Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Structural, Electrical, and Optical Properties of Al–Mg Co-Doped ZnO Thin Films
- Jong-Mu Kim, Jun-Seo Park, Jun-Ha Lee, Min-Woo Kim, Jung-Woo Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2026;33(1):44-50. Published online February 28, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2026.00031
- 15 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
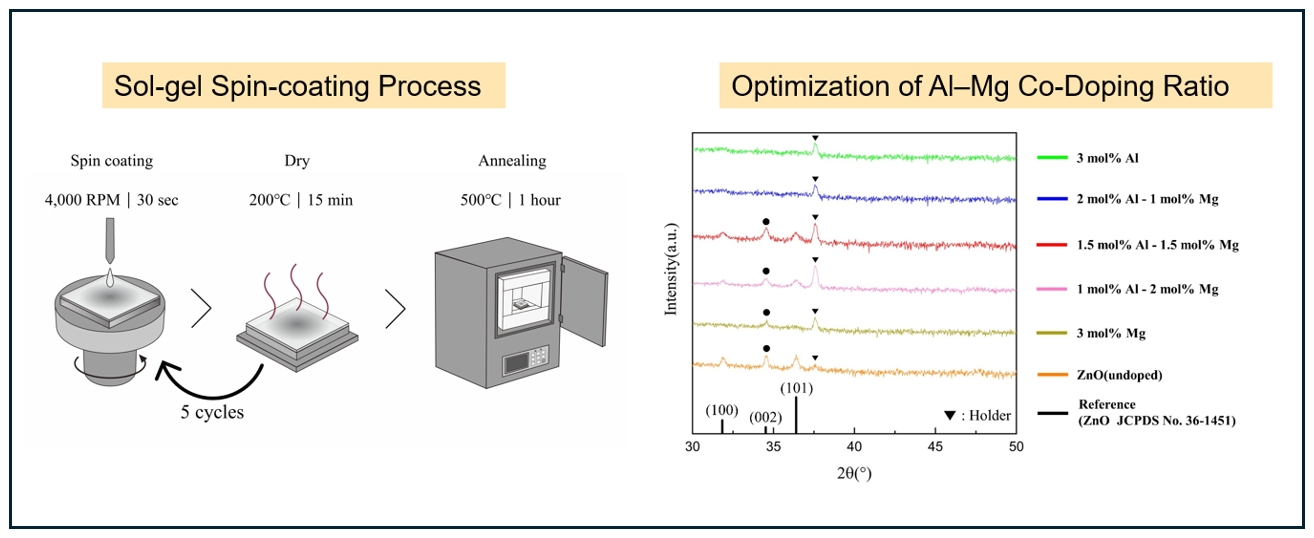
PDF - Al–Mg co-doped ZnO thin films were fabricated by a sol–gel spin-coating process to investigate the effect of dopant ratio on their structural, electrical, and optical properties. The total dopant concentration was fixed at 3 mol%, while the Al-to-Mg ratio was systematically varied in AlₓMg₀.₀₃₋ₓZn₀.₉₇O (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.03). X-ray diffraction analysis showed that the films maintained a hexagonal wurtzite structure with a preferred (002) orientation up to an Al concentration of 1.5 mol%, whereas higher Al contents resulted in a degradation of crystallinity due to exceeding the solid solubility limit of Al in the ZnO lattice. Hall effect measurements revealed a decrease in carrier mobility with increasing Al content, attributed to enhanced ionized impurity scattering, while the carrier concentration and electrical conductivity reached optimal values at an Al–Mg co-doping ratio of 1.5 mol%–1.5 mol%. All films exhibited high optical transmittance in the visible region, with the highest average transmittance of approximately 83% observed at the same composition. These results demonstrate that controlling the Al/Mg dopant ratio is crucial for optimizing the performance of ZnO-based transparent conducting oxide thin films.
- [English]
- Microstructure and Properties Comparison of Pure Cu and Cu-5 wt.% Al2O3 Composite Processed by Spark Plasma Sintering
- Dinh Van Cong, Dong-Wan Lee, Su-Wan Lee, Nguyen Minh Thuyet, Nguyen Viet Hoang, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2026;33(1):51-60. Published online February 28, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00472
- 7 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
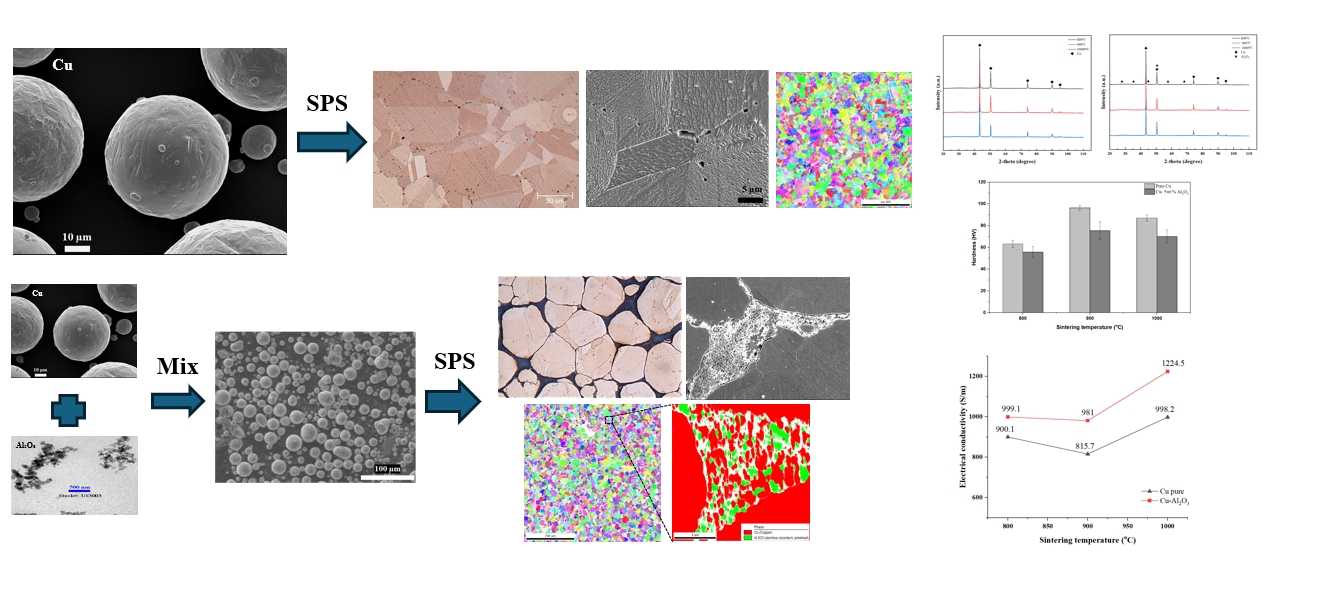
PDF - This study compares the microstructure and properties of pure Cu and Cu-5 wt.% Al2O3 composites fabricated by spark plasma sintering under strictly identical processing conditions at 800-1000 °C. Pure Cu samples achieved near-full densification and exhibited a bimodal grain structure dominated by coarse grains with increasing sintering temperature. In contrast, the composite samples showed lower density and non-monotonic densification behavior, with a minimum relative density at 900 oC and significantly refined equiaxed grains due to strong grain-boundary pinning by nano Al2O3 particles. The higher fractions of high-angle boundaries and pronounced orientation disruption were observed in the composite samples, while high-resolution analysis confirmed the presence of grain-boundary Al2O3-rich regions that restricted Cu grain coalescence and continuity of grain boundary migration. X-ray diffraction results confirmed the absence of reaction phases in both materials. Hardness peaked at 900 °C for both samples, and the composite samples showed consistently lower hardness due to retained porosity. The apparent electrical conductivity of the composite displays a non-linear temperature dependence, reflecting the competing influences of densification, microstructural recovery, and the insulating nature of Al2O3.
- [Korean]
- Preparation of Porous W-Cu by Freeze Casting of Tert-butyl Alcohol Slurry Mixed with WO3-CuO Powder
- Youngmin Kim, Ji Young Kim, Minju Son, Wonyong Kwon, Eui Seon Lee, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):466-471. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00437
- 742 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
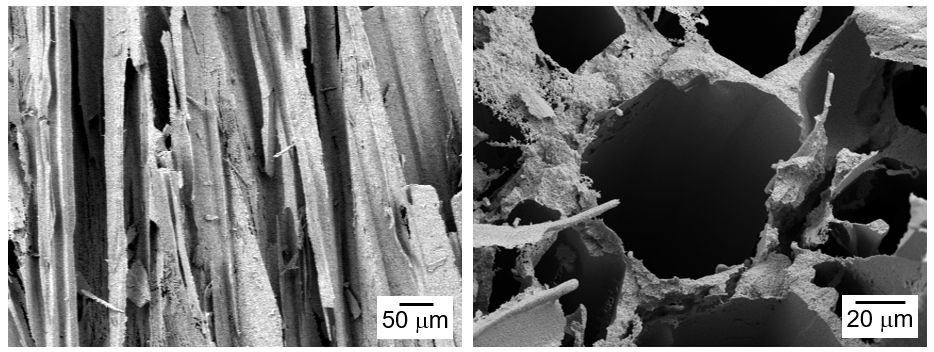
PDF - The influence of process conditions on the microstructure of porous W-Cu, fabricated by freeze casting using tert-butyl alcohol as the freezing agent, was investigated. The slurries containing 10 vol% of WO3-CuO powder were prepared by milling with a small amount of citric acid and polyethylene glycol as dispersants. The slurries with dispersion stability were frozen in a mold with the lower part cooled to -25°C, followed by sublimation in a vacuum to remove the freezing agent. The sintered W-1 vol% Cu in a hydrogen atmosphere exhibited aligned pores with the size of 50 μm, which were generated by sublimation of directionally solidified tert-butyl alcohol crystals. In the cross-section of the specimen, hexagonal pores corresponding to the crystal structure of tert-butyl alcohol was observed. Microstructure analysis of the struts revealed that Cu was distributed non-uniformly due to the mutual insolubility and low wettability of the W-Cu system.
- [Korean]
- Comparison of the Properties of Rare-Earth Zirconate Thermal Barrier Coatings for Hydrogen-Fueled Gas Turbines
- Gun-Woong Lee, Min-Soo Nam, Min-Ji Kim, HyunSuk Jung, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):472-480. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00423
- 791 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) for hydrogen-fueled gas turbines withstand higher combustion temperatures and increased steam concentrations compared to conventional natural-gas systems. These harsh operating conditions significantly accelerate the thermal degradation of widely used YSZ coatings, emphasizing the need for alternative top-coat materials with improved phase stability and reduced thermal conductivity. In this study, rare-earth zirconate ceramics, Gd2Zr2O7 (GdZO), Tm2Zr2O7 (TmZO), and a mixed composition (Gd0.5Tm0.5)2Zr2O7 (Gd/TmZO), are synthesized and investigated as potential next-generation TBC candidates. Each material was comparatively examined with a focus on crystal structure, thermophysical properties, and thermal conductivity. Furthermore, high-temperature steam exposure experiments were performed to simulate hydrogen combustion environments. Microstructural analyses, high-temperature degradation behavior, and phase stability evaluations were carried out to obtain fundamental experimental data. This study provides essential baseline information for the design and development of high-performance TBC materials suitable for the hydrogen-fueled gas turbine systems.
- [English]
- Finite Element and Discrete Element Analyses of Anisotropic Powder Compaction for Axial Flux Motor Cores
- Jeong Ah Lee, Do Won Lee, , Hyojeong Ha, Ki Hyuk Kwon, Eon Byeong Park, Taeyoung Kim, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):451-458. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00409
- 889 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
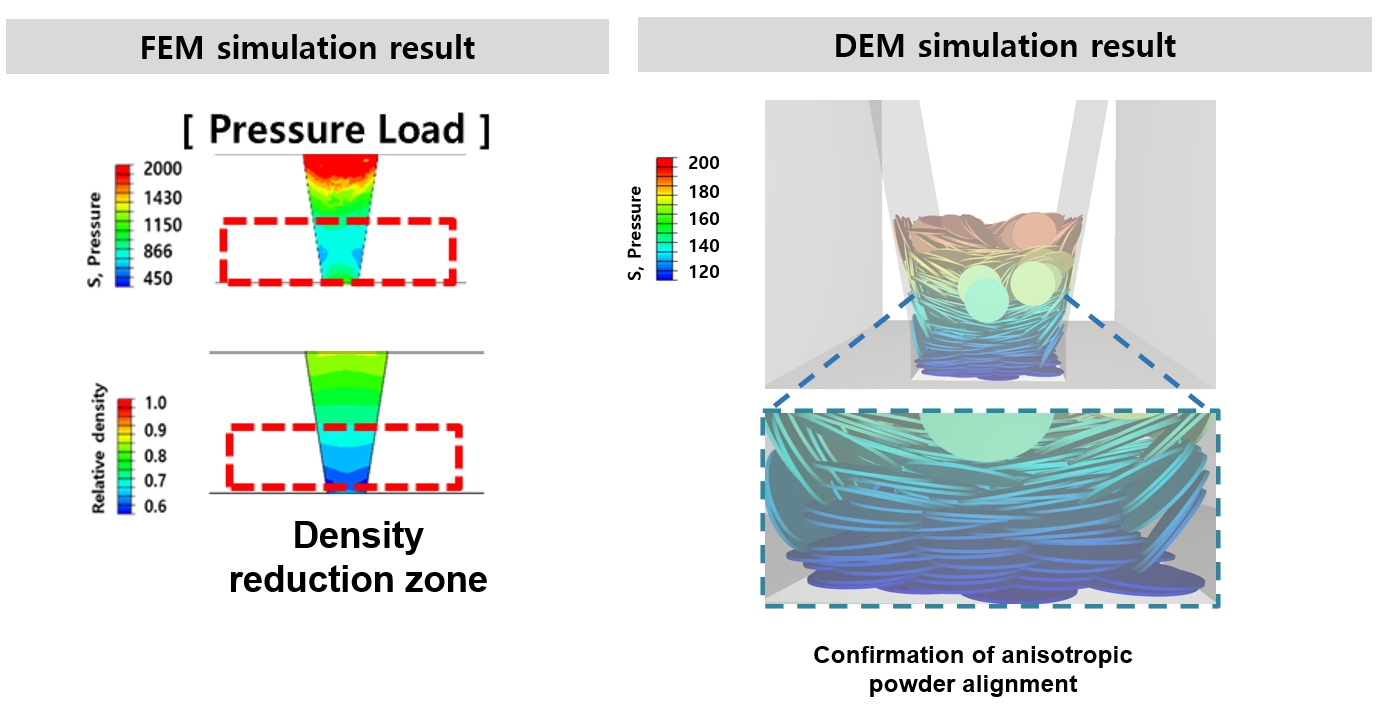
PDF - This study investigates the compaction behavior of anisotropic, plate-like powders used in axial flux motor cores through a combined FEM–DEM approach. A porous continuum FEM model captures stress and density evolution during die pressing, revealing strong gradients along the compaction direction, with higher stress and densification near the upper punch and reduced compaction in the lower region. Guided by these results, DEM simulations examine particle packing, orientation, and contact pressure in representative zones. The DEM analysis shows that higher local pressure promotes denser packing and in-plane particle alignment near the upper punch, while the lower region exhibits more random orientations and lower contact forces. As a result, the multi-scale FEM–DEM framework clarifies how anisotropic particle behavior governs local densification and offers practical guidance for die design and process optimization to achieve more uniform density and controlled magnetic-property-relevant particle alignment in axial flux motor cores.
- [Korean]
- Ultrafast Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide via Flashlamp Annealing
- Chan Hyeon Yang, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):509-516. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00339
- 700 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
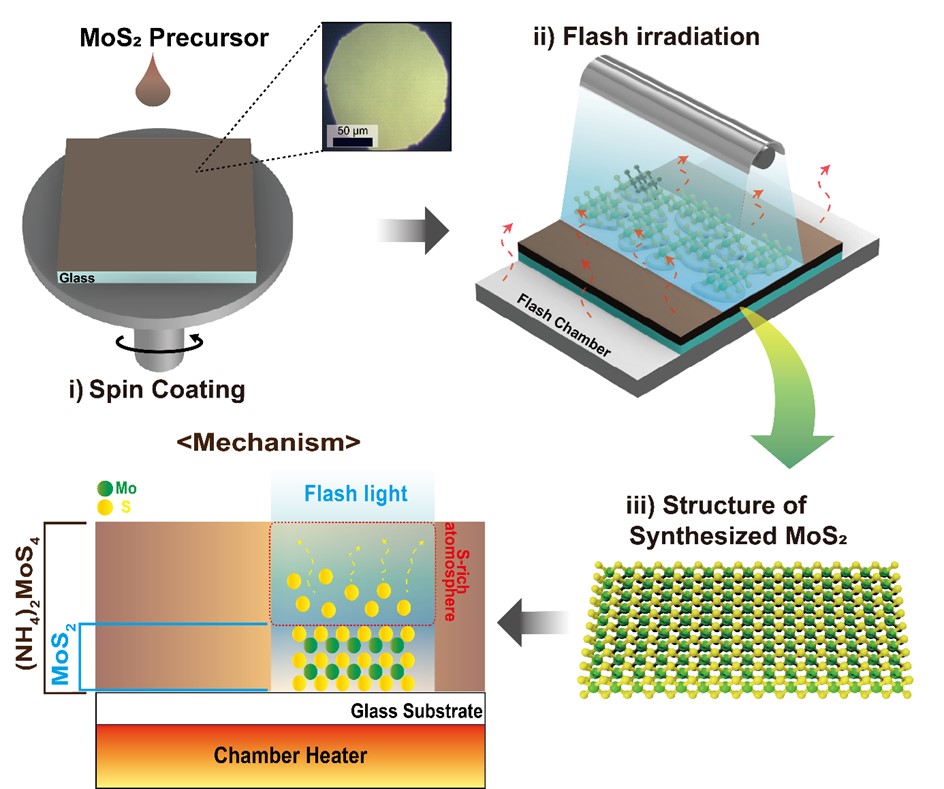
PDF - This study presents the synthesis of molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) using flashlamp annealing and provides a comprehensive investigation of its structural and physical properties. The proposed flash-induced approach enables rapid production of high-quality MoS₂, offering superior process efficiency compared to conventional synthesis techniques. The structural, electronic, and thermal characteristics of the synthesized MoS₂ were systematically examined using multiple analytical methods, with particular attention to how synthesis conditions influence layer structure, crystallinity, and defect density. The results indicate that MoS₂ produced through this method exhibits material properties suitable for high-performance electronic devices and energy storage applications. Moreover, this work demonstrates the potential of flash-induced synthesis for scalable and practical fabrication of MoS₂-based nanomaterials, thereby contributing to the broader advancement of transition metal dichalcogenide technologies across diverse nanotechnology applications.
- [English]
- Preparation of Flake-shape Cobalt Powders by High-Energy Ball Milling for rSOC Current Collectors
- Poong-Yeon Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Hyeon Ju Kim, Su-Jin Yun, Si Young Chang, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):383-389. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00241
- 449 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
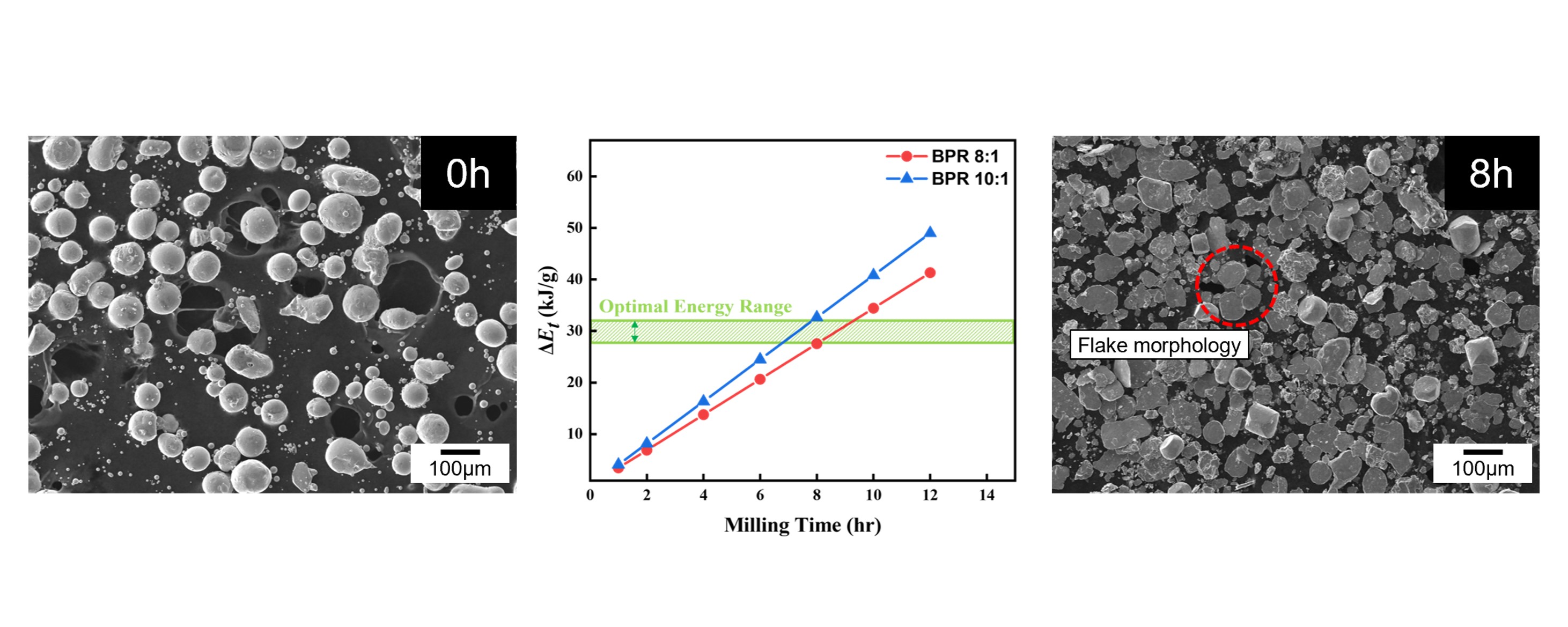
PDF - Reversible solid oxide cells (rSOCs), which enable two-way conversion between electricity and hydrogen, have gained attention with the rise of hydrogen energy. However, foam-type current collectors in rSOC stacks exhibit poor structural controllability and limited electrode contact area. To address these limitations, this study aimed to convert spherical cobalt powders into flake-type morphology via high-energy ball milling, as a preliminary step toward fabricating flake-based current collectors. Milling parameters—specifically, the ball-to-powder ratio (BPR), milling time, and process control agent (PCA) content—were varied. At an 8:1 BPR, over 90% of the powder became flake-shaped after 8 hours, while extended milling caused cold welding. In contrast, a 10:1 BPR resulted in dominant fragmentation. The Burgio–Rojac model quantified energy input and defined the optimal range for flake formation. Increasing the PCA to 4 wt% delayed flake formation to 16 hours and induced cold welding, as shown by bimodal particle size distributions. These results support the development of Co-based current collectors for use in rSOCs.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Morphology Control of Needle Type 513 MHSH and Mg(OH)2 from Dolomite
- Jiyeon Kim, HyunSeung Shim, Seong-Ju Hwang, YooJin Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):399-405. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00227
- 446 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
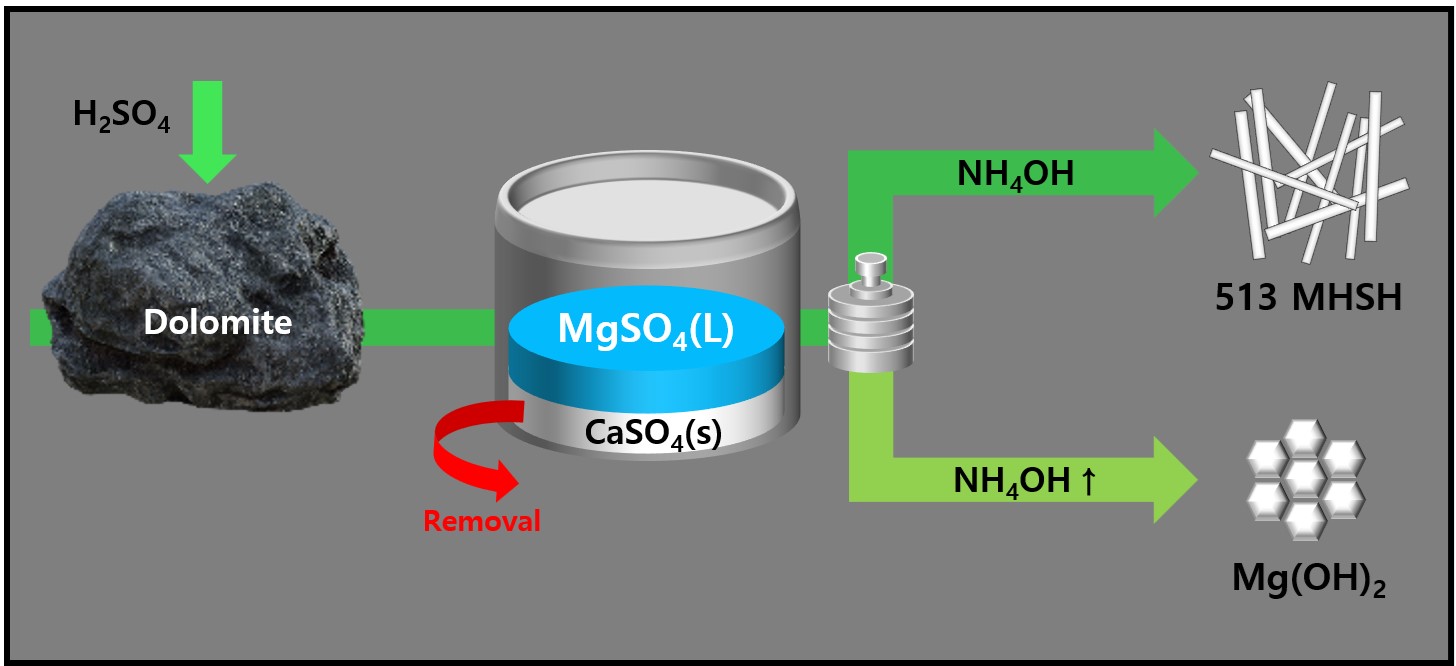
PDF - 513 magnesium hydroxide sulfate hydrate (MHSH) and Mg(OH)₂ were synthesized by controlling the pH and concentration using a domestic resource, dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2), as the raw material. The MgSO₄ was extracted by treating dolomite with sulfuric acid under various conditions. Hexagonal plate-shaped Mg(OH)₂ and needle-like 513 MHSH were synthesized under the hydrothermal condition. The morphology of the synthesized materials was controlled by adjusting the pH (SO42-/OH- ratio) and hydrothermal reaction time. As the pH of the solution increased, the formation of plate-like structures became dominant, whereas lower pH values (higher SO42- concentration) led to needle-like forms. The results of the 513 MHSH, which was synthesized using reagents and sea bittern, are consistent with the synthesis conditions, and we observed changes in the length and aspect ratio of the needle-shaped structure in response to adjusting the hydrothermal reaction time.
- [Korean]
- The Recycling Process and Powderization Technology of Stellite 6 Scrap: A Thermodynamic and Heat Transfer Analysis
- YongKwan Lee, Hyun-chul Kim, Myungsuk Kim, Soong Ju Oh, Kyoungtae Park, JaeJin Sim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):330-343. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00136

