Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Comparison of the Properties of Rare-Earth Zirconate Thermal Barrier Coatings for Hydrogen-Fueled Gas Turbines
- Gun-Woong Lee, Min-Soo Nam, Min-Ji Kim, HyunSuk Jung, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):472-480. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00423
- 783 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) for hydrogen-fueled gas turbines withstand higher combustion temperatures and increased steam concentrations compared to conventional natural-gas systems. These harsh operating conditions significantly accelerate the thermal degradation of widely used YSZ coatings, emphasizing the need for alternative top-coat materials with improved phase stability and reduced thermal conductivity. In this study, rare-earth zirconate ceramics, Gd2Zr2O7 (GdZO), Tm2Zr2O7 (TmZO), and a mixed composition (Gd0.5Tm0.5)2Zr2O7 (Gd/TmZO), are synthesized and investigated as potential next-generation TBC candidates. Each material was comparatively examined with a focus on crystal structure, thermophysical properties, and thermal conductivity. Furthermore, high-temperature steam exposure experiments were performed to simulate hydrogen combustion environments. Microstructural analyses, high-temperature degradation behavior, and phase stability evaluations were carried out to obtain fundamental experimental data. This study provides essential baseline information for the design and development of high-performance TBC materials suitable for the hydrogen-fueled gas turbine systems.
- [Korean]
- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
- Min Gi An, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):492-500. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00332
- 753 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A flexible heater with high thermal efficiency and mechanical durability was developed by fabricating laser-induced porous graphene (LIPG) electrodes on polyimide films using a 532 nm green laser. Laser power, scan speed, and line distance were precisely optimized based on photothermal simulations to generate uniform porous graphene structures with large surface area and excellent heat dissipation characteristics. Raman, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analyses confirmed that the optimized LIPG exhibited highly graphitized features with low oxygen defects. Scanning electron microscope analysis revealed that porous morphologies formed only within a specific laser scan speed range, whereas excessive or insufficient irradiation resulted in collapsed or absent porosity. The serpentine-patterned LIPG heater maintained stable electrical resistance under repeated multidirectional bending, demonstrating excellent flexibility and mechanical stability. The heater also achieved rapid and uniform heating up to 80 °C within seconds, maintaining consistent temperature distribution even on curved surfaces.
- [Korean]
- Enhanced H2S Gas Sensing Using ZnO Porous Nanorod Synthesized via a Rotational Hydrothermal Method
- Jimyeong Park, Changyu Kim, Minseo Kim, Jiyeon Shin, Jae-Hyoung Lee, Myung Sik Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):406-415. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00262
- 446 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, ZnO porous nanorods were synthesised using a rotational hydrothermal process, and their performance as hydrogen sulphide (H2S) gas sensors was analysed. Compared to commercial ZnO nanoparticles and conventionally hydrothermally synthesised ZnO nanorods, the ZnO porous nanorods exhibited a more uniform structure and improved crystal growth in the (002) plane, with surfaces rich in porosity and oxygen vacancies. These structural and chemical characteristics significantly improved the sensitivity toward H2S, showing high detection performance at 250°C across various concentrations of H2S gas. Additionally, the sensor demonstrated excellent selectivity against other gases such as C2H5OH, C6H6, C7H8, and NH3. This study indicated that the rotational hydrothermal process is an effective method for developing high-performance ZnO-based gas sensors and suggests its applicability to other metal oxide materials.
- [English]
- Fabrication and Pore Characteristics of Metal Powder Filters with a Cross-Sealed Honeycomb Shape Using Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
- Minji Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Su-Jin Yun, Poong-Yeon Kim, Hyeon Ju Kim, Juyong Kim, Jung Woo Lee, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):299-308. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00234

- 972 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The development of high-performance metal filters is essential for maintaining ultra-clean environments in semiconductor manufacturing. In this study, cross-sealed honeycomb filters were fabricated using STS316L powder via material extrusion additive manufacturing (MEAM) for semiconductor gas filtration. The effects of filter geometry (4 or 9 channels) and sintering temperature (850°C, 950°C, or 1,050°C) on performance were examined. First, 4-channel and 9-channel filters sintered at the same temperature (950°C) exhibited similar porosities of 50.08% and 50.57%, but the 9-channel filter showed a higher pressure-drop (0.26 bar) and better filtration-efficiency (3.55 LRV) than the 4-channel filter (0.19 bar and 3.25 LRV, respectively). Second, for filters with the same geometry (4-channel) increasing the sintering temperature reduced porosity from 64.52% to 40.33%, while the pressure-drop increased from 0.13 bar to 0.22 bar and filtration-efficiency improved from 2.53 LRV to 3.51 LRV. These findings demonstrate that filter geometry and sintering temperature are key factors governing the trade-off between air permeability, pressure-drop, and filtration efficiency. This work provides insights and data for optimizing MEAM-based high-performance metal powder filter design.
- [Korean]
- Influence of Powder Particle Size on the Microstructure of UO2 Fuel Pellets with High Gd2O3 Content
- Ji-Hwan Lee, Jae Ho Yang, Ji-Hae Yoon, Dong-Joo Kim, Dong-wook Shin, Dong Seok Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):344-353. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00178

- 1,025 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The recent development of small modular reactors (SMRs) and the adoption of higher-enrichment fuels have intensified the need for advanced burnable absorbers to ensure effective reactivity control and extended fuel cycles. Among various designs, UO2 fuels with high Gd2O3 (gadolinium oxide) content provide notable benefits; in particular, they are compatible with established fabrication methods for burnable absorber fuels. However, achieving a homogeneous dispersion of Gd2O3 at high loading levels remains challenging, and the frequent occurrence of phase segregation and non-uniform microstructures can limit fuel reliability and performance. Overcoming these limitations requires an understanding of the powder characteristics and mixing behaviors during fabrication. In this study, we investigate the effects of the initial particle size and mixing method of UO2 and Gd2O3 powders on the microstructure and mixing homogeneity of high-Gd2O3-content fuels. The findings indicate that both the mixing method and the preparation state of the starting powders significantly affect the resulting microstructure and mixing uniformity.
- [Korean]
- Friction Stir Spot Welding Characteristics of Dissimilar Materials of Aluminum-Based Damping Composites and Steel Plates
- Si-Seon Park, Young-Keun Jeong
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):43-49. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00010
- 689 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Friction Stir Spot Welding (FSSW) is a solid-state welding technology that is rapidly growing in the automotive industry. Achieving superior welding characteristics requires the proper selection of tool geometry and process conditions. In this study, FSSW was performed on dissimilar materials comprising AA5052-HO/hot-melt aluminum alloy sheets and Steel Plate Cold Rolled for Deep Drawing Use(SPCUD) steel sheets. The effects of tool geometry, plate arrangement, and tool plunge depth on the welding process were investigated. At the joint interface between the aluminum alloy and the steel sheet, new intermetallic compounds (IMCs) were observed. As the plunge depth increased, thicker and more continuous IMC layers were formed. However, excessive plunge depth led to discontinuous layers and cracking defects. An analysis of the IMCs revealed a correlation between the IMC thickness and the shear tensile load. Furthermore, compared to the conventional Al-Top arrangement, the St-Top arrangement exhibited reduced deformation and superior shear tensile load values. These findings indicate that plate arrangement significantly influences the mechanical properties of the joint.
- [English]
- Recent Advances in Thermoelectric Materials and Devices: Improving Power Generation Performance
- Momanyi Amos Okirigiti, Cheol Min Kim, Hyejeong Choi, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Kwi-Il Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):1-15. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00395
- 9,867 View
- 218 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
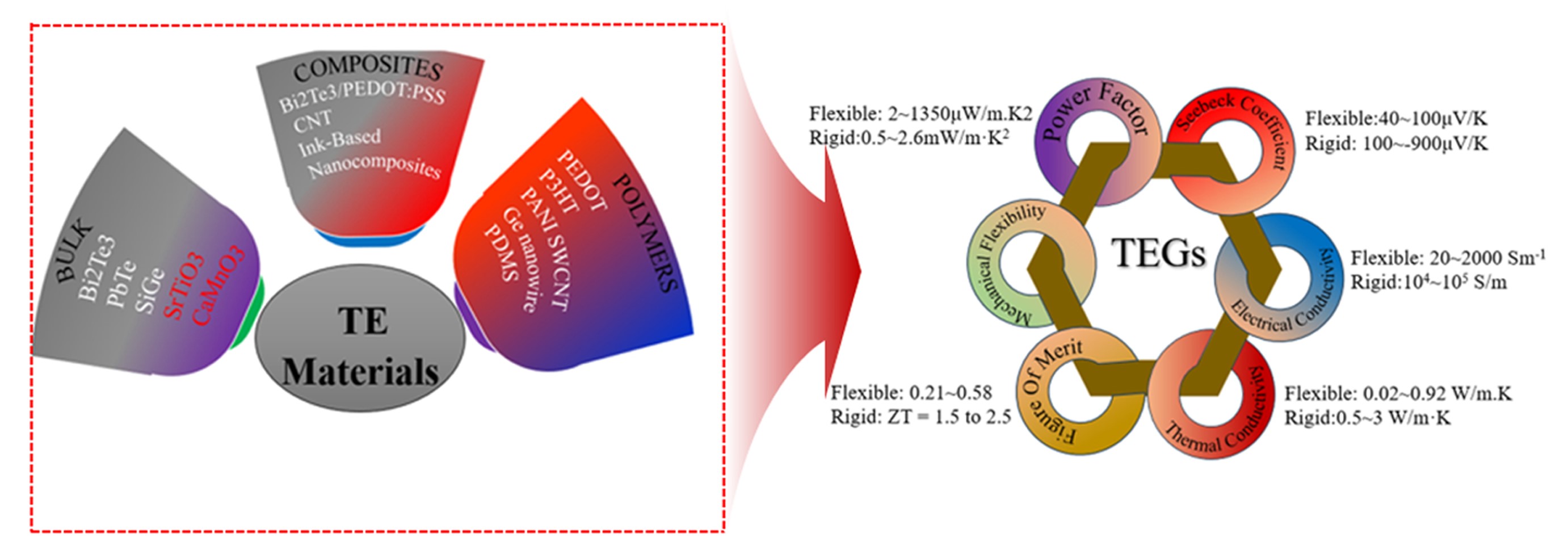
PDF - Thermoelectric materials have been the focus of extensive research interest in recent years due to their potential in clean power generation from waste heat. Their conversion efficiency is primarily reflected by the dimensionless figure of merit, with higher values indicating better performance. There is a pressing need to discover materials that increase output power and improve performance, from the material level to device fabrication. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of recent advancements, such as Bi2Te3-based nanostructures that reduce thermal conductivity while maintaining electrical conductivity, GeTe-based high entropy alloys that utilize multiple elements for improved thermoelectric properties, porous metal-organic frameworks offering tunable structures, and organic/hybrid films that present low-cost, flexible solutions. Innovations in thermoelectric generator designs, such as asymmetrical geometries, segmented modules, and flexible devices, have further contributed to increased efficiency and output power. Together, these developments are paving the way for more effective thermoelectric technologies in sustainable energy generation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- State-of-the-art research in conducting polymer thermoelectric composites: Design strategies, doping innovations, and emerging technologies
Vilakshana Acharya, Shivani Verma, Seema Gupta, Gaurav Pandey, Aanchal Sethi, Pooja Rawat
Journal of Applied Physics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Mathematical and simulation modeling of photovoltaic systems utilizing thermoelectric modules for effective thermal management
Muhammad Sohaib Tahir, Xue Dong, Muhammad Mansoor Khan
Results in Engineering.2025; 27: 106344. CrossRef - Summary of Publications in the Special Issue: Advances in Corrosion Resistant Coatings
Yong X. Gan
Coatings.2025; 15(11): 1350. CrossRef - Standard Reference Thermoelectric Modules Based on Metallic Combinations and Geometric Design
EunA Koo, Hanhwi Jang, SuDong Park, Sang Hyun Park, Sae-byul Kang
Applied Sciences.2025; 15(18): 10273. CrossRef - Research Trends in Magneto-Mechano-Electric (MME) Energy Harvesting Devices
So Ie Jeong, Geon-Tae Hwang
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 529. CrossRef - Transient In-Situ Identification of Thermal Parameters in Commercial Thermoelectric Modules using Transfer-Function Models
Gurum Ahmad Pauzi, Irfan Alfiansyah, Agus Riyanto, Donni Kis Apriyanto, Yanti Yulianti, Warsito Warsito
Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan Fisika Al-Biruni.2025; 14(2): 187. CrossRef
- State-of-the-art research in conducting polymer thermoelectric composites: Design strategies, doping innovations, and emerging technologies
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and High-Temperature Performance Evaluation of Light-Weight Insulation Materials and Coatings for Reusable Thermal Protection Systems
- Min-Soo Nam, Jong-Il Kim, Jaesung Shin, Hyeonjun Kim, Bum-Seok Oh, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):521-529. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00318

