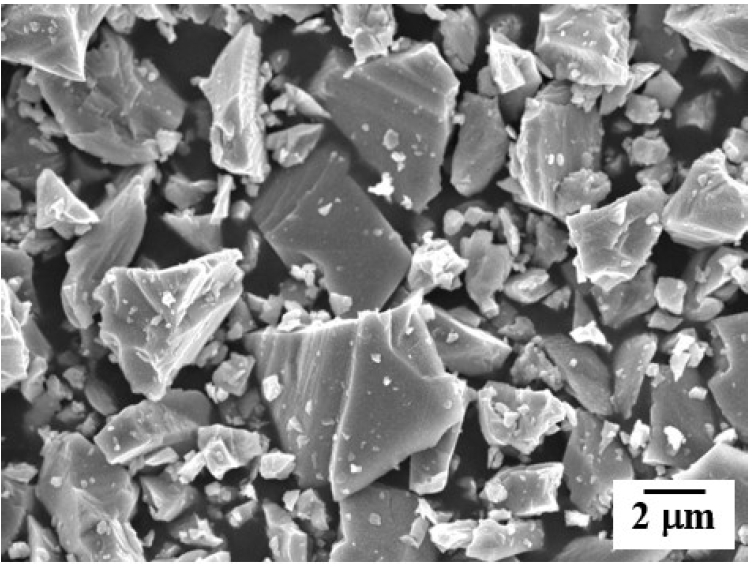
PDF - This study investigated the effects of revolution speed and ball size in planetary milling on the microstructure and dehydrogenation behavior of TiH2 powder. The particle size analysis showed that the large particles present in the raw powder were effectively refined as the revolution speed increased, and when milled at 500 rpm, the median particle size was 1.47 m. Milling with a mixture of balls of two or three sizes was more effective in refining the raw powder than milling with balls of a single size. A mixture of 3-mm and 5-mm-diameter balls was the optimal condition for particle refinement, and the measured median particle size was 0.71 m. The dependence of particle size on revolution speed and ball size was explained by changes in input energy and the number of contact points of the balls. In the milled powder, the endothermic peak measured using differential thermal analysis was observed at a relatively low temperature. This finding was interpreted as the activation of a dehydrogenation reaction, mainly due to the increase in the specific surface area and the concentration of lattice defects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation and Microstructural Characteristics of Ti Nanopowder by Ball Milling and Dehydrogenation of TiH2 Powder
Ji Young Kim, Eui Seon Lee, Ji Won Choi, Youngmin Kim, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(4): 324. CrossRef
- Preparation and Microstructural Characteristics of Ti Nanopowder by Ball Milling and Dehydrogenation of TiH2 Powder
- [Korean]
- Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Si Sintered Alloys with and Without High-energy Ball Milling
- Junho Lee, Seonghyun Park, Sang-Hwa Lee, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):470-477. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.470
- 2,803 View
- 32 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
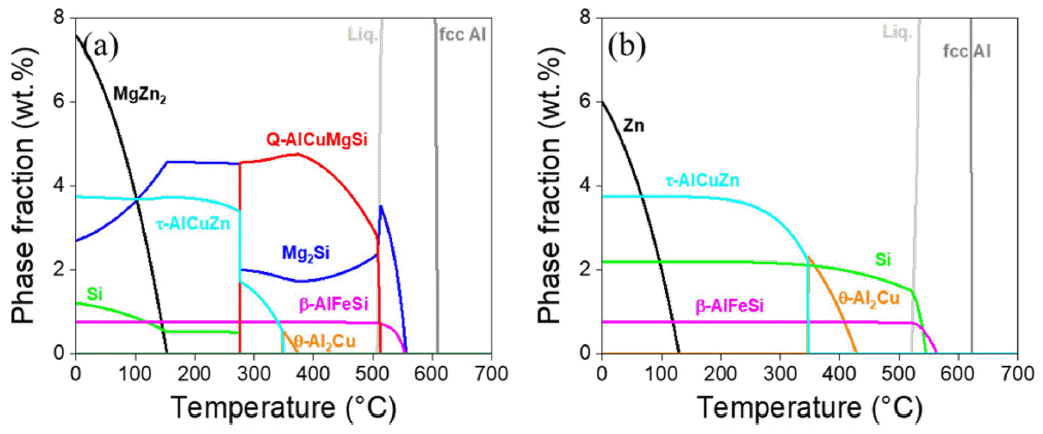
PDF The effects of annealing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Si alloys fabricated by high-energy ball milling (HEBM) and spark plasma sintering (SPS) were investigated. The HEBM-free sintered alloy primarily contained Mg2Si, Q-AlCuMgSi, and Si phases. Meanwhile, the HEBM-sintered alloy contains Mg-free Si and θ-Al2Cu phases due to the formation of MgO, which causes Mg depletion in the Al matrix. Annealing without and with HEBM at 500°C causes partial dissolution and coarsening of the Q-AlCuMgSi and Mg2Si phases in the alloy and dissolution of the θ-Al2Cu phase in the alloy, respectively. In both alloys, a thermally stable α-AlFeSi phase was formed after long-term heat treatment. The grain size of the sintered alloys with and without HEBM increased from 0.5 to 1.0 μm and from 2.9 to 6.3 μm, respectively. The hardness of the sintered alloy increases after annealing for 1 h but decreases significantly after 24 h of annealing. Extending the annealing time to 168 h improved the hardness of the alloy without HEBM but had little effect on the alloy with HEBM. The relationship between the microstructural factors and the hardness of the sintered and annealed alloys is discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructural evolution and thermal stability of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Si–Zr alloy fabricated via spark plasma sintering
Junho Lee, Seonghyun Park, Sang-Hwa Lee, Seung Bae Son, Hanjung Kwon, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2024; 31: 205. CrossRef
- Microstructural evolution and thermal stability of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Si–Zr alloy fabricated via spark plasma sintering
- [Korean]
- Alloy Design and Powder Manufacturing of Al-Cu-Si alloy for Low-Temperature Aluminum Brazing
- Heeyeon Kim, Chun Woong Park, Won Hee Lee, Young Do Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):339-345. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.339
- 1,541 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
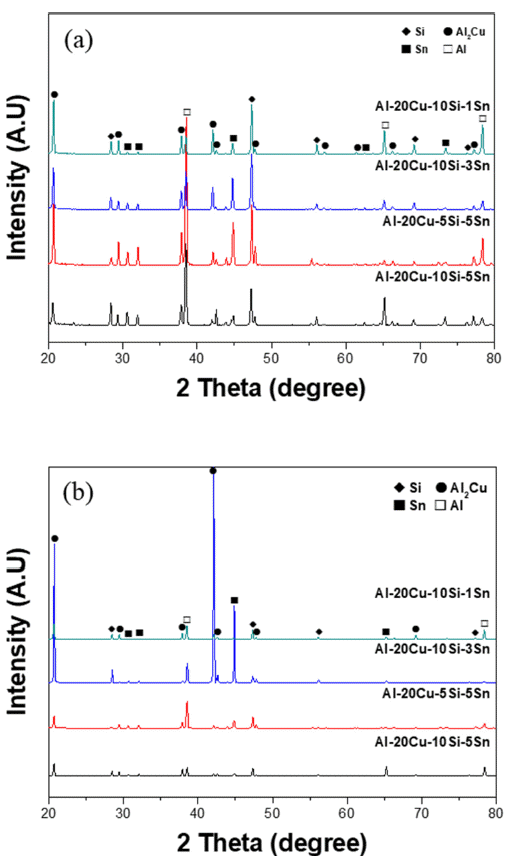
PDF This study investigates the melting point and brazing properties of the aluminum (Al)-copper (Cu)-silicon (Si)-tin (Sn) alloy fabricated for low-temperature brazing based on the alloy design. Specifically, the Al-20Cu-10Si-Sn alloy is examined and confirmed to possess a melting point of approximately 520°C. Analysis of the melting point of the alloy based on composition reveals that the melting temperature tends to decrease with increasing Cu and Si content, along with a corresponding decrease as the Sn content rises. This study verifies that the Al-20Cu-10Si-5Sn alloy exhibits high liquidity and favorable mechanical properties for brazing through the joint gap filling test and Vickers hardness measurements. Additionally, a powder fabricated using the Al-20Cu-10Si-5Sn alloy demonstrates a melting point of around 515°C following melting point analysis. Consequently, it is deemed highly suitable for use as a low-temperature Al brazing material.
- [Korean]
- Controlling Particle Size of Recycled Copper Oxide Powder for Copper Thermite Welding Characteristics
- Hansung Lee, Minsu Kim, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):332-338. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.332