- 1,109 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Co-Cr alloys are widely used in cutting tools and turbine components due to their high strength and resistance against wear and corrosion. However, scrap generated during hardfacing is often discarded due to impurities and oxidation, and research on its recycling remains limited. This study aimed to optimize the recycling process of Stellite 6 scrap to reduce waste and minimize costs while maintaining material quality. Melting, casting, and powdering processes were designed using HSC Chemistry, FactSage, and COMSOL Multiphysics, with optimization of key parameters such as the crucible material and temperature control. The recycled alloy and powder were analyzed using X-ray fluorescence analysis, inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy, and X-ray diffractometry, showing mechanical and chemical properties comparable to commercial Stellite 6. The Co and Cr contents were maintained, with a slight increase in Fe. These findings demonstrate the potential for producing high-quality recycled Stellite 6 materials, contributing to the sustainable utilization of metal resources in high-performance applications.
- [English]
- Enhanced Compressive Strength of Fired Iron Ore Pellets: Effects of Blending Fine and Coarse Particle Concentrates
- Ngo Quoc Dung, Tran Xuan Hai, Nguyen Minh Thuyet, Nguyen Quang Tung, Arvind Barsiwal, Nguyen Hoang Viet
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):315-329. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00129

- 1,856 View
- 70 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the effects of oxidative firing parameters and raw material characteristics on the pelletization of Australian and Minh Son (Vietnam) iron ore concentrates. The influence of firing temperature (1050°C–1150°C) and holding time (15–120 min) on pellet compressive strength was examined, focusing on microstructural changes during consolidation. Green pellets were prepared using controlled particle size distributions and bentonite as a binder. Scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analyses revealed that grain boundary diffusion, liquid phase formation, and densification significantly improved mechanical strength. X-ray diffraction confirmed the complete oxidation of magnetite to hematite at elevated temperatures, a critical transformation for metallurgical performance. Optimal firing conditions for both single and blended ore compositions yielded compressive strengths above 250 kgf/pellet, satisfying the requirements for blast furnace applications. These results provide valuable guidance for improving pellet production, promoting the efficient utilization of diverse ore types, and enhancing the overall performance of ironmaking operations.
- [Korean]
- Development of Aluminum Alloys for Additive Manufacturing Using Machine Learning
- Sungbin An, Juyeon Han, Seoyeon Jeon, Dowon Kim, Jae Bok Seol, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):202-211. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00150
- 797 View
- 51 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
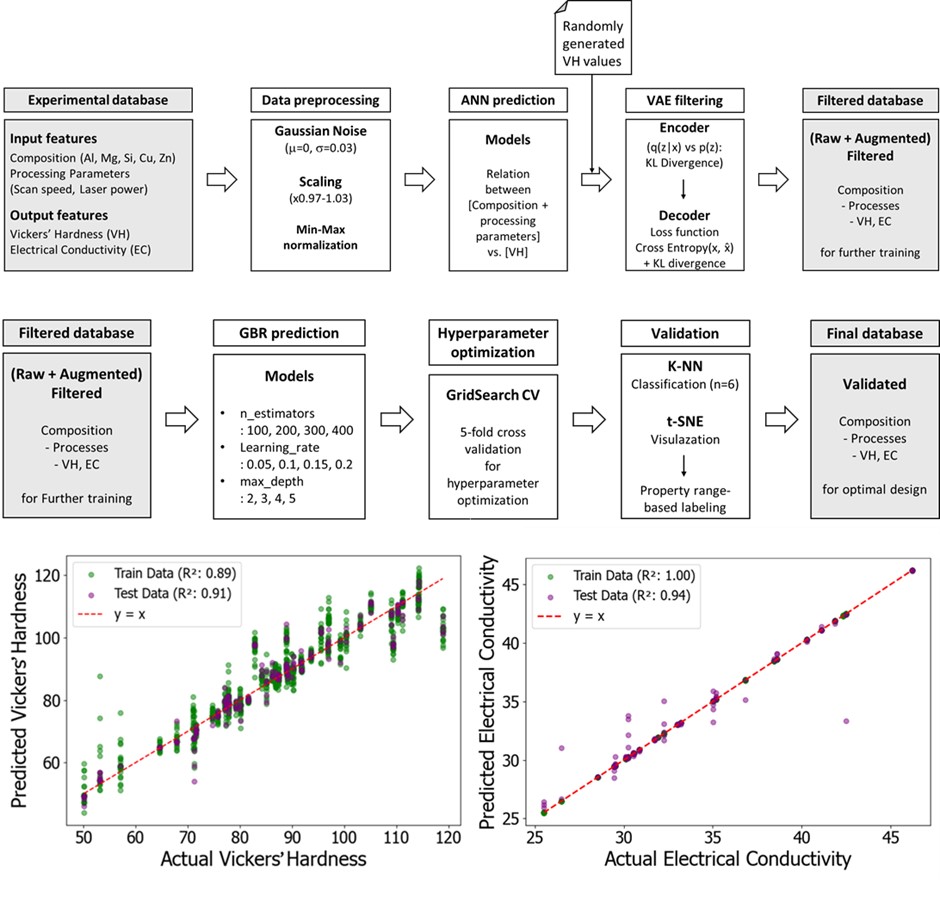
PDF - The present study introduces a machine learning approach for designing new aluminum alloys tailored for directed energy deposition additive manufacturing, achieving an optimal balance between hardness and conductivity. Utilizing a comprehensive database of powder compositions, process parameters, and material properties, predictive models—including an artificial neural network and a gradient boosting regression model, were developed. Additionally, a variational autoencoder was employed to model input data distributions and generate novel process data for aluminum-based powders. The similarity between the generated data and the experimental data was evaluated using K-nearest neighbor classification and t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding, with accuracy and the F1-score as metrics. The results demonstrated a close alignment, with nearly 90% accuracy, in numerical metrics and data distribution patterns. This work highlights the potential of machine learning to extend beyond multi-property prediction, enabling the generation of innovative process data for material design.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):244-253. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00087
- 1,110 View
- 46 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
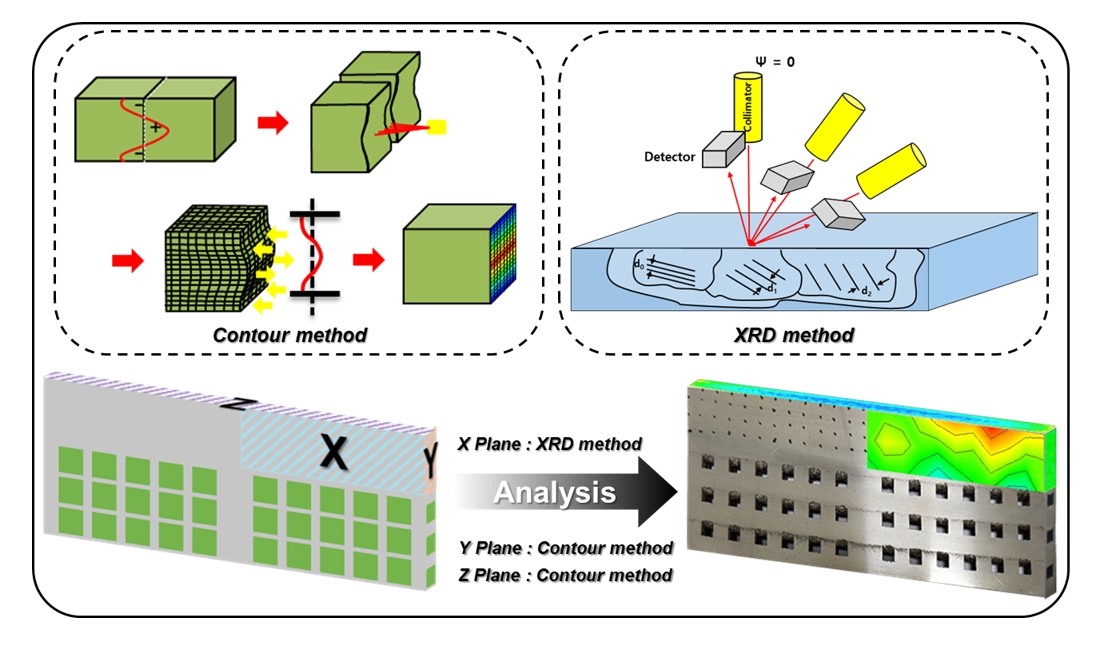
PDF - Ti-6Al-4V alloy is widely utilized in aerospace and medical sectors due to its high specific strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. However, its low machinability makes it difficult to manufacture complex-shaped products. Advancements in additive manufacturing have focused on producing high-performance, complex components using the laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) process, which is a specialized technique for customized geometries. The LPBF process exposes materials to extreme thermal conditions and rapid cooling rates, leading to residual stresses within the parts. These stresses are intensified by variations in the thermal history across regions of the component. These variations result in differences in microstructure and mechanical properties, causing distortion. Although support structure design has been researched to minimize residual stress, few studies have conducted quantitative analyses of stress variations due to different support designs. This study investigated changes in the residual stress and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy fabricated using LPBF, focusing on support structure design.
- [Korean]
- Effect of the Initial Porosity of Needle Coke-Pitch Carbonized Blocks on Impregnation-Related Physical Properties
- U-Sang Youn, Sang-Hye Lee, Jae-Seung Roh
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):138-144. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00038

- 738 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Carbonized blocks with different porosities were prepared by varying the particle size of the filler and subsequent impregnation. The impregnated carbonized blocks were re-carbonized. The use of smaller particles in the filler in the carbonized block was associated with larger porosity, smaller pore size, and a higher impregnation ratio. The block with the smallest average particle size (53 μm), CB-53, had a porosity of 35.9% and pores of approximately 40 μm, while the block with the largest average particle size (413 μm), CB-413, had a porosity of 30.5% and pores of approximately 150 μm. CB-53 had the highest bulk density, electrical resistivity, flexural strength, and impregnation ratio. This is due to the large porosity, which is believed to be due to the presence of more interfaces between particles during the re-carbonization of the impregnated carbonized block, resulting in a better pore-filling effect.
- [Korean]
- 3D-Printed Stretchable Electrodes Enabled by a Titanium/Acrylamide-Based Hydrogel Nanocomposite
- Se Jin Choi, Han Eol Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):67-72. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00465
- 873 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
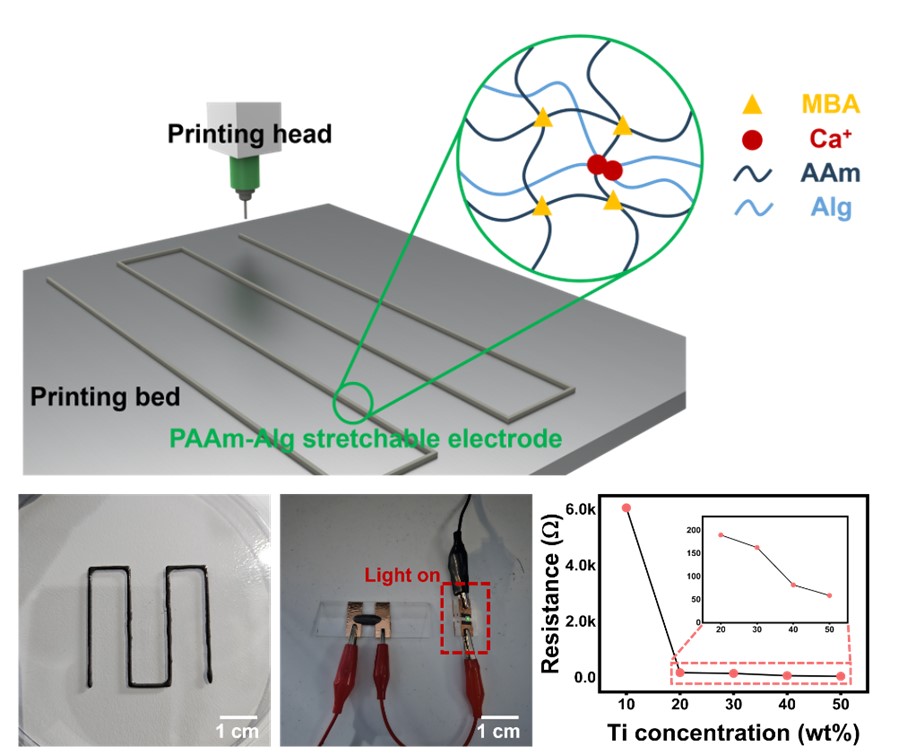
PDF - Wearable electronics have been the focus of considerable interest in various fields, such as human-machine interfaces, soft robotics, and medical treatments, due to their flexibility, stretchability, and light weight. To address the shortcomings of existing metal thin film-based wearable devices, stretchable conductive polymers have been developed. In particular, double networking hydrogels are being actively studied as a polymer with a three-dimensional stereoscopic structure that can be patterned. Nonetheless, they have shortcomings such as poor electrical properties and cumbersome manufacturing processes, making it difficult to apply them in electronic devices. Herein, we report 3D-printed stretchable electrodes enabled by a titanium/polyacrylamide-alginate-based hydrogel nanocomposite. This research suggests the strategy for resolving the challenges of high costs and complex fabrication processes associated with stretchable electrode, providing a solution to accelerate the commercialization of wearable electronic devices.
- [Korean]
- Optimized Process and Mechanical and Electrical Analysis of Polyimide/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Composites
- Junki Lee, Sang-il Yoon, Hyunseung Kim, Chang Kyu Jeong
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):16-22. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00444
- 999 View
- 30 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
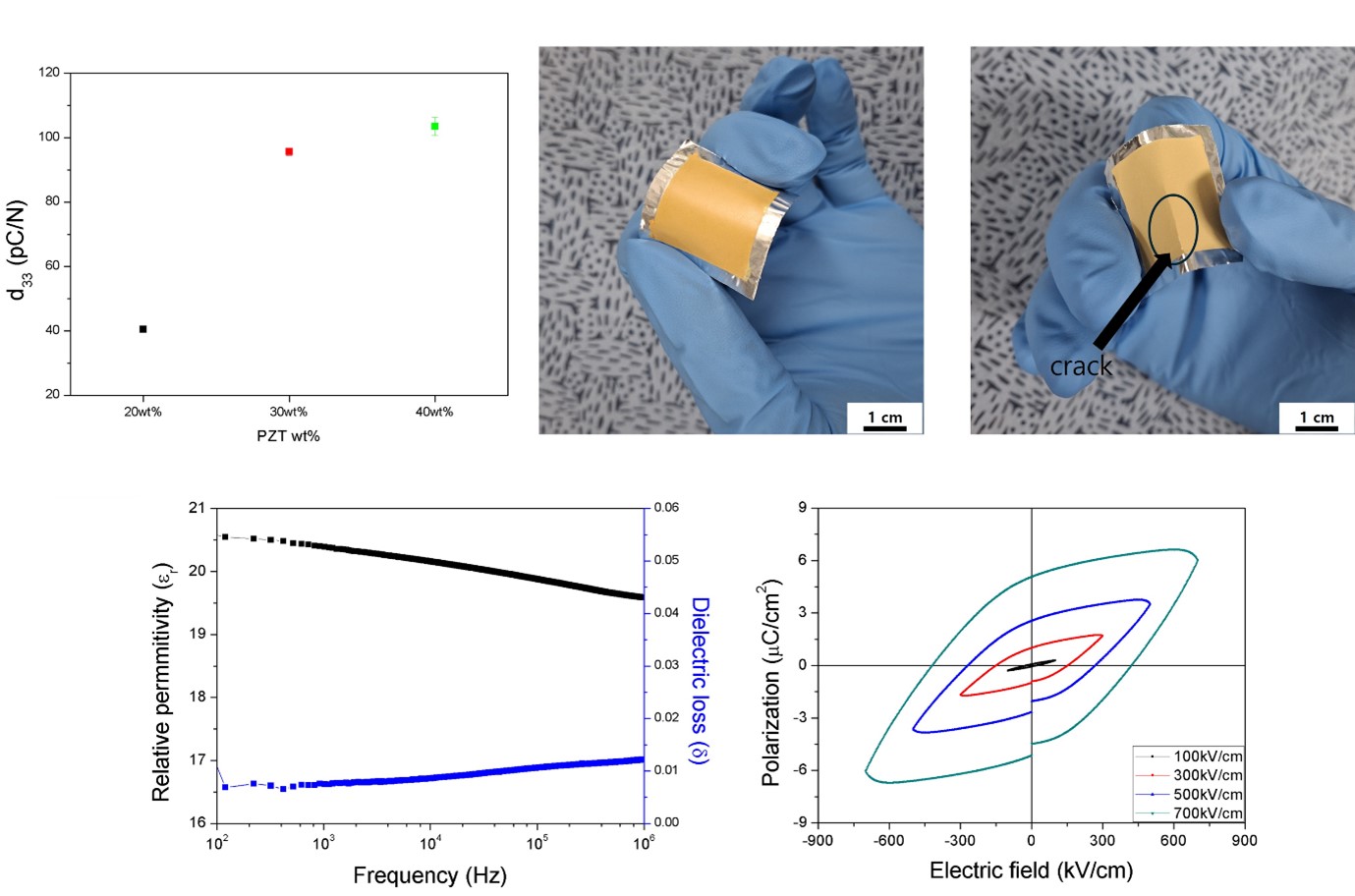
PDF - Piezoelectric composites have attracted significant research interest as sustainable power sources for electronic devices due to their high mechanical stability and electrical output characteristics. This study investigated the optimal processing conditions for fabricating a flexible piezoelectric energy harvester based on Pb(Zr,Ti)O₃ (PZT) powder and a polyimide (PI) matrix composite. Various parameters, including the optimal mixing ratio of PI/PZT, ultrasonic treatment, homogenization, vacuum oven, and UV/O₃ treatment, were optimized to achieve a uniform piezoelectric composite. A PZT content of 30 wt% and 20 minutes of homogenization were identified as the most effective conditions for increasing the uniformity of the composite. The optimized composite exhibited a high piezoelectric coefficient, a typical P-E hysteresis loop, and dielectric properties, exhibiting a voltage output that adjusts in response to variations in the applied touch force. This study provides foundational data for the uniform fabrication of flexible piezoelectric energy harvesters and next-generation miniaturized electronic devices.
- [English]
- Design of Conductive Inks Containing Carbon Black and Silver Nanowires for Patternable Screen-Printing on Fabrics
- Seokhwan Kim, Geumseong Lee, Jinwoo Park, Dahye Shin, Ki-Il Park, Kyoung Jin Jung, Yuho Min
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):500-507. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00409

- 2,020 View
- 58 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study developed conductive inks composed of carbon black (CB) and silver nanowires (Ag NWs) for cost-effective screen-printing on fabrics. The Ag NW density within the CB matrix was precisely controlled, achieving tunable electrical conductivity with minimal Ag NW usage. The resulting inks were successfully patterned into shapes such as square grids and circles on textile surfaces, demonstrating excellent conductivity and fidelity. Adding 19.9 wt% Ag NWs reduced sheet resistance by ~92% compared to CB-only inks, highlighting the effectiveness and potential of this hybrid approach for cost-effective, high-performance textile-based electronics. The one-dimensional morphology of Ag NWs facilitated the formation of conductive percolation networks, creating efficient electron pathways within the CB matrix even at low loadings. This work advances the field of CB-based conductive inks and provides a scalable and practical method for producing functional, patterned electronic textiles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multifunctional Screen-Printed Conductive Inks: Design Principles, Performance Challenges, and Application Horizons
Nahid Islam, Manisha Das, Bashir Ahmed Johan, Syed Shaheen Shah, Atif Saeed Alzahrani, Md. Abdul Aziz
ACS Applied Electronic Materials.2025; 7(16): 7503. CrossRef
- Multifunctional Screen-Printed Conductive Inks: Design Principles, Performance Challenges, and Application Horizons
- [English]
- High-Temperature Steam Oxidation Behavior of Silicide- or Aluminide- Coated Mo and Nb Refractory Metals
- Woojin Lim, Je-Kyun Baek, JaeJoon Kim, Hyun Gil Kim, Ho Jin Ryu
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):546-555. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00381

- 1,521 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Refractory materials, such as molybdenum and niobium, are potential candidates for cladding material due to their high melting temperatures and desirable mechanical properties at higher temperatures than those of zirconium alloys. However, refractory materials have low resistance to oxidation at elevated temperatures. Therefore, this study examined silicide or aluminide surface coatings as protection against rapid oxidation of refractory materials at elevated temperatures for a potential accident-tolerant fuel cladding. Silicide or aluminide layers were formed on refractory metal substrates by using the pack cementation method. The steam oxidation behavior of both coated and uncoated samples was compared by thermogravimetric analysis at 1200°C. The weight changes of the coated samples were greatly reduced than those of uncoated samples. Microstructural analyses demonstrated that the silicide and aluminide layers were oxidized to form a protective surface oxide that prevented rapid oxidation of the refractory substrate at elevated temperatures.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of SiCf/SiC Composites with a BN Interphase Prepared by the Wet Method
- Kyung Ho Kim, Yoonsoo Han
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):530-536. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00339