- 1,561 View
- 54 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Light-weight ceramic insulation materials and high-emissivity coatings were fabricated for reusable thermal protection systems (TPS). Alumina-silica fibers and boric acid were used to fabricate the insulation, which was heat treated at 1250 °C. High-emissivity coating of borosilicate glass modified with TaSi2, MoSi2, and SiB6 was applied via dip-and-spray coating methods and heat-treated at 1100°C. Testing in a high-velocity oxygen fuel environment at temperatures over 1100 °C for 120 seconds showed that the rigid structures withstood the flame robustly. The coating effectively infiltrated into the fibers, confirmed by scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction analyses. Although some oxidation of TaSi2 occurred, thereby increasing the Ta2O5 and SiO2 phases, no significant phase changes or performance degradation were observed. These results demonstrate the potential of these materials for reusable TPS applications in extreme thermal environments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Durability Assessment of Tile-Type Reusable Thermal Protection Materials
Minjeong Kim, Seong Man Choi
Materials.2026; 19(2): 303. CrossRef
- Durability Assessment of Tile-Type Reusable Thermal Protection Materials
- [English]
- Investigation of the Thermal-to-Electrical Properties of Transition Metal-Sb Alloys Synthesized for Thermoelectric Applications
- Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Sooho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Kwi-Il Park, Kyung Tae Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):236-242. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00031
- 1,828 View
- 44 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
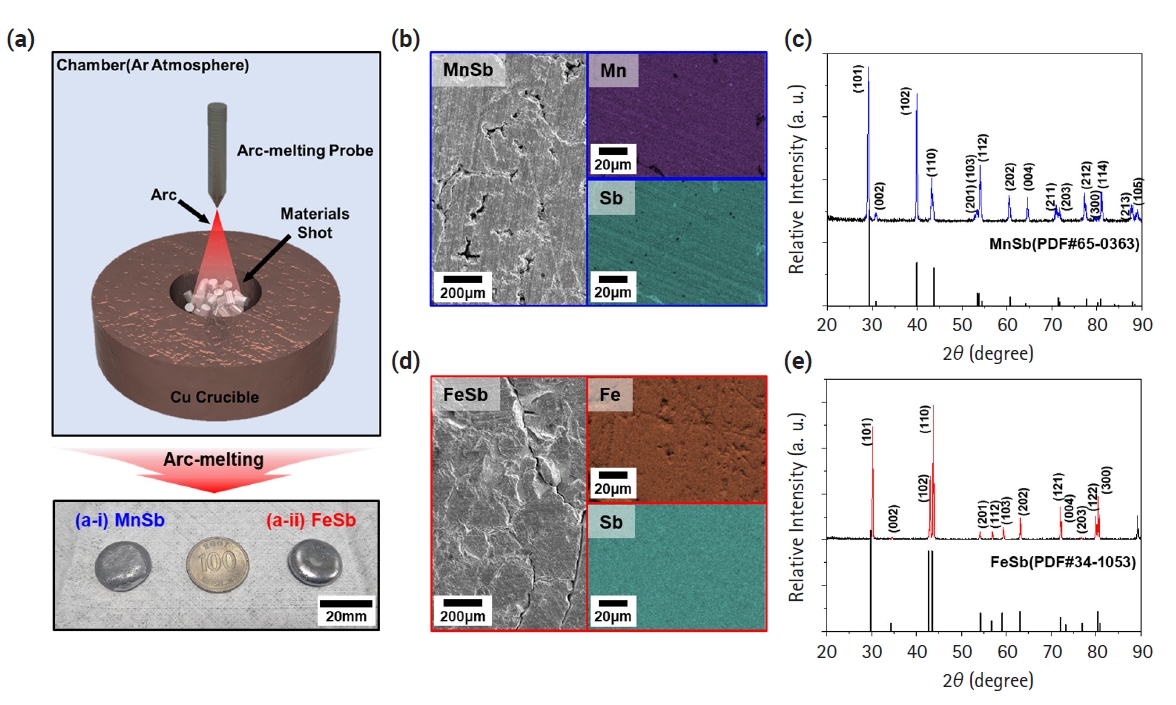
PDF - The development of thermoelectric (TE) materials to replace Bi2Te3 alloys is emerging as a hot issue with the potential for wider practical applications. In particular, layered Zintl-phase materials, which can appropriately control carrier and phonon transport behaviors, are being considered as promising candidates. However, limited data have been reported on the thermoelectric properties of metal-Sb materials that can be transformed into layered materials through the insertion of cations. In this study, we synthesized FeSb and MnSb, which are used as base materials for advanced thermoelectric materials. They were confirmed as single-phase materials by analyzing X-ray diffraction patterns. Based on electrical conductivity, the Seebeck coefficient, and thermal conductivity of both materials characterized as a function of temperature, the zT values of MnSb and FeSb were calculated to be 0.00119 and 0.00026, respectively. These properties provide a fundamental data for developing layered Zintl-phase materials with alkali/alkaline earth metal insertions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Jihun Yu, Kyung Tae Kim
Materials Letters.2025; 381: 137796. CrossRef - Highly deformable and hierarchical 3D composite sponge for versatile thermoelectric energy conversion
Jong Min Park, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Kwi-Il Park
Applied Surface Science.2025; 692: 162730. CrossRef
- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
- [Korean]
- Hydrogen Reduction Behavior of NCM-based Lithium-ion Battery Cathode Materials
- So-Yeong Lee, So-Yeon Lee, Dae-Hyeon Lee, Ho-Sang Sohn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):163-168. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00017
- 1,677 View
- 43 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
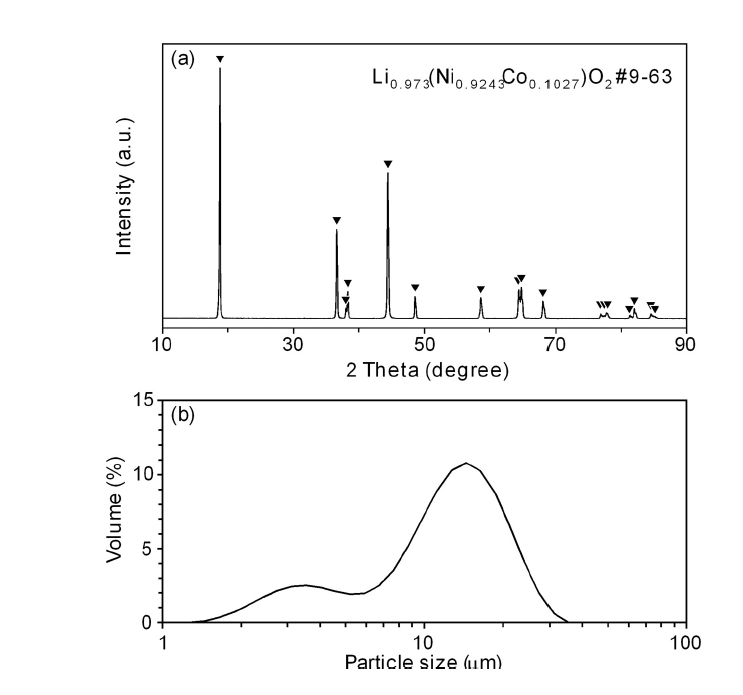
PDF - As the demand for lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles is increasing, it is important to recover valuable metals from waste lithium-ion batteries. In this study, the effects of gas flow rate and hydrogen partial pressure on hydrogen reduction of NCM-based lithium-ion battery cathode materials were investigated. As the gas flow rate and hydrogen partial pressure increased, the weight loss rate increased significantly from the beginning of the reaction due to the reduction of NiO and CoO by hydrogen. At 700 °C and hydrogen partial pressure above 0.5 atm, Ni and Li2O were produced by hydrogen reduction. From the reduction product and Li recovery rate, the hydrogen reduction of NCM-based cathode materials was significantly affected by hydrogen partial pressure. The Li compounds recovered from the solution after water leaching of the reduction products were LiOH, LiOH·H2O, and Li2CO3, with about 0.02 wt% Al as an impurity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reduction Roasting of Black Mass Recovered from NCM-based Spent Lithium-ion Batteries Using CH4 Gas
Sang-Yeop Lee, Jae-Ho Hwang, Ho-Sang Sohn
Resources Recycling.2025; 34(5): 93. CrossRef
- Reduction Roasting of Black Mass Recovered from NCM-based Spent Lithium-ion Batteries Using CH4 Gas
- [Korean]
- Effect of Tool Shape and Insertion Depth on Joining Properties in Friction Stir Spot Welding of Aluminum Alloy/high-strength Steel Sheets
- Su-Ho An, Young-Keun Jeong
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):37-42. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.37
- 1,148 View
- 23 Download
- 1 Citations
- [Korean]
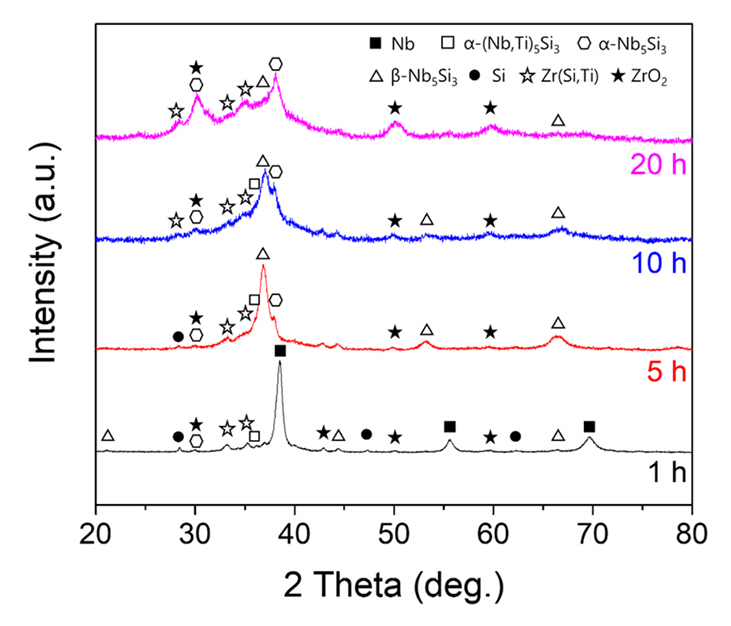
- Development of High-strength, High-temperature Nb-Si-Ti Alloys through Mechanical Alloying
- Jung-Joon Kim, Sang-Min Yoon, Deok-Hyun Han, Jongmin Byun, Young-Kyun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):30-36. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.30
- 2,146 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
Yeon-Joo Lee, Pil-Ryung Cha, Hyoung-Seop Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(1): 144. CrossRef
- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
- [English]
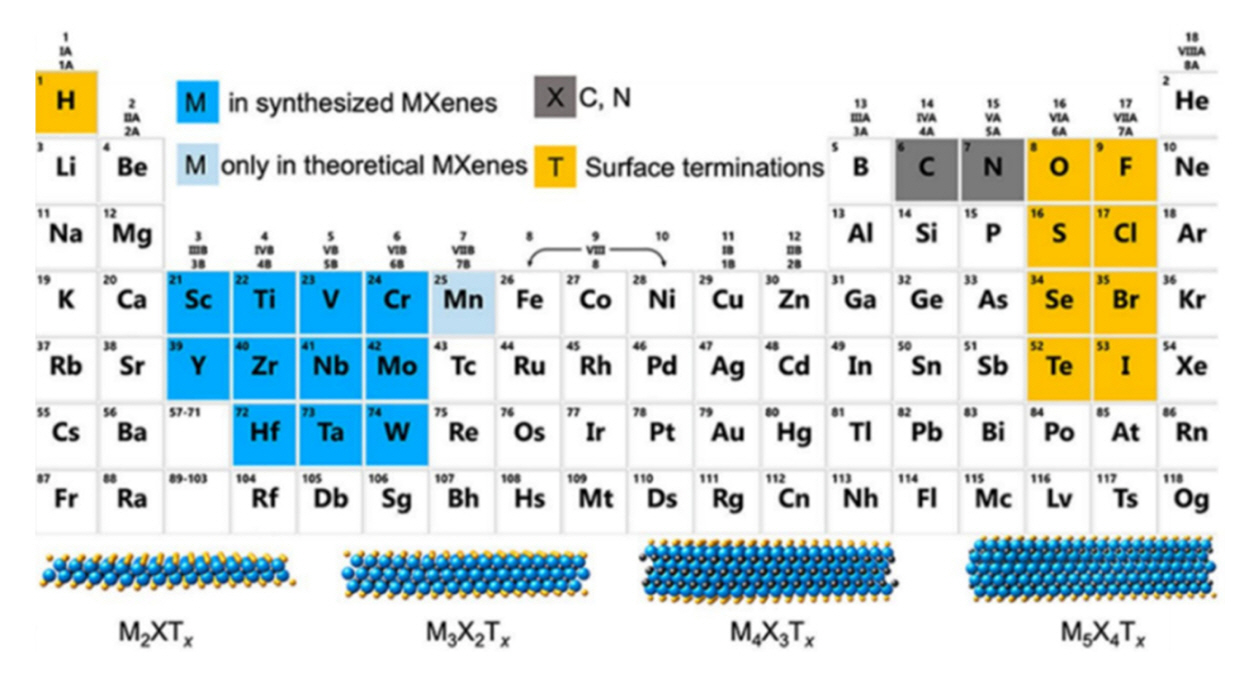
- Research Trends in Electromagnetic Shielding using MXene-based Composite Materials
- Siyeon Kim, Jongmin Byun
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):57-76. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.57
- 8,352 View
- 163 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Recent advancements in electronic devices and wireless communication technologies, particularly the rise of 5G, have raised concerns about the escalating electromagnetic pollution and its potential adverse impacts on human health and electronics. As a result, the demand for effective electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials has grown significantly. Traditional materials face limitations in providing optimal solutions owing to inadequacy and low performance due to small thickness. MXene-based composite materials have emerged as promising candidates in this context owing to their exceptional electrical properties, high conductivity, and superior EMI shielding efficiency across a broad frequency range. This review examines the recent developments and advantages of MXene-based composite materials in EMI shielding applications, emphasizing their potential to address the challenges posed by electromagnetic pollution and to foster advancements in modern electronics systems and vital technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Designing dual phase hexaferrite (SrFe12O19) – Perovskite (La0.5Nd0.5FeO3) composites for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption and band gap modulation
Pramod D. Mhase, Varsha C. Pujari, Santosh S. Jadhav, Abdullah G. Al-Sehemi, Sarah Alsobaie, Sunil M. Patange
Composites Communications.2025; 54: 102284. CrossRef - Microstructure tailoring of Nb-based MAX phase by low temperature synthesis with layer-structured Nb2C powder and molten salt method
Chaehyun Lim, Wonjune Choi, Jongmin Byun
Materials Characterization.2025; 225: 115106. CrossRef - Fabrication of MOF@MXene composites via surface modification of MXene under acidic conditions
Ji-Haeng Jeong, Woong-Ryeol Yu
Functional Composites and Structures.2025; 7(2): 025006. CrossRef - V2CTx MXene@ZIF-8 composite as an efficient adsorbent for Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution
Sarina Khojasteh Fard, Golshan Mazloom, Manoochehr Sobhani, Mohsen Tamtaji
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering.2025; 13(6): 120099. CrossRef
- Designing dual phase hexaferrite (SrFe12O19) – Perovskite (La0.5Nd0.5FeO3) composites for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption and band gap modulation
- [Korean]
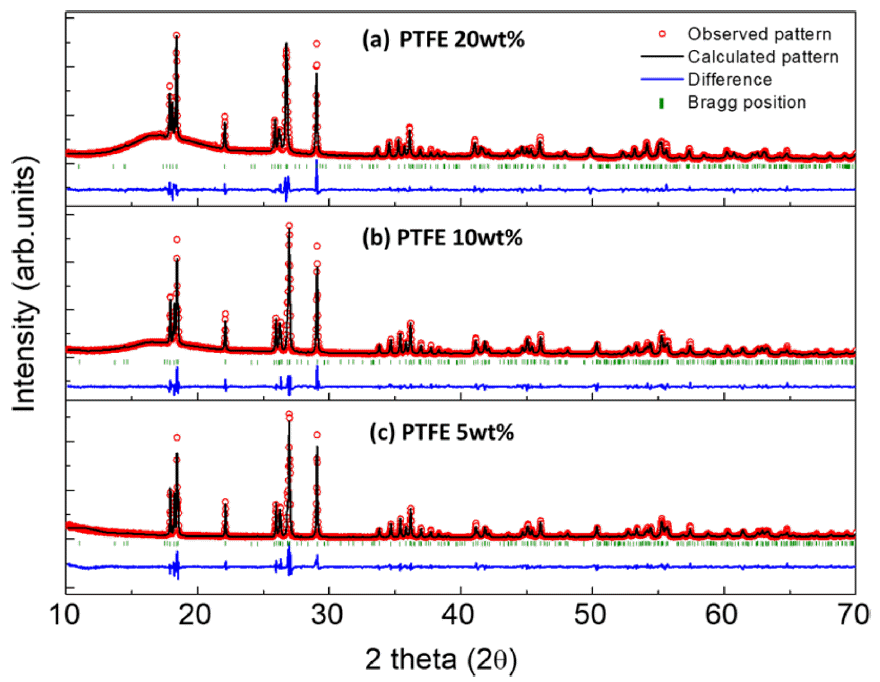
- Synthesis and Investigation of LiVPO4O1-xFxvia Control of the Fluorine Content for Cathode of Lithium-ion Batteries
- Minkyung Kim, Dong-hee Lee, Changyu Yeo, Sooyeon Choi, Chiwon Choi, Hyunmin Yoon
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):516-520. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.516
- 1,037 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Highly safe lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are required for large-scale applications such as electrical vehicles and energy storage systems. A highly stable cathode is essential for the development of safe LIBs. LiFePO4 is one of the most stable cathodes because of its stable structure and strong bonding between P and O. However, it has a lower energy density than lithium transition metal oxides. To investigate the high energy density of phosphate materials, vanadium phosphates were investigated. Vanadium enables multiple redox reactions as well as high redox potentials. LiVPO4O has two redox reactions (V5+/V4+/V3+) but low electrochemical activity. In this study, LiVPO4O is doped with fluorine to improve its electrochemical activity and increase its operational redox potential. With increasing fluorine content in LiVPO4O1-xFx, the local vanadium structure changed as the vanadium oxidation state changed. In addition, the operating potential increased with increasing fluorine content. Thus, it was confirmed that fluorine doping leads to a strong inductive effect and high operating voltage, which helps improve the energy density of the cathode materials.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Carbon Coated Nickel Cobalt Sulfide Yolk-shell Microsphere and Their Application as Anode Materials for Sodium Ion Batteries
- Hyo Yeong Seo, Gi Dae Park
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(5):387-393. Published online October 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.5.387