- 935 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Thermite welding is an exceptional process that does not require additional energy supplies, resulting in welded joints that exhibit mechanical properties and conductivity equivalent to those of the parent materials. The global adoption of thermite welding is growing across various industries. However, in Korea, limited research is being conducted on the core technology of thermite welding. Currently, domestic production of thermite powder in Korea involves recycling copper oxide (CuO). Unfortunately, controlling the particle size of waste CuO poses challenges, leading to the unwanted formation of pores and cracks during thermite welding. In this study, we investigate the influence of powder particle size on thermite welding in the production of Cu-thermite powder using waste CuO. We conduct the ball milling process for 0.5–24 h using recycled CuO. The evolution of the powder shape and size is analyzed using particle size analysis and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Furthermore, we examine the thermal reaction characteristics through differential scanning calorimetry. Additionally, the microstructures of the welded samples are observed using optical microscopy and SEM to evaluate the impact of powder particle size on weldability. Lastly, hardness measurements are performed to assess the strengths of the welded materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Friction Welding of Casted SCM440 and Sintered F-05-140 Dissimilar Steels and Their Joint Properties under Various Welding Conditions
Jisung Lee, Hansung Lee, Eunhyo Song, Byungmin Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 414. CrossRef
- Friction Welding of Casted SCM440 and Sintered F-05-140 Dissimilar Steels and Their Joint Properties under Various Welding Conditions
- [Korean]
- A Study on Mechano-chemical Ball Milling Process for Fabricating Tungsten Disulfide Nanosheets
- Seulgi Kim, Yunhee Ahn, Dongju Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):376-381. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.376

- 569 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tungsten disulfide (WS2) nanosheets have attracted considerable attention because of their unique optical and electrical properties. Several methods for fabrication of WS2 nanosheets have been developed. However, methods for mass production of high-quality WS2 nanosheets remain challenging. In this study, WS2 nanosheets were fabricated using mechano-chemical ball milling based on the synergetic effects of chemical intercalation and mechanical exfoliation. The ball-milling time was set as a variable for the optimized fabricating process of WS2 nanosheets. Under the optimized conditions, the WS2 nanosheets had lateral sizes of 500–600 nm with either a monolayer or bilayer. They also exhibited high crystallinity in the 2H semiconducting phase. Thus, the proposed method can be applied to the exfoliation of other transition metal dichalcogenides using suitable chemical intercalants. It can also be used with highperformance WS2-based photodiodes and transistors used in practical semiconductor applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultrafast Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide via Flashlamp Annealing
Chan Hyeon Yang, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 509. CrossRef
- Ultrafast Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide via Flashlamp Annealing
- [Korean]
- Preparation and Refinement Behavior of (Hf-Ti-Ta-Zr-Nb)C High-Entropy Carbide Powders by Ultra High Energy Ball Milling Process
- Junwoo Song, Junhee Han, Song-Yi Kim, Jinwoo Seok, Hyoseop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):34-40. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.34

- 1,378 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Recently, high-entropy carbides have attracted considerable attention owing to their excellent physical and chemical properties such as high hardness, fracture toughness, and conductivity. However, as an emerging class of novel materials, the synthesis methods, performance, and applications of high-entropy carbides have ample scope for further development. In this study, equiatomic (Hf-Ti-Ta-Zr-Nb)C high-entropy carbide powders have been prepared by an ultrahigh- energy ball-milling (UHEBM) process with different milling times (1, 5, 15, 30, and 60 min). Further, their refinement behavior and high-entropy synthesis potential have been investigated. With an increase in the milling time, the particle size rapidly reduces (under sub-micrometer size) and homogeneous mixing of the prepared powder is observed. The distortions in the crystal lattice, which occur as a result of the refinement process and the multicomponent effect, are found to improve the sintering, thereby notably enhancing the formation of a single-phase solid solution (high-entropy). Herein, we present a procedure for the bulk synthesis of highly pure, dense, and uniform FCC single-phase (
Fm3m crystal structure) (Hf-Ti-Ta-Zr-Nb)C high-entropy carbide using a milling time of 60 min and a sintering temperature of 1,600°C.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Controlling Particle Size of Recycled Copper Oxide Powder for Copper Thermite Welding Characteristics
Hansung Lee, Minsu Kim, Byungmin Ahn
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 332. CrossRef
- Controlling Particle Size of Recycled Copper Oxide Powder for Copper Thermite Welding Characteristics
- [Korean]
- Electrochemical Properties of Ball-milled Tin-Graphite Composite Anode Materials for Lithium-Ion Battery
- Tae-Hui Lee, Hyeon-A Hong, Kwon-Koo Cho, Yoo-Young Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):462-469. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.462