- 996 View
- 27 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study presents a cost-effective wet chemical coating process for fabricating a boron nitride (BN) interphase on silicon carbide (SiC) fibers, increasing the oxidation resistance and performance of SiCf/SiC ceramic matrix composites. Using urea as a precursor, optimal nitriding conditions were determined by adjusting the composition, concentration, and immersion time. X-ray diffraction analysis revealed distinct BN phase formation at 1300°C and 1500°C, while a mixture of BN and B₂O₃ was observed at 1200°C. HF treatment improved coating uniformity by removing SiO₂ layers formed during the de-sizing process. Optimization of the boric acid-to-urea molar ratio resulted in a uniform, 130-nm-thick BN layer. This study demonstrates that the wet coating process offers a viable and economical alternative to chemical vapor deposition for fabricating high-performance BN interphases in SiCf/SiC composites that are suitable for high-temperature applications.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and High-Temperature Performance Evaluation of Light-Weight Insulation Materials and Coatings for Reusable Thermal Protection Systems
- Min-Soo Nam, Jong-Il Kim, Jaesung Shin, Hyeonjun Kim, Bum-Seok Oh, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):521-529. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00318

- 1,574 View
- 55 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Light-weight ceramic insulation materials and high-emissivity coatings were fabricated for reusable thermal protection systems (TPS). Alumina-silica fibers and boric acid were used to fabricate the insulation, which was heat treated at 1250 °C. High-emissivity coating of borosilicate glass modified with TaSi2, MoSi2, and SiB6 was applied via dip-and-spray coating methods and heat-treated at 1100°C. Testing in a high-velocity oxygen fuel environment at temperatures over 1100 °C for 120 seconds showed that the rigid structures withstood the flame robustly. The coating effectively infiltrated into the fibers, confirmed by scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction analyses. Although some oxidation of TaSi2 occurred, thereby increasing the Ta2O5 and SiO2 phases, no significant phase changes or performance degradation were observed. These results demonstrate the potential of these materials for reusable TPS applications in extreme thermal environments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Durability Assessment of Tile-Type Reusable Thermal Protection Materials
Minjeong Kim, Seong Man Choi
Materials.2026; 19(2): 303. CrossRef
- Durability Assessment of Tile-Type Reusable Thermal Protection Materials
- [English]
- Epsilon Iron Oxide (ε-Fe2O3) as an Electromagnetic Functional Material: Properties, Synthesis, and Applications
- Ji Hyeong Jeong, Hwan Hee Kim, Jung-Goo Lee, Youn-Kyoung Baek
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):465-479. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00290

- 3,589 View
- 93 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Iron oxide (ε-Fe₂O₃) is emerging as a promising electromagnetic material due to its unique magnetic and electronic properties. This review focuses on the intrinsic properties of ε-Fe₂O₃, particularly its high coercivity, comparable to that of rare-earth magnets, which is attributed to its significant magnetic anisotropy. These properties render it highly suitable for applications in millimeter wave absorption and high-density magnetic storage media. Furthermore, its semiconducting behavior offers potential applications in photocatalytic hydrogen production. The review also explores various synthesis methods for fabricating ε-Fe₂O₃ as nanoparticles or thin films, emphasizing the optimization of purity and stability. By exploring and harnessing the properties of ε-Fe₂O₃, this study aims to contribute to the advancement of next-generation electromagnetic materials with potential applications in 6G wireless telecommunications, spintronics, high-density data storage, and energy technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Review of GPR Data Analysis for Bridge Deck Evaluation: From Conventional Methods to Emerging Artificial Intelligence Approaches
Babak Enami Alamdari, Yu Tang, Danilo Erricolo, Lesley H. Sneed
Journal of Nondestructive Evaluation.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemical Pressure Induced Strain Control of Magnetic Anisotropy in the Simple Perovskite ϵ-Fe2O3
Subir Roy, Gurleen K. Uppal, Alberto Acosta, Rachel Nickel, Charles A. Roberts, Johan van Lierop
Nano Letters.2026; 26(1): 34. CrossRef - Superparamagnetism of Baked Clays Containing Polymorphs of Iron Oxides: Experimental Study and Theoretical Modeling
Petr Kharitonskii, Andrei Krasilin, Nadezhda Belskaya, Svetlana Yanson, Nikita Bobrov, Andrey Ralin, Kamil Gareev, Nikita Zolotov, Dmitry Zaytsev, Elena Sergienko
Magnetochemistry.2025; 11(12): 103. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Review of GPR Data Analysis for Bridge Deck Evaluation: From Conventional Methods to Emerging Artificial Intelligence Approaches
- [Korean]
- Effect of TiO2 Content on High-Temperature Degradation Behavior of Nd2O3 and Yb2O3 Doped YSZ Composite Materials
- Gye-Won Lee, Seonung Choi, Tae-jun Park, Jong-il Kim, In-hwan Lee, Yoon-seok Oh
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):431-436. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00269

- 683 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hot section components of gas turbines are exposed to a high operating temperature environment. To protect these components, thermal barrier coatings (TBC) are applied to their surfaces. Yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ), which is widely used as a TBC material, faces limitations at temperatures above 1200℃. To mitigate these issues, research has focused on adding lanthanide rare earth oxides and tetravalent oxides to prevent the phase-transformation of the monoclinic phase in zirconia. This study investigated the effects of varying TiO2 content in Nd2O3 and Yb2O3 co-doped YSZ composites. Increasing TiO2 content effectively suppressed formation of the monoclinic phase and increased the thermal degradation resistance compared to YSZ in environments over 1200℃. These findings will aid in developing more thermally stable and efficient TBC materials for application in high-temperature environments.
- [Korean]
- Inter-laminar Strength of NITE-SiC/SiC Composites With Various Fiber Reinforcing Architecture
- Jong-il Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):437-444. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00248
- 920 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
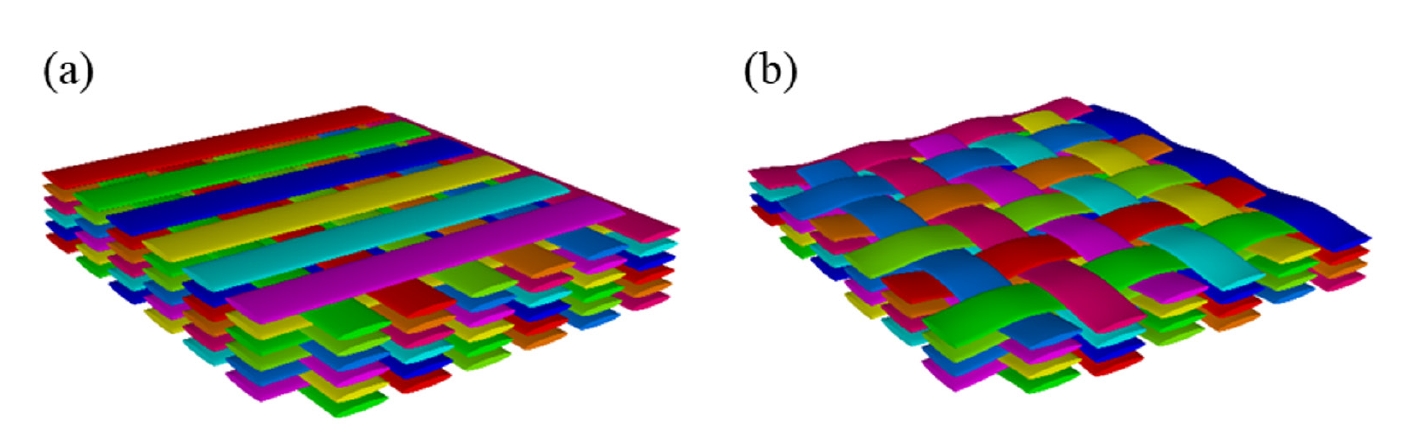
PDF - The mechanical performance of SiC/SiC composites is significantly influenced by the architecture of fiber reinforcement. Among the various fabrication methods, the nano-powder infiltration transition/eutectic (NITE) process is a promising technique that is capable of achieving a dense and stoichiometric SiC matrix. The reinforcement architecture, such as cross-ply (CP) or woven prepreg (WP), is determined during the preform stage of the NITE process, which is crucial in determining the mechanical properties of SiC/SiC composites. In this study, the tensile test and double notch shear (DNS) test were conducted using NITE-SiC/SiC composites to investigate the effect of the fiber reinforcing architecture on the fracture mechanism of SiC/SiC composites. The tensile strength and maximum shear strength of both CP and WP specimens were nearly identical. However, other mechanical properties, particularly those of CP specimens, exhibited significant variability. A comparison of fracture surfaces and load-displacement curve analyses from the DNS tests revealed that the cross points of the longitudinal or transverse fibers act as obstacles to both deformation and crack propagation. These obstacles were found to be more densely distributed in WP specimens than in CP specimens. The variability observed in the mechanical properties of CP specimens is likely due to size effects caused by the sparser distribution of these obstacles compared to the WP specimens.
- [English]
- Machine Learning Modeling of the Mechanical Properties of Al2024-B4C Composites
- Maurya A. K., Narayana P. L., Wang X.-S., Reddy N. S.
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):382-389. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00234
- 1,605 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
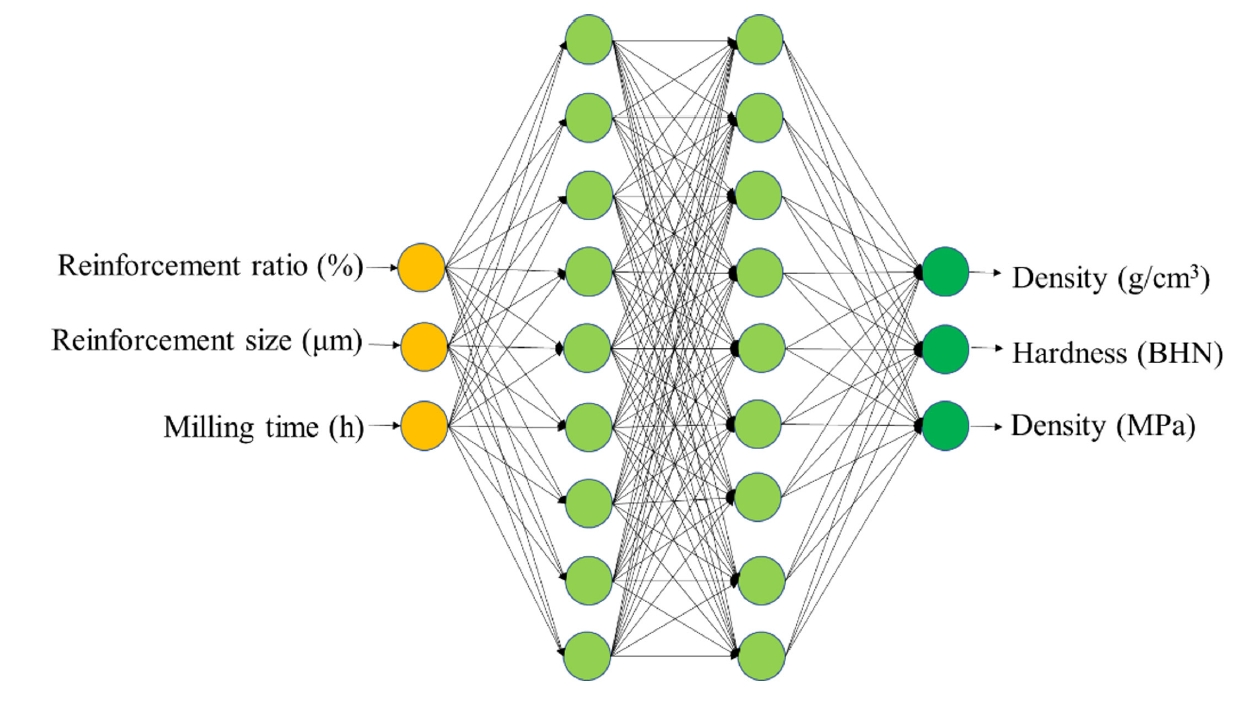
PDF - Aluminum-based composites are in high demand in industrial fields due to their light weight, high electrical conductivity, and corrosion resistance. Due to its unique advantages for composite fabrication, powder metallurgy is a crucial player in meeting this demand. However, the size and weight fraction of the reinforcement significantly influence the components' quality and performance. Understanding the correlation of these variables is crucial for building high-quality components. This study, therefore, investigated the correlations among various parameters—namely, milling time, reinforcement ratio, and size—that affect the composite’s physical and mechanical properties. An artificial neural network model was developed and showed the ability to correlate the processing parameters with the density, hardness, and tensile strength of Al2024-B4C composites. The predicted index of relative importance suggests that the milling time has the most substantial effect on fabricated components. This practical insight can be directly applied in the fabrication of high-quality Al2024-B4C composites.
- [Korean]
- Characterization of Compacted and Pressureless Sintered Parts for Molybdenum Oxide Powder according to Hydrogen Reduction Temperature
- Jong Hoon Lee, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):336-341. Published online August 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00241