- 795 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Transition metal chalcogenides are promising cathode materials for next-generation battery systems, particularly sodium-ion batteries. Ni3Co6S8-pitch-derived carbon composite microspheres with a yolk-shell structure (Ni3Co6S8@C-YS) were synthesized through a three-step process: spray pyrolysis, pitch coating, and post-heat treatment process. Ni3Co6S8@C-YS exhibited an impressive reversible capacity of 525.2 mA h g-1 at a current density of 0.5 A g-1 over 50 cycles when employed as an anode material for sodium-ion batteries. However, Ni3Co6S8 yolk shell nanopowder (Ni3Co6S8-YS) without pitch-derived carbon demonstrated a continuous decrease in capacity during charging and discharging. The superior sodium-ion storage properties of Ni3Co6S8@C-YS were attributed to the pitchderived carbon, which effectively adjusted the size and distribution of nanocrystals. The carbon-coated yolk-shell microspheres proposed here hold potential for various metal chalcogenide compounds and can be applied to various fields, including the energy storage field.
- [English]
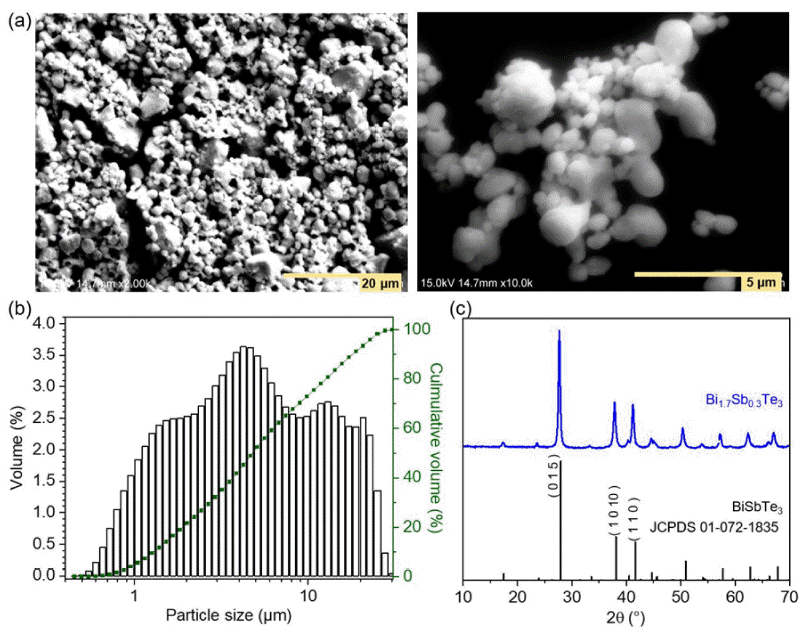
- Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
- Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):318-323. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.318
- 1,812 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The thermoelectric effect, which converts waste heat into electricity, holds promise as a renewable energy technology. Recently, bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3)-based alloys are being recognized as important materials for practical applications in the temperature range from room temperature to 500 K. However, conventional sintering processes impose limitations on shape-changeable and tailorable Bi2Te3 materials. To overcome these issues, three-dimensional (3D) printing (additive manufacturing) is being adopted. Although some research results have been reported, relatively few studies on 3D printed thermoelectric materials are being carried out. In this study, we utilize extrusion 3D printing to manufacture n-type Bi1.7Sb0.3Te3 (N-BST). The ink is produced without using organic binders, which could negatively influence its thermoelectric properties. Furthermore, we introduce graphene oxide (GO) at the crystal interface to enhance the electrical properties. The formed N-BST composites exhibit significantly improved electrical conductivity and a higher Seebeck coefficient as the GO content increases. Therefore, we propose that the combination of the extrusion 3D printing process (Direct Ink Writing, DIW) and the incorporation of GO into N-BST offers a convenient and effective approach for achieving higher thermoelectric efficiency.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
Min Gi An, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 492. CrossRef - Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
Linh Ba Vu, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son, Seungki Jo
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 119. CrossRef
- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
- [Korean]
- Effect of WC Particle Size on the Microstructure, Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Ag/WC Sintered Electrical Contact Material
- Soobin Kim, So-Yeon Park, Jong-Bin Lim, Soon Ho Kwon, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):242-248. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.242
- 966 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
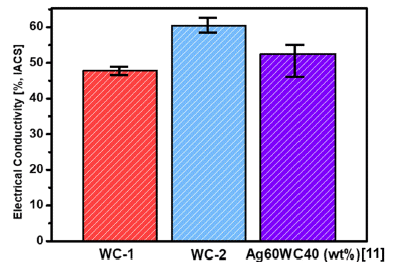
PDF The Ag/WC electrical contacts were prepared via powder metallurgy using 60 wt% Ag, 40 wt% WC, and small amounts of Co3O4 with varying WC particle sizes. After the fabrication of the contact materials, microstructure observations confirmed that WC-1 had an average grain size (AGS) of 0.27 μm, and WC-2 had an AGS of 0.35 μm. The Ag matrix in WC-1 formed fine grains, whereas a significantly larger and continuous growth of the Ag matrix was observed in WC-2. This indicates the different flow behaviors of liquid Ag during the sintering process owing to the different WC sizes. The electrical conductivities of WC-1 and WC-2 were 47.8% and 60.4%, respectively, and had a significant influence on the Ag matrix. In particular, WC-2 exhibited extremely high electrical conductivity owing to its large and continuous Ag-grain matrix. The yield strengths of WC-1 and WC-2 after compression tests were 349.9 MPa and 280.7 MPa, respectively. The high yield strength of WC-1 can be attributed to the Hall–Petch effect, whereas the low yield strength of WC-2 can be explained by the high fraction of high-angle boundaries (HAB) between the WC grains. Furthermore, the relationships between the microstructure, electrical/mechanical properties, and deformation mechanisms were evaluated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhanced Epoxy Composites Reinforced by 3D-Aligned Aluminum Borate Nanowhiskers
Hyunseung Song, Kiho Song, Haejin Hwang, Changui Ahn
Materials.2024; 17(19): 4727. CrossRef
- Enhanced Epoxy Composites Reinforced by 3D-Aligned Aluminum Borate Nanowhiskers
- [Korean]
- Enhancement of Thermoelectric Performance in Spark Plasma Sintered p-Type Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3.0 Compound via Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) Induced Reduction of Lattice Thermal Conductivity
- Soo-Ho Jung, Ye Jin Woo, Kyung Tae Kim, Seungki Jo
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(2):123-129. Published online April 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.2.123
- 1,620 View
- 9 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
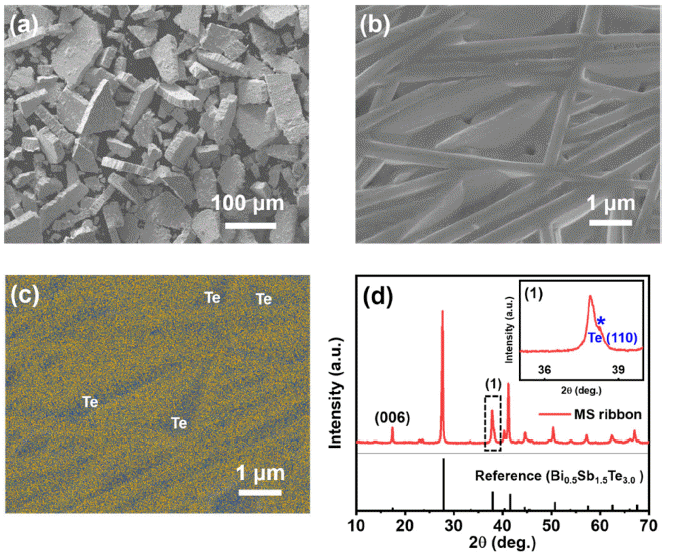
PDF High-temperature and high-pressure post-processing applied to sintered thermoelectric materials can create nanoscale defects, thereby enhancing their thermoelectric performance. Here, we investigate the effect of hot isostatic pressing (HIP) as a post-processing treatment on the thermoelectric properties of
p -type Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3.0 compounds sintered via spark plasma sintering. The sample post-processed via HIP maintains its electronic transport properties despite the reduced microstructural texturing. Moreover, lattice thermal conductivity is significantly reduced owing to activated phonon scattering, which can be attributed to the nanoscale defects created during HIP, resulting in an ~18% increase in peakzT value, which reaches ~1.43 at 100°C. This study validates that HIP enhances the thermoelectric performance by controlling the thermal transport without having any detrimental effects on the electronic transport properties of thermoelectric materials.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhanced Electrical Properties of 3D Printed Bi2Te3-Based Thermoelectric Materials via Hot Isostatic Pressing
Seungki Jo
Ceramist.2025; 28(1): 126. CrossRef - Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
Linh Ba Vu, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son, Seungki Jo
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 119. CrossRef - Investigation of the Thermal-to-Electrical Properties of Transition Metal-Sb Alloys Synthesized for Thermoelectric Applications
Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Sooho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Kwi-Il Park, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(3): 236. CrossRef - Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 318. CrossRef
- Enhanced Electrical Properties of 3D Printed Bi2Te3-Based Thermoelectric Materials via Hot Isostatic Pressing
- [English]
- Selective Laser Sintering of Co-Cr Alloy Powders and Sintered Products Properties
- Dong-Wan Lee, Minh-Thuyet Nguyen, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(1):7-12. Published online February 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.1.7