- 1,209 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tin/graphite composites are prepared as anode materials for Li-ion batteries using a dry ball-milling process. The main experimental variables in this work are the ball milling time (0–8 h) and composition ratio (tin:graphite=5:95, 15:85, and 30:70 w/w) of graphite and tin powder. For comparison, a tin/graphite composite is prepared using wet ball milling. The morphology and structure of the different tin/graphite composites are investigated using X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and scanning and transmission electron microscopy. The electrochemical properties of the samples are also examined. The optimal dry ball milling time for the uniform mixing of graphite and tin is 6 h in a graphite-30wt.%Sn sample. The electrode prepared from the composite that is dry-ballmilled for 6 h exhibits the best cycle performance (discharge capacity after 50th cycle: 308 mAh/g and capacity retention: 46%). The discharge capacity after the 50th cycle is approximately 112 mAh/g, higher than that when the electrode is composed of only graphite (196 mAh/g after 50th cycle). This result indicates that it is possible to manufacture a tin/graphite composite anode material that can effectively buffer the volume change that occurs during cycling, even using a simple dry ball-milling process.
- [Korean]
- Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Ti-20Mo-0.5EB Composites
- Suhyun Bae, Wonki Jeong, Se-Eun Shin
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):403-409. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.403
- 657 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, Ti-Mo-EB composites are prepared by ball milling and spark plasma sintering (SPS) to obtain a low elastic modulus and high strength and to evaluate the microstructure and mechanical properties as a function of the process conditions. As the milling time and sintering temperature increased, Mo, as a β-Ti stabilizing element, diffused, and the microstructure of β-Ti increased. In addition, the size of the observed phase was small, so the modulus and hardness of α-Ti and β-Ti were measured using nanoindentation equipment. In both phases, as the milling time and sintering temperature increased, the modulus of elasticity decreased, and the hardness increased. After 12 h of milling, the specimen sintered at 1000°C showed the lowest values of modulus of elasticity of 117.52 and 101.46 GPa for α-Ti and β-Ti, respectively, confirming that the values are lower compared to the that in previously reported studies.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and High Temperature Mechanical Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steels Manufactured by Combination Milling Process
- Jung-Uk Lee, Young-Kyun Kim, Jeoung Han Kim, Hwi-Jin Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):389-395. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.389
- 818 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
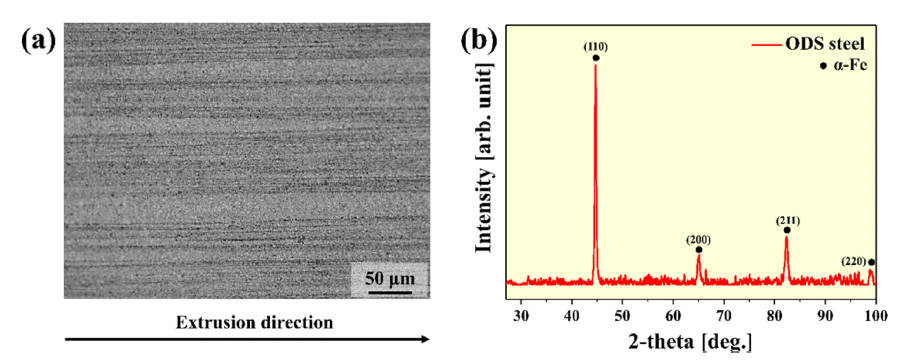
PDF Oxide dispersion-strengthened (ODS) steel has excellent high-temperature properties, corrosion resistance, and oxidation resistance, and is expected to be applicable in various fields. Recently, various studies on mechanical alloying (MA) have been conducted for the dispersion of oxide particles in ODS steel with a high number density. In this study, ODS steel is manufactured by introducing a complex milling process in which planetary ball milling, cryogenic ball milling, and drum ball milling are sequentially performed, and the microstructure and high-temperature mechanical properties of the ODS steel are investigated. The microstructure observation revealed that the structure is stretched in the extrusion direction, even after the heat treatment. In addition, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis confirmed the presence of oxide particles in the range of 5 to 10 nm. As a result of the room-temperature and high-temperature compression tests, the yield strengths were measured as 1430, 1388, 418, and 163 MPa at 25, 500, 700, and 900°C, respectively. Based on these results, the correlation between the microstructure and mechanical properties of ODS steel manufactured using the composite milling process is also discussed.
- [Korean]
- Influence of Milling Conditions on the Microstructural Characteristics and Mechanical Properties of Non-equiatomic High Entropy Alloy
- Namhyuk Seo, Junhyub Jeon, Gwanghoon Kim, Jungbin Park, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):103-109. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.103
- 867 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF High-entropy alloys have excellent mechanical properties under extreme environments, rendering them promising candidates for next-generation structural materials. It is desirable to develop non-equiatomic high-entropy alloys that do not require many expensive or heavy elements, contrary to the requirements of typical high-entropy alloys. In this study, a non-equiatomic high-entropy alloy powder Fe49.5Mn30Co10Cr10C0.5 (at.%) is prepared by high energy ball milling and fabricated by spark plasma sintering. By combining different ball milling times and ball-topowder ratios, we attempt to find a proper mechanical alloying condition to achieve improved mechanical properties. The milled powder and sintered specimens are examined using X-ray diffraction to investigate the progress of mechanical alloying and microstructural changes. A miniature tensile specimen after sintering is used to investigate the mechanical properties. Furthermore, quantitative analysis of the microstructure is performed using electron backscatter diffraction.
- [Korean]
- Development of Fe-Mn-based Hybrid Materials Containing Nano-scale Oxides by a Powder Metallurgical Route
- Jonggyu Jeon, Jungjoon Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):203-209. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.203

- 907 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The automotive industry has focused on the development of metallic materials with high specific strength, which can meet both fuel economy and safety goals. Here, a new class of ultrafine-grained high-Mn steels containing nano-scale oxides is developed using powder metallurgy. First, high-energy mechanical milling is performed to dissolve alloying elements in Fe and reduce the grain size to the nanometer regime. Second, the ball-milled powder is consolidated using spark plasma sintering. During spark plasma sintering, nanoscale manganese oxides are generated in Fe-15Mn steels, while other nanoscale oxides (e.g., aluminum, silicon, titanium) are produced in Fe-15Mn-3Al-3Si and Fe-15Mn-3Ti steels. Finally, the phases and resulting hardness of a variety of high-Mn steels are compared. As a result, the sintered pallets exhibit superior hardness when elements with higher oxygen affinity are added; these elements attract oxygen from Mn and form nanoscale oxides that can greatly improve the strength of high-Mn steels.
- [Korean]
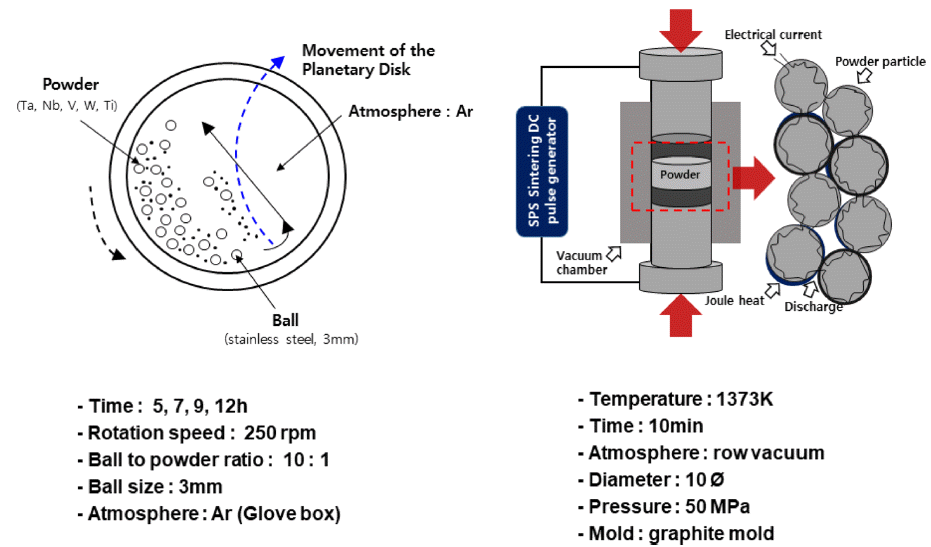
- Effect of Milling Time on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ta20Nb20V20W20Ti20 High Entropy Alloy
- Da Hye Song, Yeong Gyeom Kim, Jin Kyu Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):52-57. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.52
- 899 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we report the microstructure and characterization of Ta20Nb20V20W20Ti20 high-entropy alloy powders and sintered samples. The effects of milling time on the microstructure and mechanical properties were investigated in detail. Microstructure and structural characterization were performed by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. The mechanical properties of the sintered samples were analyzed through a compressive test at room temperature with a strain rate of 1 × 10−4 s−1. The microstructure of sintered Ta20Nb20V20W20Ti20 high-entropy alloy is composed of a BCC phase and a TiO phase. A better combination of compressive strength and strain was achieved by using prealloyed Ta20Nb20V20W20Ti20 powder with low oxygen content. The results suggest that the oxide formed during the sintering process affects the mechanical properties of Ta20Nb20V20W20Ti20 high-entropy alloys, which are related to the interfacial stability between the BCC matrix and TiO phase.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mechanisms of high-entropy carbide formation (TiVTaNbW)C via high-energy milling: structural, chemical, and spectroscopic analysis
Anderson C. Marques, Thalita Q. Silva, Pâmala S. Vieira, Celmo Hudson Reis Paula, Maria J.S. Lima, Rubens M. Nascimento, Marcello Filgueira, Uílame U. Gomes, Meysam Mashhadikarimi
Materials Science and Engineering: B.2026; 323: 118787. CrossRef
- Mechanisms of high-entropy carbide formation (TiVTaNbW)C via high-energy milling: structural, chemical, and spectroscopic analysis
- [Korean]
- Investigation on Size Distribution of Tungsten-based Alloy Particles with Solvent Viscosity During Ultrasonic Ball Milling Process
- KeunHyuk Ryu, HyeongSub So, JiSeok Yun, InHo Kim, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):201-207. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.201