- 1,269 View
- 16 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Molybdenum, valued for its high melting point and exceptional physical and chemical properties, is studied in diverse fields such as electronics, petrochemicals, and aviation. Among molybdenum oxides, molybdenum dioxide stands out for its higher electrical conductivity than other transition metal oxides due to its structural characteristics, exhibiting metallic properties. It is applied as pellets to gas sensors, semiconductors, and secondary batteries for its properties. Thus, research on molybdenum dioxide compaction and pressureless sintering is necessary, yet research on pressureless sintering is currently insufficient. This study synthesized MoO₃ powder via solution combustion synthesis and reduced it using the 3% hydrogen/argon gas mixture to investigate the effect of reduction temperature on the powder. Additionally, the reduced powder was compacted and subjected to pressureless sintering with temperature as a variable. The density and the microstructure of brown parts were analyzed and discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High-sensitivity optical fiber hydrogen sensing with MoO3/PANI/Pd nanocomposite
Mohammed M. Alkhabet, Saad H. Girei, Ammar H. Farhan, Fatimah F. Hashim, Jaafar A. Jaafar, Husam K. Salih, Manar F. Abbood, Mohd H. Yaacob
Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing.2025; 200: 110021. CrossRef
- High-sensitivity optical fiber hydrogen sensing with MoO3/PANI/Pd nanocomposite
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of 3D Aligned h-BN based Polymer Composites with Enhanced Mechanical Properties for Battery Housing
- Kiho Song, Hyunseung Song, Sang In Lee, Changui Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):329-335. Published online August 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00220
- 1,410 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
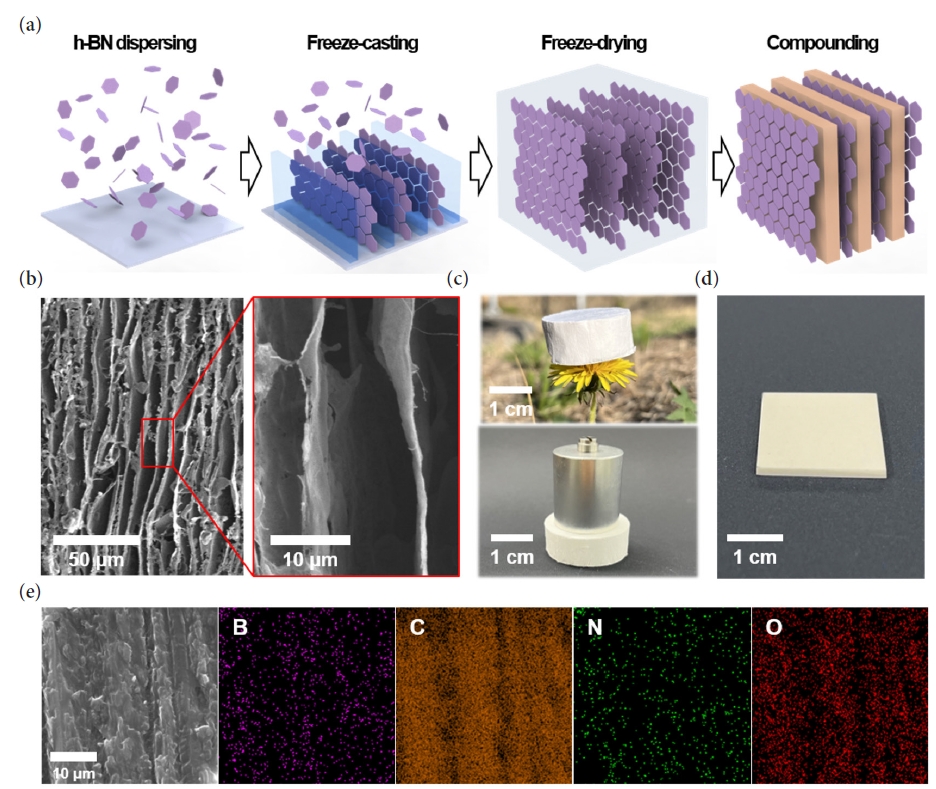
Supplementary Material - As the demand for electric vehicles increases, the stability of batteries has become one of the most significant issues. The battery housing, which protects the battery from external stimuli such as vibration, shock, and heat, is the crucial element in resolving safety problems. Conventional metal battery housings are being converted into polymer composites due to their lightweight and improved corrosion resistance to moisture. The transition to polymer composites requires high mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and thermal stability. In this paper, we proposes a high-strength nanocomposite made by infiltrating epoxy into a 3D aligned h-BN structure. The developed 3D aligned h-BN/epoxy composite not only exhibits a high compressive strength (108 MPa) but also demonstrates excellent electrical insulation and thermal stability, with a stable electrical resistivity at 200 °C and a low thermal expansion coefficient (11.46ⅹppm/℃), respectively.
- [English]
- A Review of Inorganic Solid Electrolytes for All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries: Challenges and Progress
- Seul Ki Choi, Jaehun Han, Gi Jeong Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Jaewon Choi, MinHo Yang
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):293-301. Published online August 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00206
- 11,870 View
- 289 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
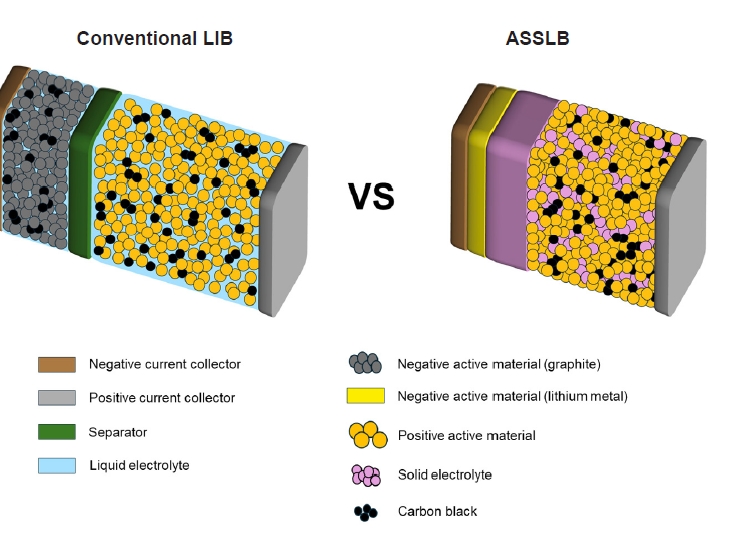
PDF - All-solid-state lithium batteries (ASSLBs) are receiving attention as a prospective next-generation secondary battery technology that can reduce the risk of commercial lithium-ion batteries by replacing flammable organic liquid electrolytes with non-flammable solid electrolytes. The practical application of ASSLBs requires developing robust solid electrolytes that possess ionic conductivity at room temperature on a par with that of organic liquids. These solid electrolytes must also be thermally and chemically stable, as well as compatible with electrode materials. Inorganic solid electrolytes, including oxide and sulfide-based compounds, are being studied as promising future candidates for ASSLBs due to their higher ionic conductivity and thermal stability than polymer electrolytes. Here, we present the challenges currently facing the development of oxide and sulfide-based solid electrolytes, as well as the research efforts underway aiming to resolve these challenges.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A facile synthesis of bulk LiPON in solution for solid-state electrolytes
Osma J. Gomez, Adam Antar, Alex T. Hall, Leopoldo Tapia-Aracayo, Joshua Seo, Nam Kim, Zihan Sun, Ryan Lim, Fu Chen, Yue Li, John Cumings, Gary Rubloff, Sang Bok Lee, David Stewart, Yang Wang
Journal of Materials Chemistry A.2025; 13(34): 28368. CrossRef - Uniform lithium deposition using Cu teepee structures for anode-free lithium metal batteries
Seo Yun Jung, Jaehun Han, Seul Ki Choi, Se Youn Cho, Jong Ho Won, Jaewon Choi, Minho Yang
Chemical Engineering Journal.2025; 522: 167302. CrossRef - Garnet-type LLZO electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries: Interfaces, conductivity, in-situ processing, and industrial prospects
Kaleab Habtamu Ayalew, Nithyadharseni Palaniyandy, Mkhulu K. Mathe, Phumlani F. Msomi
Chemical Engineering Journal.2025; 524: 168098. CrossRef
- A facile synthesis of bulk LiPON in solution for solid-state electrolytes
- [English]
- Trends in Materials Modeling and Computation for Metal Additive Manufacturing
- Seoyeon Jeon, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):213-219. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00150
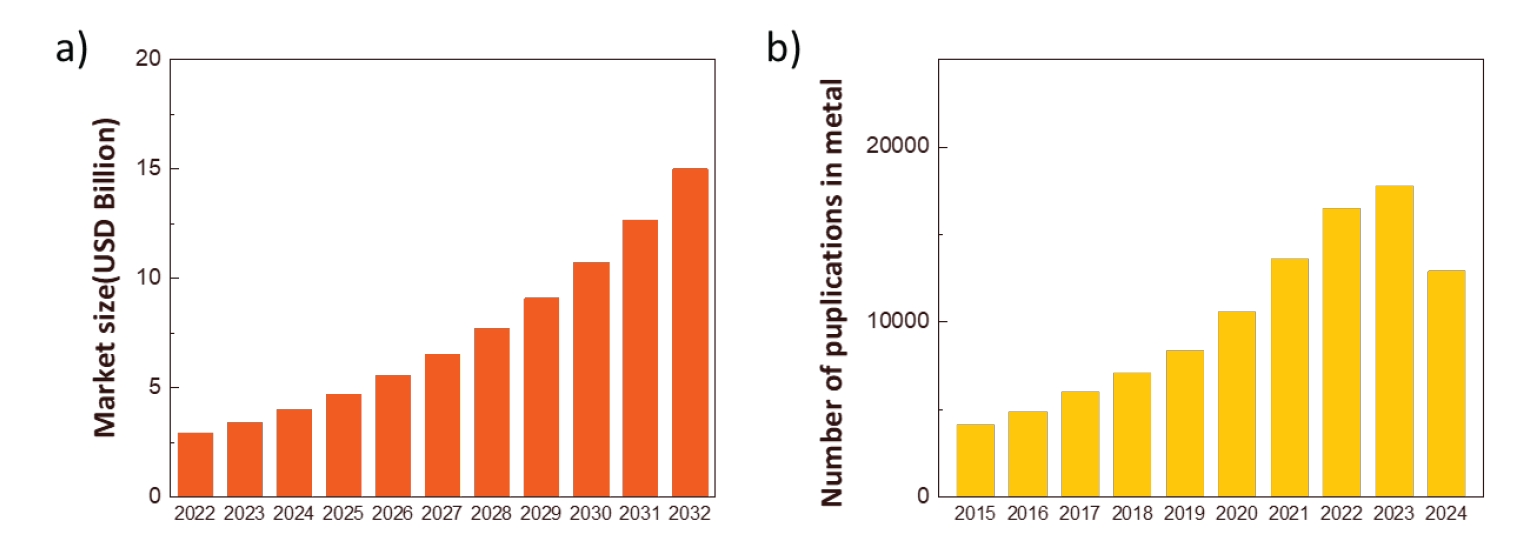
- 2,710 View
- 74 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Additive Manufacturing (AM) is a process that fabricates products by manufacturing materials according to a three-dimensional model. It has recently gained attention due to its environmental advantages, including reduced energy consumption and high material utilization rates. However, controlling defects such as melting issues and residual stress, which can occur during metal additive manufacturing, poses a challenge. The trial-and-error verification of these defects is both time-consuming and costly. Consequently, efforts have been made to develop phenomenological models that understand the influence of process variables on defects, and mechanical/electrical/thermal properties of geometrically complex products. This paper introduces modeling techniques that can simulate the powder additive manufacturing process. The focus is on representative metal additive manufacturing processes such as Powder Bed Fusion (PBF), Direct Energy Deposition (DED), and Binder Jetting (BJ) method. To calculate thermal-stress history and the resulting deformations, modeling techniques based on Finite Element Method (FEM) are generally utilized. For simulating the movements and packing behavior of powders during powder classification, modeling techniques based on Discrete Element Method (DEM) are employed. Additionally, to simulate sintering and microstructural changes, techniques such as Monte Carlo (MC), Molecular Dynamics (MD), and Phase Field Modeling (PFM) are predominantly used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
Yeon-Joo Lee, Pil-Ryung Cha, Hyoung-Seop Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(1): 144. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef
- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
- [English]
- Investigation of the Thermal-to-Electrical Properties of Transition Metal-Sb Alloys Synthesized for Thermoelectric Applications
- Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Sooho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Kwi-Il Park, Kyung Tae Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):236-242. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00031
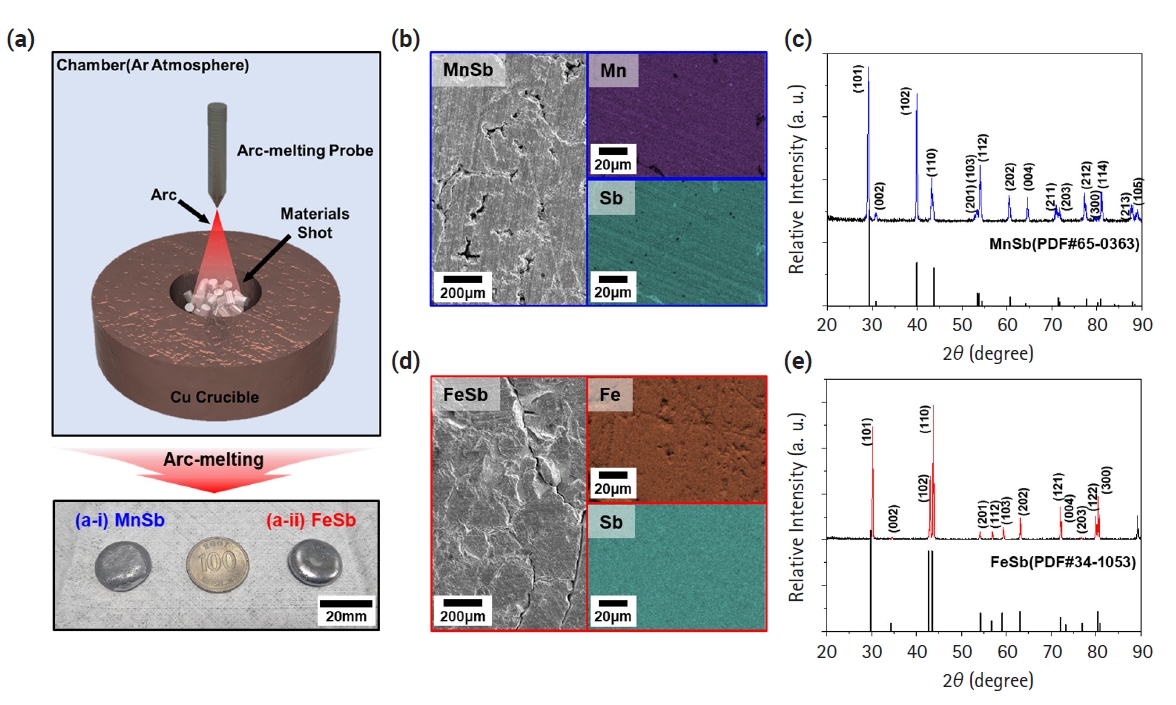
- 1,839 View
- 44 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The development of thermoelectric (TE) materials to replace Bi2Te3 alloys is emerging as a hot issue with the potential for wider practical applications. In particular, layered Zintl-phase materials, which can appropriately control carrier and phonon transport behaviors, are being considered as promising candidates. However, limited data have been reported on the thermoelectric properties of metal-Sb materials that can be transformed into layered materials through the insertion of cations. In this study, we synthesized FeSb and MnSb, which are used as base materials for advanced thermoelectric materials. They were confirmed as single-phase materials by analyzing X-ray diffraction patterns. Based on electrical conductivity, the Seebeck coefficient, and thermal conductivity of both materials characterized as a function of temperature, the zT values of MnSb and FeSb were calculated to be 0.00119 and 0.00026, respectively. These properties provide a fundamental data for developing layered Zintl-phase materials with alkali/alkaline earth metal insertions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Jihun Yu, Kyung Tae Kim
Materials Letters.2025; 381: 137796. CrossRef - Highly deformable and hierarchical 3D composite sponge for versatile thermoelectric energy conversion
Jong Min Park, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Kwi-Il Park
Applied Surface Science.2025; 692: 162730. CrossRef
- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
- [English]
- Bandgap Tuning and Quenching Effects of In(Zn)P@ZnSe@ZnS Quantum Dots
- Sang Yeon Lee, Su Hyun Park, Gyungsu Byun, Chang-Yeoul Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):226-235. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00003
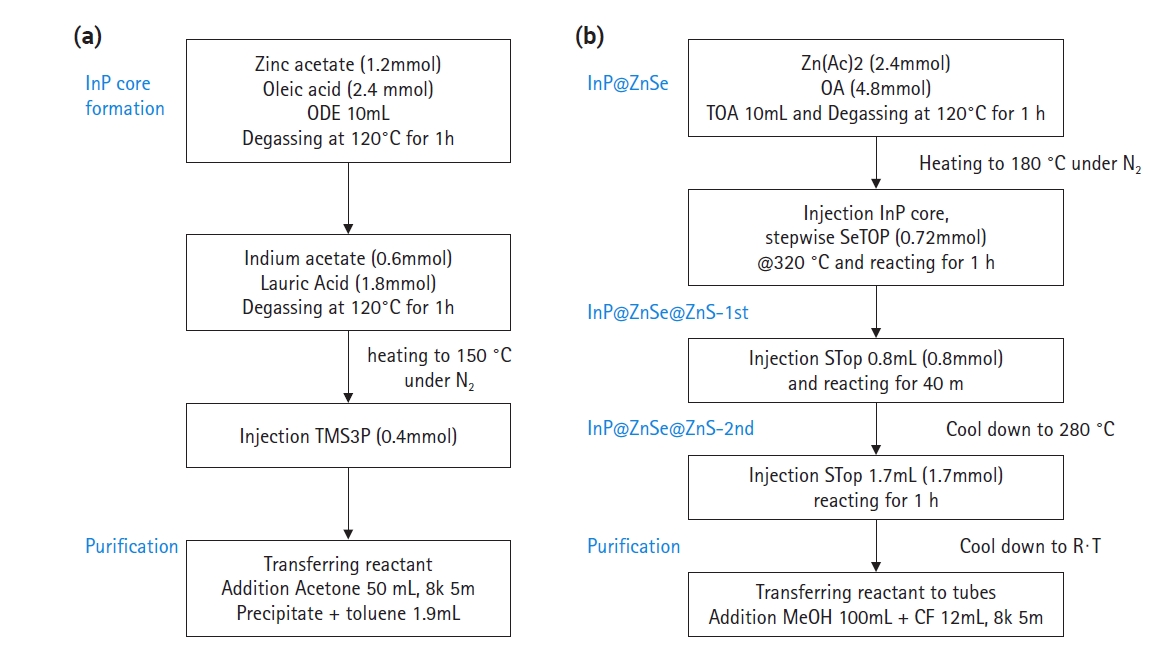
- 3,084 View