- 1,486 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metal-additive manufacturing techniques, such as selective laser sintering (SLS), are increasingly utilized for new biomaterials, such as cobalt-chrome (Co-Cr). In this study, Co-Cr gas-atomized powders are used as charge materials for the SLS process. The aim is to understand the consolidation of Co-Cr alloy powder and characterization of samples sintered using SLS under various conditions. The results clearly suggest that besides the matrix phase, the second phase, which is attributed to pores and oxidation particles, is observed in the sintered specimens. The as-built samples exhibit completely different microstructural features compared with the casting or wrought products reported in the literature. The microstructure reveals melt pools, which represent the characteristics of the scanning direction, in particular, or of the SLS conditions, in general. It also exposes extremely fine grain sizes inside the melt pools, resulting in an enhancement in the hardness of the as-built products. Thus, the hardness values of the samples prepared by SLS under all parameter conditions used in this study are evidently higher than those of the casting products.
- [Korean]
- Evaluation of Microstructures and Mechanical Properties in Functionally Graded Materials (STS 316L and Low Alloy Steel) Produced by DED Processes
- G. Shin, W. Choo, J. H. Yoon, S. Y. Yang, J. H. Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(4):309-313. Published online August 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.4.309

- 802 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, additive manufacturing of a functionally graded material (FGM) as an alternative to joining dissimilar metals is investigated using directed energy deposition (DED). FGM consists of five different layers, which are mixtures of austenitic stainless steel (type 316 L) and low-alloy steel (LAS, ferritic steel) at ratios of 100:0 (A layer), 75:25 (B layer), 50:50 (C layer), 25:75 (D layer), and 0:100 (E layer), respectively, in each deposition layer. The FGM samples are successfully fabricated without cracks or delamination using the DED method, and specimens are characterized using optical and scanning electron microscopy to monitor their microstructures. In layers C and D of the sample, the tensile strength is determined to be very high owing to the formation of ferrite and martensite structures. However, the elongation is high in layers A and B, which contain a large fraction of austenite.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication, Microstructure and Adhesion Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal/Ag Plate Clad Material by Using High Velocity Oxygen Fuel Thermal Spray Process
- Yeun A Joo, Yong-Hoon Cho, Jae-Sung Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(3):226-232. Published online June 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.3.226

- 941 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, a new manufacturing process for a multilayer-clad electrical contact material is suggested. A thin and dense BCuP-5 (Cu-15Ag-5P filler metal) coating layer is fabricated on a Ag plate using a high-velocity oxygen-fuel (HVOF) process. Subsequently, the microstructure and bonding properties of the HVOF BCuP-5 coating layer are evaluated. The thickness of the HVOF BCuP-5 coating layer is determined as 34.8 μm, and the surface fluctuation is measured as approximately 3.2 μm. The microstructure of the coating layer is composed of Cu, Ag, and Cu-Ag-Cu3P ternary eutectic phases, similar to the initial BCuP-5 powder feedstock. The average hardness of the coating layer is 154.6 HV, which is confirmed to be higher than that of the conventional BCuP-5 alloy. The pull-off strength of the Ag/BCup-5 layer is determined as 21.6 MPa. Thus, the possibility of manufacturing a multilayer-clad electrical contact material using the HVOF process is also discussed.
- [Korean]
- Recent Studies on Performance Enhancement of Polycrystal SnSe Thermoelectric Materials
- Myeong Jun Jung, Byung Joon Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(2):152-158. Published online April 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.2.152
- 1,323 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
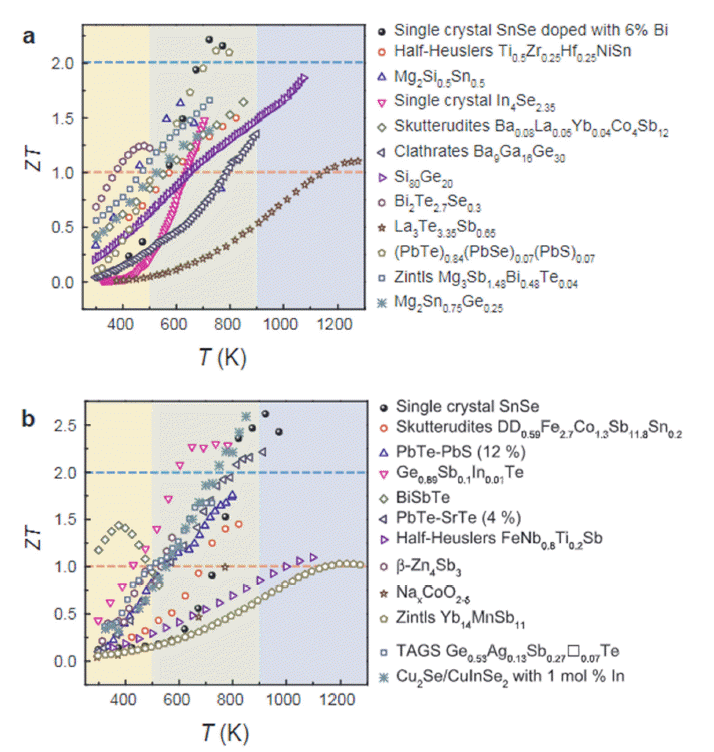
PDF Thermoelectric materials can reversely convert heat and electricity into each other; therefore, they can be very useful for energy harvesting from heat waste. Among many thermoelectrical materials, SnSe exhibits outstanding thermoelectric performance along the particular direction of a single crystal. However, single-crystal SnSe has poor mechanical properties and thus it is difficult to apply for mass production. Therefore, polycrystalline SnSe materials may be used to replace single-crystal SnSe by overcoming its inferior thermoelectric performance owing to surface oxidation. Considerable efforts are currently focused on enhancing the thermoelectric performance of polycrystalline SnSe. In this study, we briefly review various enhancement methods for SnSe thermoelectric materials, including doping, texturing, and nano-structuring. Finally, we discuss the future prospects of SnSe thermoelectric powder materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Mechanism Behind the High zT of SnSe2 Added SnSe at High Temperatures
JunSu Kim, Seong-Mee Hwang, Hyunjin Park, Yinglu Tang, Won-Seon Seo, Chae Woo Ryu, Heesun Yang, Weon Ho Shin, Hyun-Sik Kim
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(11): 857. CrossRef
- The Mechanism Behind the High zT of SnSe2 Added SnSe at High Temperatures
- [Korean]
- Recent progress on Performance Improvements of Thermoelectric Materials using Atomic Layer Deposition
- Seunghyeok Lee, Tae Joo Park, Seong Keun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):56-62. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.56
- 1,640 View
- 31 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is a promising technology for the uniform deposition of thin films. ALD is based on a self-limiting mechanism, which can effectively deposit thin films on the surfaces of powders of various sizes. Numerous studies are underway to improve the performance of thermoelectric materials by forming core-shell structures in which various materials are deposited on the powder surface using ALD. Thermoelectric materials are especially relevant as clean energy storage materials due to their ability to interconvert between thermal and electrical energy by the Seebeck and Peltier effects. Herein, we introduce a surface and interface modification strategy based on ALD to control the performance of thermoelectric materials. We also discuss the properties of the interface between various deposition materials and thermoelectric materials.
- [Korean]
- Recycling of Hardmetal Tool through Alkali Leaching Process and Fabrication Process of Nano-sized Tungsten Carbide Powder using Self-propagation High-temperature Synthesis
- Hee-Nam Kang, Dong Il Jeong, Young Il Kim, In Yeong Kim, Sang Cheol Park, Cheol Woo Nam, Seok-Jun Seo, Jin Yeong Lee, Bin Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):47-55. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.47