- 1,138 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tungsten heavy alloys (W–Ni–Fe) play an important role in various industries because of their excellent mechanical properties, such as the excellent hardness of tungsten, low thermal expansion, corrosion resistance of nickel, and ductility of iron. In tungsten heavy alloys, tungsten nanoparticles allow the relatively low-temperature molding of high-melting-point tungsten and can improve densification. In this study, to improve the densification of tungsten heavy alloy, nanoparticles are manufactured by ultrasonic milling of metal oxide. The physical properties of the metal oxide and the solvent viscosity are selected as the main parameters. When the density is low and the Mohs hardness is high, the particle size distribution is relatively high. When the density is high and the Mohs hardness is low, the particle size distribution is relatively low. Additionally, the average particle size tends to decrease with increasing viscosity. Metal oxides prepared by ultrasonic milling in high-viscosity solvent show an average particle size of less than 300 nm based on the dynamic light scattering and scanning electron microscopy analysis. The effects of the physical properties of the metal oxide and the solvent viscosity on the pulverization are analyzed experimentally.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Morphological Control and Surface Modification Characteristics of Nickel Oxalate Synthesized via Oxalic Acid Precipitation
Eunbi Park, Jongwon Bae, Sera Kang, Minsu Kang, Suseong Lee, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(5): 375. CrossRef - Manufacture of high sensitive Ag-Fe3O4-PDMS nanocomposite pressure sensor through morphology control of conductive filler
Keunhyuk Ryu, Namhun Kwon, Kun-Jae Lee
Advanced Powder Technology.2021; 32(7): 2441. CrossRef - Grinding behavior of WO3, NiO, Fe2O3 by ultrasonic milling parameters control and preparation of nanocomposite powder
Keunhyuk Ryu, Kun-Jae Lee
Advanced Powder Technology.2020; 31(9): 3867. CrossRef
- Morphological Control and Surface Modification Characteristics of Nickel Oxalate Synthesized via Oxalic Acid Precipitation
- [Korean]
- Prediction the Phase Transformation Time of Binary Alloy System by calculating the Input Energy of Mechanical Alloying
- Dong-Kyu Park, In-Shup Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):107-111. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.107

- 616 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The activation energy to create a phase transformation or for the reaction to move to the next stage in the milling process can be calculated from the slop of the DSC plot, obtained at the various heating rates for mechanically activated Al-Ni alloy systems by using Kissinger’s equation. The mechanically activated material has been called “the driven material” as it creates new phases or intermetallic compounds of AlNi in Al-Ni alloy systems. The reaction time for phase transformation by milling can be calculated using the activation energy obtained from the above mentioned method and from the real required energy. The real required energy (activation energy) could be calculated by subtracting the loss energy from the total input energy (calculated input energy from electric motor). The loss energy and real required energy divided by the reaction time are considered the “metabolic energy” and “the effective input energy”, respectively. The milling time for phase transformation at other Al-Co alloy systems from the calculated data of Al-Ni systems can be predicted accordingly.
- [Korean]
- Analysis on Milling Behavior of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Ni-based Atomizing Powder with Ni5Y Intermetallic Phase
- Chun Woong Park, Jong Min Byun, Won June Choi, Young Do Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):101-106. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.101

- 997 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Ni-based oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) alloys have a higher usable temperature and better hightemperature mechanical properties than conventional superalloys. They are therefore being explored for applications in various fields such as those of aerospace and gas turbines. In general, ODS alloys are manufactured from alloy powders by mechanical alloying of element powders. However, our research team produces alloy powders in which the Ni5Y intermetallic phase is formed by an atomizing process. In this study, mechanical alloying was performed using a planetary mill to analyze the milling behavior of Ni-based oxide dispersions strengthened alloy powder in which the Ni5Y is the intermetallic phase. As the milling time increased, the Ni5Y intermetallic phase was refined. These results are confirmed by SEM and EPMA analysis on microstructure. In addition, it is confirmed that as the milling increased, the mechanical properties of Ni-based ODS alloy powder improve due to grain refinement by plastic deformation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficient prediction of corrosion behavior in ternary Ni-based alloy systems: Theoretical calculations and experimental verification
Xuelian Xiao, Keke Chang, Kai Xu, Ming Lou, Liping Wang, Qunji Xue
Journal of Materials Science & Technology.2023; 167: 94. CrossRef - Effect of high-energy ball milling on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ni-based ODS alloys fabricated using gas-atomized powder
Chun Woong Park, Won June Choi, Jongmin Byun, Young Do Kim
Journal of Materials Science.2022; 57(38): 18195. CrossRef
- Efficient prediction of corrosion behavior in ternary Ni-based alloy systems: Theoretical calculations and experimental verification
- [Korean]
- Development of Metal Composite Powder Non-corrosive Flux for Low Temperature Forming of the Aluminum Brazing Filler Material
- Dae-Young Kim, Ha-Neul Jang, Dae-Ho Yoon, Yun-Ho Shin, Seong-Ho Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):16-21. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.16

- 798 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In aluminum brazing processes, corrosive flux, which is used in preventing oxidation, is currently raising environmental concerns because it generates many pollutants such as dioxin. The brazing process involving noncorrosive flux is known to encounter difficulties because the melting temperature of the flux is similar to that of the base material. In this study, a new brazing filler material is developed based on aluminum and non-corrosive flux composite powder. To minimize the interference of consolidation aluminum alloy powder by the flux, the flux is intentionally embedded in the aluminum alloy powder using a mechanical milling process. This study demonstrates that the morphology of the composite powder can be varied according to the mixing process, and this significantly affects the relative density and mechanical properties of the final filler samples.
- [Korean]
- Effects of Morphologies of Carbon Nanomaterials on Conductivity of Composites Containing Copper/Carbon Nanomaterial Hybrid Fillers
- Yeonjoo Lee, Sung-uk Hong, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):435-440. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.435