- 45 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - InP quantum dot (QDs) have attracted researchers’ interest due to their applicability in quantum dot light-emitting displays (QLED) or biomarkers for detecting cancers or viruses. The surface or interface control of InP QD core/shell has substantially increased quantum efficiency, with a quantum yield of 100% reached by introducing HF to inhibit oxide generation. In this study, we focused on the control of bandgap energy of quantum dots by changing the Zn/(In+Zn) ratio in the In(Zn)P core. Zinc incorporation can change the photoluminescent light colors of green, yellow, orange, and red. Diluting a solution of as-synthesized QDs by more than 100 times did not show any quenching effects by the Förster resonance energy transfer phenomenon between neighboring QDs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing luminescence of QD thin films, polymer composite films, and LED devices by nanostructures
Hongcheng Yang, Junjie Hao, Mingyu Sun, Yujie Song, Kai Wang, Yujie Song, Xiao Wei Sun, Wenda Zhang
The Innovation.2026; 7(2): 101121. CrossRef
- Enhancing luminescence of QD thin films, polymer composite films, and LED devices by nanostructures
- [English]
- The Effect of TiO2 Addition on Low-temperature Sintering Behaviors in a SnO2-CoO-CuO System
- Jae-Sang Lee, Kyung-Sik Oh, Yeong-Kyeun Paek
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):146-151. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00024
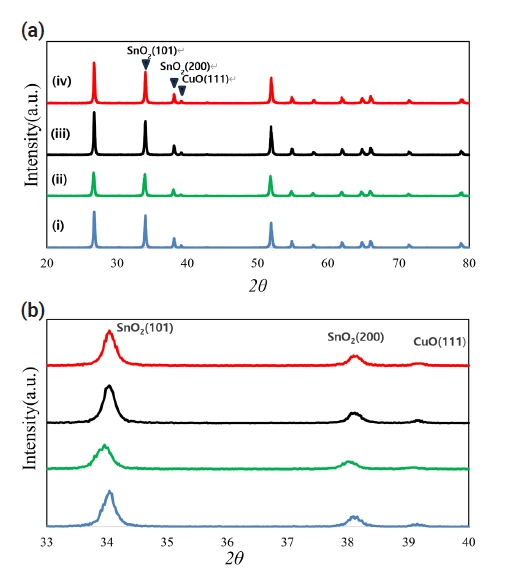
- 1,211 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pure SnO2 has proven very difficult to densify. This poor densification can be useful for the fabrication of SnO2 with a porous microstructure, which is used in electronic devices such as gas sensors. Most electronic devices based on SnO2 have a porous microstructure, with a porosity of > 40%. In pure SnO2, a high sintering temperature of approximately 1300C is required to obtain > 40% porosity. In an attempt to reduce the required sintering temperature, the present study investigated the low-temperature sinterability of a current system. With the addition of TiO2, the compositions of the samples were Sn1-xTixO2-CoO(0.3wt%)-CuO(2wt%) in the range of x ≤ 0.04. Compared to the samples without added TiO2, densification was shown to be improved when the samples were sintered at 950C. The dominant mass transport mechanism appears to be grain-boundary diffusion during heat treatment at 950C.
- [Korean]
- Inorganic Compound and Cycloserine Composite Particles for Improved Stability
- Dongwon Kim, Heeseo Kim, Hongjun Yoon, Hyuk Jun Cho, Sung Giu Jin
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):126-131. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00002
- 6,558 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
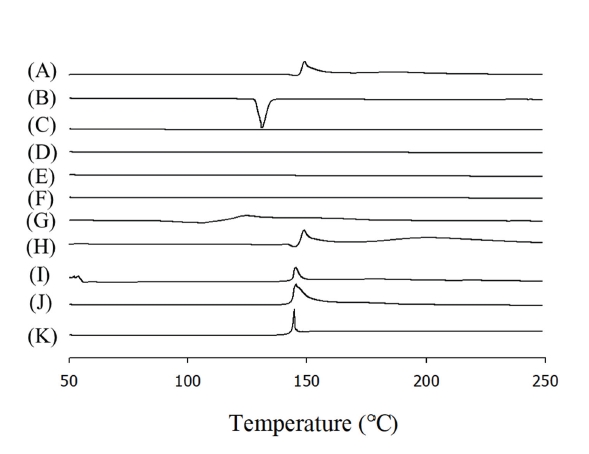
PDF - The aim of this study was to improve the chemical stability of cycloserine containing organic and inorganic compounds. Composite particles were manufactured with a 1:1 weight ratio of organic/inorganic compounds and cycloserine. The influence of organic/inorganic compounds on the stability of cycloserine was investigated under accelerated stress conditions at 60°C/75% RH for 24 hours. In addition, the properties of the composite particles were evaluated using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and the dissolution of the drug was assessed by preparing it as a hard capsule. Among the organic and inorganic compounds investigated, calcium hydroxide most improved the stability of cycloserine under accelerated stress conditions (53.3 ± 2.2% vs 1.7 ± 0.2%). DSC results confirmed the compatibility between calcium hydroxide and the cycloserine, and SEM results confirmed that it was evenly distributed around the cycloserine. Calcium hydroxide also showed more than 90% cycloserine dissolution within 15 minutes. Therefore, the calcium hydroxide and cycloserine composite particles may be candidates for cycloserine oral pharmaceuticals with enhanced drug stability.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Bi2Te2.5Se0.5 by Combining Oxide-reduction and Compressive-forming Process and Its Thermoelectric Properties
- Young Soo Lim, Gil-Geun Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):50-56. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.50
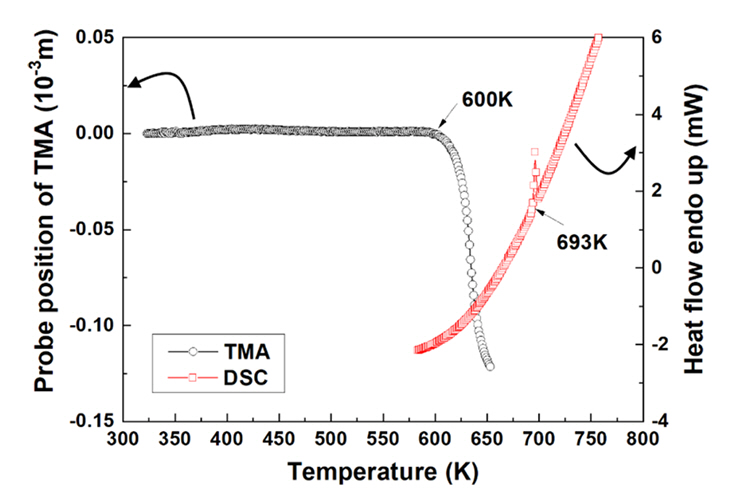
- 1,100 View
- 21 Download
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Ti-Mo Core-shell Powder and Sintering Properties for Application as a Sputtering Target
- Won Hee Lee, Chun Woong Park, Heeyeon Kim, Yuncheol Ha, Jongmin Byun, Young Do Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):43-49. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.43
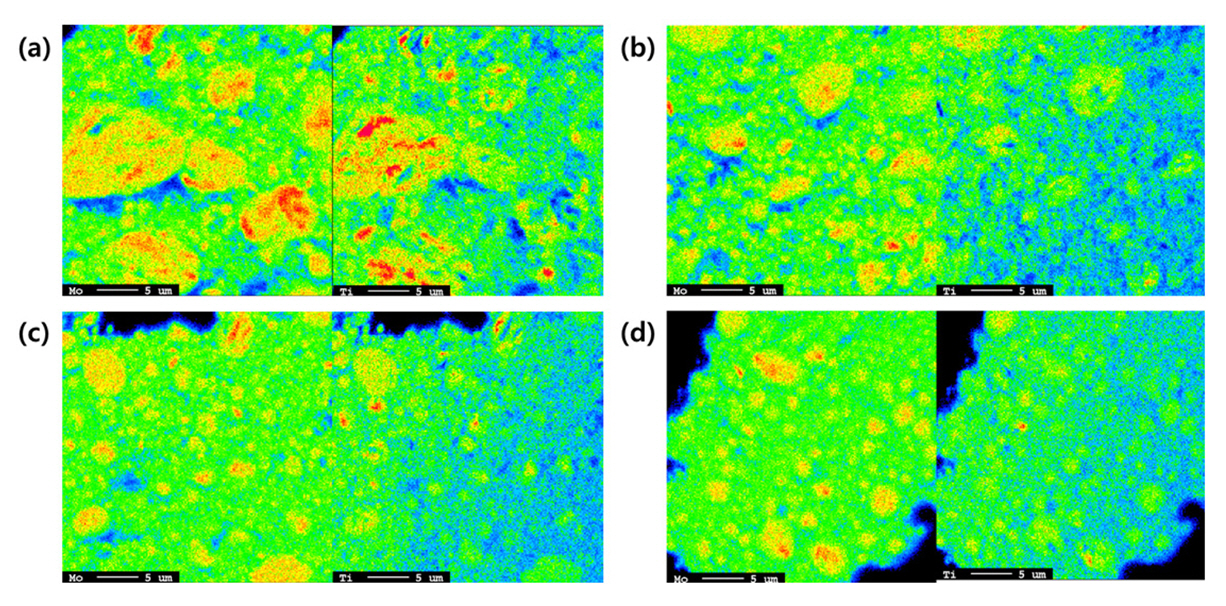
- 1,550 View
- 36 Download
- [Korean]
- Effect of Abnormal Grain Growth on Ionic Conductivity in LATP
- Hyungik Choi, Yoonsoo Han
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):23-29. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.23
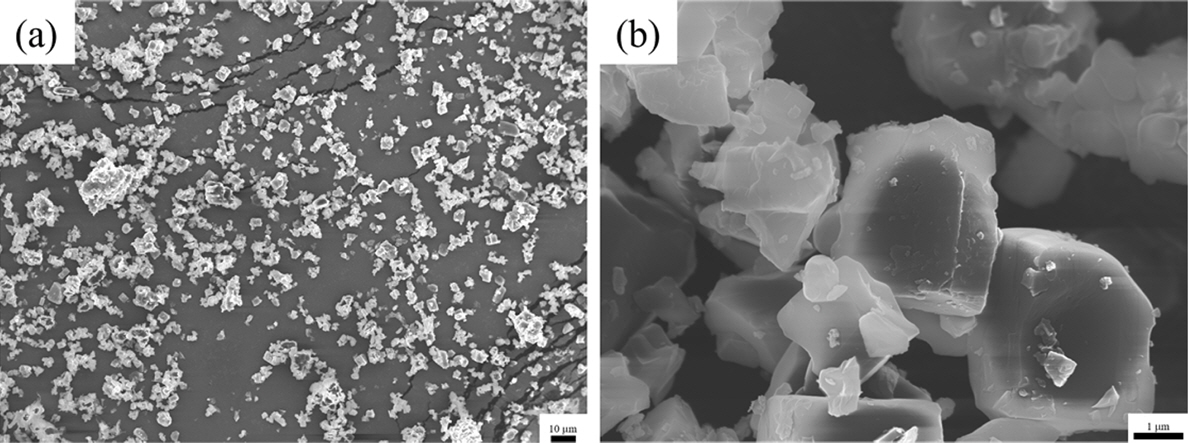
- 3,007 View
- 66 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Temperature-dependent microstructural evolution in a compositionally complex solid electrolyte: The role of a grain boundary transition
Shu-Ting Ko, Chaojie Du, Huiming Guo, Hasti Vahidi, Jenna L. Wardini, Tom Lee, Yi Liu, Jingjing Yang, Francisco Guzman, Timothy J. Rupert, William J. Bowman, Shen J. Dillon, Xiaoqing Pan, Jian Luo
Journal of Advanced Ceramics.2025; 14(3): 9221047. CrossRef - Effect of bimodal particle size distribution on Li1.5Al0.5Ti1.5(PO4)3 solid electrolytes: Microstructures and electrochemical properties
Gi Jeong Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Seul Ki Choi, Jong Won Bae, Kun-Jae Lee, Minho Yang
Powder Technology.2025; 466: 121407. CrossRef
- Temperature-dependent microstructural evolution in a compositionally complex solid electrolyte: The role of a grain boundary transition
- [English]
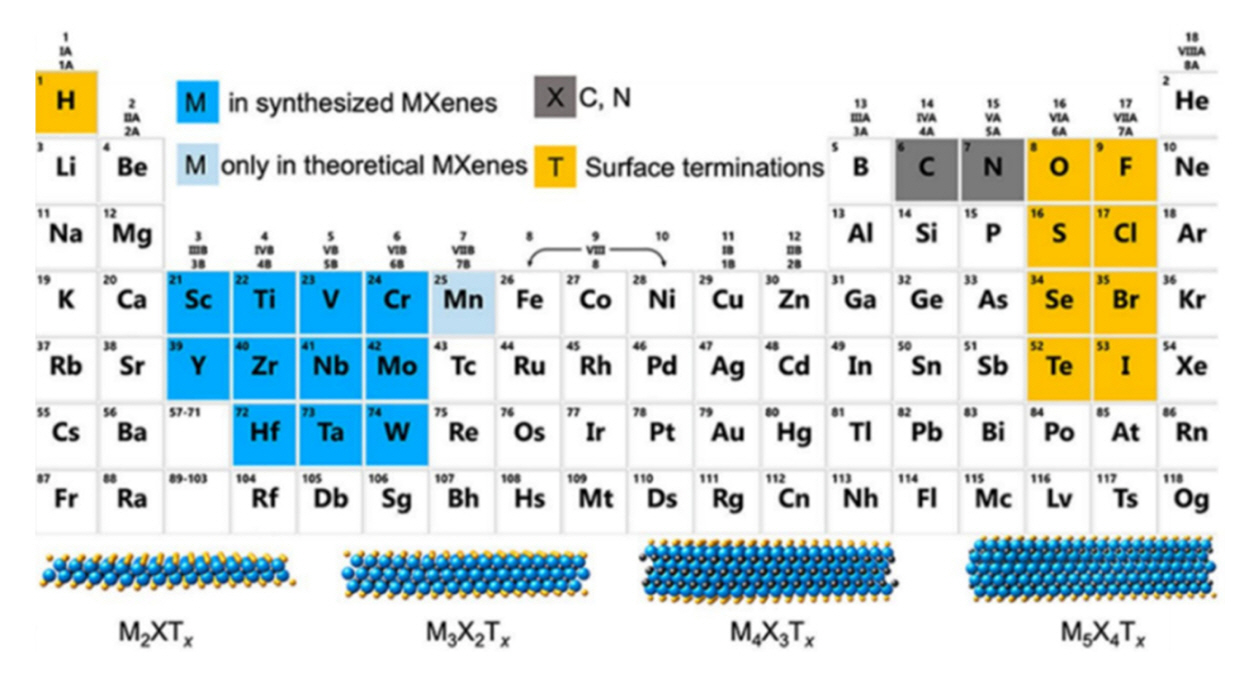
- Research Trends in Electromagnetic Shielding using MXene-based Composite Materials
- Siyeon Kim, Jongmin Byun
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):57-76. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.57
- 8,369 View
- 163 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Recent advancements in electronic devices and wireless communication technologies, particularly the rise of 5G, have raised concerns about the escalating electromagnetic pollution and its potential adverse impacts on human health and electronics. As a result, the demand for effective electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials has grown significantly. Traditional materials face limitations in providing optimal solutions owing to inadequacy and low performance due to small thickness. MXene-based composite materials have emerged as promising candidates in this context owing to their exceptional electrical properties, high conductivity, and superior EMI shielding efficiency across a broad frequency range. This review examines the recent developments and advantages of MXene-based composite materials in EMI shielding applications, emphasizing their potential to address the challenges posed by electromagnetic pollution and to foster advancements in modern electronics systems and vital technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Designing dual phase hexaferrite (SrFe12O19) – Perovskite (La0.5Nd0.5FeO3) composites for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption and band gap modulation
Pramod D. Mhase, Varsha C. Pujari, Santosh S. Jadhav, Abdullah G. Al-Sehemi, Sarah Alsobaie, Sunil M. Patange
Composites Communications.2025; 54: 102284. CrossRef - Microstructure tailoring of Nb-based MAX phase by low temperature synthesis with layer-structured Nb2C powder and molten salt method
Chaehyun Lim, Wonjune Choi, Jongmin Byun
Materials Characterization.2025; 225: 115106. CrossRef - Fabrication of MOF@MXene composites via surface modification of MXene under acidic conditions
Ji-Haeng Jeong, Woong-Ryeol Yu
Functional Composites and Structures.2025; 7(2): 025006. CrossRef - V2CTx MXene@ZIF-8 composite as an efficient adsorbent for Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution
Sarina Khojasteh Fard, Golshan Mazloom, Manoochehr Sobhani, Mohsen Tamtaji
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering.2025; 13(6): 120099. CrossRef
- Designing dual phase hexaferrite (SrFe12O19) – Perovskite (La0.5Nd0.5FeO3) composites for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption and band gap modulation
- [Korean]
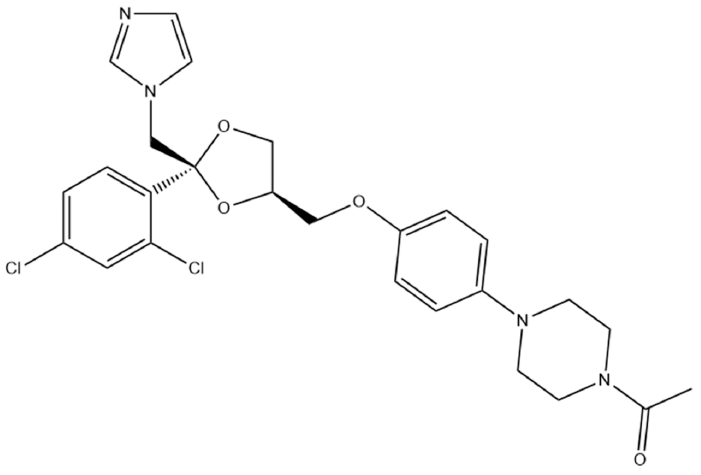
- Preparation and Evaluation of Ketoconazole-loaded Solid-SNEDDS (Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System) using Various Solidification Carriers
- Da Young Song, Kyeong Soo Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):493-501. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.493
- 1,009 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study aimed to develop a solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (solid-SNEDDS) to enhance the formulation of ketoconazole (KTZ), a BCS Class II drug with poor solubility. Ketoconazole, which is insoluble above pH 3, requires solubilization for effective delivery. This SNEDDS comprises oil, surfactant, and co-surfactant, which spontaneously emulsify in the gastrointestinal tract environment to form nanoemulsions with droplet sizes less than 100 nm. The optimal SNE-vehicle composition of oleic acid, TPGS, and PEG 400 at a 10:80:10 weight ratio was determined based on the smallest droplet size achieved. This composition was used to prepare liquid SNEDDS containing ketoconazole. The droplet size and polydispersity index (PDI) of the resulting liquid SNEDDS were analyzed. Subsequently, solid-SNEDDS was fabricated using a spray-drying method with solidifying carriers such as silicon dioxide, crospovidone, and magnesium alumetasilicate. The physicochemical properties of the solid-SNEDDS were characterized by scanning electron microscopy and powder X-ray diffraction, and its solubility, droplet size, and PDI were evaluated. In particular, the solid-SNEDDS containing ketoconazole and crospovidone in a 2:1 weight ratio exhibited significantly enhanced solubility, highlighting its potential for improved medication adherence and dissolution rates.
- [Korean]
- Combinatorial Experiment for Al-6061 and Al-12Si alloy Based on Directed Energy Deposition (DED) Process
- Seoyeon Jeon, Suwon Park, Yongwook Song, Jiwon Park, Hyunyoung Park, Boram Lee, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):463-469. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.463