- 1,434 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tungsten carbide is widely used in carbide tools. However, its production process generates a significant number of end-of-life products and by-products. Therefore, it is necessary to develop efficient recycling methods and investigate the remanufacturing of tungsten carbide using recycled materials. Herein, we have recovered 99.9% of the tungsten in cemented carbide hard scrap as tungsten oxide via an alkali leaching process. Subsequently, using the recovered tungsten oxide as a starting material, tungsten carbide has been produced by employing a self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) method. SHS is advantageous as it reduces the reaction time and is energy-efficient. Tungsten carbide with a carbon content of 6.18 wt % and a particle size of 116 nm has been successfully synthesized by optimizing the SHS process parameters, pulverization, and mixing. In this study, a series of processes for the highefficiency recycling and quality improvement of tungsten-based materials have been developed.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Characteristics of Ag-SnO2-Bi2O3 Contact Materials by Powder Compaction
- Jin Kyu Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):41-46. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.41
- 545 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we report the microstructure and characteristics of Ag-SnO2-Bi2O3 contact materials using a controlled milling process with a subsequent compaction process. Using magnetic pulsed compaction (MPC), the milled Ag-SnO2-Bi2O3 powders have been consolidated into bulk samples. The effects of the compaction conditions on the microstructure and characteristics have been investigated in detail. The nanoscale SnO2 phase and microscale Bi2O3 phase are well-distributed homogeneously in the Ag matrix after the consolidation process. The successful consolidation of Ag-SnO2-Bi2O3 contact materials was achieved by an MPC process with subsequent atmospheric sintering, after which the hardness and electrical conductivity of the Ag-SnO2-Bi2O3 contact materials were found to be 62–75 HV and 52–63% IACS, respectively, which is related to the interfacial stability between the Ag matrix, the SnO2 phase, and the Bi2O3 phase.
- [Korean]
- Recent Advances in Soft Magnetic Actuators and Sensors using Magnetic Particles
- Hyeonseo Song, Hajun Lee, Junghyo Kim, Jiyun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):509-517. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.509

- 946 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Smart materials capable of changing their characteristics in response to stimuli such as light, heat, pH, and electric and magnetic fields are promising for application to flexible electronics, soft robotics, and biomedicine. Compared with conventional rigid materials, these materials are typically composed of soft materials that improve the biocompatibility and allow for large and dynamic deformations in response to external environmental stimuli. Among them, smart magnetic materials are attracting immense attention owing to their fast response, remote actuation, and wide penetration range under various conditions. In this review, we report the material design and fabrication of smart magnetic materials. Furthermore, we focus on recent advances in their typical applications, namely, soft magnetic actuators, sensors for self-assembly, object manipulation, shape transformation, multimodal robot actuation, and tactile sensing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advanced Magnetic Actuation: Harnessing the Dynamics of Sm2Fe17–xCuxN3 Composites
Kangmo Koo, Young-Tae Kwon, Ji Young Park, Yong-Ho Choa
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.2024; 16(9): 11872. CrossRef
- Advanced Magnetic Actuation: Harnessing the Dynamics of Sm2Fe17–xCuxN3 Composites
- [Korean]
- Electrochemical Properties of Ball-milled Tin-Graphite Composite Anode Materials for Lithium-Ion Battery
- Tae-Hui Lee, Hyeon-A Hong, Kwon-Koo Cho, Yoo-Young Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):462-469. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.462

- 1,209 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tin/graphite composites are prepared as anode materials for Li-ion batteries using a dry ball-milling process. The main experimental variables in this work are the ball milling time (0–8 h) and composition ratio (tin:graphite=5:95, 15:85, and 30:70 w/w) of graphite and tin powder. For comparison, a tin/graphite composite is prepared using wet ball milling. The morphology and structure of the different tin/graphite composites are investigated using X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and scanning and transmission electron microscopy. The electrochemical properties of the samples are also examined. The optimal dry ball milling time for the uniform mixing of graphite and tin is 6 h in a graphite-30wt.%Sn sample. The electrode prepared from the composite that is dry-ballmilled for 6 h exhibits the best cycle performance (discharge capacity after 50th cycle: 308 mAh/g and capacity retention: 46%). The discharge capacity after the 50th cycle is approximately 112 mAh/g, higher than that when the electrode is composed of only graphite (196 mAh/g after 50th cycle). This result indicates that it is possible to manufacture a tin/graphite composite anode material that can effectively buffer the volume change that occurs during cycling, even using a simple dry ball-milling process.
- [Korean]
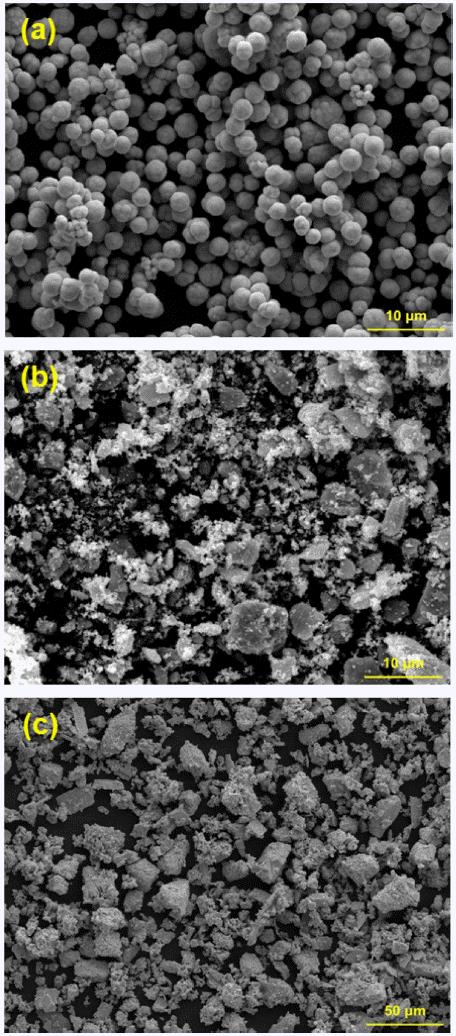
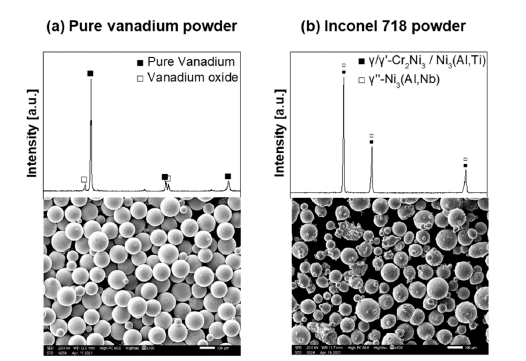
- Joint Properties of Inconel 718 Additive Manufactured on Ti-6Al-4V by FGM method
- Chan Woong Park, Jin Woong Park, Ki Chae Jung, Se-Hwan Lee, Sung-Hoon Kim, Jeoung Han Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):417-422. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.417
- 589 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In the present work, Inconel 718 alloy is additively manufactured on the Ti-6Al-4V alloy, and a functionally graded material is built between Inconel 718 and Ti-6Al-4V alloys. The vanadium interlayer is applied to prevent the formation of detrimental intermetallic compounds between Ti-6Al-4V and Inconel 718 by direct joining. The additive manufacturing of Inconel 718 alloy is performed by changing the laser power and scan speed. The microstructures of the joint interface are characterized by scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and micro X-ray diffraction. Additive manufacturing is successfully performed by changing the energy input. The micro Vickers hardness of the additive manufactured Inconel 718 dramatically increased owing to the presence of the Cr-oxide phase, which is formed by the difference in energy input.
- [Korean]
- A Study on the Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Fe83.2Si5.33-0.33
x B10.67-0.67x Px Cu0.8 Nanocrystalline Soft Magnetic Alloys with varying P Content - Hyun Ah Im, Kyoung-Hoon Bae, Yeong gyun Nam, Subong An, Sangsun Yang, Yong-Jin Kim, Jung Woo Lee, Jae Won Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(4):293-300. Published online August 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.4.293

- 889 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We investigate the effect of phosphorous content on the microstructure and magnetic properties of Fe83.2Si5.33-0.33
x B10.67-0.67x Px Cu0.8 (x = 1–4 at.%) nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloys. The simultaneous addition of Cu and P to nanocrystalline alloys reportedly decreases the nanocrystalline size significantly, to 10–20 nm. In the P-containing nanocrystalline alloy, P atoms are distributed in an amorphous residual matrix, which suppresses grain growth, increases permeability, and decreases coercivity. In this study, nanocrystalline ribbons with a composition of Fe83.2Si5.33-0.33x B10.67- 0.67x Px Cu0.8 (x = 1–4 at.%) are fabricated by rapid quenching melt-spinning and thermal annealing. It is demonstrated that the addition of a small amount of P to the alloy improves the glass-forming ability and increases the resistance to undesirable Fex(B,P) crystallization. Among the alloys investigated in this work, an Fe83.2Si5B10P1Cu0.8 nanocrystalline ribbon annealed at 460°C exhibits excellent soft-magnetic properties including low coercivity, low core loss, and high saturation magnetization. The uniform nanocrystallization of the Fe83.2Si5B10P1Cu0.8 alloy is confirmed by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy analysis.
- [Korean]
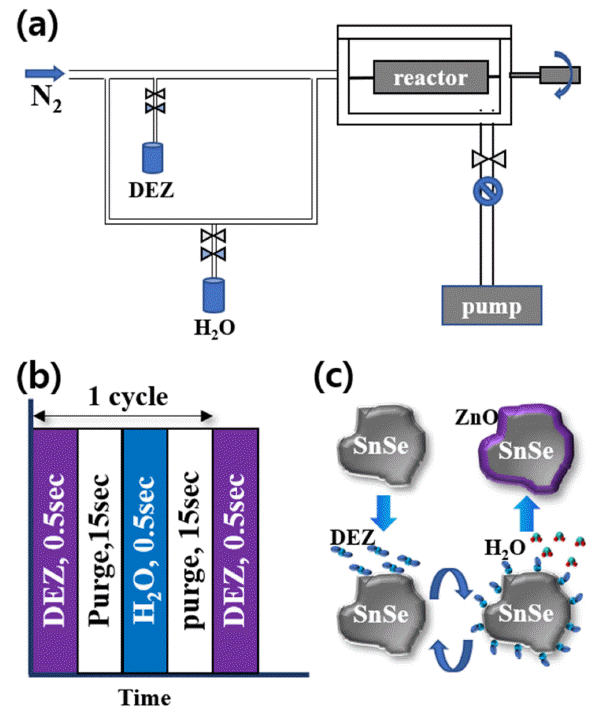
- Rotation Speed Dependence of ZnO Coating Layer on SnSe powders by Rotary Atomic Layer Deposition Reactor
- Myeong Jun Jung, Ye Jun Yun, Jongmin Byun, Byung Joon Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):239-245. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.239
- 645 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The SnSe single crystal shows an outstanding figure of merit (
ZT ) of 2.6 at 973 K; thus, it is considered to be a promising thermoelectric material. However, the mass production of SnSe single crystals is difficult, and their mechanical properties are poor. Alternatively, we can use polycrystalline SnSe powder, which has better mechanical properties. In this study, surface modification by atomic layer deposition (ALD) is chosen to increase theZT value of SnSe polycrystalline powder. SnSe powder is ground by a ball mill. An ALD coating process using a rotary-type reactor is adopted. ZnO thin films are grown by 100 ALD cycles using diethylzinc and H2O as precursors at 100°C. ALD is performed at rotation speeds of 30, 40, 50, and 60 rpm to examine the effects of rotation speed on the thin film characteristics. The physical and chemical properties of ALD-coated SnSe powders are characterized by scanning and tunneling electron microscopy combined with energy-dispersive spectroscopy. The results reveal that a smooth oxygenrich ZnO layer is grown on SnSe at a rotation speed of 30 rpm. This result can be applied for the uniform coating of a ZnO layer on various powder materials.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thermal Confinement and Filtering Effect of SnSe by Insertion of Atomic-Layer-Deposited ZnO Interfacial Layer
Myeong Jun Jung, Su Min Eun, Hogyoung Kim, Seong Keun Kim, Jongmin Byun, Byung Joon Choi
Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering.2025; 42(14): 3545. CrossRef
- Thermal Confinement and Filtering Effect of SnSe by Insertion of Atomic-Layer-Deposited ZnO Interfacial Layer
- [Korean]
- Research trends of MXenes as the Next-generation Two-dimensional Materials
- Hojun Lee, Yejun Yun, Jinkwang Jang, Jongmin Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):150-163. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.150