- 561 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In the present study, we develop a conductive copper/carbon nanomaterial additive and investigate the effects of the morphologies of the carbon nanomaterials on the conductivities of composites containing the additive. The conductive additive is prepared by mechanically milling copper powder with carbon nanomaterials, namely, multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and/or few-layer graphene (FLG). During the milling process, the carbon nanomaterials are partially embedded in the surfaces of the copper powder, such that electrically conductive pathways are formed when the powder is used in an epoxy-based composite. The conductivities of the composites increase with the volume of the carbon nanomaterial. For a constant volume of carbon nanomaterial, the FLG is observed to provide more conducting pathways than the MWCNTs, although the optimum conductivity is obtained when a mixture of FLG and MWCNTs is used.
- [English]
- Development of Carbon Nanotube-copper Hybrid Powder as Conductive Additive
- Minjae Lee, Seoungjun Haa, Yeonjoo Lee, Haneul Jang, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(4):291-295. Published online August 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.4.291
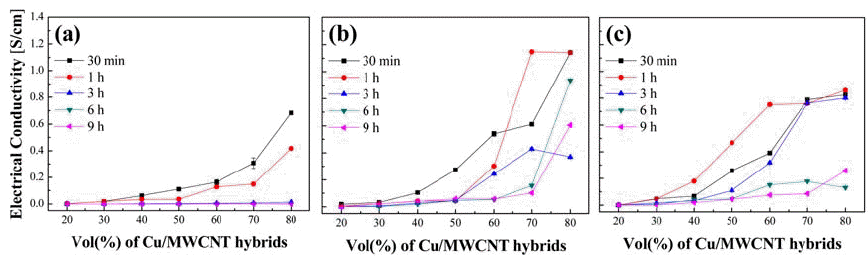
- 1,380 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A conductive additive is prepared by dispersing multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) on Cu powder by mechanical milling and is distributed in epoxy to enhance its electrical conductivity. During milling, the MWCNTs are dispersed and partially embedded on the surface of the Cu powder to provide electrically conductive pathways within the epoxy-based composite. The degree of dispersion of the MWCNTs is controlled by varying the milling medium and the milling time. The MWCNTs are found to be more homogeneously dispersed when solvents (particularly, non-polar solvent, i.e., NMP) are used. MWCNTs gradually disperse on the surface of Cu powder because of the plastic deformation of the ductile Cu powder. However, long-time milling is found to destroy the molecular structure of MWCNTs, instead of effectively dispersing the MWCNTs more uniformly. Thus, the epoxy composite film fabricated in this study exhibits a higher electrical conductivity than 1.1 S/cm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Morphologies of Carbon Nanomaterials on Conductivity of Composites Containing Copper/Carbon Nanomaterial Hybrid Fillers
Yeonjoo Lee, Sung-uk Hong, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(5): 435. CrossRef
- Effects of Morphologies of Carbon Nanomaterials on Conductivity of Composites Containing Copper/Carbon Nanomaterial Hybrid Fillers
- [Korean]
- Micro-deformation behavior of Brittle Hf-based Metallic Glass during Mechanical Milling
- Song-Yi Kim, A-Young Lee, Eun-Ji Cha, Do-Hun Kwon, Sung-Uk Hong, Min-Woo Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim, Min-Ha Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(3):246-250. Published online June 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.3.246

- 682 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we investigate the deformation behavior of Hf44.5Cu27Ni13.5Nb5Al10 metallic glass powder under repeated compressive strain during mechanical milling. High-density (11.0 g/cc) Hf-based metallic glass powders are prepared using a gas atomization process. The relationship between the mechanical alloying time and microstructural change under phase transformation is evaluated for crystallization of the amorphous phase. Planetary mechanical milling is performed for 0, 40, or 90 h at 100 rpm. The amorphous structure of the Hf-based metallic glass powders during mechanical milling is analyzed using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Microstructural analysis of the Hf-based metallic glass powder deformed using mechanical milling reveals a layered structure with vein patterns at the fracture surface, which is observed in the fracture of bulk metallic glasses. We also study the crystallization behavior and the phase and microstructure transformations under isothermal heat treatment of the Hf-based metallic glass.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Milling Time and Addition of PCA on Austenite Stability of Fe-7%Mn Alloy
- Seung-Jin Oh, In-Jin Shon, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):126-131. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.126

- 784 View
- 9 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In the present study, we investigate the effects of milling time and the addition of a process control agent (PCA) on the austenite stability of a nanocrystalline Fe-7%Mn alloy by XRD analysis and micrograph observation. Nanocrystalline Fe-7%Mn alloys samples are successfully fabricated by spark plasma sintering. The crystallite size of ball-milled powder and the volume fraction of austenite in the sintered sample are calculated using XRD analysis. Changes in the shape and structure of alloyed powder according to milling conditions are observed through FE-SEM. It is found that the crystallite size is reduced with increasing milling time and amount of PCA addition due to the variation in the balance between the cold-welding and fracturing processes. As a result, the austenite stability increased, resulting in an exceptionally high volume fraction of austenite retained at room temperature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of mechanical milling on microstructure and mechanical properties of CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy fabricated via spark plasma sintering
Seonghyun Park, Sang-Hwa Lee, Eunjoo Shin, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2025; 39: 4854. CrossRef - Effect of Cooling Rate on Microstructure and Hardness during Solution Treatment and Aging Process of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy for Aerospace Components
Seongji Seo, Hojoon Choi, Geeyoung Lee, Kee-Ahn Lee, Jeongho Han, Minsu Jung
Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance.2021; 30(5): 3406. CrossRef - Development of Fe-Mn-based Hybrid Materials Containing Nano-scale Oxides by a Powder Metallurgical Route
Jonggyu Jeon, Jungjoon Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 203. CrossRef - Austenite Stability of Sintered Fe-based Alloy
Seunggyu Choi, Namhyuk Seo, Junhyub Jun, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(5): 414. CrossRef - Austenite Stability of Nanocrystalline FeMnNiC Alloy
Seung-Jin Oh, Junhyub Jeon, In-Jin Shon, Seok-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(5): 389. CrossRef
- Effects of mechanical milling on microstructure and mechanical properties of CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy fabricated via spark plasma sintering
- [Korean]
- Insulating Behavior of Sintered AlN Ceramics Prepared by High-Energy Bead Milling of AlN Powder
- Sung-Soo Ryu, Sung-Min Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):444-449. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.444

- 797 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Aluminum nitride (AlN) powder specimens are treated by high-energy bead milling and then sintered at various temperatures. Depending on the solvent and milling time, the oxygen content in the AlN powder varies significantly. When isopropyl alcohol is used, the oxygen content increases with the milling time. In contrast, hexane is very effective at suppressing the oxygen content increase in the AlN powder, although severe particle sedimentation after the milling process is observed in the AlN slurry. With an increase in the milling time, the primary particle size remains nearly constant, but the particle agglomeration is reduced. After spark plasma sintering at 1400°C, the second crystalline phase changes to compounds containing more Al2O3 when the AlN raw material with an increased milling time is used. When the sintering temperature is decreased from 1750°C to 1400°C, the DC resistivity increases by approximately two orders of magnitude, which implies that controlling the sintering temperature is a very effective way to improve the DC resistivity of AlN ceramics.
- [Korean]
- Characteristics of WO3-CuO Powder Mixture Prepared by High-Energy Ball Milling in a Bead Mill for the Synthesis of W-Cu Nanocomposite Powder
- Hae-Ryong Park, Sung-Soo Ryu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):406-413. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.406

- 1,050 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A Nanosized WO3 and CuO powder mixture is prepared using novel high-energy ball milling in a bead mill to obtain a W-Cu nanocomposite powder, and the effect of milling time on the structural characteristics of WO3-CuO powder mixtures is investigated. The results show that the ball-milled WO3-CuO powder mixture reaches at steady state after 10 h milling, characterized by the uniform and narrow particle size distribution with primary crystalline sizes below 50 nm, a specific surface area of 37 m2/g, and powder mean particle size (D50) of 0.57 μm. The WO3-CuO powder mixtures milled for 10 h are heat-treated at different temperatures in H2 atmosphere to produce W-Cu powder. The XRD results shows that both the WO3 and CuO phases can be reduced to W and Cu phases at temperatures over 700°C. The reduced W-Cu nanocomposite powder exhibits excellent sinterability, and the ultrafine W-Cu composite can be obtained by the Cu liquid phase sintering process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Morphological Characteristics of W/Cu Composite Nanoparticles with Complex Phase Structure Synthesized via Reactive Radio Frequency (RF) Thermal Plasma
Chulwoong Han, Song-Yi Kim, Soobin Kim, Ji-Woon Lee
Metals.2024; 14(9): 1070. CrossRef
- Morphological Characteristics of W/Cu Composite Nanoparticles with Complex Phase Structure Synthesized via Reactive Radio Frequency (RF) Thermal Plasma
- [Korean]
- Effect of Powder Mixing Process on the Characteristics of Hybrid Structure Tungsten Powders with Nano-Micro Size
- Na-Yeon Kwon, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):384-388. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.384