- 2,079 View
- 45 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Aluminum alloys, known for their high strength-to-weight ratios and impressive electrical and thermal conductivities, are extensively used in numerous engineering sectors, such as aerospace, automotive, and construction. Recently, significant efforts have been made to develop novel aluminum alloys specifically tailored for additive manufacturing. These new alloys aim to provide an optimal balance between mechanical properties and thermal/ electrical conductivities. In this study, nine combinatorial samples with various alloy compositions were fabricated using direct energy deposition (DED) additive manufacturing by adjusting the feeding speeds of Al6061 alloy and Al-12Si alloy powders. The effects of the alloying elements on the microstructure, electrical conductivity, and hardness were investigated. Generally, as the Si and Cu contents decreased, electrical conductivity increased and hardness decreased, exhibiting trade-off characteristics. However, electrical conductivity and hardness showed an optimal combination when the Si content was adjusted to below 4.5 wt%, which can sufficiently suppress the grain boundary segregation of the α- Si precipitates, and the Cu content was controlled to induce the formation of Al2Cu precipitates.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Aluminum Alloys for Additive Manufacturing Using Machine Learning
Sungbin An, Juyeon Han, Seoyeon Jeon, Dowon Kim, Jae Bok Seol, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 202. CrossRef - Trends in Materials Modeling and Computation for Metal Additive Manufacturing
Seoyeon Jeon, Hyunjoo Choi
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(3): 213. CrossRef - The Challenges and Advances in Recycling/Re-Using Powder for Metal 3D Printing: A Comprehensive Review
Alex Lanzutti, Elia Marin
Metals.2024; 14(8): 886. CrossRef - Microstructural Effects on the Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Fabricated by Direct Energy Deposition
Juho Kim, Seoyeon Jeon, Hwajin Park, Taeyoel Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(4): 302. CrossRef
- Development of Aluminum Alloys for Additive Manufacturing Using Machine Learning
- [Korean]
- Tribological Behavior Analysis of WC-Ni-Cr + Cr3C2 and WC-Ni-Cr + YSZ Coatings Sprayed by HVOF
- Tae-Jun Park, Gye-Won Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(5):415-423. Published online October 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.5.415