- 3,549 View
- 106 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Interest in eco-friendly materials with high efficiencies is increasing significantly as science and technology undergo a paradigm shift toward environment-friendly and sustainable development. MXenes, a class of two-dimensional inorganic compounds, are generally defined as transition metal carbides or nitrides composed of few-atoms-thick layers with functional groups. Recently MXenes, because of their desirable electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties that emerge from conductive layered structures with tunable surface terminations, have garnered significant attention as promising candidates for energy storage applications (e.g., supercapacitors and electrode materials for Li-ion batteries), water purification, and gas sensors. In this review, we introduce MXenes and describe their properties and research trends by classifying them into two main categories: transition metal carbides and nitrides, including Ti-based MXenes, Mo-based MXenes, and Nb-based MXenes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Next-generation brackish water treatment: Exploring dual-ion capacitive deionization
Yize Li, Jing He, He Liu, Chao Yan
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering.2025; 13(2): 116037. CrossRef - Microstructure tailoring of Nb-based MAX phase by low temperature synthesis with layer-structured Nb2C powder and molten salt method
Chaehyun Lim, Wonjune Choi, Jongmin Byun
Materials Characterization.2025; 225: 115106. CrossRef - Review on 2D MXene and graphene electrodes in capacitive deionization
Hammad Younes, Ding Lou, Md. Mahfuzur Rahman, Daniel Choi, Haiping Hong, Linda Zou
Environmental Technology & Innovation.2022; 28: 102858. CrossRef
- Next-generation brackish water treatment: Exploring dual-ion capacitive deionization
- [English]
- Correlation of Sintering Parameters with Density and Hardness of Nano-sized Titanium Nitride reinforced Titanium Alloys using Neural Networks
- A. K. Maurya, P. L Narayana, Hong In Kim, N. S. Reddy
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(5):365-372. Published online October 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.5.365

- 1,490 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Predicting the quality of materials after they are subjected to plasma sintering is a challenging task because of the non-linear relationships between the process variables and mechanical properties. Furthermore, the variables governing the sintering process affect the microstructure and the mechanical properties of the final product. Therefore, an artificial neural network modeling was carried out to correlate the parameters of the spark plasma sintering process with the densification and hardness values of Ti-6Al-4V alloys dispersed with nano-sized TiN particles. The relative density (%), effective density (g/cm3), and hardness (HV) were estimated as functions of sintering temperature (°C), time (min), and composition (change in % TiN). A total of 20 datasets were collected from the open literature to develop the model. The high-level accuracy in model predictions (>80%) discloses the complex relationships among the sintering process variables, product quality, and mechanical performance. Further, the effect of sintering temperature, time, and TiN percentage on the density and hardness values were quantitatively estimated with the help of the developed model.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Artificial Neural Networks for Modeling Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Spark Plasma Sintered Powders
Katarzyna Peta, Jakub Wiśniewski, Piotr Siwak
Materials.2026; 19(5): 848. CrossRef - Application of Machine Learning Algorithms and SHAP for Prediction and Feature Analysis of Tempered Martensite Hardness in Low-Alloy Steels
Junhyub Jeon, Namhyuk Seo, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee, Minsu Jung
Metals.2021; 11(8): 1159. CrossRef
- Artificial Neural Networks for Modeling Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Spark Plasma Sintered Powders
- [English]
- Multi-step Metals Additive Manufacturing Technologies
- Ji-Won Oh, Jinsu Park, Hanshin Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):256-267. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.256

- 1,676 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metal additive manufacturing (AM) technologies are classified into two groups according to the consolidation mechanisms and densification degrees of the as-built parts. Densified parts are obtained via a single-step process such as powder bed fusion, directed energy deposition, and sheet lamination AM technologies. Conversely, green bodies are consolidated with the aid of binder phases in multi-step processes such as binder jetting and material extrusion AM. Green-body part shapes are sustained by binder phases, which are removed for the debinding process. Chemical and/or thermal debinding processes are usually devised to enhance debinding kinetics. The pathways to final densification of the green parts are sintering and/or molten metal infiltration. With respect to innovation types, the multistep metal AM process allows conventional powder metallurgy manufacturing to be innovated continuously. Eliminating cost/time-consuming molds, enlarged 3D design freedom, and wide material selectivity create opportunities for the industrial adoption of multi-step AM technologies. In addition, knowledge of powders and powder metallurgy fuel advances of multi-step AM technologies. In the present study, multi-step AM technologies are briefly introduced from the viewpoint of the entire manufacturing lifecycle.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Potential and challenges for Powder Bed Fusion – Laser Beam (PBF-LB) in industrial ceramic additive manufacturing
Christian Berger, Gabriela Schimo-Aichhorn, Stefan Gronau, Franziska Saft, Sarah Seiringer, Uwe Scheithauer
Open Ceramics.2024; 18: 100614. CrossRef - Fabrication of Cu-Infiltrated Journal Bearing by Binder Jetting Additive Manufacturing
Jin Man Jang
Crystals.2024; 14(11): 912. CrossRef - SiC-Si composite part fabrication via SiC powder binder jetting additive manufacturing and molten-Si infiltration
Ji-Won Oh, Jinsu Park, Sahn Nahm, Hanshin Choi
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2021; 101: 105686. CrossRef
- Potential and challenges for Powder Bed Fusion – Laser Beam (PBF-LB) in industrial ceramic additive manufacturing
- [Korean]
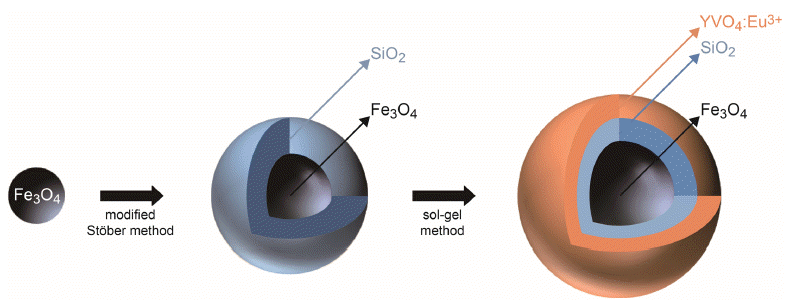
- Synthesis of the Multifunctional Core/Intermediate/Shell Nanoparticles: Tunable Magnetic and Photoluminescence Properties
- Mun-Kyoung Kim, Seyun Kim, Kyoung-Seok Moon, Weon Ho Shin, Hyung Mo Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(6):463-470. Published online December 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.6.463
- 756 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Fe3O4/SiO2/YVO4:Eu3+ multifunctional nanoparticles are successfully synthesized by facile stepwise sol-gel processes. The multifunctional nanoparticles show a spherical shape with narrow size distribution (approximately 40 nm) and the phosphor shells are well crystallized. The Eu3+ shows strong photoluminescence (red emission at 619 nm, absorbance at 290 nm) due to an effective energy transfer from the vanadate group to Eu. Core-shell structured multifunctional nanoparticles have superparamagnetic properties at 300 K. Furthermore, the core-shell nanoparticles have a quick response time for the external magnetic field. These results suggest that the photoluminescence and magnetic properties could be easily tuned by either varying the number of coating processes or changing the phosphor elements. The nanoparticles may have potential applications for appropriate fields such as laser systems, optical amplifiers, security systems, and drug delivery materials.
- [Korean]
- Research Trends of Cathode Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries used in Electric Vehicles
- Dong-Yo Shin, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):58-69. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.58

- 1,042 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF High performance lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have attracted considerable attention as essential energy sources for high-technology electrical devices such as electrical vehicles, unmanned drones, uninterruptible power supply, and artificial intelligence robots because of their high energy density (150-250 Wh/kg), long lifetime (> 500 cycles), low toxicity, and low memory effects. Of the high-performance LIB components, cathode materials have a significant effect on the capacity, lifetime, energy density, power density, and operating conditions of high-performance LIBs. This is because cathode materials have limitations with respect to a lower specific capacity and cycling stability as compared to anode materials. In addition, cathode materials present difficulties when used with LIBs in electric vehicles because of their poor rate performance. Therefore, this study summarizes the structural and electrochemical properties of cathode materials for LIBs used in electric vehicles. In addition, we consider unique strategies to improve their structural and electrochemical properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Estimation of Representative Mechanical Property of Porous Electrode for Secondary Batteries with Homogenization Method
Changmin Pyo, Jaewoong Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2022; 21(9): 85. CrossRef
- Estimation of Representative Mechanical Property of Porous Electrode for Secondary Batteries with Homogenization Method
- [Korean]
- Effect of Single and Dual Doping of Rare Earth Metal Ce and Nd Elements on Electrochemical Properties of LiNi0.83 Co0.11Mn0.06O2 Cathode Lithium-ion Battery Material
- Yoo-Young Kim, Jong-Keun Ha, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):49-57. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.49
- 2,035 View
- 22 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
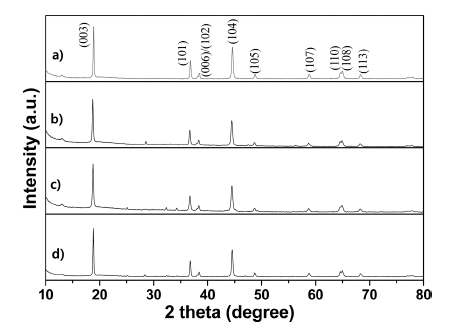
PDF Layered LiNi0.83Co0.11Mn0.06O2 cathode materials single- and dual-doped by the rare-earth elements Ce and Nd are successfully fabricated by using a coprecipitation-assisted solid-phase method. For comparison purposes, nondoping pristine LiNi0.83Co0.11Mn0.06O2 cathode material is also prepared using the same method. The crystal structure, morphology, and electrochemical performances are characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) mapping, and electrochemical techniques. The XRD data demonstrates that all prepared samples maintain a typical α-NaFeO2-layered structure with the
R-3m -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Numerical approach for lithium-ion battery performance considering various cathode active material composition for electric vehicles using 1D simulation
Heewon Choi, Nam-gyu Lim, Seong Jun Lee, Jungsoo Park
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology.2021; 35(6): 2697. CrossRef - Synthesis of CeVO4-V2O5 nanowires by cation-exchange method for high-performance lithium-ion battery electrode
Xueliu Xu, Shiying Chang, Taofang Zeng, Yidan Luo, Dong Fang, Ming Xie, Jianhong Yi
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2021; 887: 161237. CrossRef
- Numerical approach for lithium-ion battery performance considering various cathode active material composition for electric vehicles using 1D simulation
- [Korean]
- Development of Novel Composite Powder Friction Modifier for Improving Wheel-rail Adhesion in High-speed Train
- Min Chul Oh, Byungmin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):501-506. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.501

- 633 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF With the recent remarkable improvements in the average speeds of contemporary trains, a necessity has arisen for the development of new friction modifiers to improve adhesion characteristics at the wheel-rail interface. The friction modifier must be designed to reduce slippage or sliding of the trains’ wheels on the rails under conditions of rapid acceleration or braking without excessive rolling contact wear. In this study, a novel composite material consisting of metal, ceramic, and polymer is proposed as a friction modifier to improve adhesion between wheels and rails. A blend of Al-6Cu-0.5Mg metallic powder, Al2O3 ceramic powder, and Bakelite-based polymer in various weight-fractions is hot-pressed at 150°C to form a bulk composite material. Variation in the adhesion coefficient is evaluated using a high-speed wheel-rail friction tester, with and without application of the composite friction modifier, under both dry and wet conditions. The effect of varying the weighting fractions of metal and ceramic friction powders is detailed in the paper.
- [Korean]
- Technology Trend of Luminescent Nanomaterials
- Hyewon Jeong, Jae Sung Son
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):170-177. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.170