- 902 View
- 3 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The effect of the mixing method on the characteristics of hybrid-structure W powder with nano and micro sizes is investigated. Fine WO3 powders with sizes of ~0.6 μm, prepared by ball milling for 10 h, are mixed with pure W powder with sizes of 12 μm by various mixing process. In the case of simple mixing with ball-milled WO3 and micro sized W powders, WO3 particles are locally present in the form of agglomerates in the surface of large W powders, but in the case of ball milling, a relatively uniform distribution of WO3 particles is exhibited. The microstructural observation reveals that the ball milled WO3 powder, heat-treated at 750°C for 1 h in a hydrogen atmosphere, is fine W particles of ~200 nm or less. The powder mixture prepared by simple mixing and hydrogen reduction exhibits the formation of coarse W particles with agglomeration of the micro sized W powder on the surface. Conversely, in the powder mixture fabricated by ball milling and hydrogen reduction, a uniform distribution of fine W particles forming nano-micro sized hybrid structure is observed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Efficiency of Radiation Shielding Sheet to Reduce Radiation Exposure during C-arm Fluoroscopy
Hosang Jeon, Won Chul Shin, Hee Yun Seol, Yongkan Ki, Kyeong Baek Kim, Ki Seok Choo, Sang Don Lee, Suk-Woong Kang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2023; 36(4): 111. CrossRef - Microstructure and Sintering Behavior of Fine Tungsten Powders Synthesized by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis
Hyeonhui Jo, Jeong Hyun Kim, Young-In Lee, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2021; 59(5): 289. CrossRef - Facile phosphorus-embedding into SnS2 using a high-energy ball mill to improve the surface kinetics of P-SnS2 anodes for a Li-ion battery
Hongsuk Choi, Seungmin Lee, KwangSup Eom
Applied Surface Science.2019; 466: 578. CrossRef - Hydrogen reduction behavior and microstructural characteristics of WO3 and WO3-NiO powders
Hyunji Kang, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2019; 80: 69. CrossRef - Fabrication of Densified W-Ti by Reaction Treatment and Spark Plasma Sintering of WO3-TiH2 Powder Mixtures
Hyunji Kang, Heun Joo Kim, Ju-Yeon Han, Yunju Lee, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2018; 28(9): 511. CrossRef
- The Efficiency of Radiation Shielding Sheet to Reduce Radiation Exposure during C-arm Fluoroscopy
- [English]
- Influence of milling atmosphere on thermoelectric properties of p-type Bi-Sb-Te based alloys by mechanical alloying
- Suk-min Yoon, Cheenepalli Nagarjuna, Dong-won Shin, Chul-hee Lee, Babu Madavali, Soon-jik Hong, Kap-ho Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):357-363. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.357
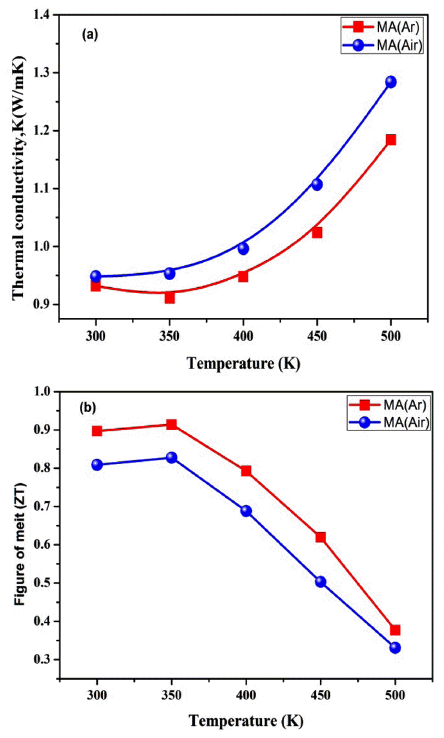
- 1,283 View
- 4 Download
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, Bi-Sb-Te thermoelectric materials are produced by mechanical alloying (MA) and spark plasma sintering (SPS). To examine the influence of the milling atmosphere on the microstructure and thermo-electric (TE) properties, a p-type Bi-Sb-Te composite powder is mechanically alloyed in the presence of argon and air atmospheres. The oxygen content increases to 55% when the powder is milled in the air atmosphere, compared with argon. All grains are similar in size and uniformly, distributed in both atmospheric sintered samples. The Seebeck coefficient is higher, while the electrical conductivity is lower in the MA (Air) sample due to a low carrier concentration compared to the MA (Ar) sintered sample. The maximum figure of merit (ZT) is 0.91 and 0.82 at 350 K for the MA (Ar) and MA (Air) sintered samples, respectively. The slight enhancement in the ZT value is due to the decrease in the oxygen content during the MA (Ar) process. Moreover, the combination of mechanical alloying and SPS process shows a higher hardness and density values for the sintered samples.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Grain Size‐Dependent Thermoelectric Performances of Al2O3 Addition into BiSbTe Alloy During Heat Treatment Fabricated by Mechanical Alloying
Ji‐Won Ha, Vasudevan Rathinam, Eun‐Ha Go, Soon‐Jik Hong
Advanced Engineering Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Revealing the improved thermoelectric performances of (BiSb)2Te3 alloy through rapid solidification of cold-water assisted water atomization approach
Eun-Ha Go, Rathinam Vasudevan, Ji-Won Ha, Sung-Jae Jo, GeonWoo Baek, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2025; 1010: 177548. CrossRef - Microstructural and Thermoelectric Properties of Heat-treated Al2O3 Doped BiSbTe Alloy
Jiwon Ha, Vasudevan Rathinam, Eunha Go, Soonjik Hong
Journal of the Japan Society of Powder and Powder Metallurgy.2025; 72(Supplement): S983. CrossRef - Advancement of thermoelectric performances through the dispersion of expanded graphene on p-type BiSbTe alloys
Eun-Ha Go, Rathinam Vasudevan, Babu Madavali, Peyala Dharmaiah, Min-Woo Shin, Sung Ho Song, Soon-Jik Hong
Powder Metallurgy.2023; 66(5): 722. CrossRef - Influence of milling atmosphere on the structure and magnetic properties of mechanically alloyed Fe40Co30Ni30
Alex Abraham Paul, Anuj Rathi, Ganesh Varma Thotakura, Tanjore V. Jayaraman
Materials Chemistry and Physics.2021; 258: 123897. CrossRef - Enhancement of mechanical properties and thermoelectric performance of spark plasma sintered P-type Bismuth Telluride by powder surface oxide reduction
Ahmed A. Abdelnabi, Vickram Lakhian, Joseph R. McDermid, Yu-Chih Tseng, James S. Cotton
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2021; 858: 157657. CrossRef - Solid solution evolution during mechanical alloying in Cu-Nb-Al compounds
Kaouther Zaara, Mahmoud Chemingui, Virgil Optasanu, Mohamed Khitouni
International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials.2019; 26(9): 1129. CrossRef
- Grain Size‐Dependent Thermoelectric Performances of Al2O3 Addition into BiSbTe Alloy During Heat Treatment Fabricated by Mechanical Alloying
- [Korean]
- High Temperature Oxidation Behavior of Fe-14Cr Ferritic Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steels Manufactured by Mechanical Alloying Process
- Young-Kyun Kim, Jong-Kwan Park, Hwi-Jun Kim, Man-Sik Kong, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):133-140. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.133