- 1,000 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF With the increasing attention to environmental pollution caused by particulate matter globally, the automotive industry has also become increasingly interested in particulate matter, especially particulate matter generated by automobile brake systems. Here, we designed a coating composition and analyzed its mechanical properties to reduce particulate matter generated by brake systems during braking of vehicles. We designed a composition to check the mechanical properties change by adding Cr3C2 and YSZ to the WC-Ni-Cr composite composition. Based on the designed composition, coating samples were manufactured, and the coating properties were analyzed by Vickers hardness and ball-on-disk tests. As a result of the experiments, we found that the hardness and friction coefficient of the coating increased as the amount of Cr3C2 added decreased. Furthermore, we found that the hardness of the coating layer decreased when YSZ was added at 20vol%, but the friction coefficient was higher than the composition with Cr3C2 addition.
- [Korean]
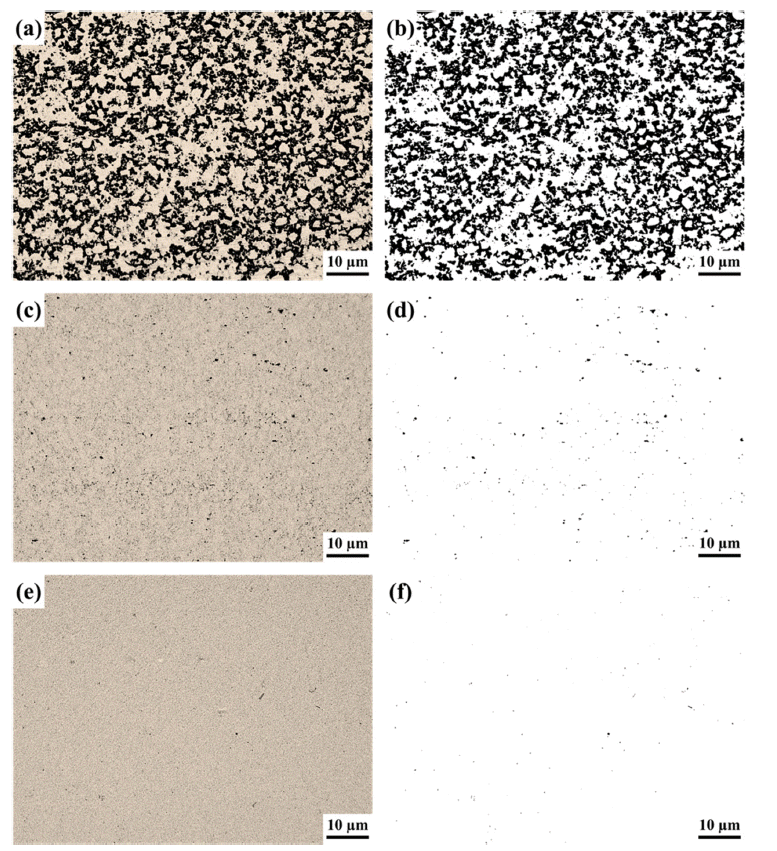
- Phase Formation and Mechanical Property of YSZ‒30 vol.% WC Composite Ceramics Fabricated by Hot Pressing
- Jin-Kwon Kim, Jae-Hyeong Choi, Nahm Sahn, Sung-Soo Ryu, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(5):409-414. Published online October 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.5.409
- 608 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF YSZ (Y2O3-stabilized zirconia)-based ceramics have excellent mechanical properties, such as high strength and wear resistance. In the application, YSZ is utilized in the bead mill, a fine-grinding process. YSZ-based parts, such as the rotor and pin, can be easily damaged by continuous application with high rpm in the bead mill process. In that case, adding WC particles improves the tribological and mechanical properties. YSZ-30 vol.% WC composite ceramics are manufactured via hot pressing under different pressures (10/30/60 MPa). The hot-pressed composite ceramics measure the physical properties, such as porosity and bulk density values. In addition, the phase formation of these composite ceramics is analyzed and discussed with those of physical properties. For the increased applied pressure of hot pressing, the tetragonality of YSZ and the crystallinity of WC are enhanced. The mechanical properties indicate an improved tendency with the increase in the applied pressure of hot pressing.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Carbon Coated Nickel Cobalt Sulfide Yolk-shell Microsphere and Their Application as Anode Materials for Sodium Ion Batteries
- Hyo Yeong Seo, Gi Dae Park
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(5):387-393. Published online October 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.5.387

- 802 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Transition metal chalcogenides are promising cathode materials for next-generation battery systems, particularly sodium-ion batteries. Ni3Co6S8-pitch-derived carbon composite microspheres with a yolk-shell structure (Ni3Co6S8@C-YS) were synthesized through a three-step process: spray pyrolysis, pitch coating, and post-heat treatment process. Ni3Co6S8@C-YS exhibited an impressive reversible capacity of 525.2 mA h g-1 at a current density of 0.5 A g-1 over 50 cycles when employed as an anode material for sodium-ion batteries. However, Ni3Co6S8 yolk shell nanopowder (Ni3Co6S8-YS) without pitch-derived carbon demonstrated a continuous decrease in capacity during charging and discharging. The superior sodium-ion storage properties of Ni3Co6S8@C-YS were attributed to the pitchderived carbon, which effectively adjusted the size and distribution of nanocrystals. The carbon-coated yolk-shell microspheres proposed here hold potential for various metal chalcogenide compounds and can be applied to various fields, including the energy storage field.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Polymer Composite with Enhanced Insulation and Mechanical Properties using Aluminum Borate Nanowhiskers
- Junhyeok Choi, Sangin Lee, Kiho Song, Taekyung Kim, Changui Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):356-362. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.356

- 968 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Inorganic-organic composites find extensive application in various fields, including electronic devices and light-emitting diodes. Notably, encapsulation technologies are employed to shield electronic devices (such as printed circuit boards and batteries) from stress and moisture exposure while maintaining electrical insulation. Polymer composites can be used as encapsulation materials because of their controllable mechanical and electrical properties. In this study, we propose a polymer composite that provides good electrical insulation and enhanced mechanical properties. This is achieved by using aluminum borate nanowhiskers (ABOw), which are fabricated using a facile synthesis method. The ABOw fillers are created via a hydrothermal method using aluminum chloride and boric acid. We confirm that the synthesis occurs in various morphologies based on the molar ratio. Specifically, nanowhiskers are synthesized at a molar ratio of 1:3 and used as fillers in the composite. The fabricated ABOw/epoxy composites exhibit a 48.5% enhancement in mechanical properties, similar to those of pure epoxy, while maintaining good electrical insulation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Al18B4O33 Spherical Powder with Increased Fluidity via Control of B2O3 Particle Size and Distribution
Kiho Song, Sang in Lee, Hyunseung Song, Changui Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(6): 513. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Al18B4O33 Spherical Powder with Increased Fluidity via Control of B2O3 Particle Size and Distribution
- [Korean]
- Epoxy-Based Siloxane/Silica Composites for Electronic Packaging by Composition and Molecular Structure of Siloxane, and Analysis of Changes in Properties
- Junho Jang, Dong Jun Kang, Hyeon-Gyun Im
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):346-355. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.346

- 1,183 View
- 14 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Epoxy-based composites find extensive application in electronic packaging due to their excellent processability and insulation properties. However, conventional epoxy-based polymers exhibit limitations in terms of thermal properties and insulation performance. In this study, we develop epoxy-based siloxane/silica composites that enhance the thermal, mechanical, and insulating properties of epoxy resins. This is achieved by employing a sol–gelsynthesized siloxane hybrid and spherical fused silica particles. Herein, we fabricate two types of epoxy-based siloxane/ silica composites with different siloxane molecular structures (branched and linear siloxane networks) and investigate the changes in their properties for different compositions (with or without silica particles) and siloxane structures. The presence of a branched siloxane structure results in hardness and low insulating properties, while a linear siloxane structure yields softness and highly insulating properties. Both types of epoxy-based siloxane/silica composites exhibit high thermal stability and low thermal expansion. These properties are considerably improved by incorporating silica particles. We expect that our developed epoxy-based composites to hold significant potential as advanced electronic packaging materials, offering high-performance and robustness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Toughening epoxy matrices via elastomeric blending for enhanced compatibility with auxetic reinforcements in composites
Usama Khalid, Shiza Shahid, Muhammad Bilal Qadir, Mumtaz Ali, Zubair Khaliq, Aamir Naseem Satti, Zaheer Anwar Randhawa, Danish Umer
Mechanics Based Design of Structures and Machines.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Enhanced Epoxy Composites Reinforced by 3D-Aligned Aluminum Borate Nanowhiskers
Hyunseung Song, Kiho Song, Haejin Hwang, Changui Ahn
Materials.2024; 17(19): 4727. CrossRef
- Toughening epoxy matrices via elastomeric blending for enhanced compatibility with auxetic reinforcements in composites
- [Korean]
- Controlling Particle Size of Recycled Copper Oxide Powder for Copper Thermite Welding Characteristics
- Hansung Lee, Minsu Kim, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):332-338. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.332