- 1,112 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Colloidally synthesized luminescent nanocrystals (NCs) have attracted tremendous attention due to their unique nanoscale optical and electronic properties. The emission properties of these NCs can be precisely tuned by controlling their size, shape, and composition as well as by introducing appropriate dopant impurities. Nowadays, these NCs are actively utilized for various applications such as optoelectronic devices including light emitting diodes (LEDs), lasers, and solar cells, and bio-medical applications such as imaging agents and bio-sensors. In this review, we classify luminescent nanomaterials into quantum dots (QDs), upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs), and perovskite NCs and present their intrinsic emission mechanism. Furthermore, the recently emerging issues of efficiency, toxicity, and durability in these materials are discussed for better understanding of industry demands. As well, the future outlook will be offered for researchers to guide the direction of future research.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Structural Relationship between University Dance Students’ Emotional Regulation, Emotion Response, and Engagement in Classes
Jinhee Gong
The Journal of Korean Institute of Information Technology.2020; 18(4): 121. CrossRef
- A Structural Relationship between University Dance Students’ Emotional Regulation, Emotion Response, and Engagement in Classes
- [Korean]
- Technology Trend of the additive Manufacturing (AM)
- Ji-Won Oh, Hyunwoong Na, Hanshin Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):494-507. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.494
- 1,937 View
- 11 Download
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
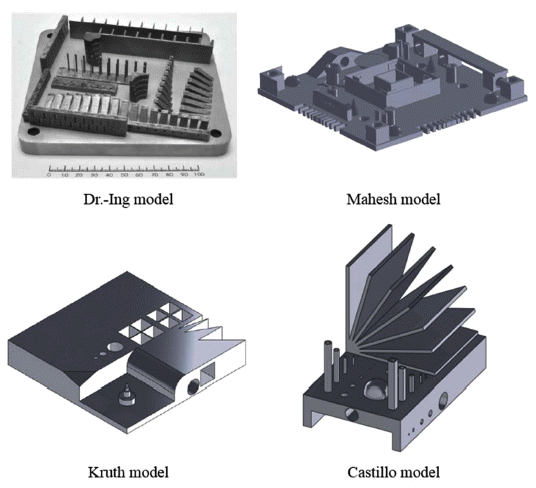
PDF A three-dimensional physical part can be fabricated from a three-dimensional digital model in a layer-wise manner via additive manufacturing (AM) technology, which is different from the conventional subtractive manufacturing technology. Numerous studies have been conducted to take advantage of the AM opportunities to penetrate bespoke custom product markets, functional engineering part markets, volatile low-volume markets, and spare part markets. Nevertheless, materials issues, machines issues, product issues, and qualification/certification issues still prevent the AM technology from being extensively adopted in industries. The present study briefly reviews the standard classification, technological structures, industrial applications, technological advances, and qualification/certification activities of the AM technology. The economics, productivity, quality, and reliability of the AM technology should be further improved to pass through the technology adoption lifecycle of innovation technology. The AM technology is continuously evolving through the introduction of PM materials, hybridization of AM and conventional manufacturing technologies, adoption of process diagnostics and control systems, and enhanced standardization of the whole lifecycle qualification and certification methodology.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Convolutional LSTM based melt-pool prediction from images of laser tool path strategy in laser powder bed fusion for additive manufacturing
Joung Min Park, Minho Choi, Jumyung Um
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.2024; 130(3-4): 1871. CrossRef - Color evaluation by thickness of interim restorative resin produced by digital light processing 3D printer
Wol Kang, Won-Gi Kim
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2021; 43(3): 77. CrossRef - Optimization of Metal Powder Particle Size Distribution for Powder Bed Fusion Process via Simulation
Hwaseon Lee, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Young Il Kim, Jieun Nam, Yong Son, Taek-Soo Kim, Bin Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(1): 44. CrossRef - Technology Trend of Additive Manufacturing Standardization
Hanshin Choi, Jinsu Park
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(5): 420. CrossRef - Multi-step Metals Additive Manufacturing Technologies
Ji-Won Oh, Jinsu Park, Hanshin Choi
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 256. CrossRef - Anisotropy in Green Body Bending Strength due to Additive Direction in the Binder-Jetting Additive Manufacturing Process
Ji-Won Oh, Sahn Nahm, Byoungmoon Kim, Hanshin Choi
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2019; 57(4): 227. CrossRef - Effect of Porosity on Mechanical Anisotropy of 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel Additively Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting
Jeong Min Park, Jin Myoung Jeon, Jung Gi Kim, Yujin Seong, Sun Hong Park, Hyoung Seop Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(6): 475. CrossRef
- Convolutional LSTM based melt-pool prediction from images of laser tool path strategy in laser powder bed fusion for additive manufacturing
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Electric Contact Properties of Spark Plasma Sintered Ta-Cu Composite
- Won Ju, Young Do Kim, Jae Jin Sim, Sang-Hoon Choi, Soong Keun Hyun, Kyoung Mook Lim, Kyoung-Tae Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):377-383. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.377

- 1,204 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Microstructure, electric, and thermal properties of the Ta-Cu composite is evaluated for the application in electric contact materials. This material has the potential to be used in a medium for a high current range of current conditions, replacing Ag-MO, W, and WC containing materials. The optimized SPS process conditions are a temperature of 900°C for a 5 min holding time under a 30 MPa mechanical pressure. Comparative research is carried out for the calculated and actual values of the thermal and electric properties. The range of actual thermal and electric properties of the Ta-Cu composite are 50~300W/mk and 10~90 %IACS, respectively, according to the compositional change of the 90 to 10 wt% Ta-Cu system. The results related to the electric contact properties, suggest that less than 50 wt% of Ta compositions are possible in applications of electric contact materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Formation mechanism, microstructural features and dry-sliding behaviour of “Bronze/WC carbide” composite synthesised by atmospheric pulsed-plasma deposition
V.G. Efremenko, Yu.G. Chabak, V.I. Fedun, K. Shimizu, T.V. Pastukhova, I. Petryshynets, A.M. Zusin, E.V. Kudinova, B.V. Efremenko
Vacuum.2021; 185: 110031. CrossRef
- Formation mechanism, microstructural features and dry-sliding behaviour of “Bronze/WC carbide” composite synthesised by atmospheric pulsed-plasma deposition
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Fe3O4/Fe/Graphene nanocomposite powder by Electrical Wire Explosion in Liquid Media and its Electrochemical Properties
- Yoo-Young Kim, Ji-Seub Choi, Hoi-Jin Lee, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):308-314. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.308

- 1,032 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder is synthesized by electrical wire explosion of Fe wire and dispersed graphene in deionized water at room temperature. The structural and electrochemical characteristics of the powder are characterized by the field-emission scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, field-emission transmission electron microscopy, cyclic voltammetry, and galvanometric discharge-charge method. For comparison, Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposites are fabricated under the same conditions. The Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposite particles, around 15-30 nm in size, are highly encapsulated in a graphene matrix. The Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder exhibits a high initial charge specific capacity of 878 mA/g and a high capacity retention of 91% (798 mA/g) after 50 cycles. The good electrochemical performance of the Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder is clearly established by comparison of the results with those obtained for Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposite powder and is attributed to alleviation of volume change, good distribution of electrode active materials, and improved electrical conductivity upon the addition of graphene.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation of magnetic metal and graphene hybrids with tunable morphological, structural and magnetic properties
Kyunbae Lee, Joonsik Lee, Byung Mun Jung, Byeongjin Park, Taehoon Kim, Sang Bok Lee
Applied Surface Science.2019; 478: 733. CrossRef
- Preparation of magnetic metal and graphene hybrids with tunable morphological, structural and magnetic properties
- [English]
- Development of Dark Field image Processing Technique for the Investigation of Nanostructures
- Jongchul Jeon, Kyou-Hyun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):285-291. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.285

- 1,080 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We propose a custom analysis technique for the dark field (DF) image based on transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The custom analysis technique is developed based on the DigitalMicrograph® (DM) script language embedded in the Gatan digital microscopy software, which is used as the operational software for most TEM instruments. The developed software automatically scans an electron beam across a TEM sample and records a series of electron diffraction patterns. The recorded electron diffraction patterns provide DF and ADF images based on digital image processing. An experimental electron diffraction pattern is recorded from a IrMn polycrystal consisting of fine nanograins in order to test the proposed software. We demonstrate that the developed image processing technique well resolves nanograins of ~ 5 nm in diameter.
- [English]
- Optimization of Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature Conditions for Enhancement of Thermoelectric Performance in Gas-Atomized Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 Compound
- Kwang-yong Jeong, Chul Hee Lee, Peyala Dharmaiah, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):108-114. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.108

- 1,259 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We fabricate fine (<20 μm) powders of Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 alloys using a large-scale production method and subsequently consolidate them at temperatures of 573, 623, and 673 K using a spark plasma sintering process. The microstructure, mechanical properties, and thermoelectric properties are investigated for each sintering temperature. The microstructural features of both the powders and bulks are characterized by scanning electron microscopy, and the crystal structures are analyzed by X-ray diffraction analysis. The grain size increases with increasing sintering temperature from 573 to 673 K. In addition, the mechanical properties increase significantly with decreasing sintering temperature owing to an increase in grain boundaries. The results indicate that the electrical conductivity and Seebeck coefficient (217 μV/K) of the sample sintered at 673 K increase simultaneously owing to decreased carrier concentration and increased mobility. As a result, a high
ZT value of 0.92 at 300 K is achieved. According to the results, a sintering temperature of 673 K is preferable for consolidation of fine (<20 μm) powders.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Complex microstructure induced high thermoelectric performances of p-type Bi–Sb–Te alloys
Eun-Ha Go, Babu Madavali, Min-Woo Shin, Sung Ho Song, Soon-Jik Hong
Materials Chemistry and Physics.2023; 307: 128156. CrossRef - Role of sintering temperature on electronic and mechanical properties of thermoelectric material: A theoretical and experimental study of TiCoSb half-Heusler alloy
Ajay Kumar Verma, Kishor Kumar Johari, Kriti Tyagi, Durgesh Kumar Sharma, Pawan Kumar, Sudhir Kumar, Sivaiah Bathula, S.R. Dhakate, Bhasker Gahtori
Materials Chemistry and Physics.2022; 281: 125854. CrossRef - Enhanced thermoelectric properties of Li and Mg co−substituted Bi2Sr2Co2O fabricated by combined conventional sintering and spark plasma sintering
K. Park, H.Y. Hong, S.Y. Gwon
Inorganic Chemistry Communications.2022; 145: 110005. CrossRef
- Complex microstructure induced high thermoelectric performances of p-type Bi–Sb–Te alloys
- [English]
- Representative Volume Element Analysis of Fluid-Structure Interaction Effect on Graphite Powder Based Active Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Jin Chul Yun, Seong Jin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):17-23. Published online February 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.17
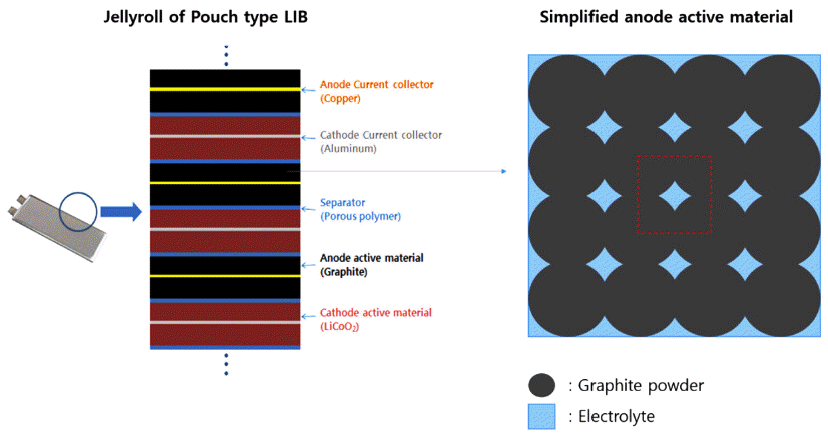
- 719 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, a finite element analysis approach is proposed to predict the fluid-structure interaction behavior of active materials for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), which are mainly composed of graphite powder. The porous matrix of graphite powder saturated with fluid electrolyte is considered a representative volume element (RVE) model. Three different RVE models are proposed to consider the uncertainty of the powder shape and the porosity. Pwave modulus from RVE solutions are analyzed based on the microstructure and the interaction between the fluid and the graphite powder matrix. From the results, it is found that the large surface area of the active material results in low mechanical properties of LIB, which leads to poor structural durability when subjected to dynamic loads. The results obtained in this study provide useful information for predicting the mechanical safety of a battery pack.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Carbon-coated Tin Nano-powders by Electrical Wire Explosion in Liquid Media and its Electrochemical Properties
- Yoo-Young Kim, Ju-Suck Song, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):317-324. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.317