- 690 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study investigates the oxidation properties of Fe-14Cr ferritic oxide-dispersion-strengthened (ODS) steel at various high temperatures (900, 1000, and 1100°C for 24 h). The initial microstructure shows that no clear structural change occurs even under high-temperature heat treatment, and the average measured grain size is 0.4 and 1.1 μm for the as-fabricated and heat-treated specimens, respectively. Y–Ti–O nanoclusters 10–50 nm in size are observed. High-temperature oxidation results show that the weight increases by 0.27 and 0.29 mg/cm2 for the asfabricated and heat-treated (900°C) specimens, and by 0.47 and 0.50 mg/cm2 for the as-fabricated and heat-treated (1000°C) specimens, respectively. Further, after 24 h oxidation tests, the weight increases by 56.50 and 100.60 mg/cm2 for the as-fabricated and heat-treated (1100°C) specimens, respectively; the latter increase is approximately 100 times higher than that at 1000°C. Observation of the surface after the oxidation test shows that Cr2O3 is the main oxide on a specimen tested at 1000°C, whereas Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 phases also form on a specimen tested at 1100°C, where the weight increases rapidly. The high-temperature oxidation behavior of Fe-14Cr ODS steel is confirmed to be dominated by changes in the Cr2O3 layer and generation of Fe-based oxides through evaporation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructure and Wear Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steel Powder Added Steel-Based Composite Material for Automotive Part
Young-Kyun Kim, Jong-Kwan Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(1): 36. CrossRef
- Microstructure and Wear Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steel Powder Added Steel-Based Composite Material for Automotive Part
- [English]
- Synthesis of Carbonyl Iron-reinforced Polystyrene by High Energy Ball Milling
- Hong-Hai Nguyen, Minh-Thuyet Nguyen, Won Joo Kim, Jin-Chun Kim, Young-Soo Kim, Young-Hyuk Kim, Olga B. Nazarenko
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):276-281. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.276
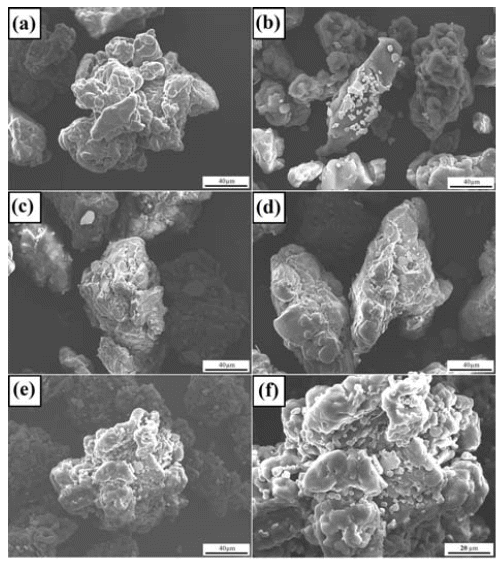
- 1,273 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Carbonyl iron (CI) is successfully incorporated as an additive into a polystyrene (PS) matrix via a highenergy ball milling method, under an n-hexane medium with volume fractions between 1% and 5% for electromagnetic interference shielding applications by the combination of magnetic CI and an insulating PS matrix. The morphology and the dispersion of CI are investigated by field emission scanning electron microscopy, which indicates a uniform distribution of CI in the PS matrix after 2 h of milling. The thermal behavior results indicate no significant degradation of the PS when there is a slight increase in the onset temperature with the addition of CI powder, when compared to the as-received PS pellet. After milling, there are no interactions between the CI and the PS matrix, as confirmed by Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy. In this study, the milled CI-PS powder is extruded to make filaments, and can have potential applications in the 3-D printing industry.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Progress toward sustainable polymer technologies with ball-mill grinding
Antonio Rizzo, Gregory I. Peterson
Progress in Polymer Science.2024; 159: 101900. CrossRef
- Progress toward sustainable polymer technologies with ball-mill grinding
- [English]
- A Study on Synthesis of Ni-Ti-B Alloy by Mechanical Alloying from Elemental Component Powder
- Jung Geun Kim, Yong Ho Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):202-206. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.202
- 1,538 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
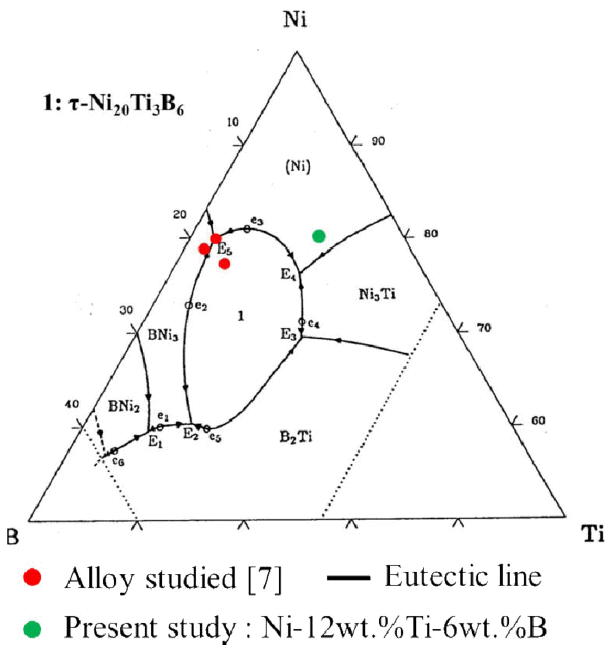
PDF A Ni-Ti-B alloy powder prepared by mechanical alloying (MA) of individual Ni, Ti, and B components is examined with the aim of elucidating the phase transitions and crystallization during heat treatment. Ti and B atoms penetrating into the Ni lattice result in a Ni (Ti, B) solid solution and an amorphous phase. Differential thermal analysis (DTA) reveals peaks related to the decomposition of the metastable Ni (Ti, B) solid solution and the separation of equilibrium Ni3Ti, TiB2, and τ-Ni20Ti3B6 phases. The exothermal effects in the DTA curves move to lower temperatures with increasing milling time. The formation of a TiB2 phase by annealing indicates that the mechanochemical reaction of the Ni-Ti-B alloy does not comply with the alloy composition in the ternary phase diagram, and Ti-B bonds are found to be more preferable than Ni-B bonds.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Solid‐State Synthesis and Characterization of the Stable Nanostructured Ni21Ti2B6 Phase
Tuncay Simsek, Baris Avar, Sadan Ozcan, Arun K. Chattopadhyay, Bora Kalkan
physica status solidi (b).2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Synthesis and analysis of nanocrystalline β1-Cu3Al and β2-NiAl intermetallic-reinforced aluminum matrix composite by high energy ball milling
Hong-Hai Nguyen, Minh-Thuyet Nguyen, Won Joo Kim, Jin-Chun Kim
Metals and Materials International.2017; 23(1): 202. CrossRef
- Solid‐State Synthesis and Characterization of the Stable Nanostructured Ni21Ti2B6 Phase
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Silver Flake Powder by the Mechanical Milling Process
- Hae-Young Jeong, Gil-Geun Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(1):54-60. Published online February 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.1.54
- 702 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study focuses on fabricating silver flake powder by a mechanical milling process and investigating the formation of flake-shaped particles during milling. The silver flake powder is fabricated by varying the mechanical milling parameters such as the amount of powder, ball size, impeller rotation speed, and milling time of the attrition ballmill. The particle size of the silver flake powder decreases with increasing amount of powder; however, it increases with increasing impeller rotation speed. The change in the particle size of the silver flake powder is analyzed based on elastic collision between the balls, taking energy loss of the balls due to the powder into consideration. The change in the particle size of the silver flake powder with mechanical milling parameters is consistent with the change in the diameter of the elastic deformation contact area of the ball, due to the collision between the balls, with milling parameters. The flake-shaped silver particles are formed at the elastic deformation contact area of the ball due to the collision.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of WC/Co composite powder from oxide of WC/Co hardmetal scrap by carbothermal reduction process
Gil-Geun Lee, Young Soo Lim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(3): 240. CrossRef
- Fabrication of WC/Co composite powder from oxide of WC/Co hardmetal scrap by carbothermal reduction process
- [Korean]
- Briquetting of Waste Silicon Carbide Obtained from Silicon Wafer Sludges
- Seong Mo Koo, Su Jong Yoon, Hye Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(1):43-48. Published online February 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.1.43
- 792 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Waste SiC powders obtained from silicon wafer sludge have very low density and a narrow particle size distribution of 10-20 μm. A scarce yield of C and Si is expected when SiC powders are incorporated into the Fe melt without briquetting. Here, the briquetting variables of the SiC powders are studied as a function of the sintering temperature, pressure, and type and contents of the binders to improve the yield. It is experimentally confirmed that Si and C from the sintered briquette can be incorporated effectively into the Fe melt when the waste SiC powders milled for 30 min with 20 wt.% Fe binder are sintered at 1100°C upon compaction using a pressure of 250 MPa. XRF-WDS analysis shows that an yield of about 90% is obtained when the SiC briquette is kept in the Fe melt at 1650°C for more than 1 h.
- [Korean]
- Spark Plasma Sintering of Fe-TiC Composite Powders
- Yong-Heui Lee, Xuan-Khoa Hyunh, Ji Soon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(5):382-388. Published online October 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.5.382