- 940 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Thermite welding is an exceptional process that does not require additional energy supplies, resulting in welded joints that exhibit mechanical properties and conductivity equivalent to those of the parent materials. The global adoption of thermite welding is growing across various industries. However, in Korea, limited research is being conducted on the core technology of thermite welding. Currently, domestic production of thermite powder in Korea involves recycling copper oxide (CuO). Unfortunately, controlling the particle size of waste CuO poses challenges, leading to the unwanted formation of pores and cracks during thermite welding. In this study, we investigate the influence of powder particle size on thermite welding in the production of Cu-thermite powder using waste CuO. We conduct the ball milling process for 0.5–24 h using recycled CuO. The evolution of the powder shape and size is analyzed using particle size analysis and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Furthermore, we examine the thermal reaction characteristics through differential scanning calorimetry. Additionally, the microstructures of the welded samples are observed using optical microscopy and SEM to evaluate the impact of powder particle size on weldability. Lastly, hardness measurements are performed to assess the strengths of the welded materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Friction Welding of Casted SCM440 and Sintered F-05-140 Dissimilar Steels and Their Joint Properties under Various Welding Conditions
Jisung Lee, Hansung Lee, Eunhyo Song, Byungmin Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 414. CrossRef
- Friction Welding of Casted SCM440 and Sintered F-05-140 Dissimilar Steels and Their Joint Properties under Various Welding Conditions
- [Korean]
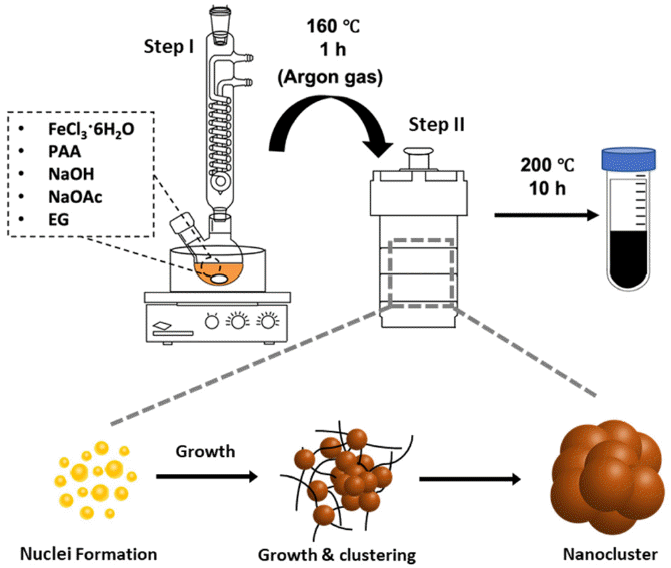
- Size Control of Iron Oxide (Fe3O4) Nanoclusters according to Reaction Factors and Consequent Change in Their Magnetic Attraction
- Sanghoon Lee, Arim Byun, Jin-sil Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):297-304. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.297
- 1,081 View
- 13 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Iron oxide (Fe2O3) nanoclusters exhibit significant potential in the biomedical and pharmaceutical fields due to their strong magnetic properties, stability in solutions, and compatibility with living systems. They excel in magnetic separation processes, displaying high responsiveness to external magnetic fields. In contrast to conventional Fe2O3 nanoparticles that can aggregate in aqueous solutions due to their ferrimagnetic properties, these nanoclusters, composed of multiple nanoparticles, maintain their magnetic traits even when scaled to hundreds of nanometers. In this study, we develop a simple method using solvothermal synthesis to precisely control the size of nanoclusters. By adjusting precursor materials and reducing agents, we successfully control the particle sizes within the range of 90 to 420 nm. Our study not only enhances the understanding of nanocluster creation but also offers ways to improve their properties for applications such as magnetic separation. This is supported by our experimental results highlighting their size-dependent magnetic response in water. This study has the potential to advance both the knowledge and practical utilization of Fe2O3 nanoclusters in various applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enzymatic properties of iron oxide nanoclusters and their application as a colorimetric glucose detection probe
Dahyun Bae, Minhee Kim, Jin-sil Choi
RSC Advances.2025; 15(6): 4573. CrossRef
- Enzymatic properties of iron oxide nanoclusters and their application as a colorimetric glucose detection probe
- [Korean]
- Exploration of Aluminum Alloy using Multi-feeder 3D Additive Manufacturing-based Combinatorial Experiment
- Suwon Park, Yongwook Song, Jiyoon Yeo, Songyun Han, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):255-261. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.255
- 1,608 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
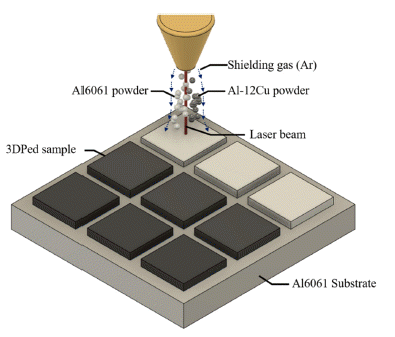
PDF Aluminum alloys are widely utilized in diverse industries, such as automobiles, aerospace, and architecture, owing to their high specific strength and resistance to oxidation. However, to meet the increasing demands of the industry, it is necessary to design new aluminum alloys with excellent properties. Thus, a new method is required to efficiently test additively manufactured aluminum alloys with various compositions within a short period during the alloy design process. In this study, a combinatory approach using a direct energy deposition system for metal 3D printing process with a dual feeder was employed. Two types of aluminum alloy powders, namely Al6061 and Al-12Cu, were utilized for the combinatory test conducted through 3D printing. Twelve types of Al-Si-Cu-Mg alloys were manufactured during this combinatory test, and the relationship between their microstructures and properties was investigated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trends in Materials Modeling and Computation for Metal Additive Manufacturing
Seoyeon Jeon, Hyunjoo Choi
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(3): 213. CrossRef - Microstructural Effects on the Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Fabricated by Direct Energy Deposition
Juho Kim, Seoyeon Jeon, Hwajin Park, Taeyoel Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(4): 302. CrossRef - Combinatorial Experiment for Al-6061 and Al-12Si alloy Based on Directed Energy Deposition (DED) Process
Seoyeon Jeon, Suwon Park, Yongwook Song, Jiwon Park, Hyunyoung Park, Boram Lee, Hyunjoo Choi
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(6): 463. CrossRef
- Trends in Materials Modeling and Computation for Metal Additive Manufacturing
- [Korean]
- Effect of WC Particle Size on the Microstructure, Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Ag/WC Sintered Electrical Contact Material
- Soobin Kim, So-Yeon Park, Jong-Bin Lim, Soon Ho Kwon, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):242-248. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.242
- 972 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
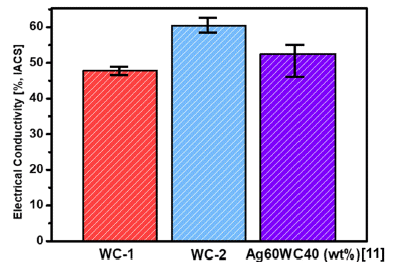
PDF The Ag/WC electrical contacts were prepared via powder metallurgy using 60 wt% Ag, 40 wt% WC, and small amounts of Co3O4 with varying WC particle sizes. After the fabrication of the contact materials, microstructure observations confirmed that WC-1 had an average grain size (AGS) of 0.27 μm, and WC-2 had an AGS of 0.35 μm. The Ag matrix in WC-1 formed fine grains, whereas a significantly larger and continuous growth of the Ag matrix was observed in WC-2. This indicates the different flow behaviors of liquid Ag during the sintering process owing to the different WC sizes. The electrical conductivities of WC-1 and WC-2 were 47.8% and 60.4%, respectively, and had a significant influence on the Ag matrix. In particular, WC-2 exhibited extremely high electrical conductivity owing to its large and continuous Ag-grain matrix. The yield strengths of WC-1 and WC-2 after compression tests were 349.9 MPa and 280.7 MPa, respectively. The high yield strength of WC-1 can be attributed to the Hall–Petch effect, whereas the low yield strength of WC-2 can be explained by the high fraction of high-angle boundaries (HAB) between the WC grains. Furthermore, the relationships between the microstructure, electrical/mechanical properties, and deformation mechanisms were evaluated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhanced Epoxy Composites Reinforced by 3D-Aligned Aluminum Borate Nanowhiskers
Hyunseung Song, Kiho Song, Haejin Hwang, Changui Ahn
Materials.2024; 17(19): 4727. CrossRef
- Enhanced Epoxy Composites Reinforced by 3D-Aligned Aluminum Borate Nanowhiskers
- [Korean]
- Analysis of the Effects of Process Variables and Alloy Composition on the Relative density and Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed Aluminum Alloys
- Suwon Park, Jiyoon Yeo, Songyun Han, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):223-232. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.223
- 3,091 View
- 16 Download
- 1 Citations
-
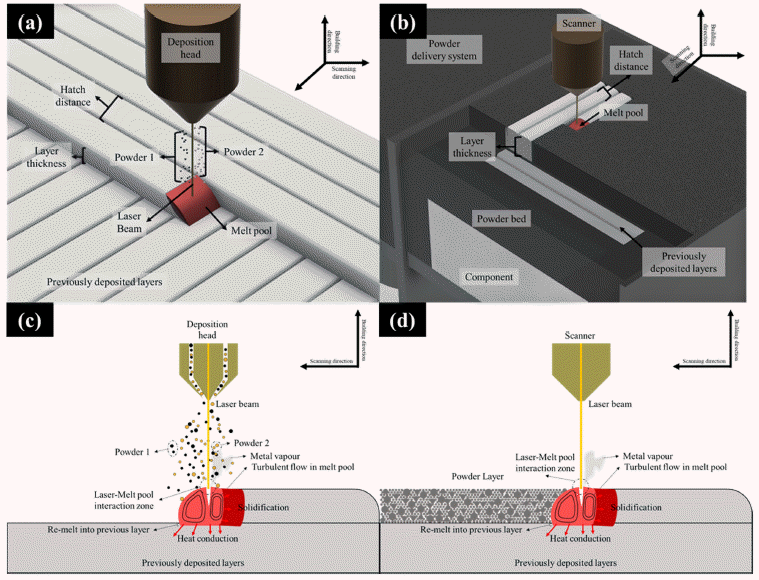
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metal additive manufacturing (AM) has transformed conventional manufacturing processes by offering unprecedented opportunities for design innovation, reduced lead times, and cost-effective production. Aluminum alloy, a material used in metal 3D printing, is a representative lightweight structural material known for its high specific strength and corrosion resistance. Consequently, there is an increasing demand for 3D printed aluminum alloy components across industries, including aerospace, transportation, and consumer goods. To meet this demand, research on alloys and process conditions that satisfy the specific requirement of each industry is necessary. However, 3D printing processes exhibit different behaviors of alloy elements owing to rapid thermal dynamics, making it challenging to predict the microstructure and properties. In this study, we gathered published data on the relationship between alloy composition, processing conditions, and properties. Furthermore, we conducted a sensitivity analysis on the effects of the process variables on the density and hardness of aluminum alloys used in additive manufacturing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Si Sintered Alloys with and Without High-energy Ball Milling
Junho Lee, Seonghyun Park, Sang-Hwa Lee, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(6): 470. CrossRef
- Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Si Sintered Alloys with and Without High-energy Ball Milling
- [Korean]
- Machine Learning-based Data Analysis for Designing High-strength Nb-based Superalloys
- Eunho Ma, Suwon Park, Hyunjoo Choi, Byoungchul Hwang, Jongmin Byun
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):217-222. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.217
- 883 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Machine learning-based data analysis approaches have been employed to overcome the limitations in accurately analyzing data and to predict the results of the design of Nb-based superalloys. In this study, a database containing the composition of the alloying elements and their room-temperature tensile strengths was prepared based on a previous study. After computing the correlation between the tensile strength at room temperature and the composition, a material science analysis was conducted on the elements with high correlation coefficients. These alloying elements were found to have a significant effect on the variation in the tensile strength of Nb-based alloys at room temperature. Through this process, a model was derived to predict the properties using four machine learning algorithms. The Bayesian ridge regression algorithm proved to be the optimal model when Y, Sc, W, Cr, Mo, Sn, and Ti were used as input features. This study demonstrates the successful application of machine learning techniques to effectively analyze data and predict outcomes, thereby providing valuable insights into the design of Nb-based superalloys.
- [Korean]
- Enhancement of Thermoelectric Performance in Spark Plasma Sintered p-Type Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3.0 Compound via Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) Induced Reduction of Lattice Thermal Conductivity
- Soo-Ho Jung, Ye Jin Woo, Kyung Tae Kim, Seungki Jo
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(2):123-129. Published online April 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.2.123
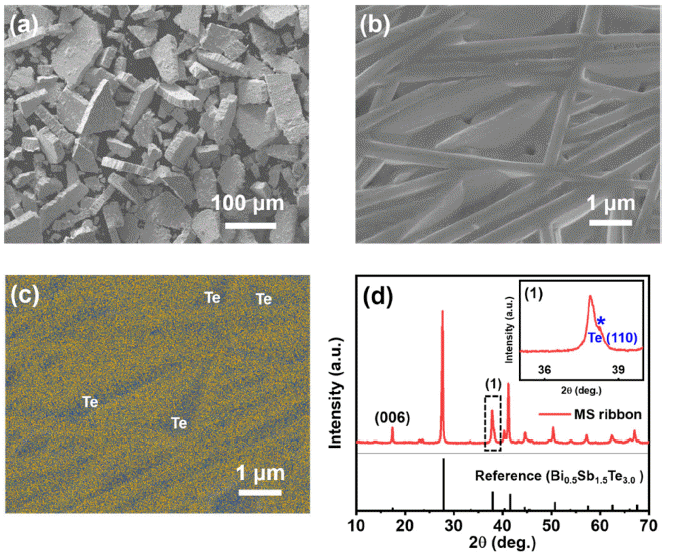
- 1,625 View
- 9 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF High-temperature and high-pressure post-processing applied to sintered thermoelectric materials can create nanoscale defects, thereby enhancing their thermoelectric performance. Here, we investigate the effect of hot isostatic pressing (HIP) as a post-processing treatment on the thermoelectric properties of
p -type Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3.0 compounds sintered via spark plasma sintering. The sample post-processed via HIP maintains its electronic transport properties despite the reduced microstructural texturing. Moreover, lattice thermal conductivity is significantly reduced owing to activated phonon scattering, which can be attributed to the nanoscale defects created during HIP, resulting in an ~18% increase in peakzT value, which reaches ~1.43 at 100°C. This study validates that HIP enhances the thermoelectric performance by controlling the thermal transport without having any detrimental effects on the electronic transport properties of thermoelectric materials.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhanced Electrical Properties of 3D Printed Bi2Te3-Based Thermoelectric Materials via Hot Isostatic Pressing
Seungki Jo
Ceramist.2025; 28(1): 126. CrossRef - Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
Linh Ba Vu, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son, Seungki Jo
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 119. CrossRef - Investigation of the Thermal-to-Electrical Properties of Transition Metal-Sb Alloys Synthesized for Thermoelectric Applications
Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Sooho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Kwi-Il Park, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(3): 236. CrossRef - Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 318. CrossRef
- Enhanced Electrical Properties of 3D Printed Bi2Te3-Based Thermoelectric Materials via Hot Isostatic Pressing
- [Korean]
- A Study on the Microstructures and Ionic Conductivity of Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 with Different Synthesis Routes
- Seul Ki Choi, Jeawon Choi, MinHo Yang
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(2):107-115. Published online April 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.2.107
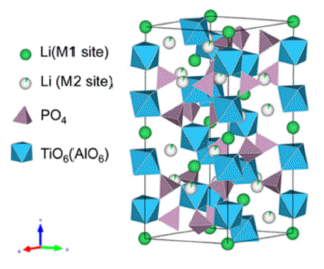
- 2,152 View
- 48 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3(LATP) is considered a promising material for all-solid-state lithium batteries owing to its high moisture stability, wide potential window (~6 V), and relatively high ion conductivity (10-3–10-4 S/cm). Solid electrolytes based on LATP are manufactured via sintering, using LATP powder as the starting material. The properties of the starting materials depend on the synthesis conditions, which affect the microstructure and ionic conductivity of the solid electrolytes. In this study, we synthesize the LATP powder using sol-gel and co-precipitation methods and characterize the physical properties of powder, such as size, shape, and crystallinity. In addition, we have prepared a disc-shaped LATP solid electrolyte using LATP powder as the starting material. In addition, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopic measurements are conducted to analyze the grain size, microstructures, and ion conduction properties. These results indicate that the synthesis conditions of the powder are a crucial factor in creating microstructures and affecting the conduction properties of lithium ions in solid electrolytes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Controlling the All-Solid Surface Reaction Between an Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 Electrolyte and Anode Through the Insertion of Ag and Al2O3 Nano-Interfacial Layers
Gwanhee Song, Bojoong Kim, Inkook Hwang, Jiwon Kim, Jinmo Kim, Chang-Bun Yoon
Materials.2025; 18(3): 609. CrossRef
- Controlling the All-Solid Surface Reaction Between an Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 Electrolyte and Anode Through the Insertion of Ag and Al2O3 Nano-Interfacial Layers
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