- 1,010 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tin is one of the most promising anode materials for next-generation lithium-ion batteries with a high energy density. However, the commercialization of tin-based anodes is still hindered due to the large volume change (over 260%) upon lithiation/delithiation cycling. To solve the problem, many efforts have been focused on enhancing structural stability of tin particles in electrodes. In this work, we synthesize tin nano-powders with an amorphous carbon layer on the surface and surroundings of the powder by electrical wire explosion in alcohol-based liquid media at room temperature. The morphology and microstructures of the powders are characterized by scanning electron microscopy, Xray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. The electrochemical properties of the powder for use as an anode material for lithium-ion battery are evaluated by cyclic voltammetry and a galvanometric dischargecharge method. It is shown that the carbon-coated tin nano-powders prepared in hexanol media exhibit a high initial charge specific capacity of 902 mAh/g and a high capacity retention of 89% after 50 cycles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimization of carbon coating thickness to prevent crack generation in Sn nanoparticles during charge/discharge process and their electrochemical properties
Ji-Seub Choi, Yeon-Ju Lee, Hoi-Jin Lee, Gyu-Bong Cho, Jai-Won Byeon, Hyo-Jun Ahn, Ki-Won Kim, Jou-Hyeon Ahn, Kwon-Koo Cho
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2020; 843: 155892. CrossRef - Fabrication of multilayer graphene-encapsulated Sn/SnO2 nanocomposite as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries and its electrochemical properties
Ju-Seok Song, Gyu-Bong Cho, Ki-Won Kim, Hyo-Jun Ahn, Hye-Sung Kim, Jou-Hyeon Ahn, Kwon-Koo Cho
Applied Surface Science.2019; 481: 736. CrossRef
- Optimization of carbon coating thickness to prevent crack generation in Sn nanoparticles during charge/discharge process and their electrochemical properties
- [Korean]
- Effects of Precursor Co-Precipitation Temperature on the Properties of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 Powders
- Woonghee Choi, Chan Hyoung Kang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):287-296. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.287
- 1,937 View
- 36 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3(OH)2 powders have been synthesized in a continuously stirred tank reactor via a co-precipitation reaction between aqueous metal sulfates and NaOH using NH4OH as a chelating agent. The co-precipitation temperature is varied in the range of 30-80°C. Calcination of the prepared precursors with Li2CO3 for 8 h at 1000°C in air results in Li Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 powders. Two kinds of obtained powders have been characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy, particle size analyzer, and tap density measurements. The co-precipitation temperature does not differentiate the XRD patterns of precursors as well as their final powders. Precursor powders are spherical and dense, consisting of numerous acicular or flaky primary particles. The precursors obtained at 70 and 80°C possess bigger primary particles having more irregular shapes than those at lower temperatures. This is related to the lower tap density measured for the former. The final powders show a similar tendency in terms of primary particle shape and tap density. Electrochemical characterization shows that the initial charge/discharge capacities and cycle life of final powders from the precursors obtained at 70 and 80°C are inferior to those at 50°C. It is concluded that the optimum co-precipitation temperature is around 50°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A kinetic descriptor to optimize Co-precipitation of Nickel-rich cathode precursors for Lithium-ion batteries
Seon Hwa Lee, Ki Young Kwon, Byeong Kil Choi, Hyun Deog Yoo
Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry.2022; 924: 116828. CrossRef
- A kinetic descriptor to optimize Co-precipitation of Nickel-rich cathode precursors for Lithium-ion batteries
- [Korean]
- Characteristics of Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3(OH)2 Powders Prepared by Co-Precipitation in Air and Nitrogen Atmospheres
- Woonghee Choi, Se-Ryen Park, Chan Hyoung Kang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):136-142. Published online April 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.136

- 2,796 View
- 59 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF As precursors of cathode materials for lithium ion batteries, Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3(OH)2 powders are prepared in a continuously stirred tank reactor via a co-precipitation reaction between aqueous metal sulfates and NaOH in the presence of NH4OH in air or nitrogen ambient. Calcination of the precursors with Li2CO3 for 8 h at 1,000°C in air produces dense spherical cathode materials. The precursors and final powders are characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy, particle size analysis, tap density measurement, and thermal gravimetric analysis. The precursor powders obtained in air or nitrogen ambient show XRD patterns identified as Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3(OH)2. Regardless of the atmosphere, the final powders exhibit the XRD patterns of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 (NCM). The precursor powders obtained in air have larger particle size and lower tap density than those obtained in nitrogen ambient. NCM powders show similar tendencies in terms of particle size and tap density. Electrochemical characterization is performed after fabricating a coin cell using NCM as the cathode and Li metal as the anode. The NCM powders from the precursors obtained in air and those from the precursors obtained in nitrogen have similar initial charge/discharge capacities and cycle life. In conclusion, the powders co-precipitated in air can be utilized as precursor materials, replacing those synthesized in the presence of nitrogen injection, which is the usual industrial practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thermodynamic modeling and parameters optimization for Ni0.8Co0.1Mn 0.1(OH)2 synthesis via transitional metal coprecipitation
Zanlang Tang, Chen Liu, Xincun Tang, Haonan Liu, Biao Qin
Materials Science and Engineering: B.2026; 326: 119205. CrossRef - Stabilization of High Nickel Cathode Materials with Core-Shell Structure via Co-precipitation Method
Minjeong Kim, Soonhyun Hong, Heongkwon Jeon, Jahun Koo, Heesang Lee, Gyuseok Choi, Chunjoong Kim
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2022; 32(4): 216. CrossRef - Spherical agglomeration of nickel-manganese-cobalt hydroxide in turbulent Batchelor vortex flow
Xiaotong Sun, Jinsoo Kim, Woo-Sik Kim
Chemical Engineering Journal.2021; 421: 129924. CrossRef - Design strategies for development of nickel-rich ternary lithium-ion battery
Kyu Hwan Choi, Xuyan Liu, Xiaohong Ding, Qiang Li
Ionics.2020; 26(3): 1063. CrossRef - Effect of Single and Dual Doping of Rare Earth Metal Ce and Nd Elements on Electrochemical Properties of LiNi0.83 Co0.11Mn0.06O2 Cathode Lithium-ion Battery Material
Yoo-Young Kim, Jong-Keun Ha, Kwon-Koo Cho
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(1): 49. CrossRef - Effects of Precursor Co-Precipitation Temperature on the Properties of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 Powders
Woonghee Choi, Chan Hyoung Kang
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(4): 287. CrossRef
- Thermodynamic modeling and parameters optimization for Ni0.8Co0.1Mn 0.1(OH)2 synthesis via transitional metal coprecipitation
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Microstructure/Properties of Bulk-type Tantalum Material by a Kinetic Spray Process
- Ji-Hye Lee, Ji-Won Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(1):8-14. Published online February 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.1.8

- 749 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A bulk-type Ta material is fabricated using the kinetic spray process and its microstructure and physical properties are investigated. Ta powder with an angular size in the range 9-37 μm (purity 99.95%) is sprayed on a Cu plate to form a coating layer. As a result, ~7 mm-sized bulk-type high-density material capable of being used as a sputter material is fabricated. In order to assess the physical properties of the thick coating layer at different locations, the coating material is observed at three different locations (surface, center, and interface). Furthermore, a vacuum heat treatment is applied to the coating material to reduce the variation of physical properties at different locations of the coating material and improve the density. OM, Vickers hardness test, SEM, XRD, and EBSD are implemented for analyzing the microstructure and physical properties. The fabricated Ta coating material produces porosity of 0.11~0.12%, hardness of 311~327 Hv, and minor variations at different locations. In addition, a decrease in the porosity and hardness is observed at different locations upon heat treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sintering Behavior and Microstructures of Tantalum and Tantalum-Tungsten Alloys Powders
Youngmoo Kim, Sung Ho Yang, Seong Lee, Sung Ho Lee, Joon-Woong Noh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(5): 373. CrossRef - Manufacturing of Large-Scale Cold-Sprayed Ta Target Material and Its Sputtering Property
Gi-Su Ham, Dong-Yeol Wi, Jun-Mo Yang, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Thermal Spray Technology.2019; 28(8): 1974. CrossRef - Mechanical properties of Mo-Nb-Si-B quaternary alloy fabricated by powder metallurgical method
Jong Min Byun, Su-Ryong Bang, Se Hoon Kim, Won June Choi, Young Do Kim
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2017; 65: 14. CrossRef
- Sintering Behavior and Microstructures of Tantalum and Tantalum-Tungsten Alloys Powders
- [Korean]
- Thermoelectric Properties in the Cu Doping Effects of the n-type Bi-Te Powders
- Min Soo Park, Hye Young Koo, Gook Hyun Ha, Yong Ho Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(4):254-259. Published online August 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.4.254

- 794 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Bi2Te3 related compounds show the best thermoelectric properties at room temperature. However, n-type Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 showed no improvement on ZT values. To improve the thermolectric propterties of n-type Bi2Te2.7Se0.3, this research has Cu-doped n-type powder. This study focused on effects of Cu-doping method on the thermoelectric properties of n-type materials, and evaluated the comparison between the Cu chemical and mechanical doping. The synthesized powder was manufactured by the spark plasma sintering(SPS). The thermoelectric properties of the sintered body were evaluated by measuring their Seebeck coefficient, electrical resistivity, thermal conductivity, and hall coefficient. An introduction of a small amount of Cu reduced the thermal conductivity and improved the electrical properties with Seebeck coefficient. The authors provided the optimal concentration of Cu0.1Bi1.99Se0.3Te2.7. A figure of merit (ZT) value of 1.22 was obtained for Cu0.1Bi1.9Se0.3Te2.7 at 373K by Cu chemical doping, which was obviously higher than those of Cu0.1Bi1.9Se0.3Te2.7 at 373K by Cu mechanical doping (ZT=0.56) and Cu-free Bi2Se0.3Te2.7 (ZT=0.51).
- [English]
- Environment Emission and Material Flow Analysis of Chromium in Korea
- Dong-won Shin, Jeong-gon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(3):187-196. Published online June 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.3.187
- 665 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF With the stabilization of Korea’s industrialization, it has become interested in the efficient use of rare metals, climate change and industrial environment and safety etc. It is thus making efforts to implement economic policies that address such issues. Therefore it is necessary to understand the demand, supply and use of metal materials. Since 2010, the Korean government has developed the integrated material flow methodology and has been trying to examine the demand, supply and use of metal materials. In 2013, the Korean government surveyed the material flow of chromium. Material flow analysis and environment emission of chromium were investigated 8 steps; (1) raw material, (2) first process, (3) Intermediate product, (4) End product, (5) Use/accumulation, (6) Collection, (7) Recycling, (8) Disposal. Chromium was used for stainless steel, alloy steel, coated sheets, refractory material and coating materials. Recycling was done mainly in use of stainless steel scrap. To ensure efficient use of chromium, process improvement is required to reduce the scrap in the intermediate product stage. In the process of producing of the products using chromium, it was confirmed that chromium was exposed to the environment. It requires more attention and protection against environment emission of chromium.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