- 932 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Fe-TiC composite powder was fabricated by high-energy milling of powder mixture of (Fe, TiC) and (FeO, TiH2, C) as starting materials, respectively. The latter one was heat-treated for reaction synthesis of TiC phase after milling. Both powders were spark-plasma sintered at various temperatures of 680-1070°C for 10 min. with sintering pressure of 70 MPa and the heating rate of 50°C/min. under vacuum of 0.133 Pa. Density and hardness of the sintered compact was investigated. Fe-TiC composite fabricated from (FeO, TiH2, C) as starting materials showed better sintered properties. It seems to be resulted from ultra-fine TiC particle size and its uniform distribution in Fe-matrix compared to the simply mixed (Fe, TiC) powder.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative study of Ni-TaC composites via high-energy ball milling activation and spark plasma sintering: Reinforcement, densification, oxidation resistance, and mechanical property
Bum-Soon Park, Jeong-Han Lee, Jae-Cheol Park, Hyun-Kuk Park
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2024; 984: 173900. CrossRef - Effect of TiC particle size on high temperature oxidation behavior of TiC reinforced stainless steel
Yeong-Hwan Lee, Sungmin Ko, Hyeonjae Park, Donghyun Lee, Sangmin Shin, Ilguk Jo, Sang-Bok Lee, Sang-Kwan Lee, Yangdo Kim, Seungchan Cho
Applied Surface Science.2019; 480: 951. CrossRef - Effect of TiC addition on surface oxidation behavior of SKD11 tool steel composites
Seungchan Cho, Ilguk Jo, Heebong Kim, Hyuk-Tae Kwon, Sang-Kwan Lee, Sang-Bok Lee
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 155. CrossRef
- Comparative study of Ni-TaC composites via high-energy ball milling activation and spark plasma sintering: Reinforcement, densification, oxidation resistance, and mechanical property
- [Korean]
- Mechanical Alloying of GaSe and GaTe Systems
- Jung Bo Choi, Jung-Ho Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(5):338-342. Published online October 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.5.338

- 724 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In the present work, we investigated the mechanical alloying of binary Ga-Se(1:1) and Ga-Te(1;1) sysyems. The high-energy ball-milling was performed at 40°C where one of constituents (Ga) is molten state. The purpose of the work was to see whether reactions between constituent elements are accelerated by the presence of a liquid phase. During the ball-milling, the liquid Ga phase completely disappeared and the resulting powders consist of nanocrystalline grain of ~20 nm with partly amorphized phases. However, no intermetallic compounds formed in spite of the presence of the liquid phases which has much higher diffusivity than solid constituents. By subsequent heat-treatments, the inter-metallic compounds such as GaSe and GaTe formed at relatively low temperatures. The formation temperature of theses compound was much lower than those predicted by equilibrium phase diagram. The comparison of the ball-milled powders with un-milled ones indicated that the easy formation of intermetallic compound or allying occurs at low temperatures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study on Synthesis of Ni-Ti-B Alloy by Mechanical Alloying from Elemental Component Powder
Jung Geun Kim, Yong Ho Park
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(3): 202. CrossRef
- A Study on Synthesis of Ni-Ti-B Alloy by Mechanical Alloying from Elemental Component Powder
- [Korean]
- Effect of Mechanical Milling Parameters on the Particle Size of Silver Flake
- Gil-Geun Lee, Hae-Young Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(4):307-312. Published online August 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.4.307

- 700 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study is focused on investigating the relation between the particle size of silver flake powder and mechanical milling parameters. Mechanical milling parameters such as ball size, impeller rotation speed and milling time of the attrition ball-mill were controlled to produce silver flake powder. The particle size of the silver flake powder increased with increasing ball size and impeller rotation speed. The change of the particle size of the silver flake powder with mechanical milling parameters was analyzed based on balls motion in the mill container of the attrition ballmill. The silver flake particles were formed at the elastic deformation area of the ball due to the collision between balls. The change of the particle size of the silver flake powder with mechanical milling parameters well consists with the change of the collision energy of ball with parameters mentioned above.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Silver Flake Powder by the Mechanical Milling Process
Hae-Young Jeong, Gil-Geun Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(1): 54. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Silver Flake Powder by the Mechanical Milling Process
- [English]
- Spark Plasma Sintering of Stainless Steel Powders Fabricated by High Energy Ball Milling
- Si Young Chang, Sung-Tag Oh, Myung-Jin Suk, Chan Seok Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(2):97-101. Published online April 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.2.97

- 1,073 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The 304 stainless steel powders were prepared by high energy ball milling and subsequently sintered by spark plasma sintering, and the microstructural characteristics and micro-hardness were investigated. The initial size of the irregular shaped 304 stainless steel powders was approximately 42 μm. After high energy ball milling at 800 rpm for 5h, the powders became spherical with a size of approximately 2 μm, and without formation of reaction compounds. From TEM analysis, it was confirmed that the as-milled powders consisted of the aggregates of the nano-sized particles. As the sintering temperature increased from 1073K to 1573K, the relative density and micro-hardness of sintered sample increased. The sample sintered at 1573K showed the highest relative density of approximately 95% and a micro-hardness of 550 Hv.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigating molybdenum’s sulphur scavenging ability for MoS2 formation in preventing pitting corrosion of stainless steels
Kai Xiang Kuah, Daniel J. Blackwood
npj Materials Degradation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Investigating molybdenum’s sulphur scavenging ability for MoS2 formation in preventing pitting corrosion of stainless steels
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


